6. Erythrocytes: Shapes Inclusions/Infective Agents
1/128
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
129 Terms
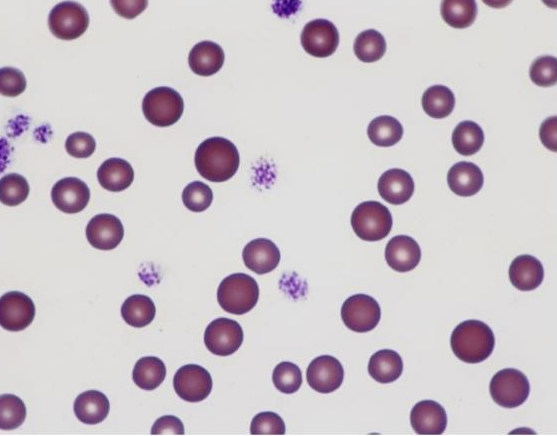
What is this showing?
anisocytosis
general term for the presence of abnormally shaped erythrocytes
poikilocytosis
In what species is poikilocytosis normal?
goats and young, healthy cattle
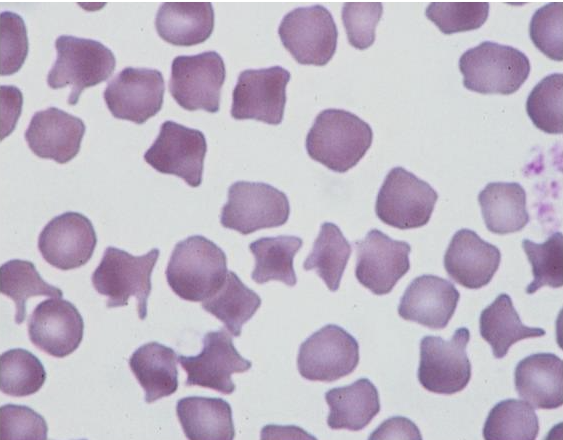
What is this showing?
poikilocytosis
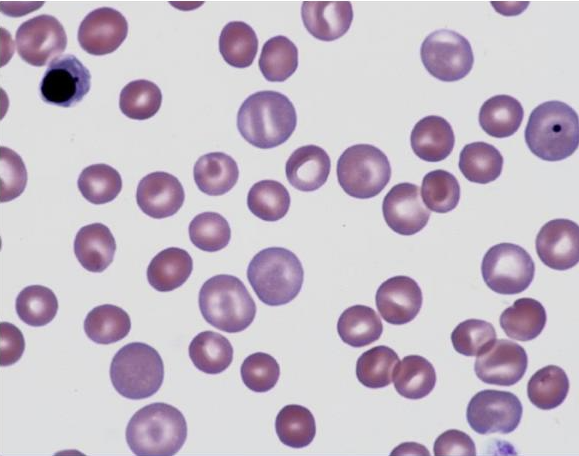
What is this showing?
polychromasia
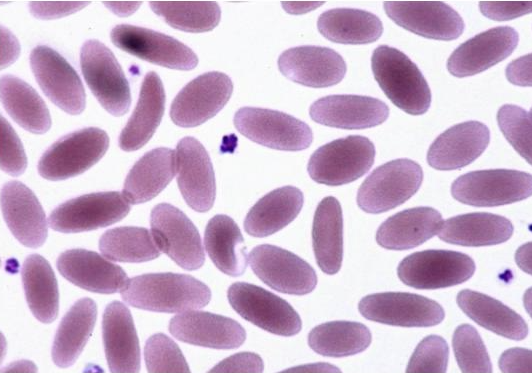
What is this showing?
normal camelid erythrocytes
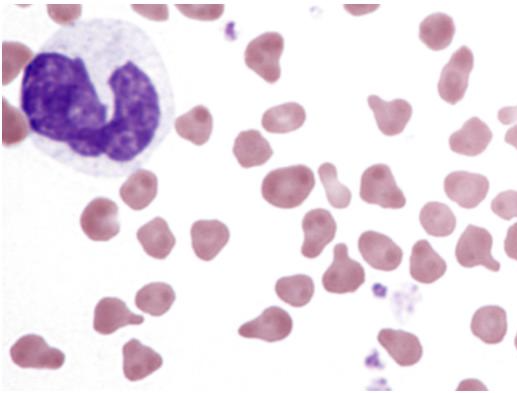
What is this showing? Is this normal?
poikilocytes in goat blood; yes
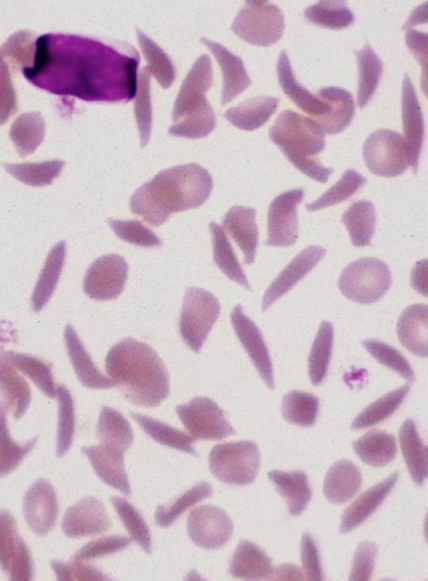
What is this showing? Is this normal?
deer blood drepanocytes; yes
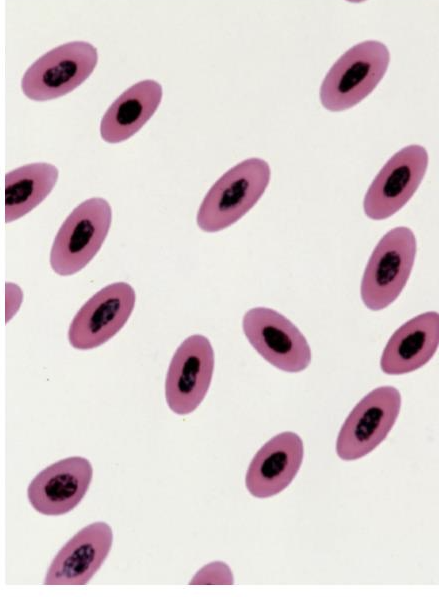
What is this showing? Is it normal?
avian erythrocytes; yes
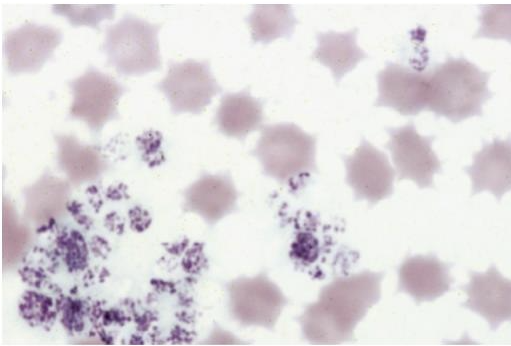
What is this showing? Is this normal?
echinocytes in pig blood; yes because it is normal in pig blood
stacking of red blood cells
rouleaux
How is rouleaux dispersed? What is the process?
using physiological saline solution; wash erythrocytes twice using physiologic saline or add one part blood to 49 parts saline
If the rouleaux adherence disappear grossly, what should be done?
examine microscopically under a coverslip to verify
Cells do not adhere with ________, but continue to adhere in saline with ________.
