BIOL 208: Lecture 7 - Temperature constraints
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
67 Terms
Macro Vs. Micro climate definition?
Macro = Large scale climate that prevail over entire regions
Micro = small scale climate patterns (down to cm)
can deviate from macroclimate patters
What CAUSES macro vs. micro climate?
Macro = Determined by climate CELLS + TOPOGRAPHY
Micro = by landscape, vegetation or small scale topography features
What are some small scale topography features?
Elevation, mountain aspect, vegetation, surface color, depression, ravines etc.
How does ELEVATION influence climate?
Increase in elevation = decrease in mean annual temperature
What reflects a shift in microclimates with increasing elevation?
TIMBERLINE/ tree line
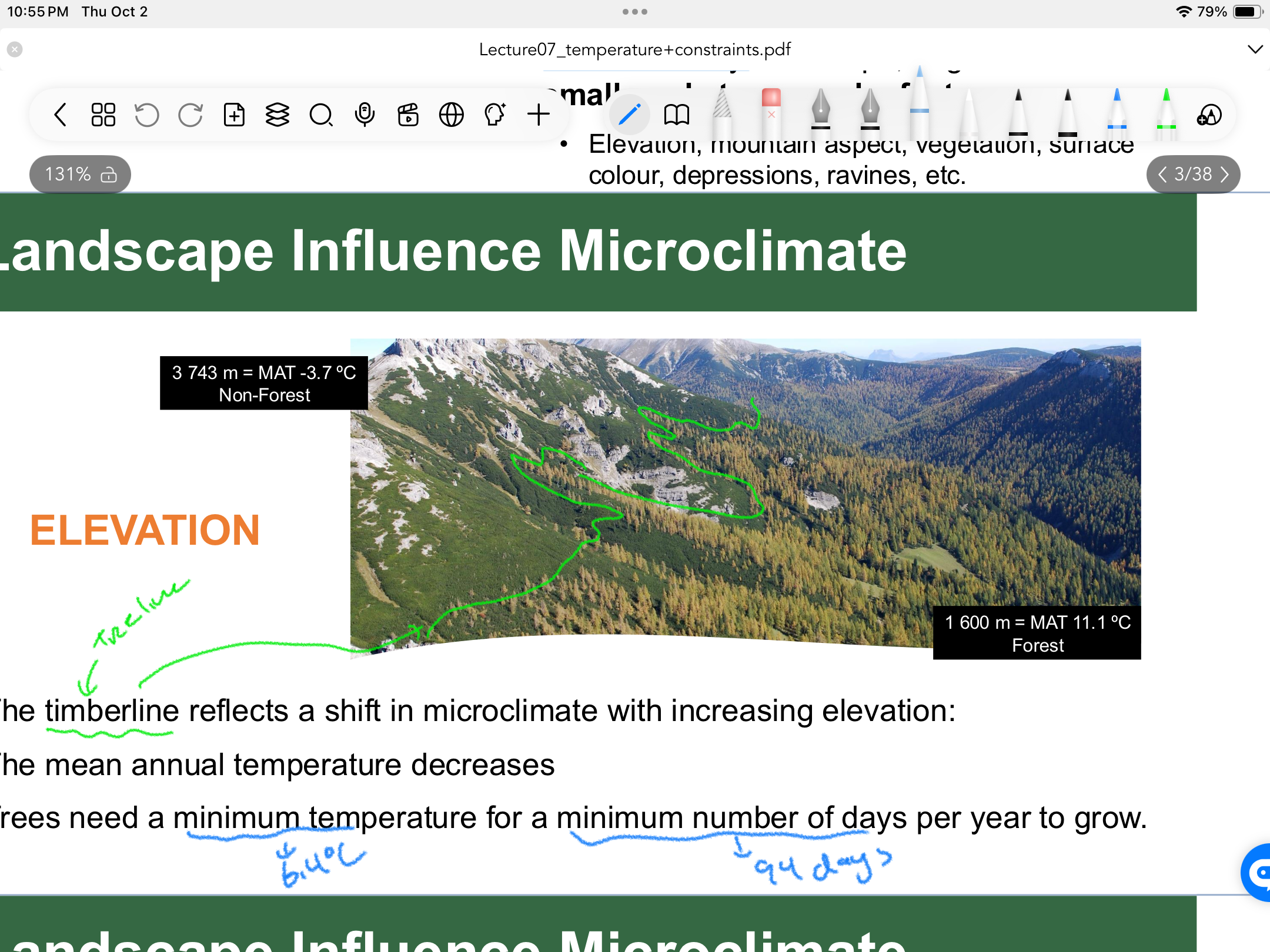
Why is there a timberline with increasing elevation?
