Baroque Art Exam 2 - Weeks 7-10
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
Things to consider
Flemish Baroque
Protestant Reformation / Counter-Reformation
Iconoclasm
calvinist iconoclastic riot, destroyed art from churches and forced a reevaluation of art/replaced art with new art
Revolt of the Netherlands
Court art
The style was fueled by patronage from both the Counter-Reformation church and powerful political entities, such as the English monarchy and the Spanish Habsburgs.
Spanish Baroque
Counter-Reformation spirituality
characterized by intense emotion, dramatic realism, and fervor, aiming to inspire piety and devotion through art that reaffirmed Catholic doctrine, tenebrism and drama
Development of a native artistic tradition
Court art
French Baroque
Influence of Italian Baroque
took drama and lighting and things from Italy but then reinterpreted it into a clear way
Artists visiting/living in Rome
French artists Nicolas Poussin and Claude Lorrain are the most significant French Baroque artists who lived and worked in Rome, developing a more classical style. Other French artists like Valentin de Boulogne worked in the more dramatic, tenebrist style influenced by Caravaggio. Additionally, French artists like Simon Vouet and were also present in rome
Influence of Caravaggio
tenebrism and naturalism
Classical Landscape tradition, historicized landscapes
Poussin & Classicism
Nicolas Poussin was a key figure in 17th-century Classicism, founding the French Classical tradition with an artistic style that emphasized order, harmony, and moral clarity over the emotional intensity of the Baroque. He drew heavily from the art of antiquity and Renaissance masters like Raphael, prioritizing structure, narrative clarity, and rationality in his history paintings and landscapes
Court art
Louis XIV—Versailles, power, & opulence
Development of French Baroque architecture
evolving from Italian Baroque to emphasize classicism, grandeur, and symmetry. focus on flaunting wealth and intricacy

Peter Paul Rubens, Marchesa Brigida Spinola Doria,
1606
Rubens, Marchesa Brigida Spinola Doria, 1606
-made during his visit to Genoa
-dramatic use of light and opulent detailing
-commissioned by her husband
-was trimmed from its original size
-made during the revolt of the netherlands
-living and breathing, a real work of art
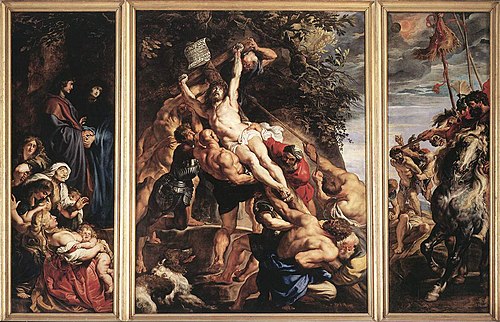
Rubens, Raising of the Cross, Antwerp Cathedral, 1610
-commissioned for a church that was torn down
-key to flemish bAROQUE!!!!!!!! commissioned during counter-reformation to teach religious truths in a dramatic way
-rubens brought knowledge from italy, particularly from caravaggio and michelangelo
-triptych
-altarpiece
-dog
-highly idealized jesus body, no marks on torso
-the visitation
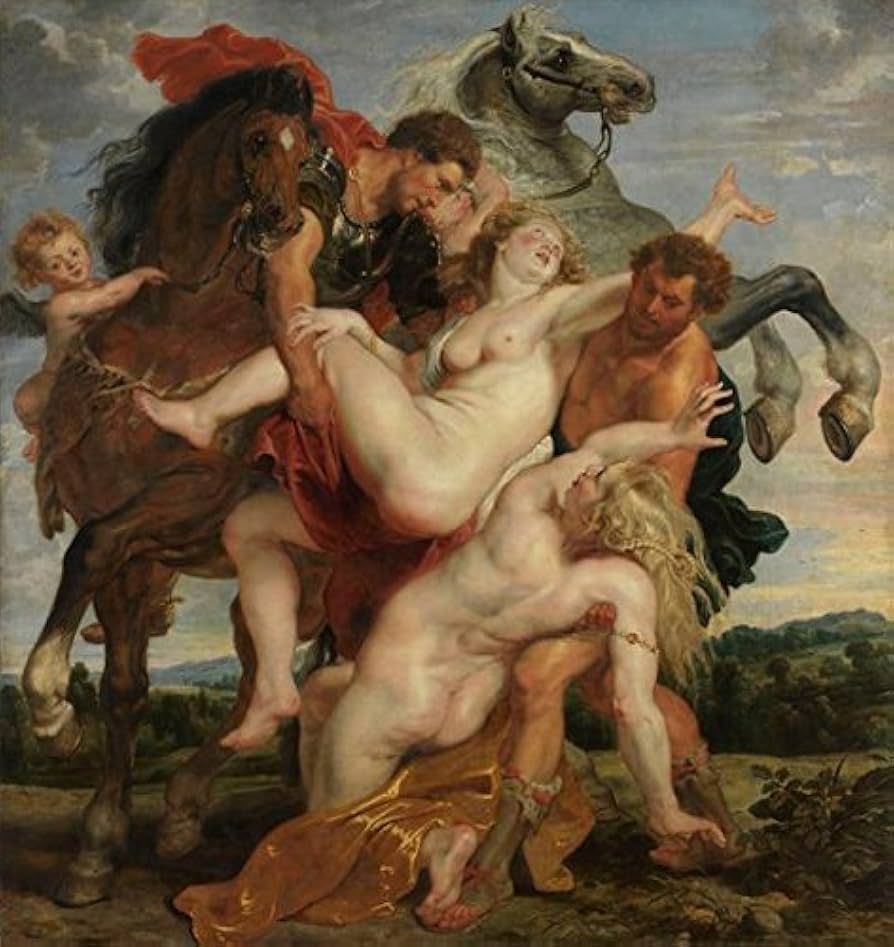

Rubens, Rape of the Daughters of Leucippus, 1618
-Rubenesque bodies
-greek mythology
-reflection of fabric on body
-jewelry
-pale skinned women

Peter Paul Rubens, Miracles of St. Francis Xavier, 1618-19
-Jesuits (Jesus)
-Jesuits wear black robes
-Hindu deities on the columns n stuff (not actually but they were intended to be)
-a large altarpiece commissioned by the Jesuits in Antwerp for their church, intended to serve as a powerful piece of Counter-Reformation propaganda
-the painting was created in hopes that it would quicken st. francis xavier’s canonization
-one of his hands is pointing towards fides, the personification of faith
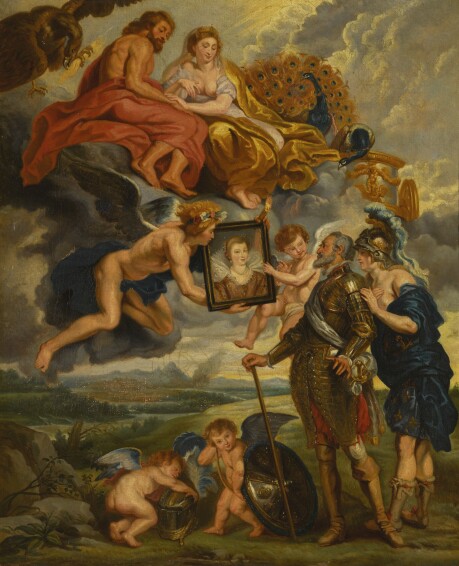

Rubens, Henri IV Receiving the Portrait of Marie de' Medici, Marie de' Medici cycle, 1622-1625
-Marie was a wealthy princess of the Medici family married to Henry IV of France
-cupid and hymen representing love and marriage
-jupiter and juno representing france and marie
-ALLEGORY^^^^^^^^
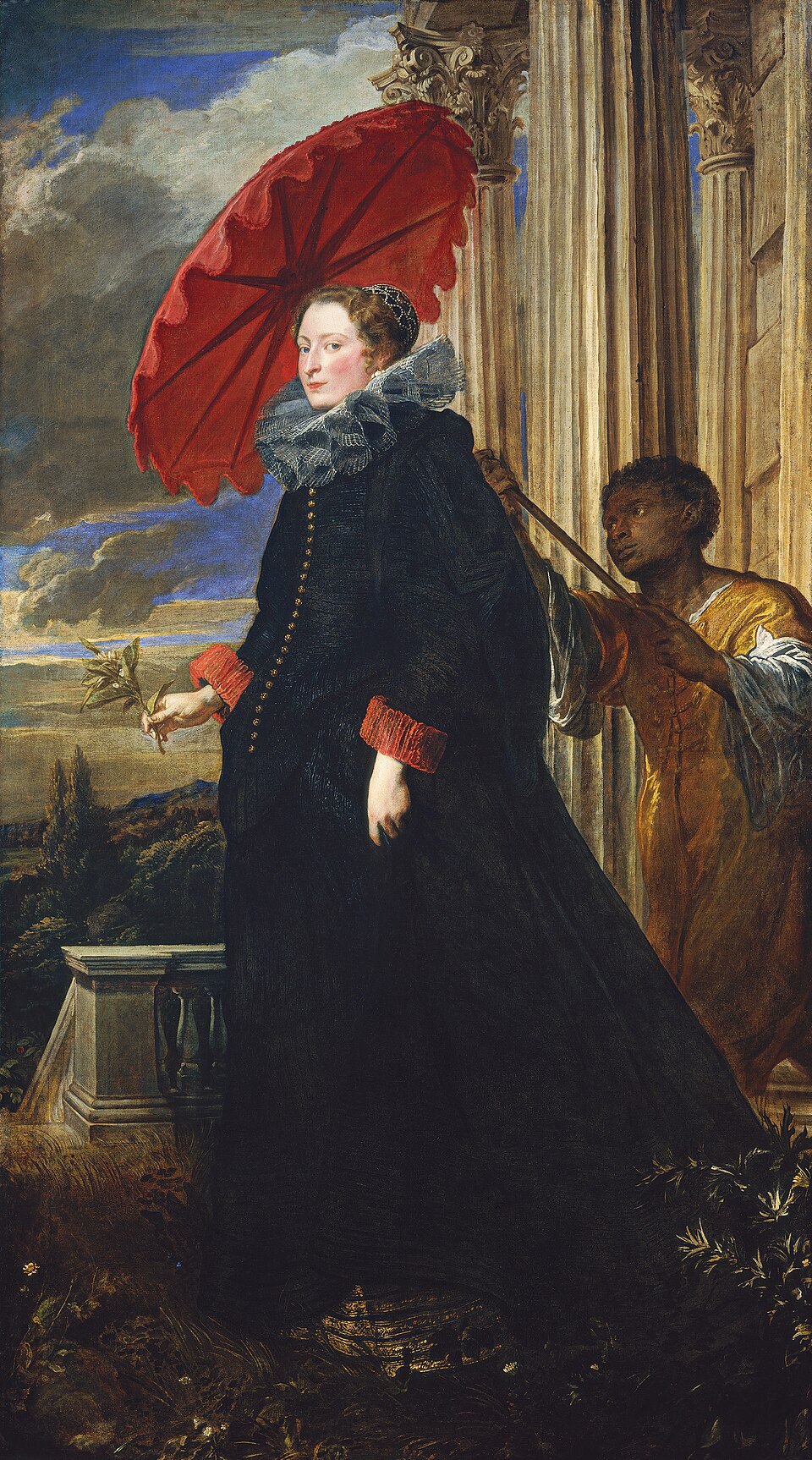