rouleaux; agglutination
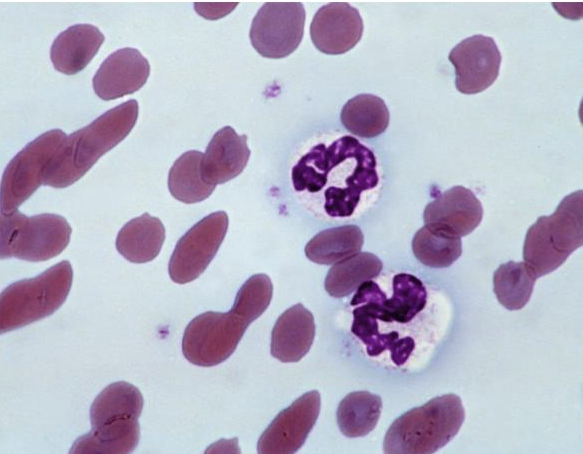
What is this showing?
rouleaux in a dog with hyperglobinemia
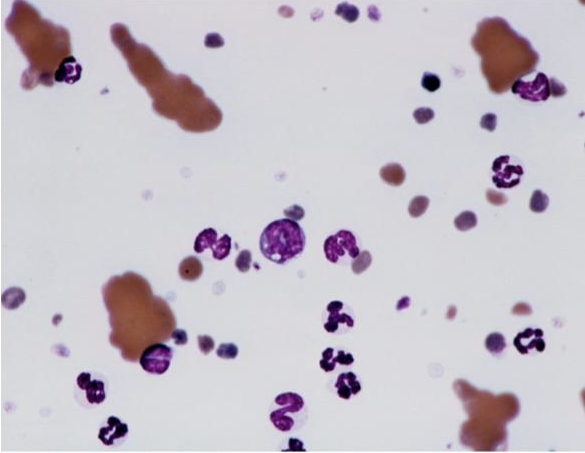
What is this showing?
erythrocyte agglutination
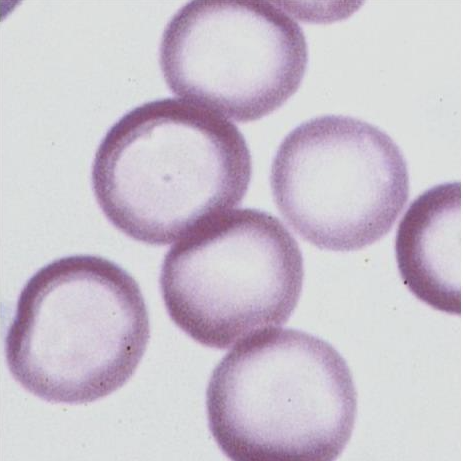
What is this showing?
hypochromic appearance due to iron deficiency anemia
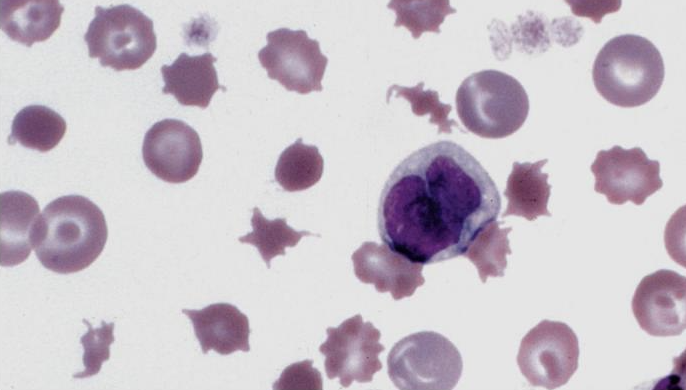
What is this showing?
poikilocytes
sickle cells or fusiform or spindle-shaped cells
drepanocytes
In what species are drepanocytes normally present in?
deer family and some angora goats
What causes drepanocytes in vitro?
hemoglobin polymerization with increased oxygen tension and increased pH
What causes drepanocytes in vivo?
hemoglobin polymerizes by low oxygen tension and low pH
crenated cells that have a reversible shape change that are usually an artifact in pigs and can be pathologic with snake envenomation
echinocytes
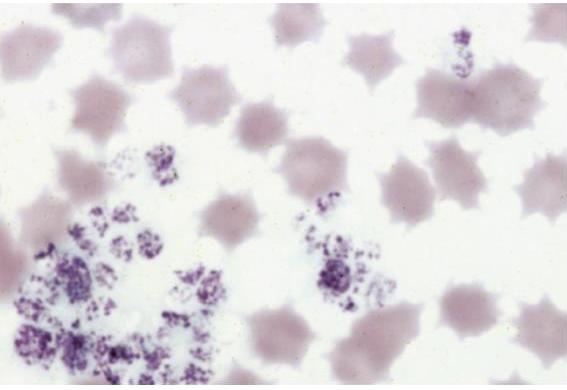
What is this showing?
echinocytes
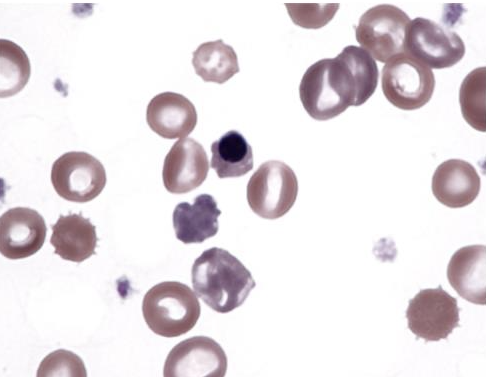
What is this showing?
echinocytes in dog with pyruvate kinase deficiency
What else can lead to echinocytes in the blood?
U
P
P
G
N
D
T
F
B
D
L
R
A
I
I
uremia
post-transfusion
PK deficiency in dogs
glomerulonephritis
neopplasia
doxorubican (dogs)
total body depletion of cations (horses)
fatty acids
bile salts
drugs
lysophospholipids
RBC dehydration
ATP depletion
increased pH
increased RBC calcium
abnormally shaped red blood cells characterized by coarse, irregularly distributed projections on their surface
acanthocytes
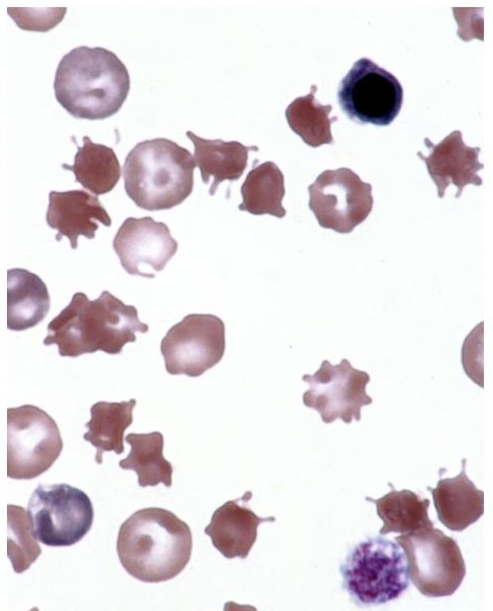
What is this showing?
acanthocytes
When are acanthocytes most commonly seen in blood?
with liver disease
When else would acanthocytes be seen?
