HOSA Sports med anatomy
1/87
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
88 Terms
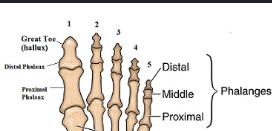
Phalanges 1-5
The bones of the fingers and toes, with each finger having three phalanges (proximal, middle, distal), while the thumb and big toe have two (proximal and distal).
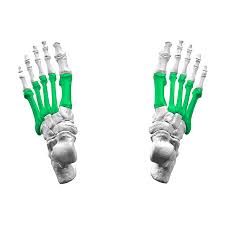
Metatarsals
The long bones in the foot, located between the tarsal bones and the phalanges, numbering five in total, which help form the arch of the foot.
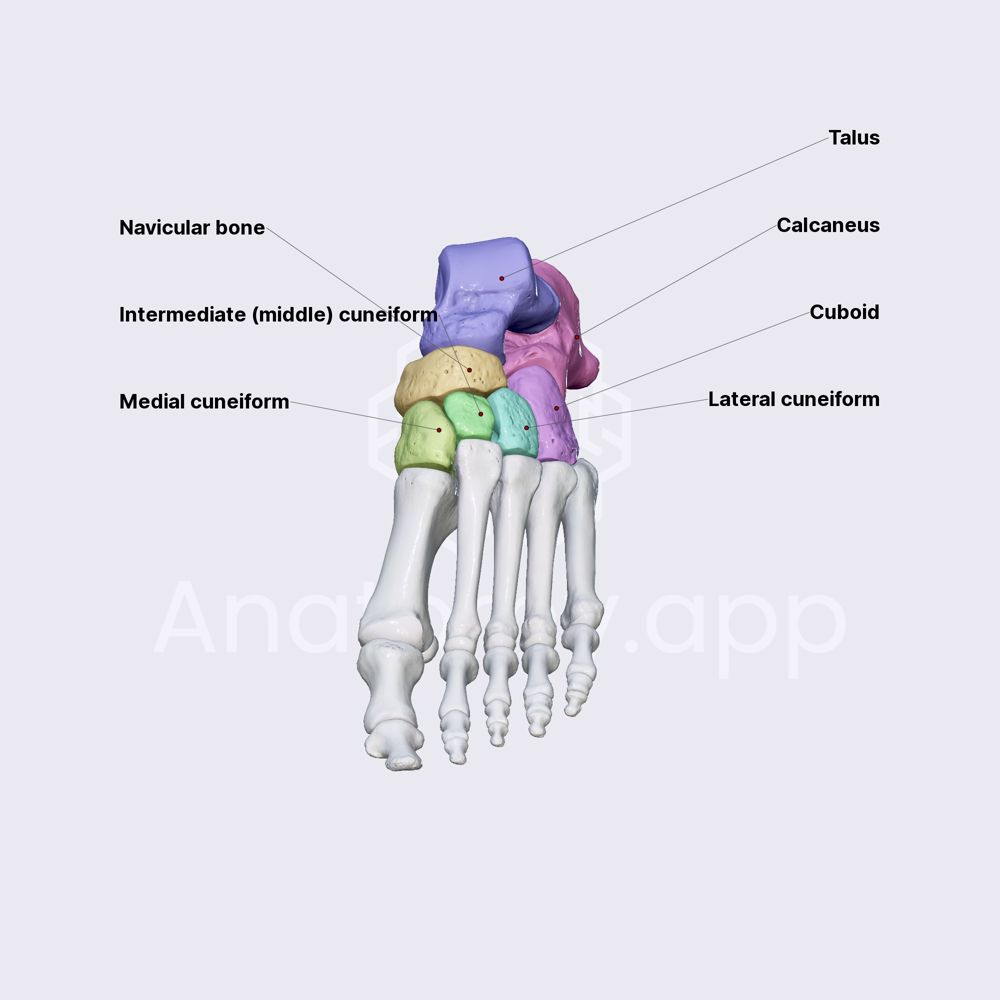
Tarsals
The group of seven bones located in the ankle, which include the calcaneus, talus, navicular, cuboid, and the three cuneiforms, providing stability and flexibility to the foot.