Anthony Van Dyck, Elena Grimaldi, 1623 (FLEMISH BAROQUE)
-”Grand Manner” portrait
-Painted during Van Dyck’s stay in Genoa
-Show of wealth, person behind her is likely a slave/servant
-During transatlantic slave trade times
-When compared to his famous peer and teacher Rubens, the subject of this painting has more implied motion
-Graceful
-Painted during the revolt of the Netherlands, Flanders was kept by Catholic Spain
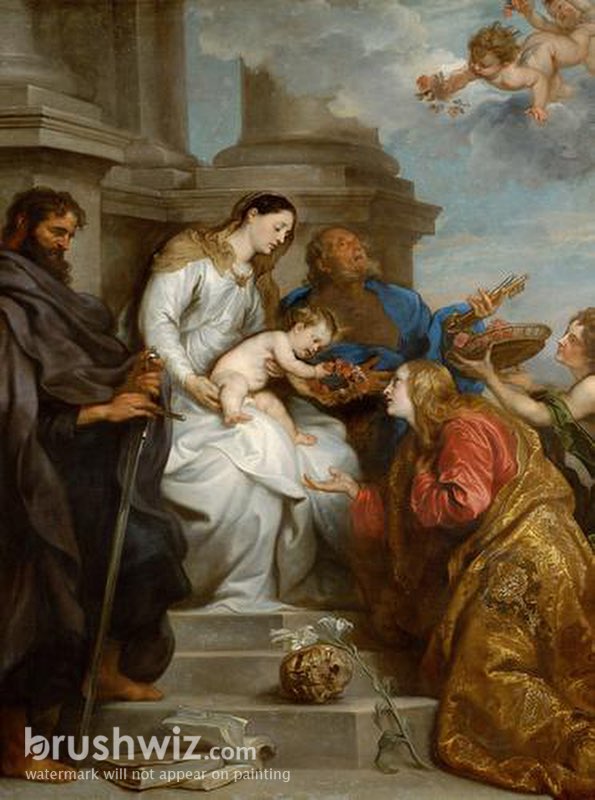

Anthony Van Dyck, Virgin & Child with St. Paul,
Peter, and Rosalie, 1629
-Confraternity "Christian Club", status symbol, commissioned him to make an altarpiece for their chapel in Antwerp
-Titian
-Veronese
-Sacra Conversazione
-Rosalie's bones cured the plague? Becomes invoked to cure the plague
-Painted during Netherlands revolt
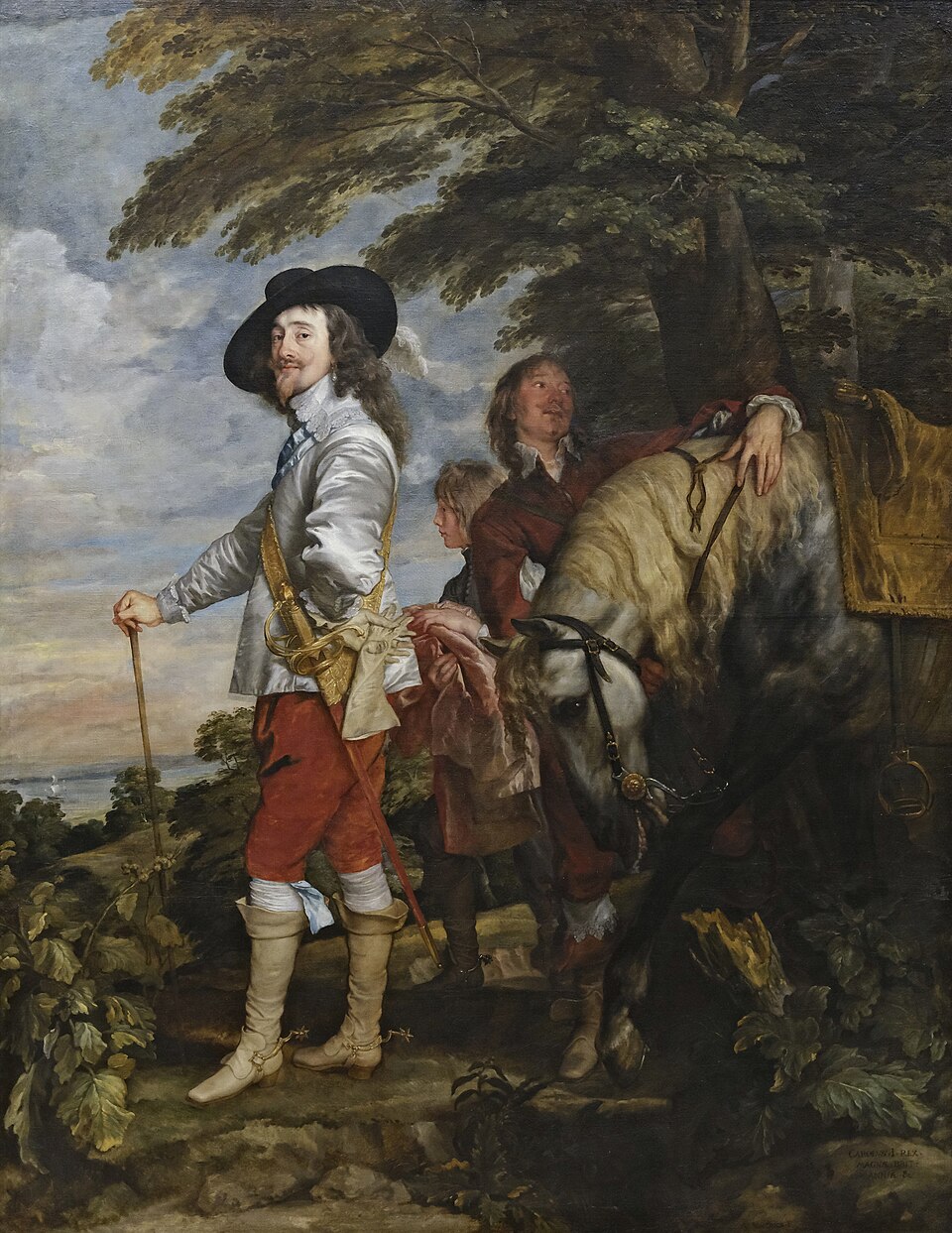