E
H
G
D
excess cholesterol vs phospholipids
hemangiosarcoma
glomerulonephritis
DIC in dogs
In what other species can you see acanthocytes?
young goats and some young cattle
these cells are most often artifacts in thick blood films
stomatocytes
What does hereditary stomatocytosis cause?
swollen erythrocytes having increased MCV and decreased MCHC
When else can stomatocytes be seen?
with drugs that preferentially bind to the inner half of the lipid bilayer
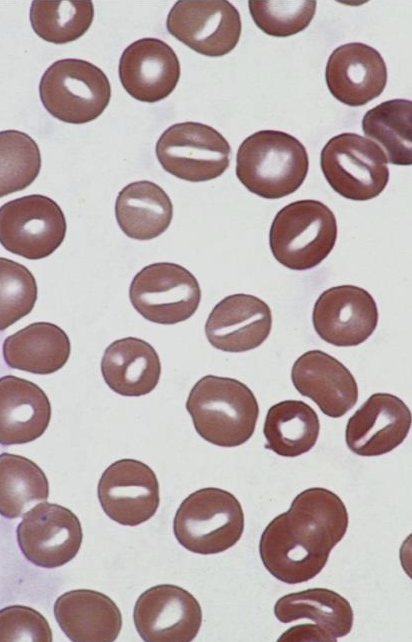
What is this showing?
stomatocytes
Although the diameter of a spherocyte is ________, there volume is generally ________ to that of disocytes.
less; close
When do disocytes and spherocytes form?
in immune-mediated anemias
In spherocyte formation, what cells have receptors for immunoglobulins and complement on their surface? What will bind to these? What can happen to that cell?
macrophages; erythrocyte with antibodies and or complement bound to their surface; the whole erythrocyte may be phagocytized
When do spherocytes only form?
when only a portion of the membrane is bound and removed (erythrocytes can reseal themselves)
What no longer allows for the formation of discocytes?
the loss of membrane
The MCV is often ________ in immune-mediated hemolytic anemias because of the presence of ________ with high cell volumes.
high; reticulocytes
When can spherocytes be seen?
I
S
Z
E
T
D
R
IMHA, especially dogs
snake bites and bee stings
zinc toxicity
erythrocyte parasites
transfusion of stored blood
dyserythropoiesis in English Springers
RBC band 3 deficiency in Japanese black cattle
immature reticulocyte
polychromatophilic erythrocyte
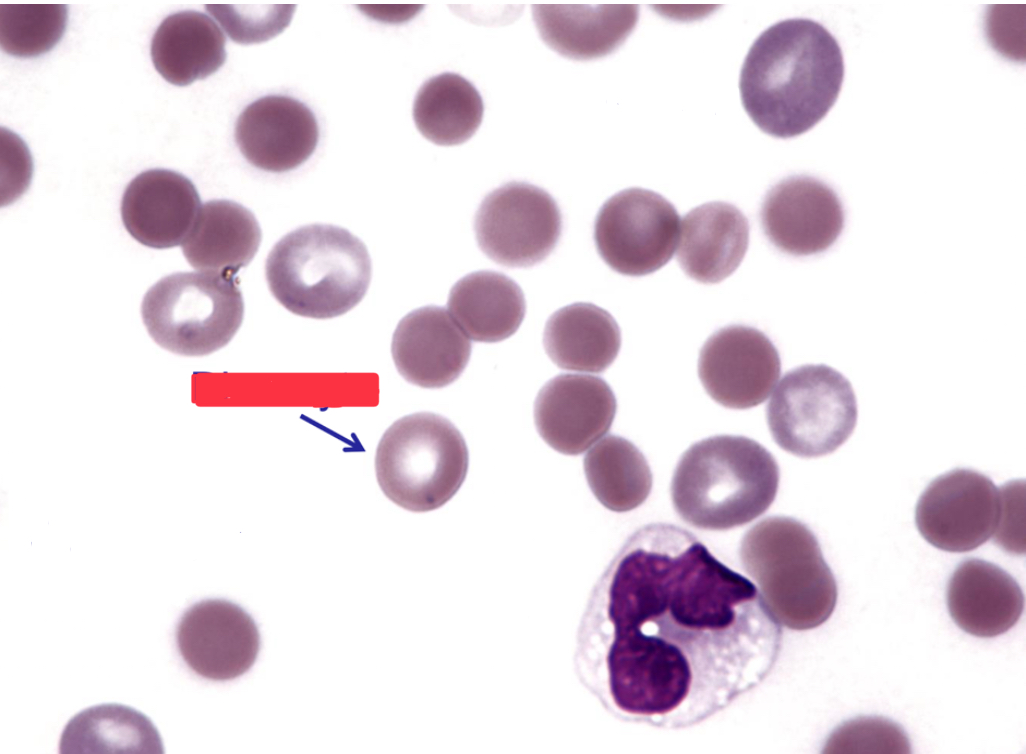
What is this cell type?
discocyte
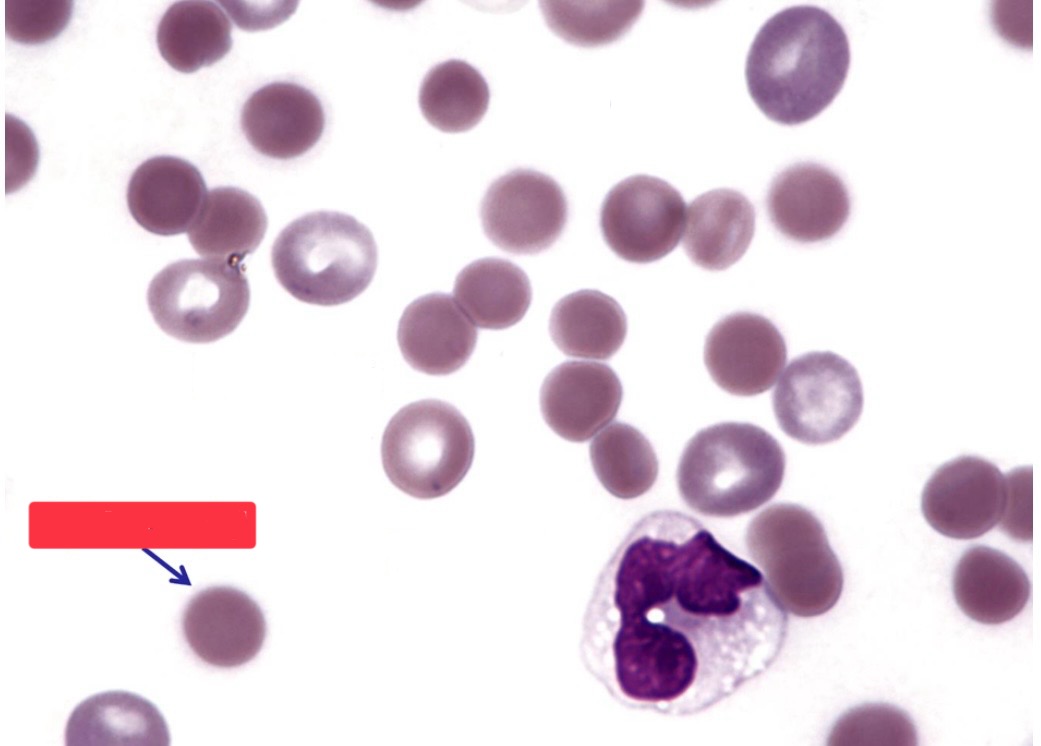
What is this image?