Trees need a MINIMUM TEMP (64) for a MIN # of DAYS (94) per year to grow
Increase in elevation = decrease in mean annual temperature
What is aspect
Direction in which a slope faces

****Specifically in the NORTHERN-HEMISPHERE, how do North and South facing aspects differ?
North facing:
Receive less radiation = lower temps
South facing:
Receive more solar radiation
Why do north facing aspects in the N-hemisphere receive less sun?
Tilt of earth
north aspect = tilted away
****How does North + south aspects differ in landscape in the N-hemisphere? WHY
North = Forest growth
Less radiation = higher snow load = more water
South = No forest growth
More radiation = less snow load = less water
What about for the southern hemisphere, how do the aspects differ?
Opposite in the south
south = less radiation = more water = tree growth
north = more radiation = less water = no tree growth
How does VEGETATION influence microclimates (2 specific effects on microclimate)
Shade (from trees + shrubs)
In understory:
Temp = cooler
Evaporation = decreased
How does surface color influence microclimate?
Lighter colors = reflect sun = no increase in temp
Darker colors = Absorb light = increase in temp
Define ALBEDO
Reflectivity of a landscape
how much light reflected + does not get absorbed
Contrast between HIGH vs. LOW albedo.
High = reflect more light = light colors
Low = Reflect less light = dark colors
How do Boulders + burrows influence microclimate?
create shade
allow inhabiting animals to avoid heat during the day
Do water temps fluctuate more or less than air temp?
Less
Why do coastal areas have more mild temp/ How does water maintain a stable temp?
Heat = ABSORBED by water as it EVAPORATES
Heat = EMITTED by water as it FREEZES
specific heat capacity
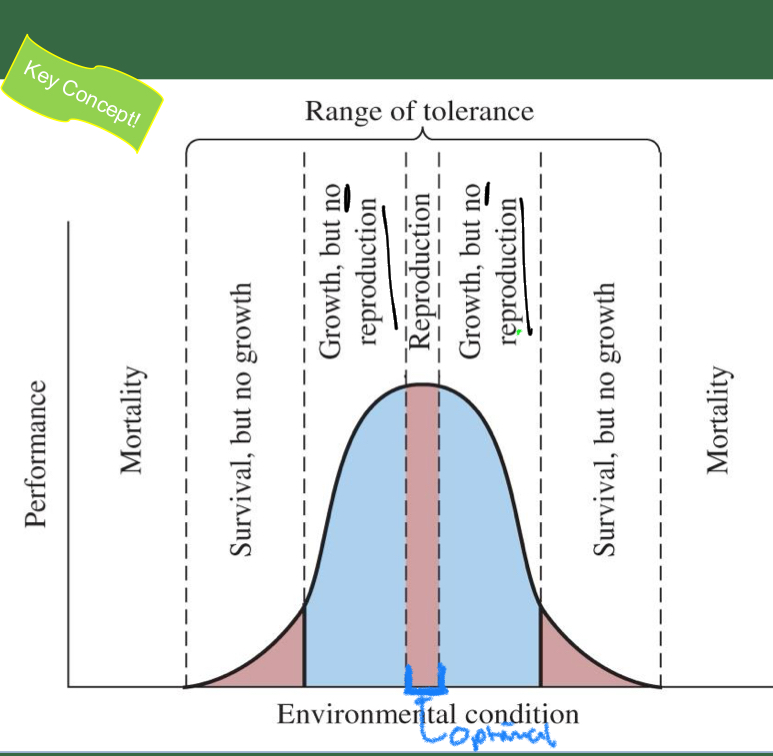
Define Range of Tolerance
ENTIRE range of environmental conditions (abiotic factors) in which the organism can survive
****what occurs in the optimal range of conditions?
Grow AND reproduce
species perform best
What occurs beyond the optimum? What does the organism experience?
survival decreases
Organism experiences physiological stress at margins of a limiting factor
What zone is beyond the range of tolerance? what occurs there?