Anthony Van Dyck, Charles I at the Hunt, 1635
-Painted while Van Dyck was a painter for the King of England
-Purposely looks up at Charles to make him seem tall
-contributed to the Van Dyck trend of portraits at the time by keeping a sense of authority yet showing subjects at leisure.
-Charles I’s clothing and attitude in this painting sort of encapsulates his attitude towards power, and shows a conflict with parliament, leading to his beheading.
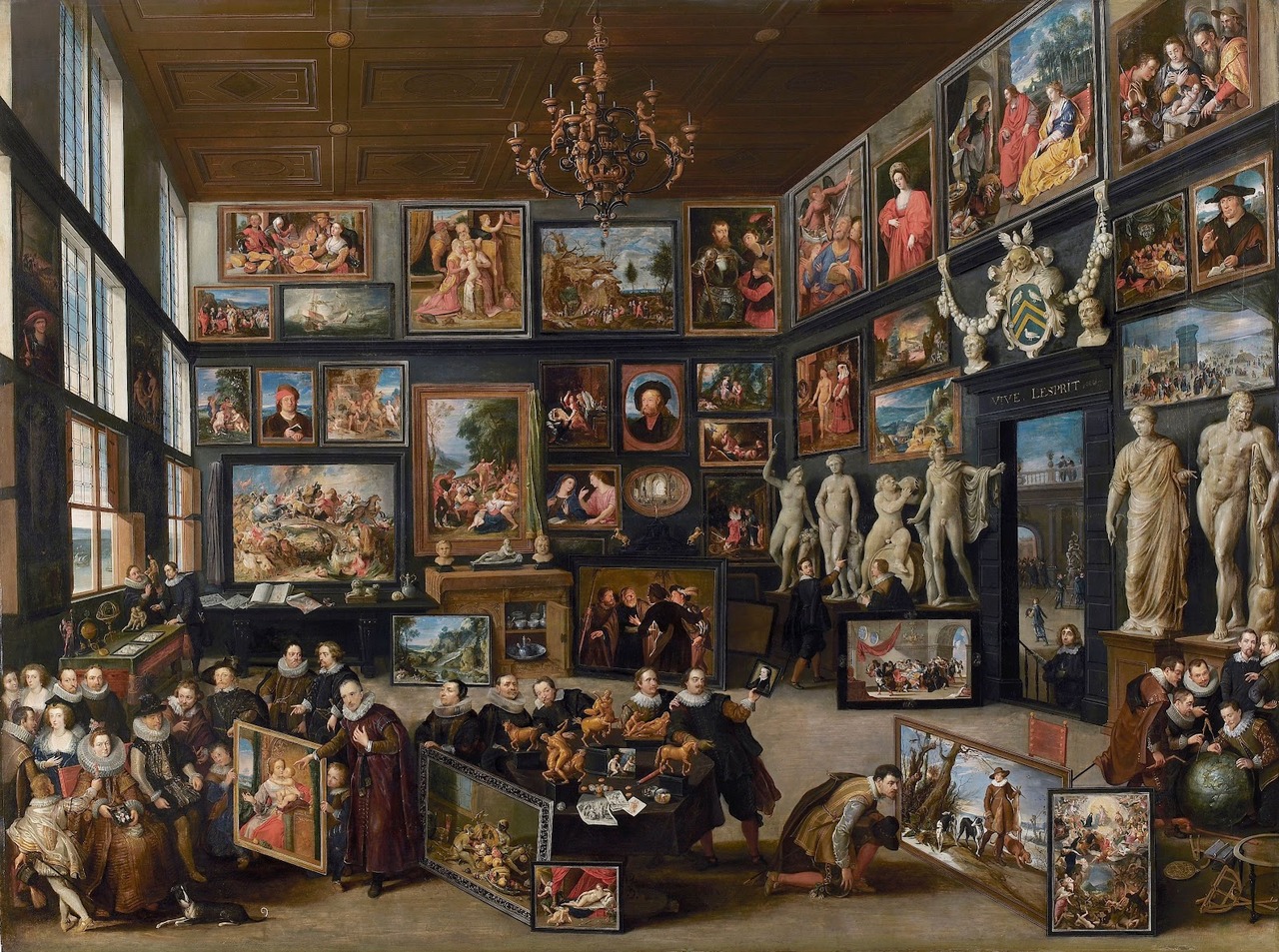

Willem van Haecht, The Art Gallery of Cornelis van
der Geest, 1628
-Van der Geest was a wealthy merchant from Antwerp.
-Not exactly a representation of real life and his actual gallery & guests, but a gallery painting made to showcase the art he has collected.
-drawing on table is a reference to an ancient roman painter and is a possible allegory for art
-vive lespirit “long live van der geest!”
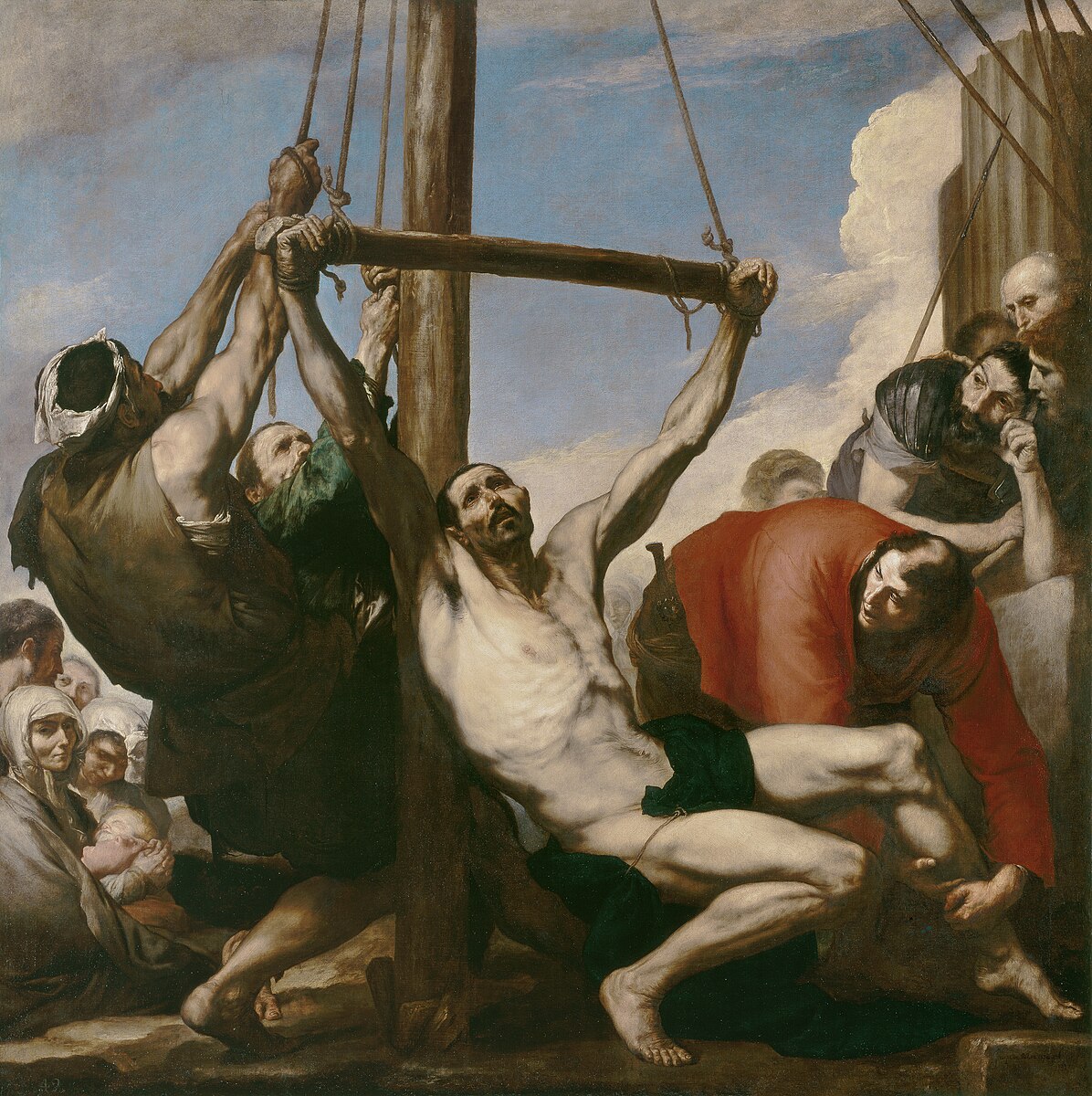

Jusepe de Ribera, Martyrdom of St. Philip, 1639
-depicts the moments before the crucifixion of the apostle, commissioned by the Duke of Medina de las Torres as a gift for King Philip IV
-Implied movement with the lifting of legs. elegant yet visceral, depicting such an intense act
-chiarascuro
-brutal themes in spanish baroque art
-commissioned by archduke, Viceroy of Naples, for King Philip IV of Spain
-Spain is poorest country at the time so only church and kings and wealthy people can commission paintings really
-St. Philip known for preaching the gospel in eastern Europe, martyred in turkey
-Definitely similar to Caravaggio's paintings
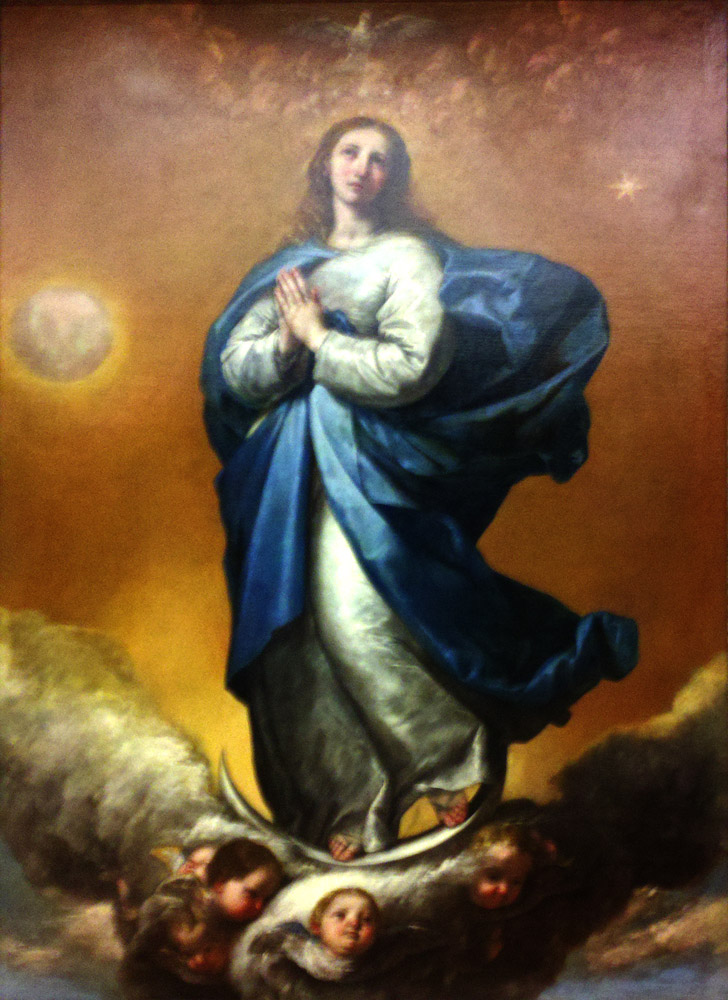

