Anatomy and Physiology for Speech Pathology 1
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
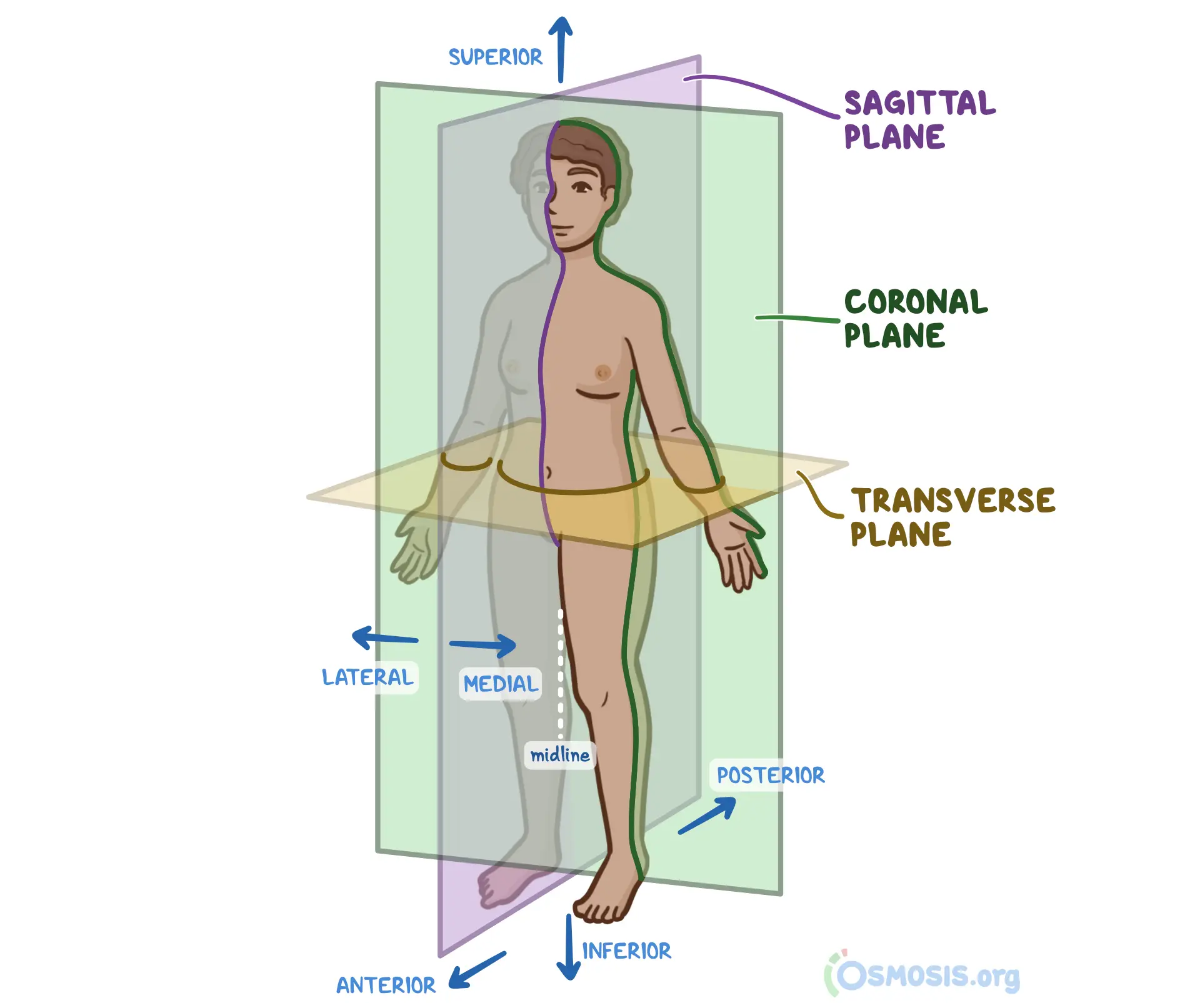
Anatomical Position

The standard position of the body used as a reference in anatomy, where the individual stands upright, facing forward, arms at the sides with palms facing forward, and feet together.
Planes of Section

The hypothetical lines that divide the body into sections for anatomical study, including sagittal, frontal (coronal), and transverse planes.
Sagittal Plane

A vertical plane that divides the body into right and left parts.
Transverse Plane

A horizontal plane that divides the body into upper and lower parts.
Coronal Plane

A vertical plane that divides the body into anterior (front) and posterior (back) sections.
Organ System
A group of organs that work together to perform complex functions essential for the body's survival and health.
Cell

The basic structural and functional unit of living organisms, capable of performing all life processes. Cells combine to form tissues, organs, and systems in the body.
Nucleus