Zone of intolerance
mortality
****How does Range of tolerance differ from Fundamental Niche?
Range of tolerance = in relation to one condition eg. temp (abiotic)
Fundamental niche = all the environmental factors (abiotic + biotic)
Define the Law of Tolerance
The survival and distribution of an organism can be determined by the deviation between location conditions + optimum conditions of the species
Environmental conditions affect abundance + distribution of organism
Diff plant species show different ranges of tolerance + optima in photosynthetic rate for different climates, Why can’t species have it all and adapt to all different temps?
Evolutionary trade off
Define evolutionary trade off
adapting to one set of environmental conditions reduces fitness in other environments
adaptations you gain in one environment won’t help you/apply to another
What is the Principle of allocation
Organisms have limited amount of energy
organisms allocate E to one function thus reducing E available to other functions
Balancing E budget
What do each of the components of the Heat loss equation represent?
Hs = total heat stored
Hm = heat GAINED through metabolism
Hcd = gain/loss Through conduction
Hcv = gain/loss through convection
Hr = heat gain/loss through radiation
He = heat LOSS through evaporation
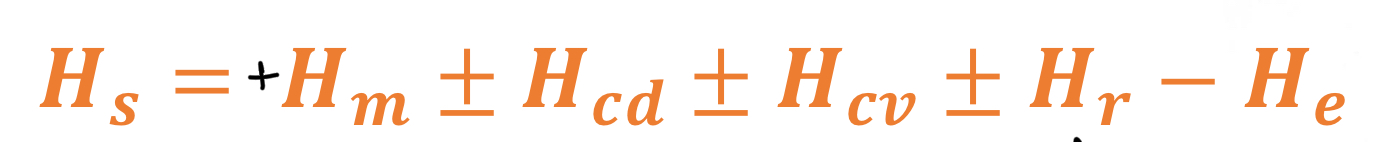
Define HOW heat is lost for Hcd, Hcv + Hr
Hcd = conduction = in physical contact
Hcv = Convection = through the movement of fluid (water/ wind)
Hr = Radiation = all things release radiating energy regardless of temperature
What variables of the Heat balance equation to do Arctic + alpine plants manipulate to adapt to COLD temperatures?
Increase heat gain from Hr
Increase heat gain from Hcd
Decrease heat loss from Hcv
What 4 adaptions do arctic + alpine plants do to adapt to cold temperatures + which of the heat balance equation variables does it affect.
Dark colored leaves = Increase heat from Hr
Leaf + Flower orientation = Increase heat from Hr
Cushion growth form (low growth form, close too ground) = Increase gain from Hcd + decrease heat loss from Hcv
Smaller SA:V ratio = decrease heat loss from Hcv
What is an example of a PLANT that can do thermogenesis? what benefit does it have to the plant?
Skunk Cabbage
warmth attracts pollinators
What variables of the Heat balance equation to do Desert plants manipulate to adapt to HOT temperatures?
Decrease heat gain from Hr
Decrease heat gain from Hcd
Increase heat loss from Hcv
What 4 adaptions do desert plants do to adapt to Hot temperatures + which of the heat balance equation variables does it affect.
Light colored leaves + reflective surfaces (eg. hairs) = decrease Hr
Decreased contact with ground = Decrease heat gain from Hcd + increase heat loss from Hcv
Open growth form = Increase heat loss from Hcv
Reduce leaves = decrease heat gain from Hr
Why is it always Hr, Hcd + Hcv manipulated for heat balance but never Hm or He?