Jusepe de Ribera, Virgin of the Immaculate Conception, 1637
-favored over the more subtle paintings because of its dramatic baroque qualities and counter-reformation subject matter
-Ribera was very influenced by Caravaggio, having spent time in Italy and having seen Caravaggio’s work, but this painting turned away from that style
-influenced by guido reni's immaculate conception which was commissioned by a Spanish king
-commissioned as a large altarpiece
-big one for altar, little one for nun
-Catholicism
-Netherlands revolt
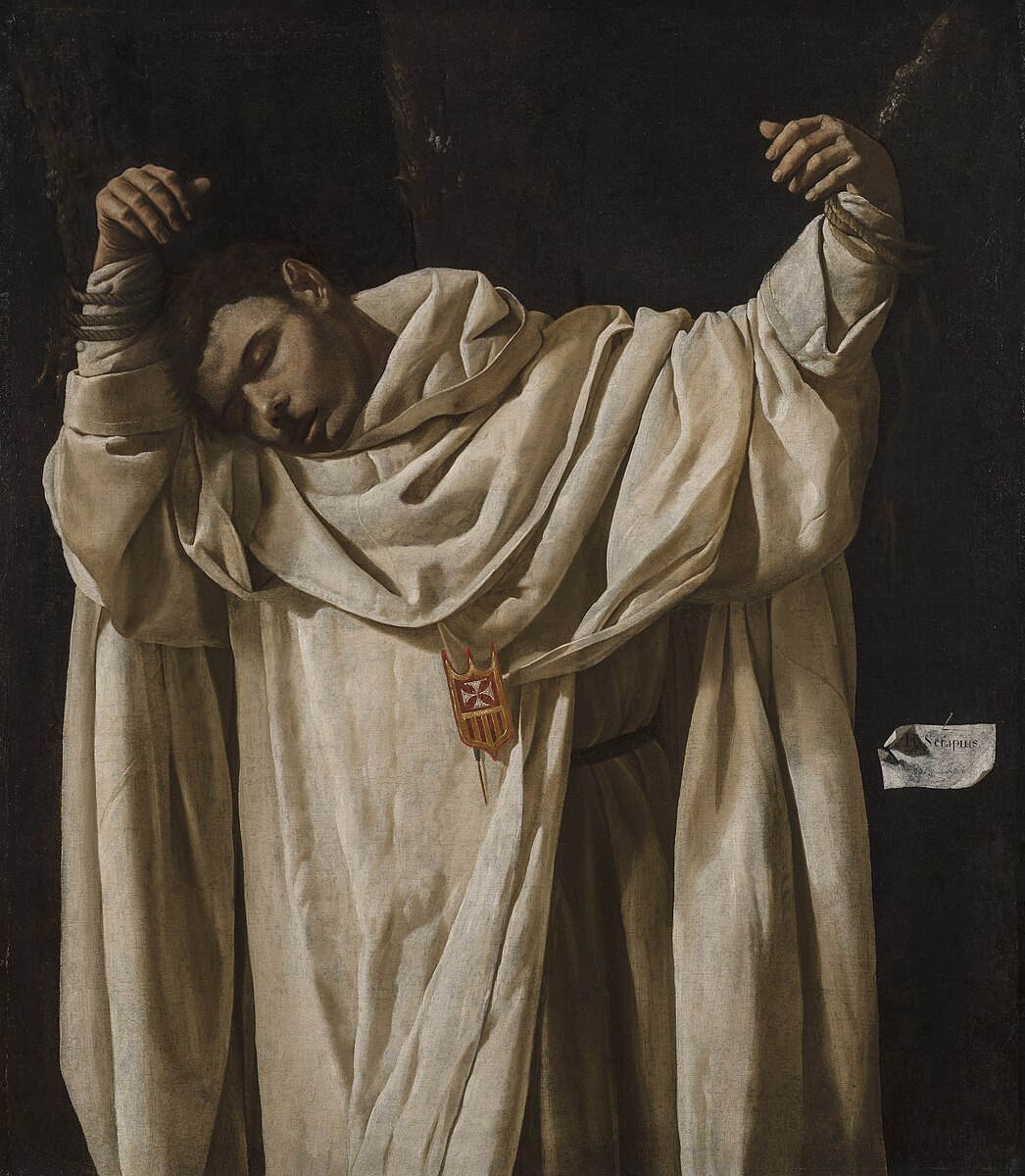

Francisco de Zurbarán, St. Serapion, 1628
-St. Serapion of Algiers
-TENEBRISM
-unique for nonviolent portrayal of martyrdom
-Third Crusade, 1196
-Badge on tunic is a symbol of the order of mercy
-Christ-like
-White robe characterizes st. serapion with the badge
-Influenced by Caravaggio AND Ribera
-Drama is communicated through the dark shadows and the dramatic lighting on the gown with all the folds and the bright highlights
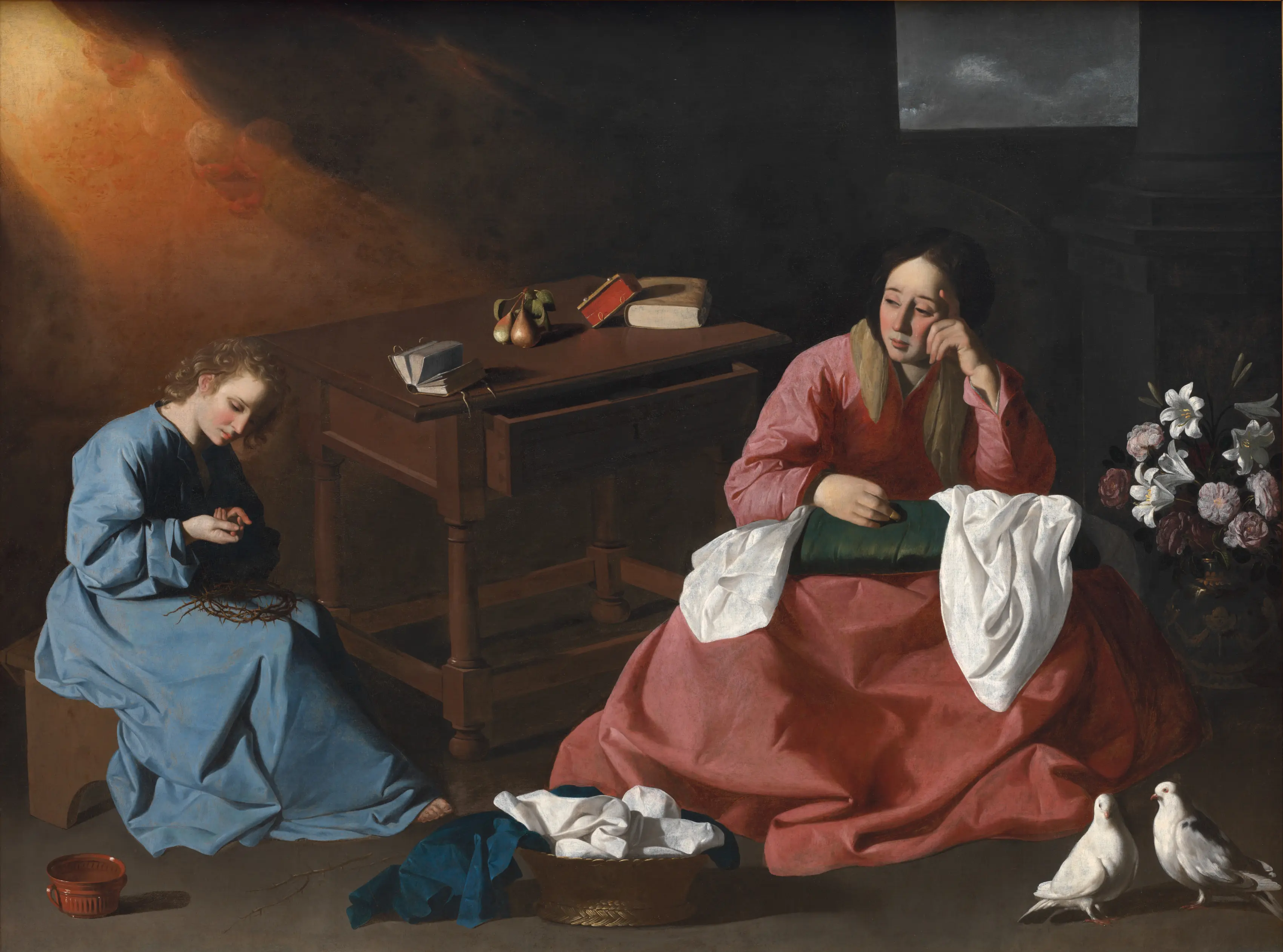