spherocyte
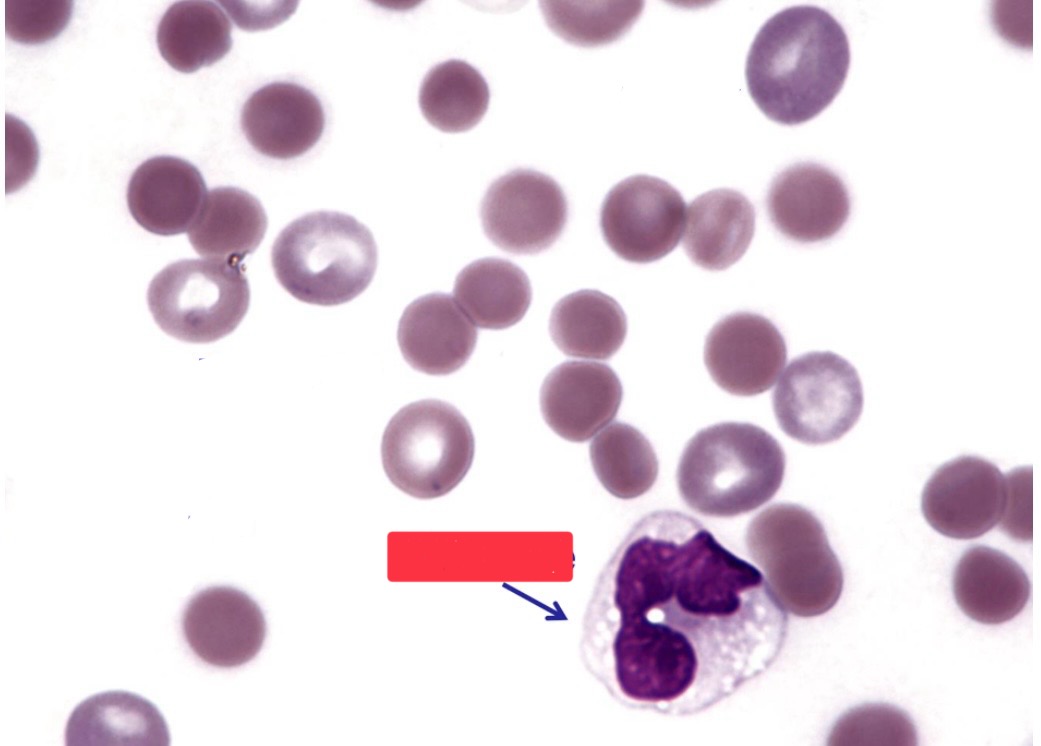
What is this image?
monocyte
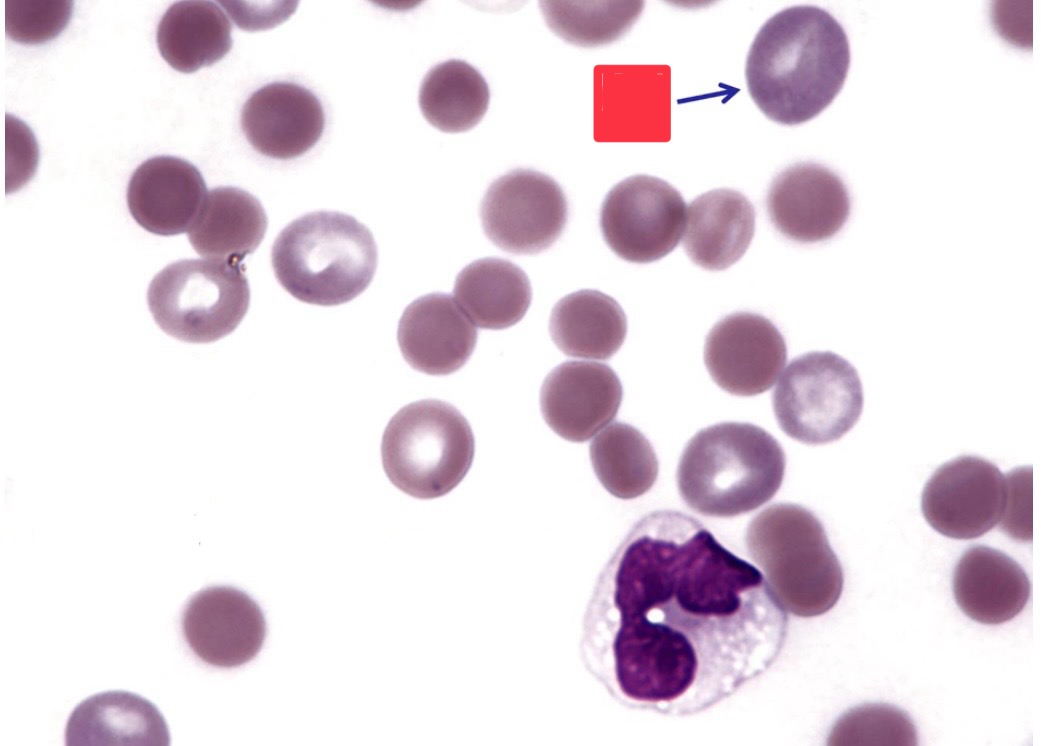
What is this image?
PE
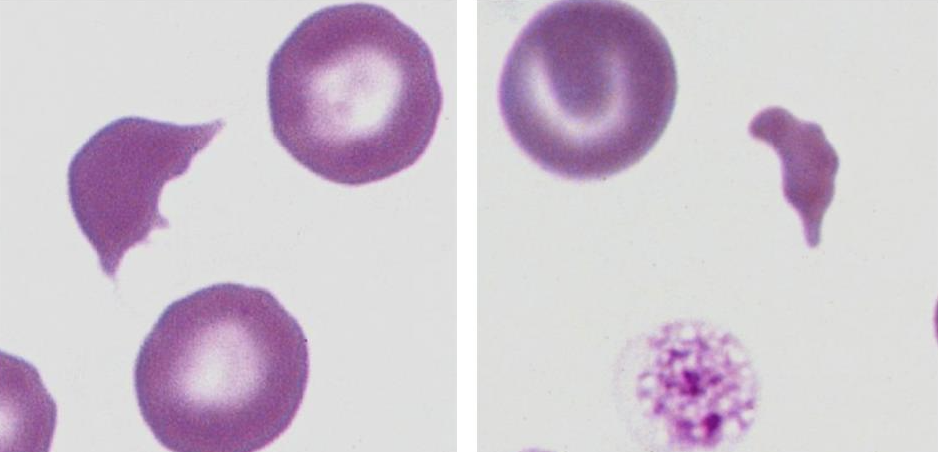
What type of cells are these?
schistocytes
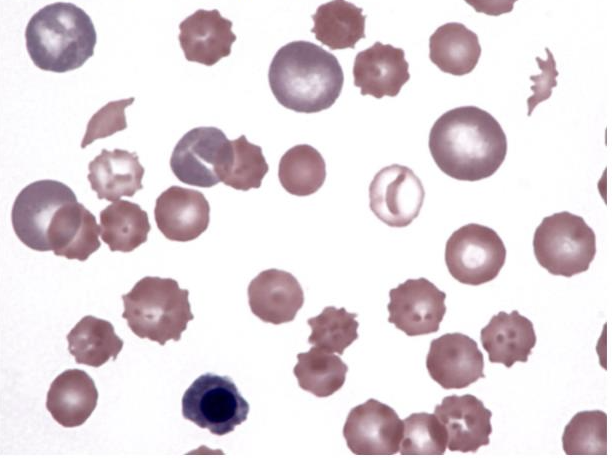
What is this showing?
DIC in a dog with heartworms
What erythrocyte changes may be seen in blood smears with fragmentation?