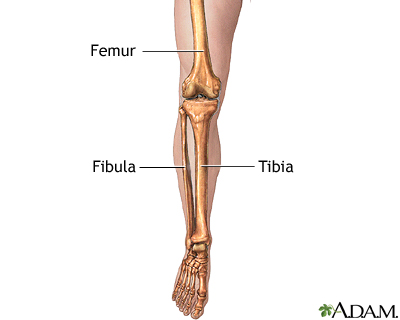
Tibia
The larger of the two bones in the lower leg, located on the inner side, it supports weight and forms the knee joint with the femur and the ankle joint with the tarsals.
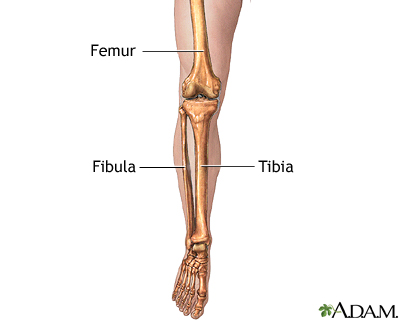
Fibula
The smaller of the two bones in the lower leg, located alongside the tibia, it helps stabilize the ankle and supports the muscles of the lower leg.
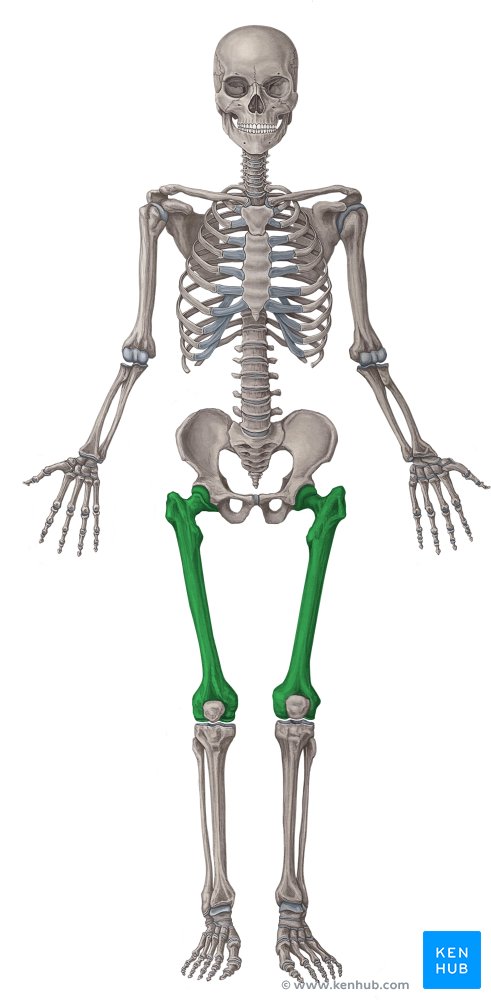
Femur
The longest bone in the human body, located in the thigh, it connects the hip joint to the knee joint and bears weight during activities such as walking and running.
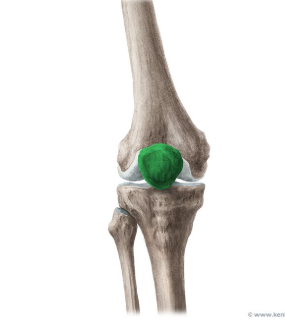
Patella
A small bone located in front of the knee joint, commonly known as the kneecap, it protects the knee and improves the leverage of thigh muscles.
humerus
The long bone in the upper arm that runs from the shoulder to the elbow, it aids in the movement of the arm and supports various muscles.
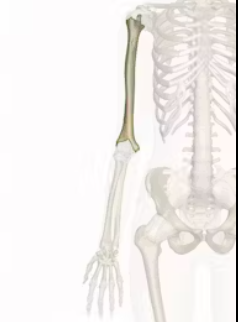
Radius
The bone in the forearm located on the thumb side, it helps in the movement of the wrist and forearm.
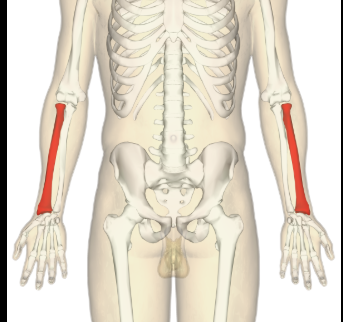
Ulna
The long bone in the forearm located on the side opposite the thumb, it works alongside the radius to allow for the movement of the wrist and elbow.