Francisco de Zurbarán, Virgin & Christ in the Holy House of Nazareth, c. 1640
-Humble presentation
-Mary is sewing and embroidering
-Apocryphal gospels
-Christ is poked by the crown of thorns, the virgin is realizing his fate and crying
-tiny thin halo above the virgin
-heavenly light illuminating the area christ sits in, the angels are barely visible in this light
-Sewing basket is a domestic symbol
-Mary is wearing a thimble to protect her finger and christ has poked himself
-Doves are what is offered in sacrifice when he was taken to the temple
-Pears on table are a momento mori
-Interesting representation of jesus
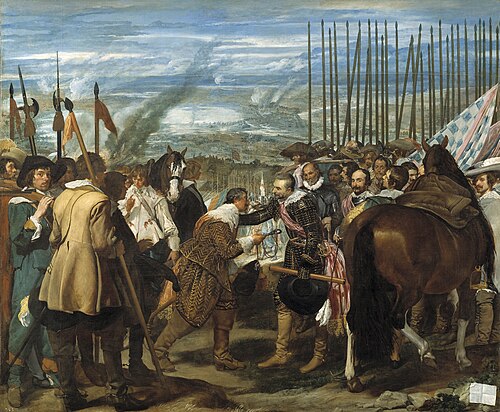

Diego Velázquez, Surrender at
Breda, 1635
-depicts the magnanimous Spanish victory over the Dutch in 1624
-has titian influence
-framed by spears
-spanish general recieving keys to the city from dutch commander, instead of shame
-symbol of mutual respect
-during the eighty years war/netherland revolt
-velazquez is a self portrait on the right side of the scene
-Painted between 1634-1635 for the Hall of Realms in King Philip IV's new palace, the painting was intended to celebrate Spanish military might

Diego Velázquez, Equestrian Portrait of Count-
Duke Olivares, 1638
-political portrait of Gaspar de Guzmán, the prime minister of Spain under King Philip IV
-This imagery was meant to showcase his power and command, emphasizing both his political role and his skill as a horseman, a metaphor for strong leadership
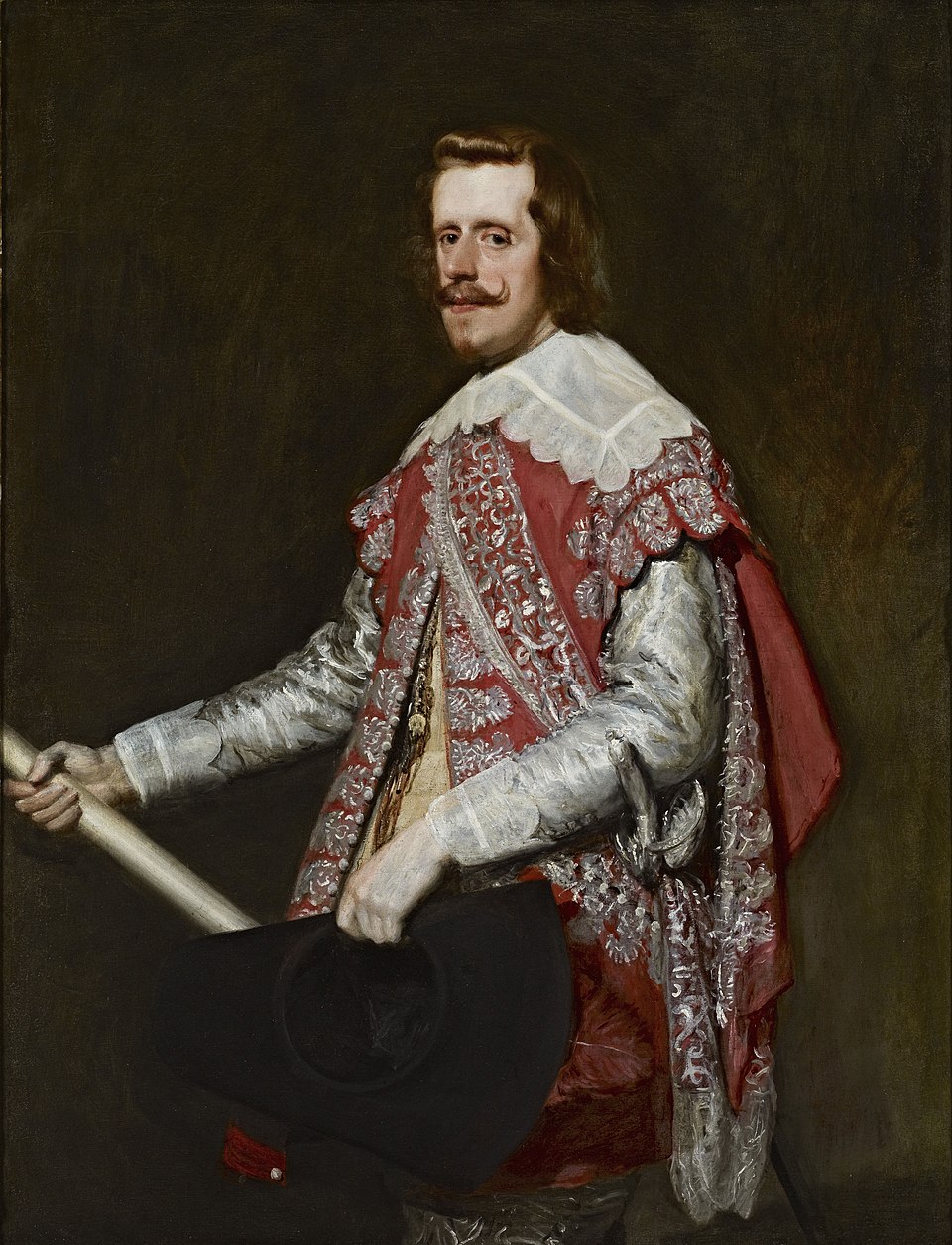

Diego Velázquez, Philip IV of Spain in Fraga,
1644
-created in a makeshift studio
-king in military attire
-immortalize the king as a victorious military leader
-tenebrism
-associated Philip with his deceased brother
-propaganda
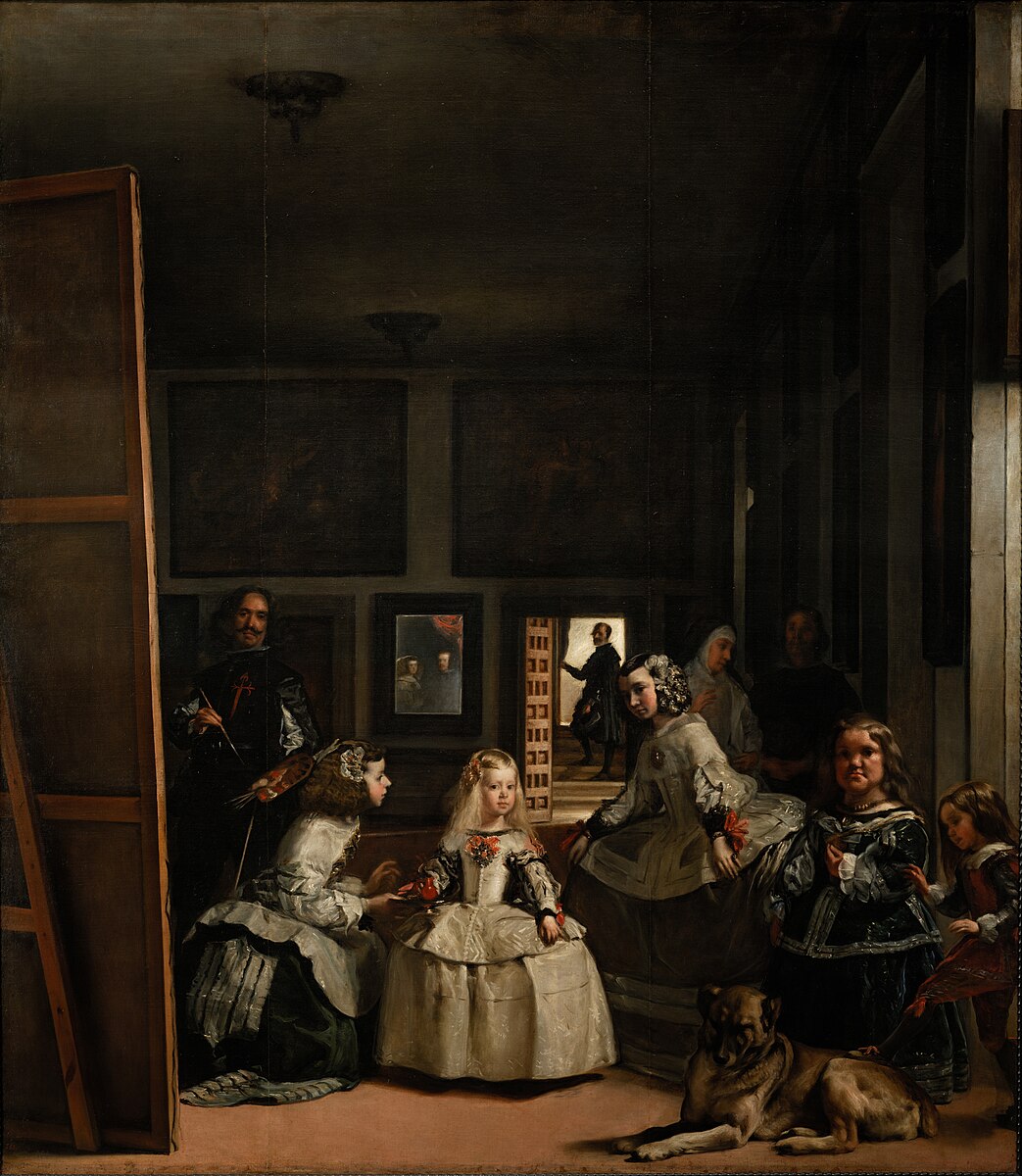