S
K
A
schistocytes
keratocytes
acanthocytes
What cell type is the best evidence for fragmentation? Why?
schistocytes; keratocytes and acanthocytes also occur in other disorders
True or false: A few spherocyte-like cells may also be seen with fragmentation and do not indicate immune-mediated disease in this setting.
true
With DIC, what will accompany the fragmentation?
thrombocytopenia and coagulation disorders
Is there anemia with erythrocyte fragmentation?
usually mild to moderate
What are ways that erythrocyte fragmentation occurs?
M
E
T
mechanical injury
endothelial injury
thermal injury
What are examples of mechanical injury?
D
C
G
C
disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC)
caval syndrome due to heartworms
glomerulonephritis
cardiac valvular stenosis
What are examples of endothelial injury?
H
V
S
hemangiosarcoma (dogs)
vasculitis
splenic or hepatic disease
What are examples of thermal injury?
H
S
heat stroke
severe burns
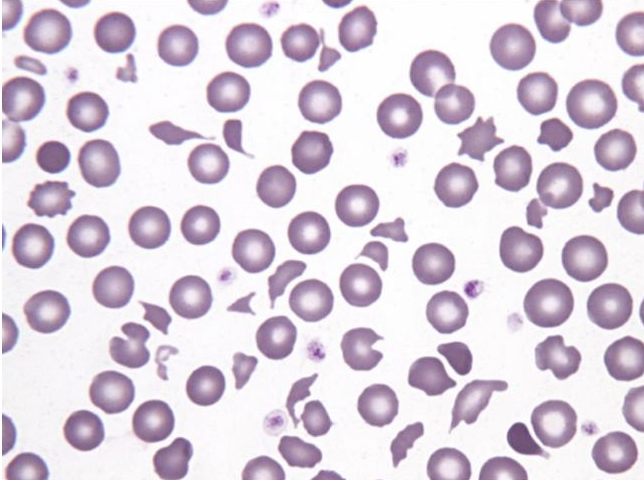
What is this showing?
heart failure in dog (fragmentation)
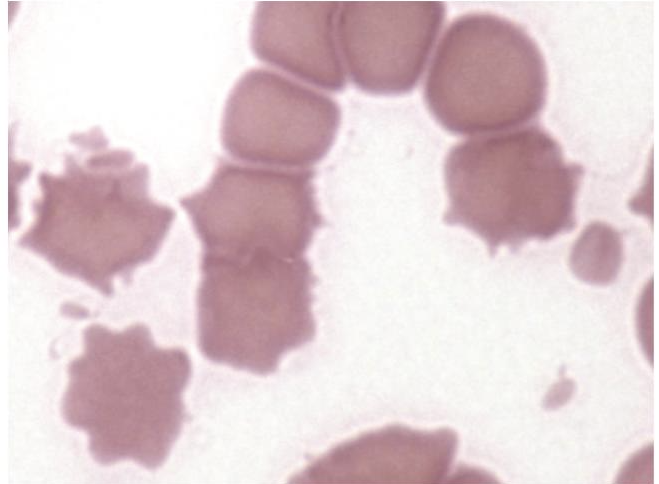
What is this showing?
thermal fragmentation
What are additional causes of fragmented erythrocytes?
S
M
H
C
P
severe iron deficnecy
myelofibrosis
hemophagic histiocytic disorder
congenital and acquired dyserythropoiesis in dogs
pyruvate kinase deficiency post-splenectomy in dogs
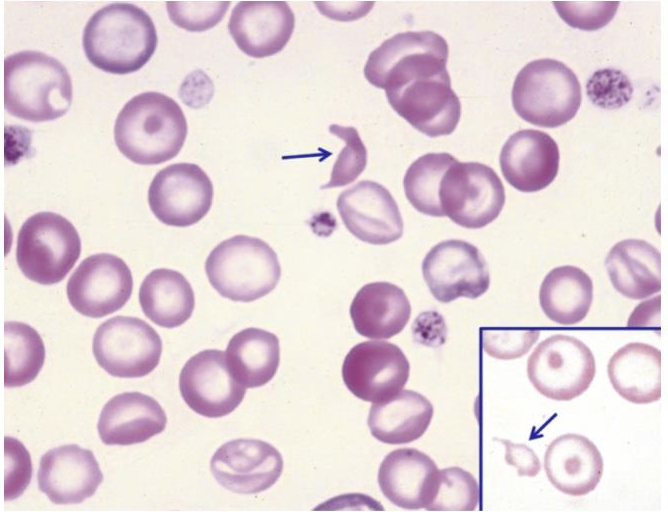
What is this showing?
canine iron deficiency (fragmentation)
formed due to membrane oxidant damage
eccentrocyte
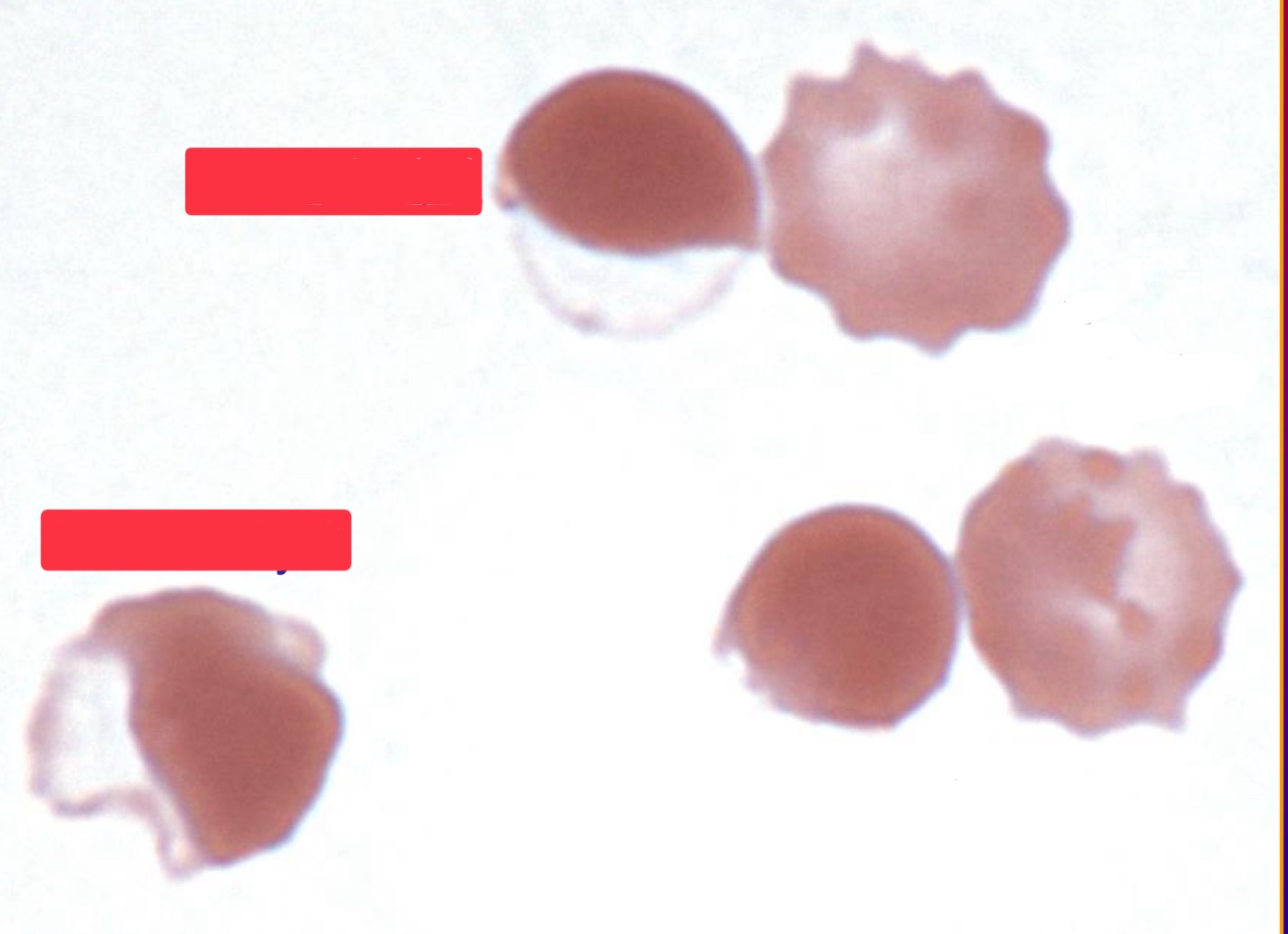
What are these cells?