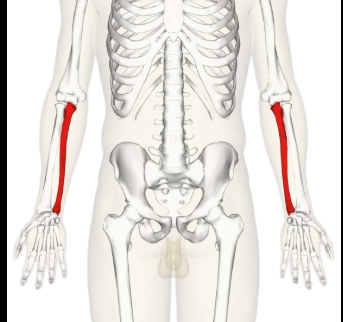
Phalanges 1-5 hands
The bones in the fingers, with each hand having 14 phalanges, allowing for dexterity and movement of the digits.
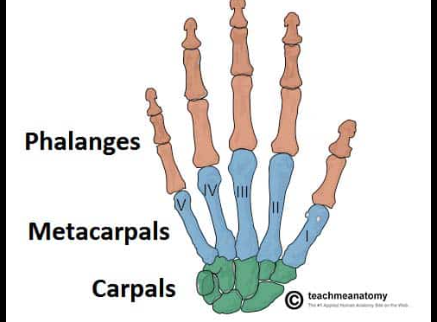
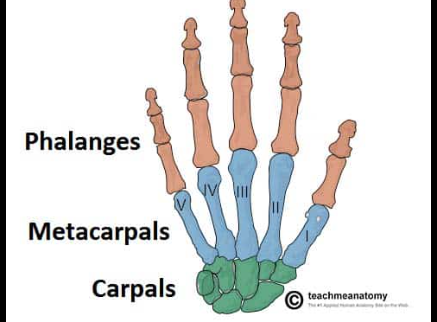
Carpals
The eight small bones that make up the wrist, allowing for a range of motion and flexibility in the hand.
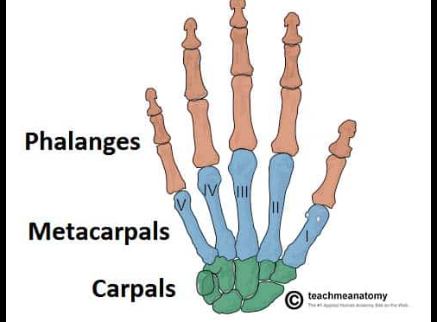
Metacarpals
The long bones in the hand that connect the wrist to the fingers, facilitating movement and support.
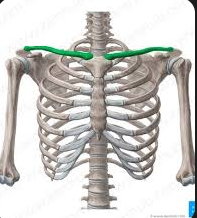
Clavicle
A long bone that connects the arm to the body, commonly known as the collarbone. It acts as a strut to support the shoulder and allows for a wide range of shoulder movement.
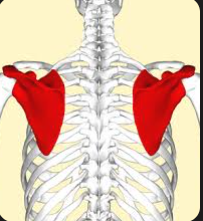
Scapula
A flat, triangular bone in the upper back that connects the humerus (arm bone) with the clavicle and plays a crucial role in shoulder stability and movement.
Cervical Spine 1-7
The seven vertebrae in the neck region that support the head and allow for its movement, playing a vital role in protecting the spinal cord.
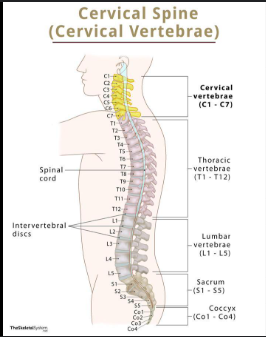
Thoracic spine 1-12
The twelve vertebrae in the upper and mid-back region that provide support for the ribcage, protect the thoracic organs, and allow for the flexibility of the spine.
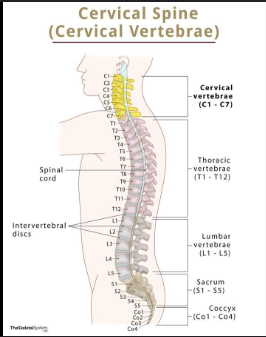
Lumbar Spine 1-5
The five vertebrae in the lower back that provide support for the upper body and maintain balance, allowing for a range of movements while bearing weight.
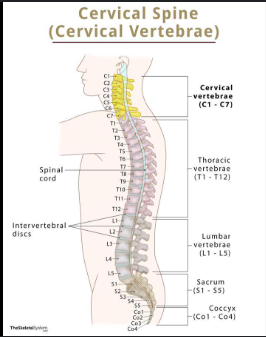
Parietal
bone located in the skull that forms the sides and roof of the cranium, playing a key role in protecting the brain.
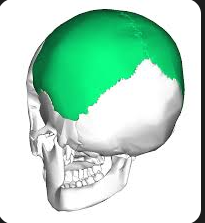
Occipital
bone located at the back of the skull that forms the base of the cranium, protecting the brain and allowing for movement of the head.