Diego Velázquez, Las Meninas, 1656
-shows the Spanish royal family and their entourage
-elevates the status of art and artists and shows the potential of painting
-King and Queen are reflected in background mirror
-places himself in the painting which emphasizes the importance of the artist

Bartolomé Esteban Murillo, The Two Trinities, c. 1680
-two "Trinities": a celestial one with God the Father, the Holy Spirit (as a dove), and Christ; and an earthly one with the Virgin Mary, Saint Joseph, and Jesus as a child
-inspired by jesuit engravings
-christ’s dual human and divine nature
-Despite the grim reality of the time, Murillo's art offered a sense of reassurance and heroism through its emotional and spiritual themes
-made during plague and war
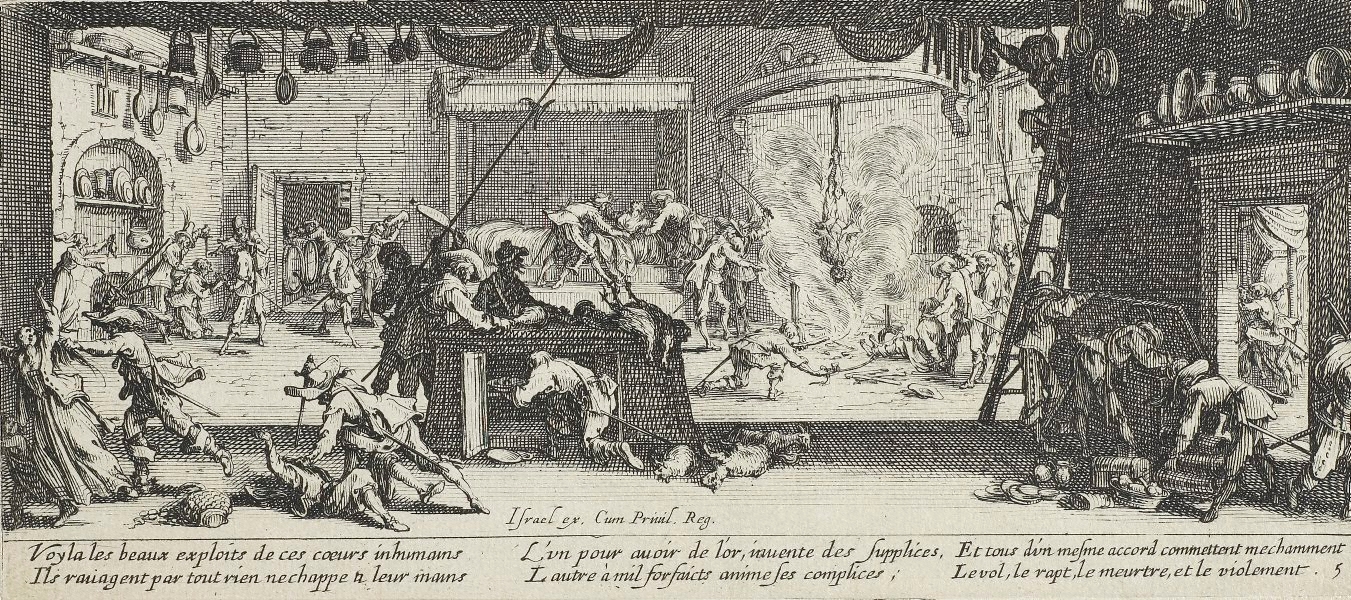

Jacques Callot, Pillage of a Farmhouse, The Great Miseries of War, 1633, etching
-theatrical presentation of real events
-interior of a domestic house
-violent
-people are begging for mercy and soldiers are either taking food or destroying wine or beer
-burning a peasant, showing how when the soldiers are in misery, so are the citizens
-soldiers didn’t get paid so some pillaged while others rotted in the streets
-etching technique
-wars in lorraine
-easily reproduced so possibly distributed to a large audience
-baroque for this one: theatrics with especially light and shadow
-THIRTY YEARS WAR
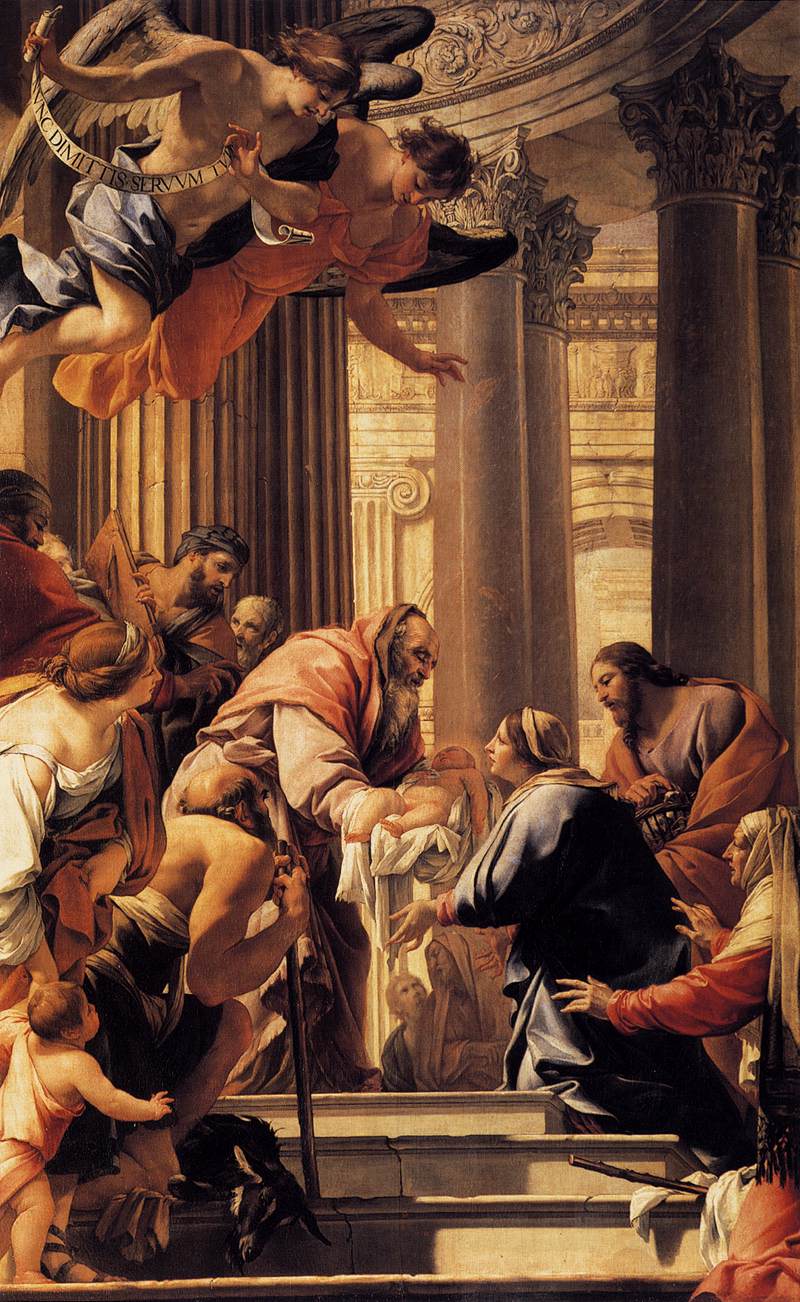

Simon Vouet, Presentation of Christ in the Temple, 1641
-Commissioned as an altarpiece for cardinal Richelieu
-Vouet is painter to the king
-christ’s infancy, tradition of taking baby into temple for priest’s blessing
-jesuit’s professed house
-jesus halo
-modeled after Veronese and Agostino Carracci
-classical architecture, modeled after what Vouet has seen in Rome
-spent 14 years in italy to establish french tradition and bring art to france
-influenced by caravaggio
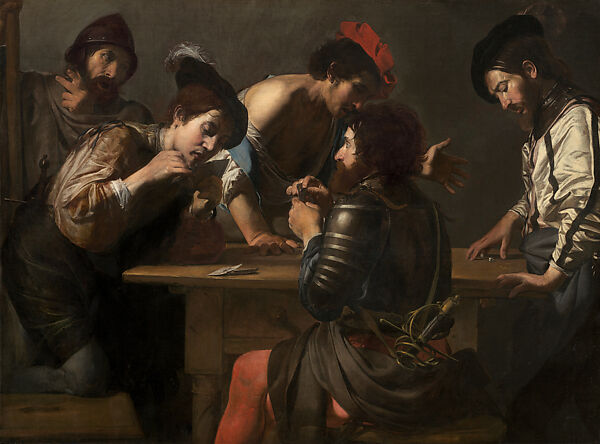