eccentrocytes
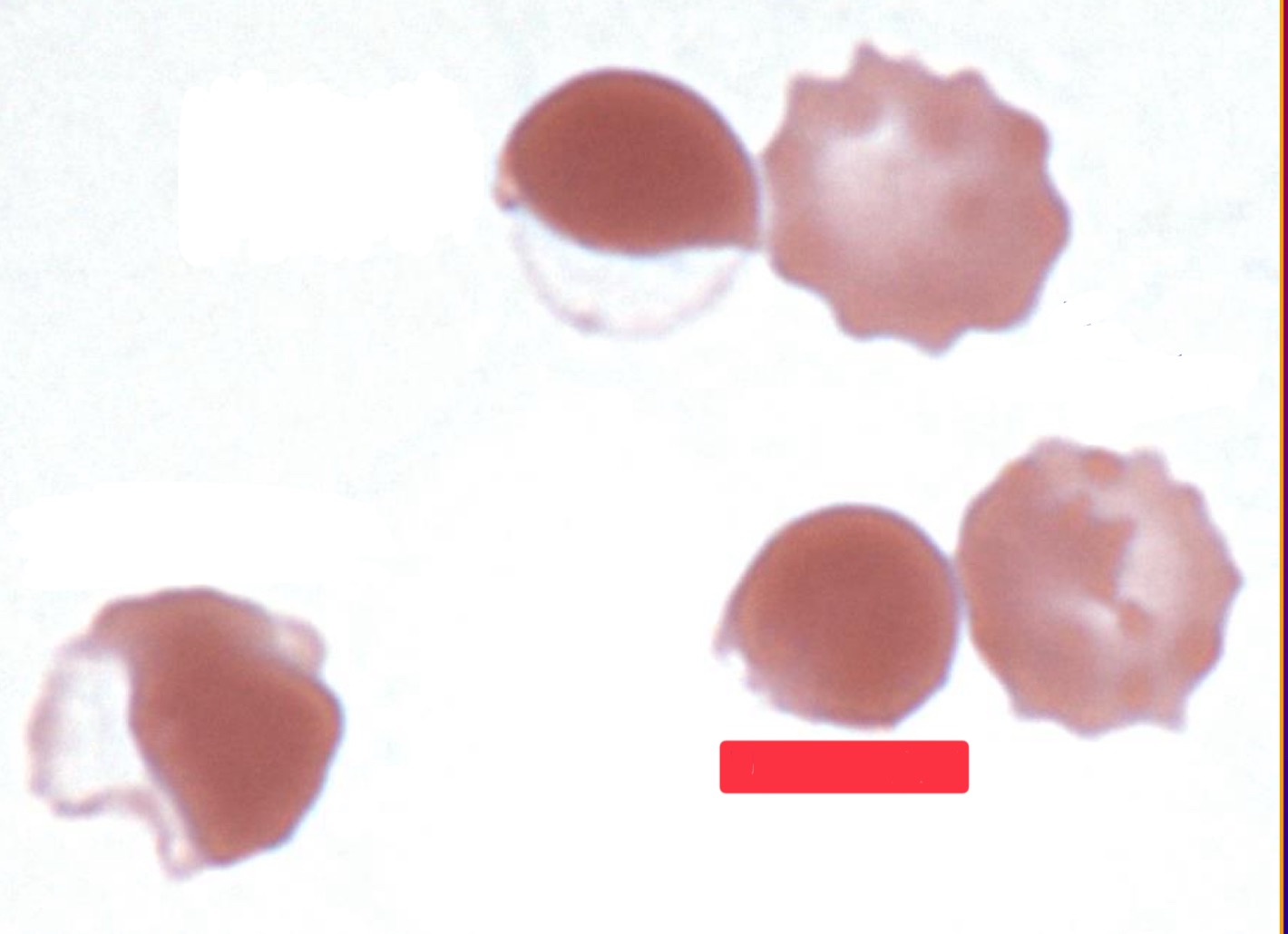
What is this cell?
pyknocyte
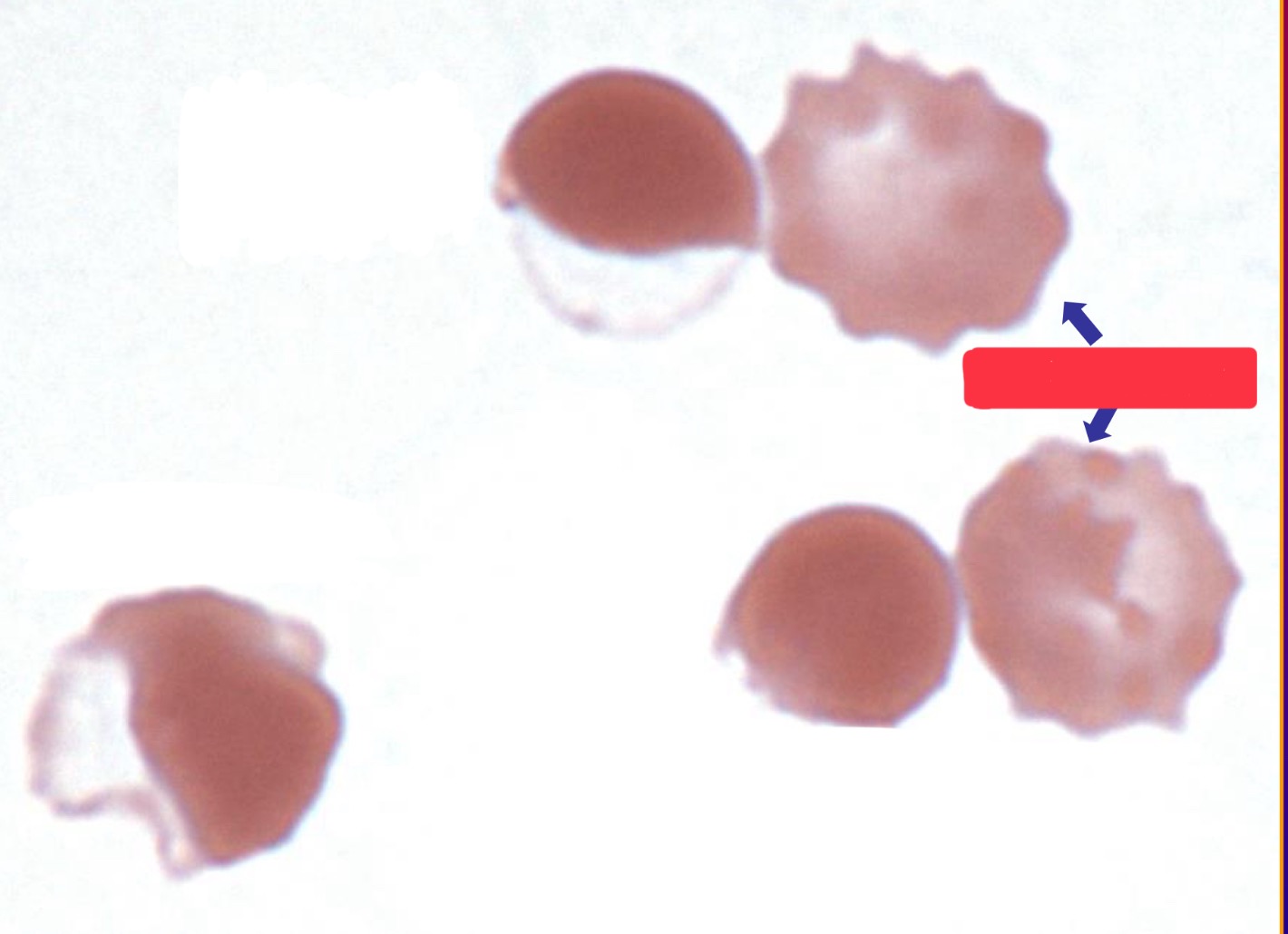
What are these cells?