Hm is always heat GAIN (always + can never be heat loss)
He is always heat LOSS (always - can never gain heat from evaporation)
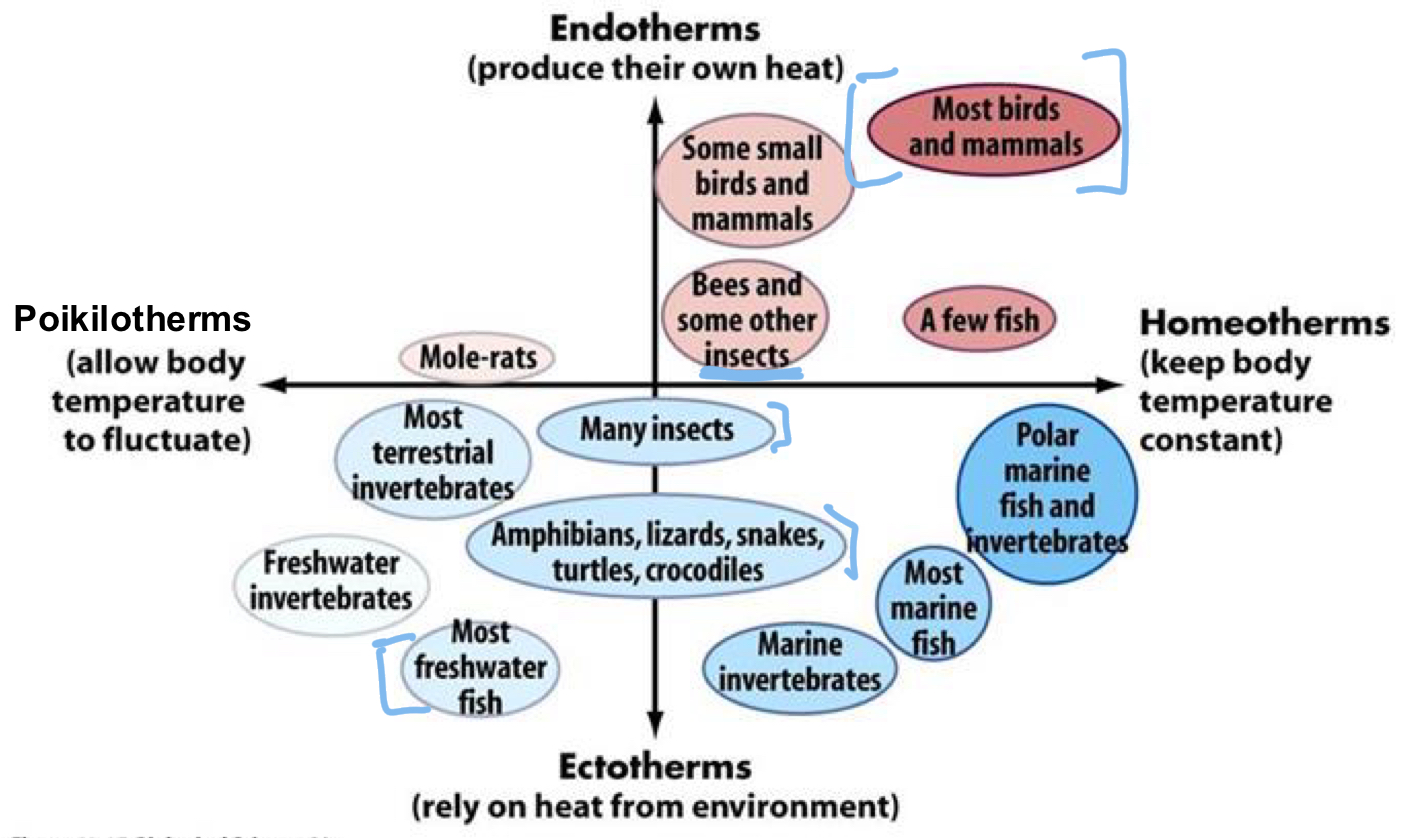
*****What are the 2 classifications of Animals regarding body temp relative to environment?
Poikilotherm = body temp VARIES with environment
Homeotherms: Body temp = relatively CONSTANT regardless of environmental temp
*****What are the 2 classifications of Animals Based on the organism controls body temp?
Ectotherm = control body temp using EXTERNAL energy
Endotherms = control body temp using INTERNAL energy
Is the diversity of ectotherms widespread over the globe?
No
diversity is limited in cold climates due to their reliance on external sources of heat
****What portions of the Heat balance equation do Ectoderms depend on to maintain body temp?
Hr, Hcd + Hcv
****What portions of the Heat balance equation do Endoderm’s depend on to maintain body temp?
Hm
Use E from METABOLISM
How do endoderm deal with cold? Hot?
Cold: Shivering (contract muscles) = generates heat
Hot: Sweating or Panting = increases CONVECTIVE (Hcv) cooling
Do endoderm’s have a very large range of tolerance for cold temps? What about hot?