Valentin de Boulogne, “The Cheats” Soldiers Playing Cards and
Dice, c. 1618
-Soldier represents the ongoing wars in the area
-bright lights and dark shadows, caravaggio influence with the intertwining and intersecting of hands and gestures
-soldiers vs “fools” with feathers in hats
-Baroque realism
-soldiers in back is cheating
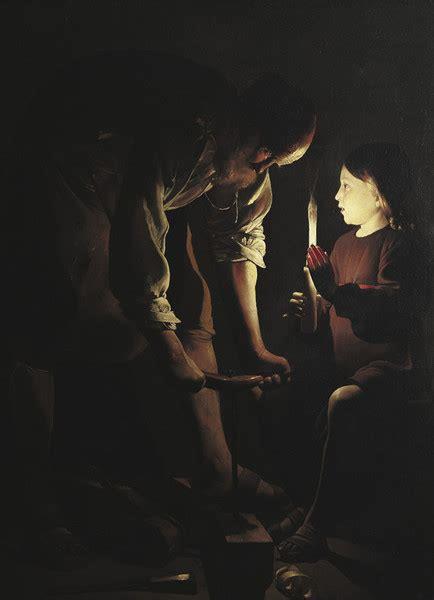

Georges de la Tour, St. Joseph the Carpenter, c. 1635
-humble presentation
-known for dark tenebristic scenes
-teaching jesus to be a carpenter
-diagonal interaction
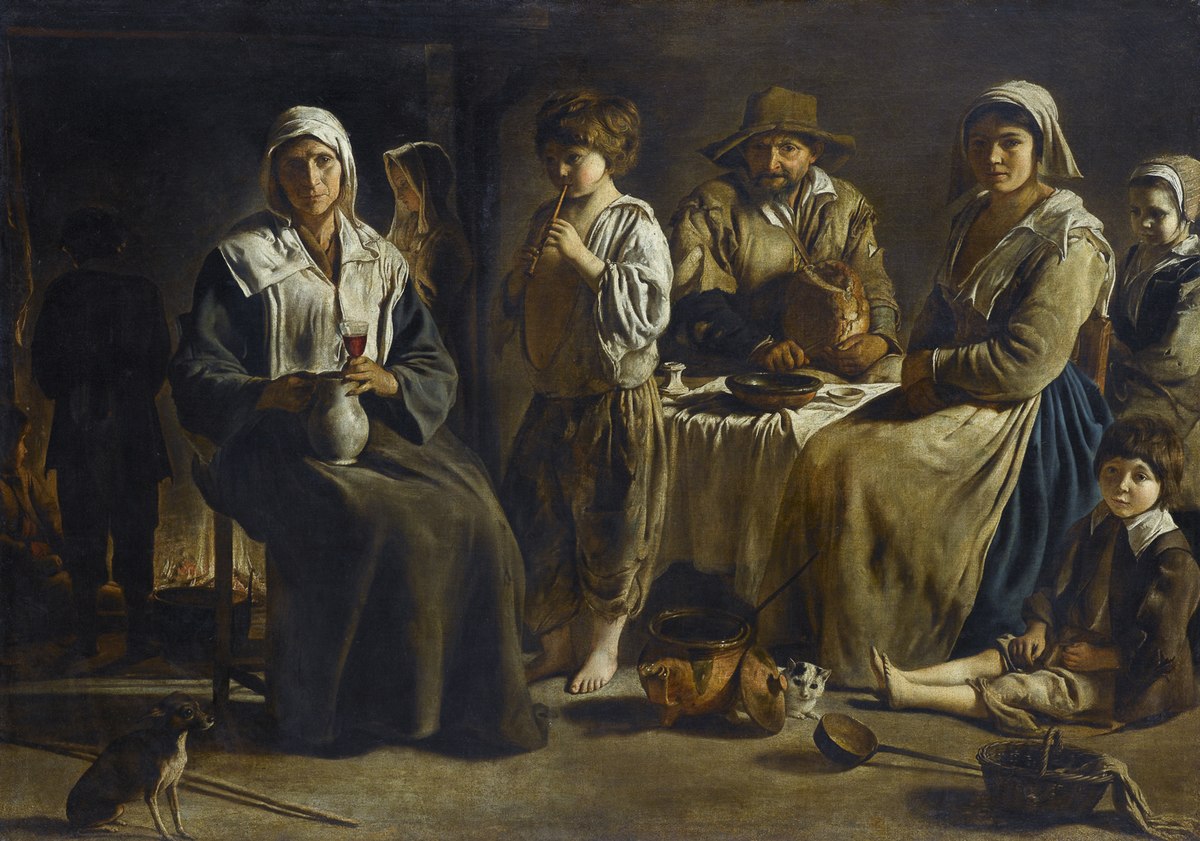

Louis Le Nain, Peasant Family, c. 1640
-rural
-common theme for Le Nain
-influenced by Dutch genre paintings
-Le Nain’s paintings showed dignity of peasants
-many ppl in the families
-two competing light sources
-rough fabric = poverty
-dog and cat and farm workers
-simple and poor but together and loving
-wine and bread = religious symbolism
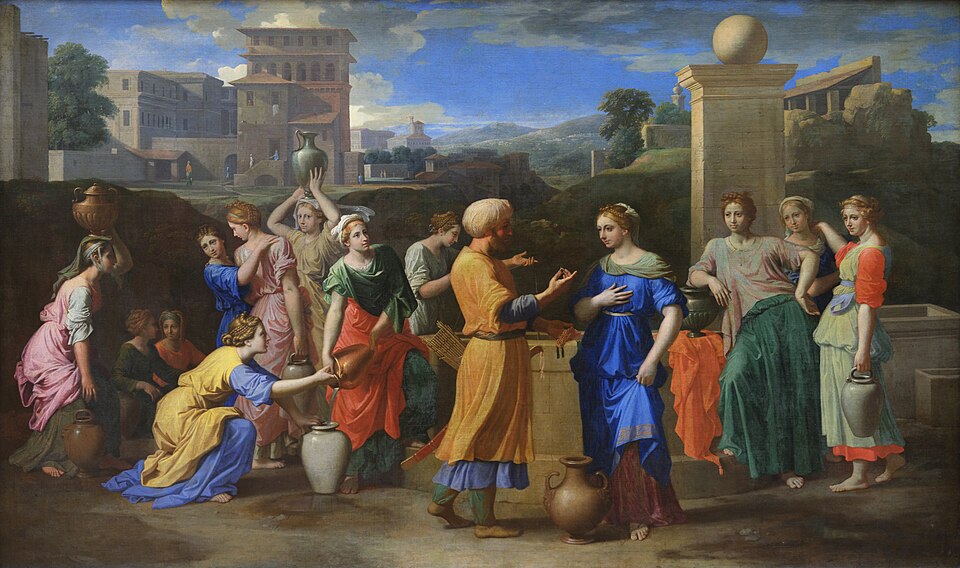

Poussin, Rebecca and Eliezer at the Well, c. 1648
-Old Testament, book of genesis
-Contrast of light and dark
-Eliezer has chosen a wife for Isaac
-Rule of thirds
-appreciation of femininity
-commissioned for a private patron
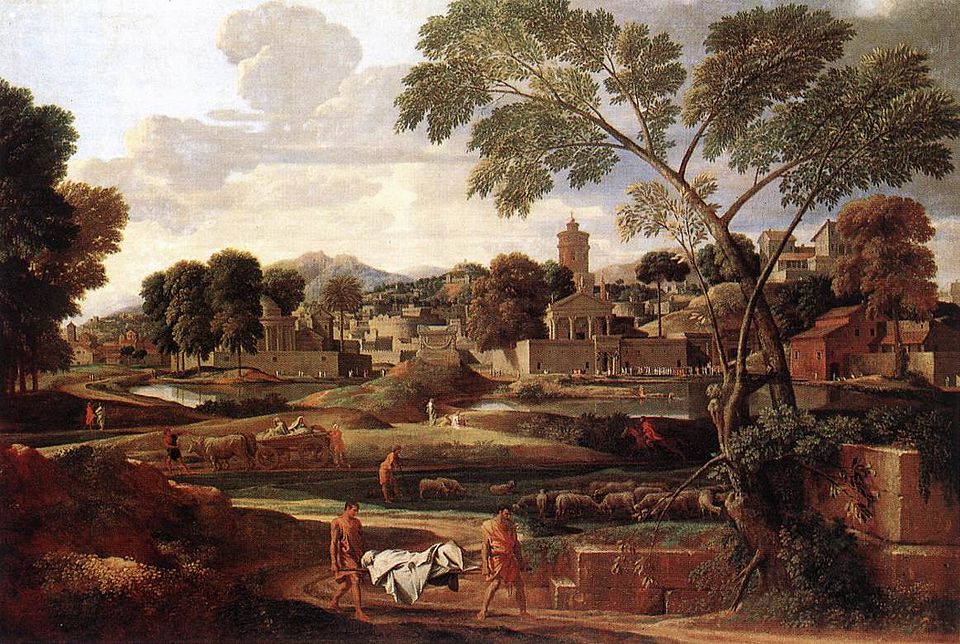