echinocytes
What are examples of endogenous oxidants? What is the anemia?
K
I
N
U
ketoacidic diabetes
inflammation
neoplasia
unknown causes
generally mild
What are examples of exogenous oxidants? What is the anemia?
O
G
N
P
V
onions
garlic
NSAID
propofol
vitamin K
mild to severe
What are other factors that can lead to eccentrocytes?
A
R
R
I
E
acetaminophin
rodenticides
red maple toxicity in horses
IV hydrogen peroxide in cows
enzyme deficiencies (G6PD and GR) in horses
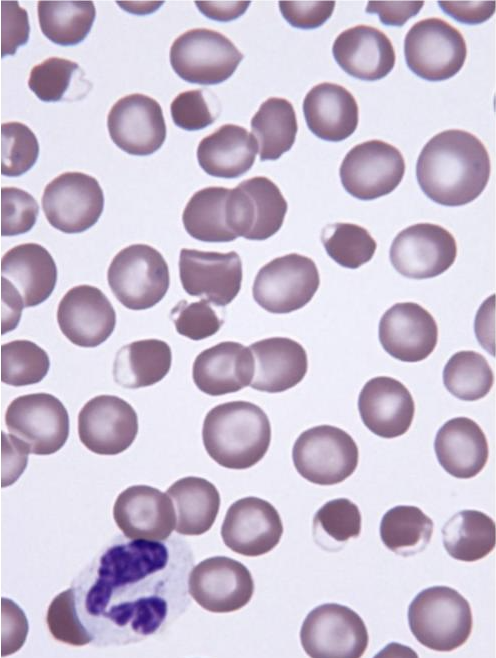
What is this showing?
eccentrocytes
What can cause multiple shape abnormalities?
L
H
G
M
D
C
D
M
C
liver disorders
hemangiosarcoma in dogs
glomerulonephritis
myeloid neoplasms
DIC (especially dogs)
chronic iron deficiency anemia (dogs and ruminants)
doxorubican toxicity in dogs and cats
myelofibrosis
congenital dyserythropoiesis
Which erytrhocytes are generally nucleated?
rubricytes and metarubricytes
When are nucleated erythrocytes generally present in low numbers?
in healthy dogs and cats
When are the three most common reasons to see nucleated erythrocytes?
R
L
H
regenerative anemias
lead toxicity
heat stroke
When else will you see nucleated erythrocytes?
M
S
V
H
narrow injury or disease
splenic dysfunction
various disorders in dogs (cardiovascular, inflammation, trauma, hyperadrenocorticism)
various disorders in cats (hepatic lipidosis, acute trauma, inflammation)
hereditary hyserythropoiesis (dogs and cattle)
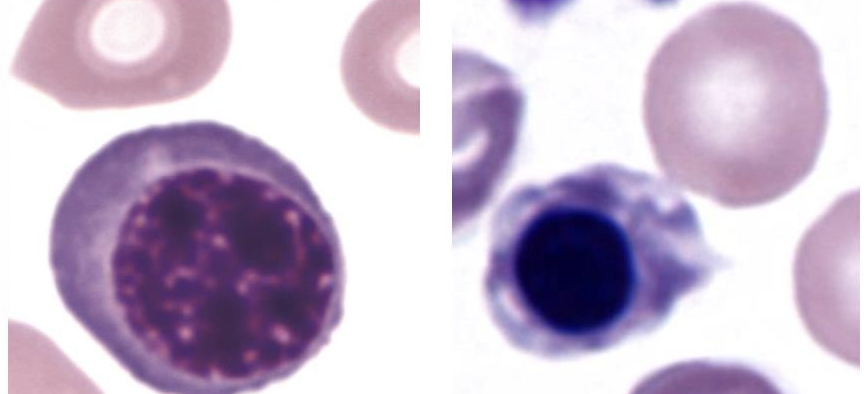
What are these cells?
nucleated erythrocytes
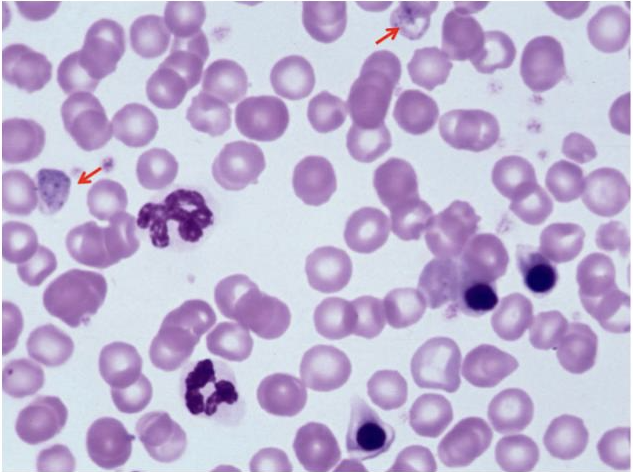
What is this showing?
lead toxicity in a dog (mild anemia with more nucleated erythrocytes than leukocytes)
Which marrow injuries may not be anemic?
S
E
D
H
septicemia
endotoxic shock
drugs
heat stroke
What are marrow diseases with nonregenerative anemia?
M
H
I
myelodysplasia
hematopoietic neoplasms
infiltrative disorders
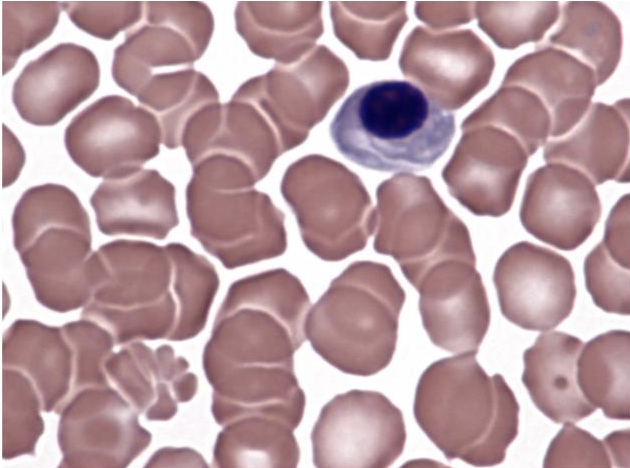
What is this showing?