Cold temps = yes
Hot temps = no
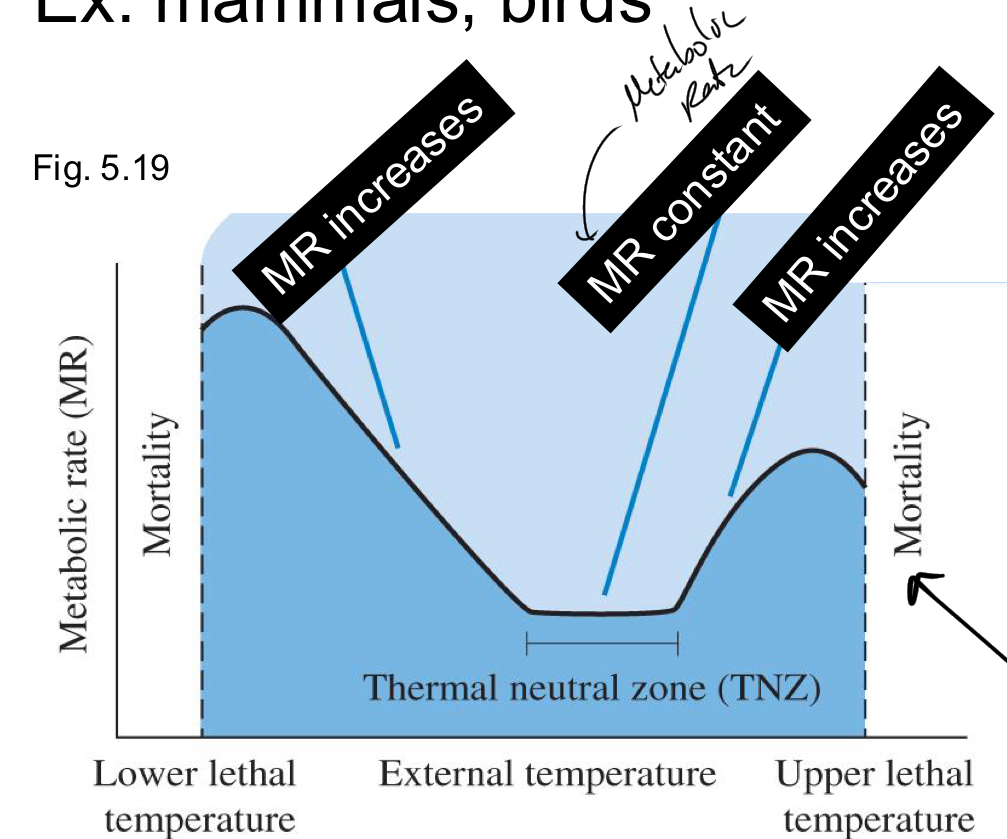
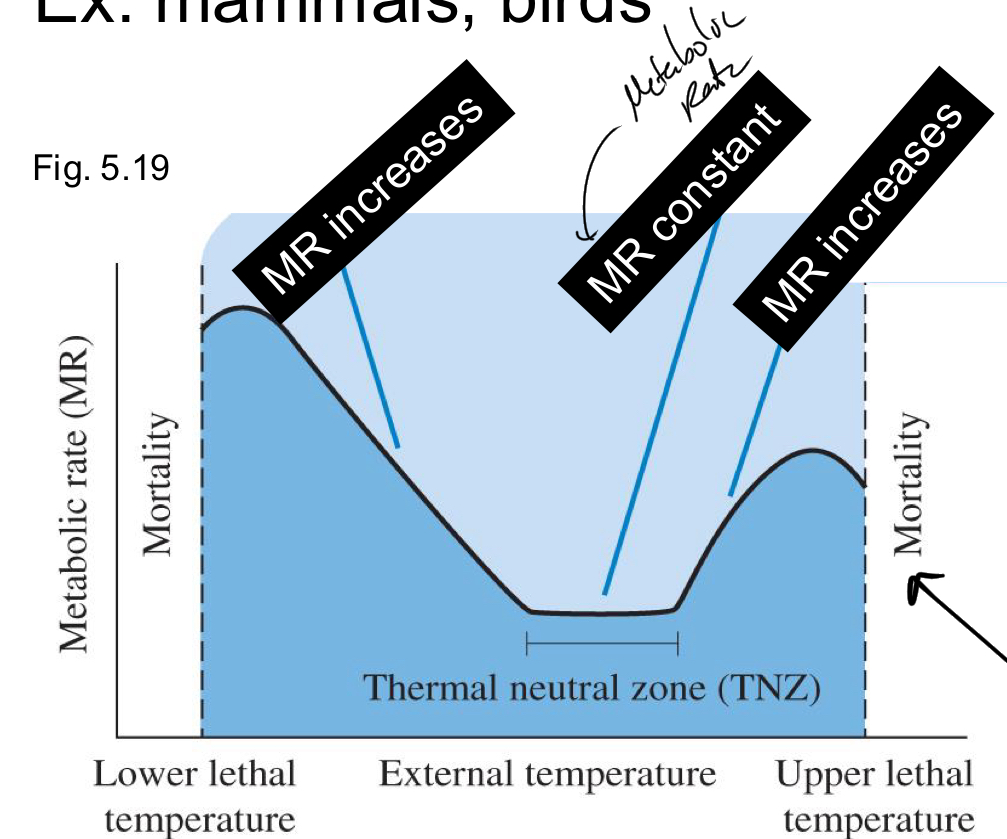
How does metabolism change with temp?