Poussin, Landscape with the Funeral of Phocion, 1648
-inspired by Annibale Carracci's Flight into Egypt
-festival while an unjustly convicted hero was thrown out
-seeing an injustice
-athenian general phocion was wrongly accused of treason
-idealized landscape to show a tragic event
-acts like a stage
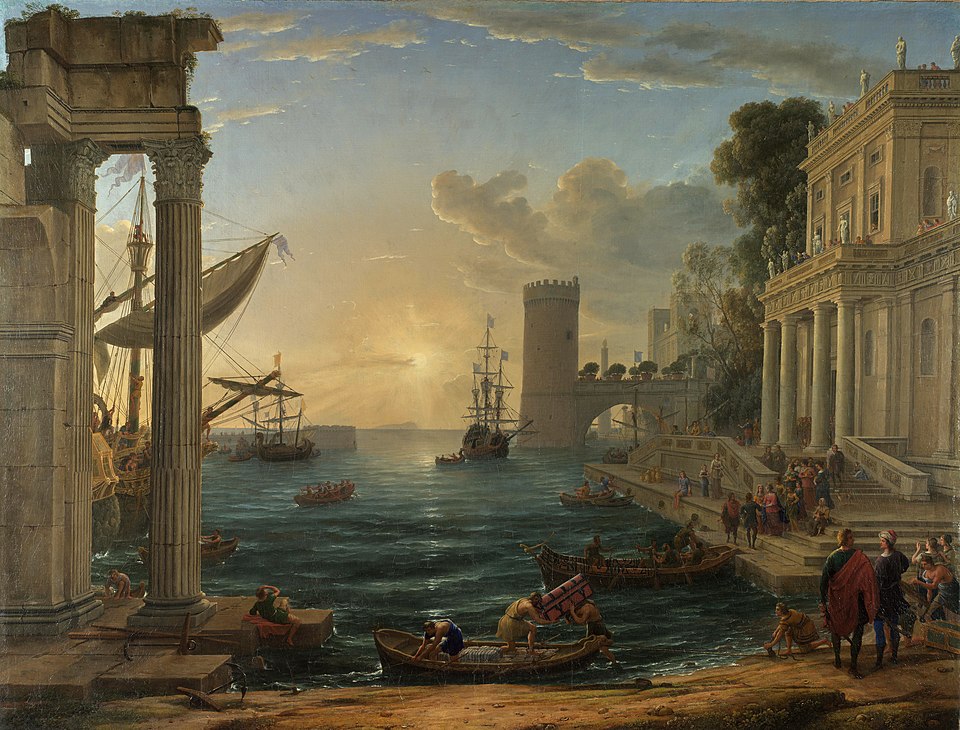
Claude Lorrain, Embarkation of the Queen of Sheba, 1648
-biblical story: book of kings
-commissioned by Cardinal Camillo Pamphili, but Lorrain had to complete it for the Duc de Bouillon after the cardinal's marriage plans caused him to renounce his commission
-Claude Lorrain was famous for his idealized landscapes. In this work, he transforms the biblical story into a serene and poetic, imaginary seascape, which was a departure from the often lively port scenes of the time
-The painting uses symbolic elements such as the dawn to represent a new beginning and a departure into a land of mystery and discovery, with the Queen's journey symbolizing a voyage into the unknown.
-
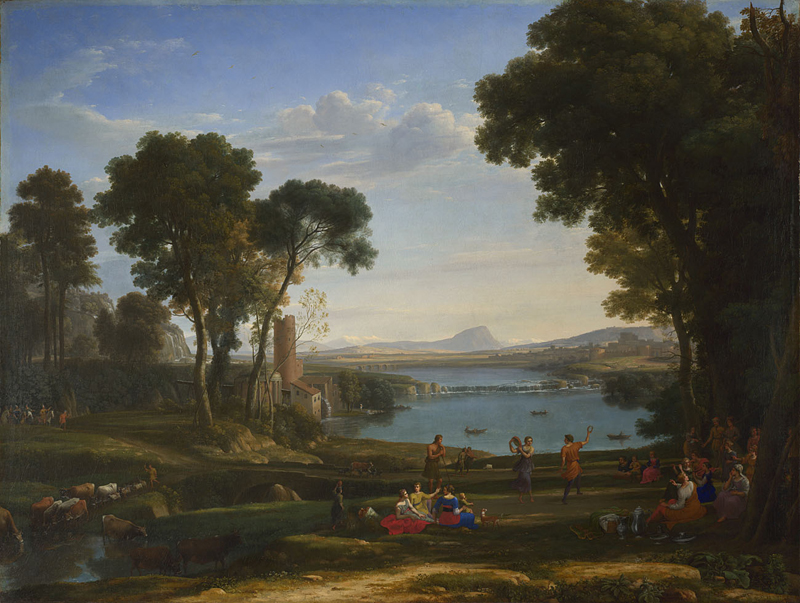
Claude Lorrain, Landscape with the Marriage of Isaac and Rebecca (The Mill), 1648
-commissioned by the Duc de Bouillon
-a drawing included in liber veritatis
-an idealized scene based on the countryside around Rome, portrays the biblical marriage of Isaac and Rebecca
-elevating landscape painting as a serious genre, pioneering new techniques in depicting light, and serving as a masterpiece of idealized, classical composition that inspired later artists
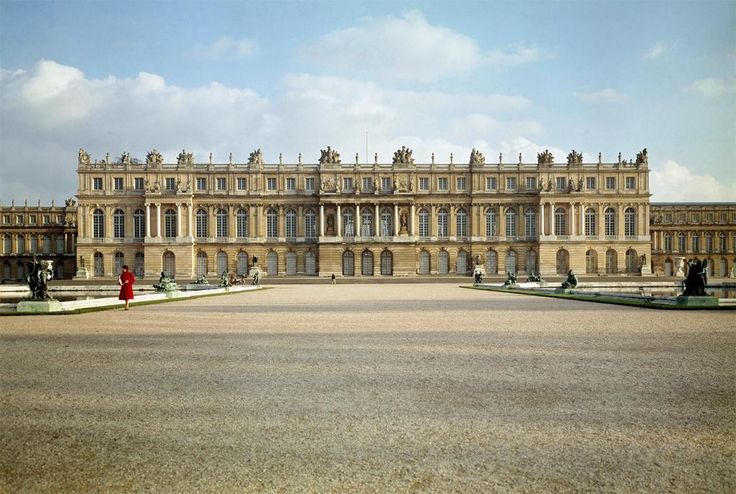

Louis Le Vau and Jules Hardouin-Mansart, Palace of Versailles, garden façade, begun 1669
-the glorification of Louis XIV's absolute power and the centralization of the French court
-King Louis XIV sought to distance himself from the Parisian populace and a powerful nobility he distrusted
-pilasters (square columns attached to a wall)
-colonnade (set of columns)
-balustrade (railing supported by columns
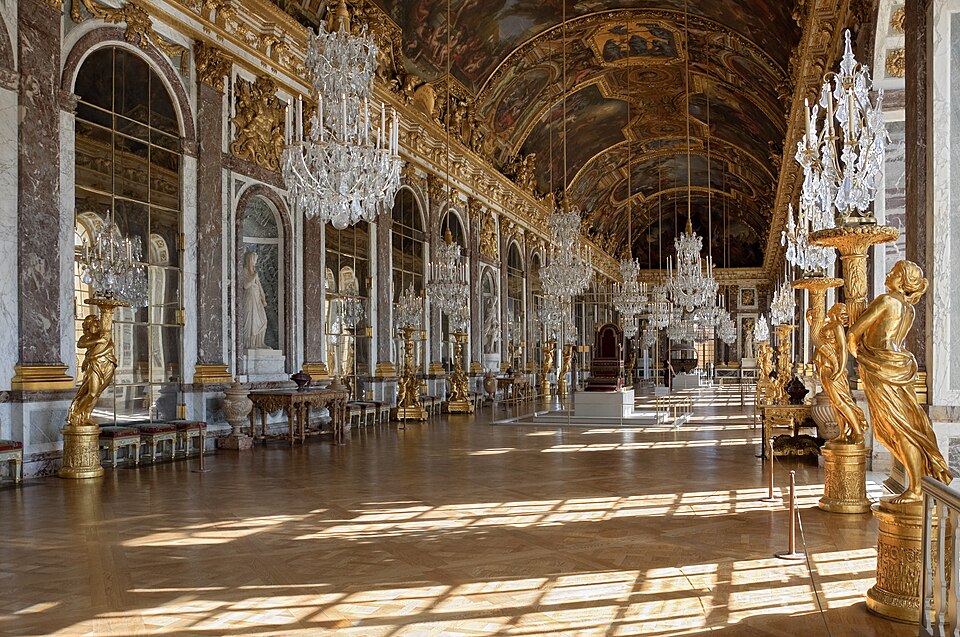

Jules Hardouin-Mansart & Charles Le Brun, Palace of Versailles,
Hall of Mirrors, begun 1678
-place for french court and show of success and power

Charles Le Brun, Louis XIV Governs Alone, Hall of Mirrors, Palace
of Versailles, begun 1678
-part of a decorative program for Louis XIV that celebrated his reign
-The ceiling contains 30 scenes that depict the early years of Louis XIV's rule, focusing on his military victories, diplomatic successes, and administrative reforms.
-It portrays Louis XIV as the sole ruler, with allegorical figures like the Three Graces and Athena watching as he is crowned by Glory, symbolizing his personal rule and the beginning of a new era for France.