dog with heat stroke (nucleated erythrocyte)
nuclear remnant that is normal in low numbers in cats and horses
Howell-Jolly body (micronucleus)
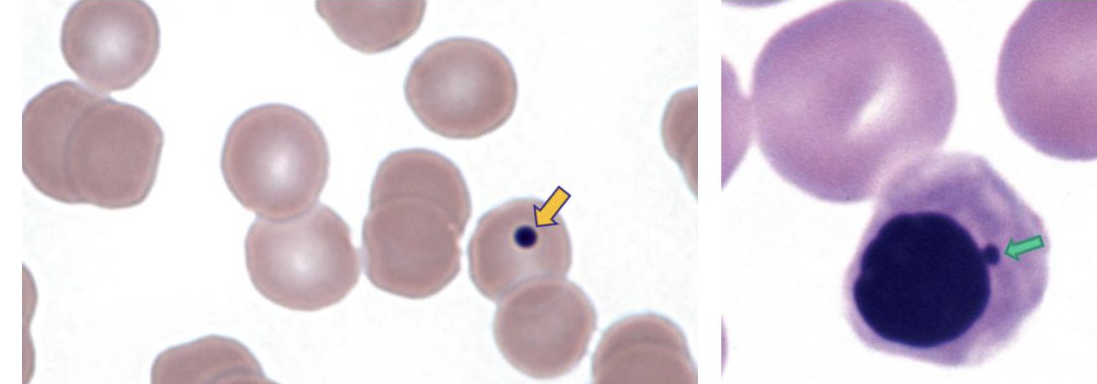
What is this cell?
Howell-Jolly body
When are Howell-Jolly body numbers increased?
regenerative anemias
When else may you see Howell-Jolly bodies?
S
G
V
N
splenectomy
glucocorticoids
vincristine therapy in regenerative anemia
nuclear fragmentation
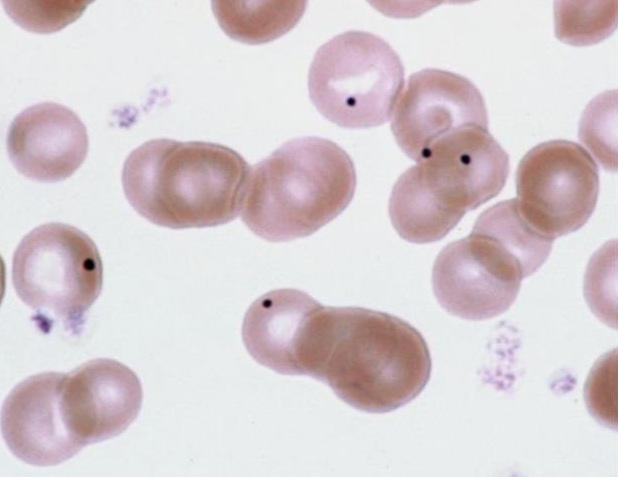
What is this showing?
dog post-splenectomy (Howell-Jolly bodies)
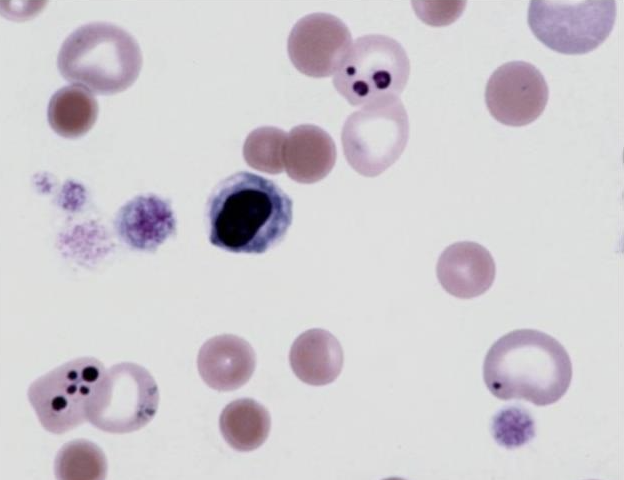
What is this showing?
dog vincristine treatment (Howell-Jolly bodies)
Up to 5% of heinz bodies is normally present in what species? With what diseases can they be increased?
D
L
H
cats;
diabetes
lymphoma
hyperthyroidism
What can cause the production of Heinz bodies in small animals?
S
A
P
Z
A
M
M
P
M
N
P
H
S
splenectomy in dogs
allium species (onion, garlic, leek, chive) ingestion
propylene glycol in soft-moist foods (cats)
zinc toxicity in dogs
acetaminophen
methylene blue
methionine
phenazopyridine
menadione (vitamin K3
naphthalene (dog)
propofol anesthesia in cats
hydrogen peroxide as an emetic
skunk musk in dogs
What can cause heinz body formation in large animals?
W
K
R
C
L
S
P
P
wild and domestic onions in livestock
kale and other brassica species in ruminants
red maple leaves in horses and alpacas
copper toxicity in sheep and goats
lush winter rye in florida cattle
selenium-deficient cattle on st. augustine grass
post-parturient New Zealand cattle on perennial ryegradd
phenothiazine in horses
diffuse pattern of aggregates of ribosomes and polyribosomes
basophilic strippling
Primarily in ruminants, what is basophilic strippling due to?
regenerative anemia
What is an extremely common reason for basophilic strippling?
lead toxicity
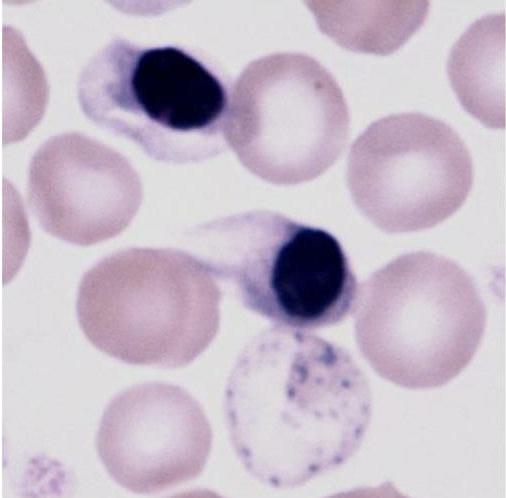
What is this showing?
lead toxicity (basophilic strippling)
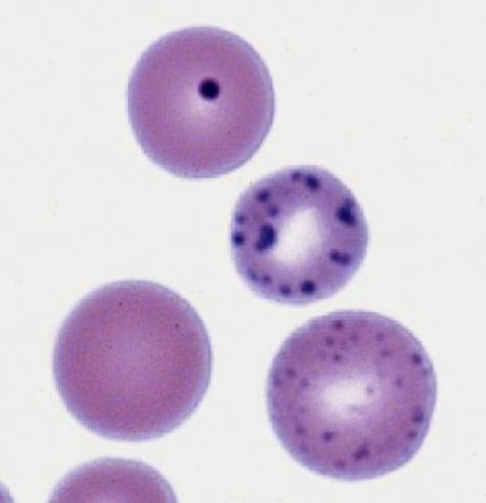
What is this showing?
regenerative anemia (basophilic strippling)
What are the infectious agents of erythrocytes?
P
R
M
B
V
protozoal organisms
rickettsial organisms
mycoplasma organisms
bacterial organisms
viral organisms
What are examples of protozoal organisms?
B
T
C
babesia species
theileria species
cytauxzoon species
What are examples of rickettsial organisms?
anaplasma species
What are examples of bacterial organisms?
bartonella species
What are examples of viral organisms?
distemper
single celled organisms with a nucleus and cytoplasm
protozoa