True or false: in practice organisms form a continuum along the four categories of temp regulation for animals?
True
***What are the 2 strategies for surviving Extreme temps (at the margins of the range of tolerance)?
Avoidance
Resistance
****What are the 2 methods for avoiding Extreme temps?
Die
Migrate
****What are the 2 methods for Resisting Extreme temps?
Adaption
Acclimate
How does DEATH work to avoid extreme temps?
Funnel all Energy to REPRODUCTION
adult dies but offspring have a chance
****What are 2 examples of using death to survive extreme temps?
Annual plants = SEED before winter
Insects = Allocate all resources to offspring which have COLD-TOLERANT life stages
How does migrating help to survive extreme temps?
Costs of staying = greater than costs of migrating to warmer regions
*****What are 3 Categories of ADAPTIONS to extreme weather?
Morphological
Physiological
Behavioral
What are some examples of morphological adaptions to extreme weather
Fur, Fat + feathers
What type of MORPHOLOGICAL adaption are made in terms of appendages. Why?
Short body appendages (eg. ears)
More volume Less surface area
How do such morphological adaptions help in extreme weather?
increase insulation
Decrease energy lost by Convection (Hcv) or Radiation (Hr)
Hibernation vs. Estivation?
Hibernation = adaptation to COLD temp
Estivation = adaptation to HOT temp
What type of Adaptation to the extremes are hibernation + estivation?
Physiological
What specific physiological adaptation occurs during hibernation/estivation? What occurs in the body?
Prolonged state of REDUCED METABOLIM
Morphological adaptation vs. Physiological adaption. What’s the difference?
Morphological = trait itself (physical structure)
Physiological = seasonal deposition + changes of fur + fat (internal functions)
Freeze avoidance, what CHEMICAL is synthesized in the body during this physiological adaptation?
Antifreeze Glycoproteins
Manipulate solute concentrations to prevent freezing of cells at cold temps
Freeze Tolerance, what CHEMICAL is synthesized in the body during this physiological adaptation?
Cryoprotectants
Protect the cells from the freezing that it goes through
*****Freeze tolerance vs. Freeze avoidance. DIFFERENCE in chemical produced, water content in body + rate of activity
Cryoprotectants vs. Antifreeze Proteins:
Freeze tolerance relies on the presence of cryoprotectants to protect cells from freezing damage,
Freeze avoidance relies on antifreeze proteins to prevent ice crystals from forming.
Water Content:
Freeze tolerance often involves dehydration, allowing cells to freeze and thaw without damage,
Freeze avoidance maintains cell water levels and prevents ice crystal growth.
Metabolic Rate:
Freeze tolerance slows down metabolic rates to conserve energy = INACTIVE
Freeze avoidance maintains normal metabolic rates while producing antifreeze molecules (ACTIVE)
What are some examples of Behavioral adaptations to extremes?
Avoidance = seek shelter/ Burrows
Define Acclimation
Physiological changes an organisms goes through in response to changes in the environment
Is acclimation the same as adaptation?
No
Acclimation is a example of what we’ve talked about before in class?
Phenotypic plasticity
*****How can acclimation be considered an adaptation?
The ABILITY TO ACCLIMATE = an adaptation
****Compare the Definitions of Adaptation vs. Acclimation. What is the DIFFERENCE?
Acclimation:
physiological changes in response to changes in the environment (pH, humidity, temp etc.) Within an individuals life time
REVERSIBLE CHANGE
Adaptation:
evolutionary process that changes anatomy, physiology or behavior across generations + on a genetic level
NOT REVERSIBLE