DNA quick flashcards
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
59 Terms
what is transformation
change in genotype and phenotype due to assimilation of external DNA by a cell
F.Griffith worked with Streptococcus pneumoniae to discover transformation, using mice
what are bacteriophages
viruses that infect bacteria
what is chargaff’s rule
A=T
G=C
how does DNA replicate
separation of two DNA strands & serve as a template
complentary base pairs join to each template
nucleotides connected, each daughter DNA molecule has one parental and one new strand
what is the semiconservative model
two strands of the parental molecule separate
each function as a template for a new complementary strand
what is the origin of replication
site where proteins attach and separate the strands of DNA
what is DNA polymerase
enzyme that adds new nucleotides to the replication fork at rate of 50 to 500/s
what is nucleoside triphosphate
energy and substrate for polymerisation
what end do nucleotides get added to
3’ end
what is the leading strand
replicated towards replication fork continuously
what is the lagging strand
replicated away from replication fork in okazaki fragments
what are okazaki fragments
100-200 nucleotide pieces that are joined by DNA ligase into a single strand
what is a primer
start of new DNA chain which is bade of RNA
about 10 base pairs long
needed to initiate replication
what is primase
enzyme that joins RNA nucleotides into a primer
can initiate the process from scratch
what are helicases
enzyme that untwists and separates the DNA helix
what are single strand binding proteins
binds to seprated strands and holds them apart
what is mismatch repair
incorrectly paired nucleotides are fixed by an enzyme
what is nuclease
enzyme that cuts DNA
what is nucleotide excision repair
excised DNA section filled in by a polymerase and ligase
nuclease cuts damaged DNA strand, DNA polymerase fills gap, DNA ligase seals the remaining nick
how can prokaryotes avoid the 5’ problem
they have circular DNA
what are telomeres
repeated short sequences of DNA added to the end of chromosomes for protection against loss of genetic material
TTAGGG in humans
what is telomerase
enzyme containing RNA which further lengthens the 3’ end to allow completion of the 5’ end
generally only in germ cells
one gene one enzyme hypothesis - beadle and tatum
Neurospora crassa grows with agar, salts, glucose and biotin
used x rays to induce mutations (strains that can’t grow with just those nutrients)
used supplemented agar treatments to see which amino acids/nutrients required for growth
what is mRNA
carries building instructions from a gene
mRNA in eukaryotes vs prokaryotes
Prokaryotes - MRNA transcribe directly from DNA, immediately translated into a polypeptide
Eukaryotes - the transcribed RNA is further processed to form mRNA
what is a codon
the mRNA triplet code for an amino acid

what direction are codons read
5’ to 3’
what is RNA polymerase
pries apart DNA helix and hooks together the RNA nucleotides
can only add nucleotides to 3’ end
what is a promoter
region of DNA where RNA polymerases attaches and initiates transcription
what is the transcription unit
the stretch of DNA that’s transcribed
what is the terminator
the DNA sequences that signal the end of transcription
what is the 5’ cap
modified guanine nucleotide
protects mRNA from hydrolytic enzymes
helps attach mRNA to ribosome
what is the Poly(A) tail
50-250 adenine nucleotides
inhibits degradation
helps ribosomes attach
helps mRNA leave nucleus
what are ribozymes
RNA that act as enzymes
what are snRNPs
small nuclear ribonucleoproteins
found in nucleus
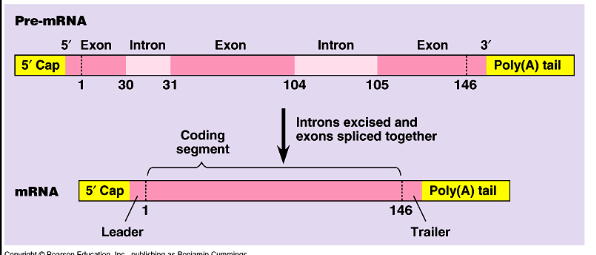
leads to spliceosome formation and catalyse the excision of introns
what is the spliceosome
several snRNPs and proteins which splice the exons into mRNA
almost as big as the ribosome
why are introns present
some introns control the activity of specific genes once excised
allows alternative RNA splicing, where different sections are excised from pre-RNA to code for different proteins
what are exons
sections of DNA and RNA that become expressed or translated into protein
transcribed into preRNA
what are introns
intervening, non expressed regions of RNA and DNA
transcribed into preRNA
what is tRNA
moves amino acids from cytoplasm into ribosome
specific to one or several codons and coded as an anti-codon
eg mRNA: CGU → tRNA: GCA
what is Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase
20 forms
each one specific to one amino acid
attaches the amino acid to an appropriate tRNA
what is an activated amino acid
tRNA with an appropriate amino acid attached
what is the ribosome
acts to couple tRNA and mRNA
composed of rRNA and proteins
3 binding sites for tRNA
what is the A site of the ribosome
attaches to next tRNA
what is the P site of the ribosome
holds tRNA iwth growing polypeptide chain
what is the E site of the ribosome
releases tRNA
what are initiating factors
proteins which attach large RS to complex
initiator tRNA in P site
how to initiate a polypeptide
small RS binds to mRNA at 5’ cap and a initiator tRNA
GTP is energy source
what is the release factor
protein which binds directly to stop codon in A site
hydrolyses the polypeptide and releases it
triggers ribosome complex to disassemble
what are polyribosomes
multiple ribosomes translating the same mRNA
makes many copies of a protein quickly
what is a signal peptide
about 20 amino acids near leading end of a polypeptide
indicate the destination of the protein
what is the SRP
protein-RNA complex that recognises signal peptides and facilitates their movement to target locations
only in eukaryotes
protein synthesis in prokaryotes vs eukaryotes
prokaryotes - transcription & translation of the same mRNA can occur simultaneously
eukaryotes - nucleus prevents simultaneous transcription & translation, allows for extra regulation of cell’s activity
point mutations
changes in one base pair of a gene
if in gametes, can pass to offspring
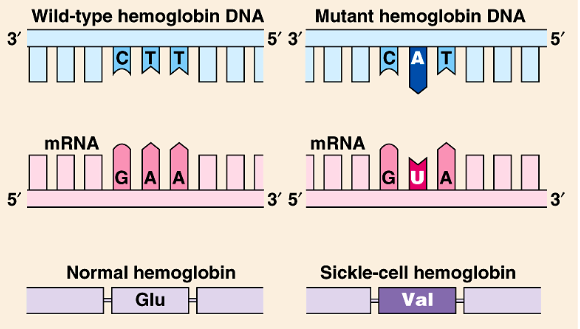
what is substitution
replacement of one base pair with another
what are silent mutations
have no effect on the protein
what are missense mutations
changes one amino acid which can alter the protein and its function
what are nonsense mutations
introduces a premature stop codon
often leads to non functional proteins
what are insertions/deletions
adding/losing a base pair in a gene
generally leads to a frameshift mutation, where insertion/deletion isn’t a multiple of three so amino acids are added incorrectly