The control center of a cell, containing genetic material (DNA) and coordinating activities such as growth, metabolism, and reproduction.
Plasma Membrane
The outer boundary of a cell that regulates the movement of substances in and out, maintaining homeostasis and protecting the cell's interior.
Anatomical Position
Cytoplasm

The gel-like substance within a cell, excluding the nucleus, that contains organelles and is the site for many metabolic processes.
Cytosol

The aqueous component of the cytoplasm in which organelles, proteins, and other cell structures are suspended, playing a crucial role in cellular metabolism. Fluid part of cytoplasm.
Cytoskeleton
A network of protein filaments and tubules that provides structural support, shape, and organization to the cell, playing key roles in intracellular transport and cell division.
Organelles
Specialized structures within a cell that perform distinct functions, such as energy production, protein synthesis, and waste processing. Examples include mitochondria, ribosomes, and the endoplasmic reticulum.
Epithelial Tissue
A type of tissue that lines the surfaces and cavities of organs and structures throughout the body, providing protection, absorption, and secretion functions.
Squamous
epithelial cells characterized by their flat, scale-like shape, often found in areas where diffusion or filtration occurs.
Cuboidal

A type of epithelial cell that is cube-shaped, commonly found in glandular tissues and involved in secretion and absorption.
Columnar

A type of epithelial cell that is taller than it is wide, often found in the digestive tract and involved in absorption and secretion. Taller and wider than other epithelial tissues.
Stratified Epithelial

cells composed of multiple layers, providing protection in areas subject to abrasion, such as the skin and lining of the mouth. More than 1 cell stacked on top of each other.
Connective Tissue

Tissue that supports, protects, and gives structure to other tissues and organs in the body.

Structural Connective Tissues
Composed primarily of an extracellular matrix and a limited number of cells.
Fluid Connective Tissue
Blood and lymph are fluid connective tissues. They contain cells, also known as formed elements, circulating in a liquid extracellular matrix, the plasma. The formed elements are derived from hematopoietic stem cells in the bone marrow.

Connective Tissue Proper

Connective tissue proper is a class of connective tissue that encompasses all mature connective tissues except bone, cartilage, blood, and lymph.

What is anatomy terminology?
Directional terms describe the positions of structures relative to other structures or locations in the body.
Where is the sagittal plane divided?
The sagittal plane is divided via the the middle of the body. It separates the left and right side of the body vertically.
How does the Coronal Plane divide the body?
The coronal plane divides the body via the front and back. Done by slicing down horizontally
Describe how the transverse plane divides the body.
The transverse plane divides the body via a cut at the hips. This separates the body into 2 half’s. The top with hands, head and stomach, and the bottom half, legs, genitals, toes, feet.
What are the main components of a cell?
Nucleus, Plasma membrane and Cytoplasm.
What are the main cytoplasm components?
Cytosol (fluid inside of cell), cytoskeleton (filaments inside and give it its structure), organelles (machines that carry out specific roles inside the cell)
What is an example of an Organelle?
An example of an organelle is the Mitochondria because its specific role is to produce energy to the cell.
Name the primary tissues
Primary Tissues= epithelial tissue, connective tissue, structural connective tissue, fluid connective tissue, and connective tissue proper.
Name the SIMPLE Epithelial tissues
Squamous (flat), cuboidal (cube shaped), columnar (taller and wider than cuboidal)
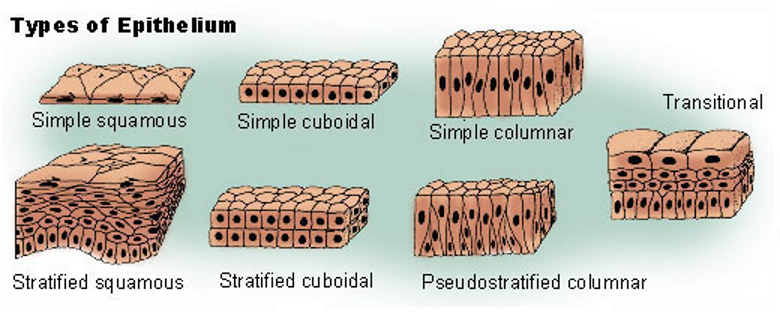
What is the tissue called if it is 1 cell thick?
A tissue that is 1 cell thick is called SIMPLE
What is the tissue called if it has more than 1 cell?
If more cells were stacked on top of each other it is referred to as stratified epithelia

What is a part of the Structural Connective Tissue?
Bones and Cartilage
What is a part of the Fluid Connective Tissue?
Blood
What is a part of the connective tissue proper?
FAT
What is a part of the connective tissue?
Stores fat. includes bone, cartilage, fat, blood, and lymphatic tissue (ref national cancer institute)