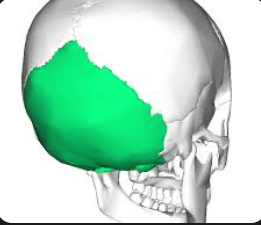
Temporal
bone located on the sides of the skull that encases the temporal lobe of the brain and contains structures related to hearing and balance.
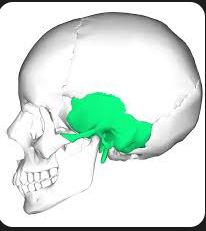
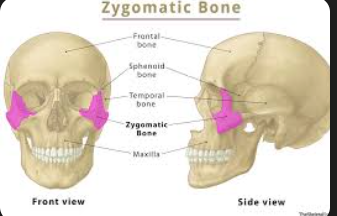
Zygomatic
bone that forms the prominence of the cheek and part of the eye socket, often referred to as the cheekbone.
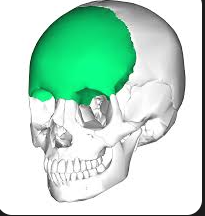
Frontal
bone located at the front of the skull, forming the forehead and part of the eye sockets, contributing to the structure of the face.
Nasal
bones that form the bridge of the nose and support the structure of the nasal cavity.
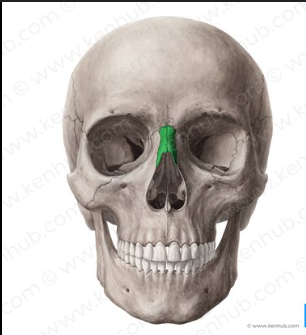
Maxilla
Bones that form the upper jaw
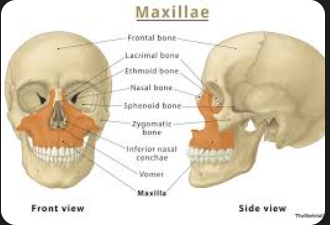
Mandible
The lower jawbone which holds the teeth in place
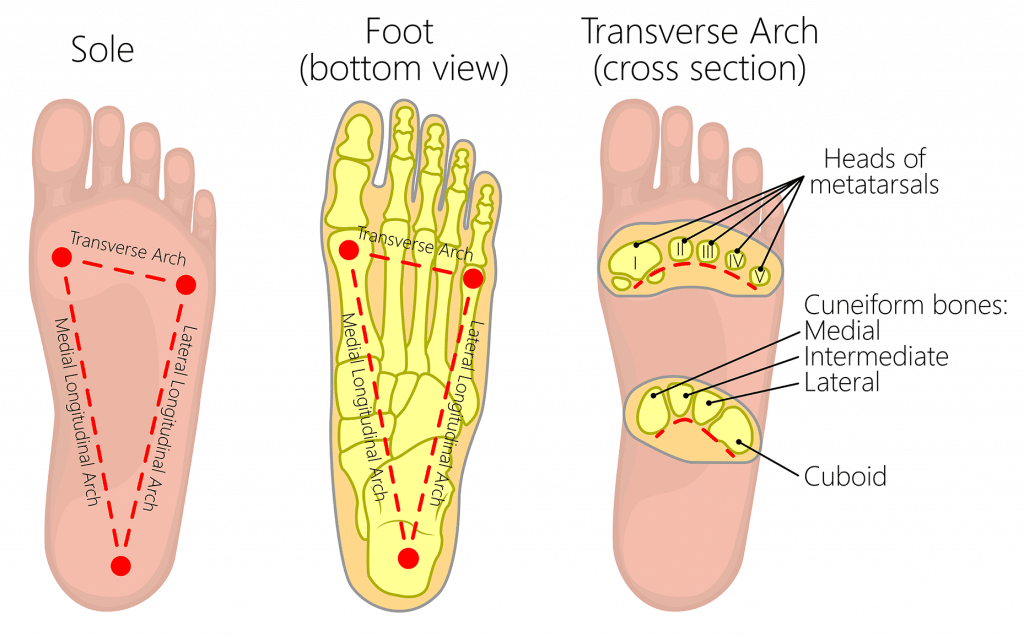
Transverse Arch
One of the three arches of the foot, running across the midfoot at the level of the metatarsal bases and cuneiforms, which helps distribute weight and absorb shock. (back one of the third foot)
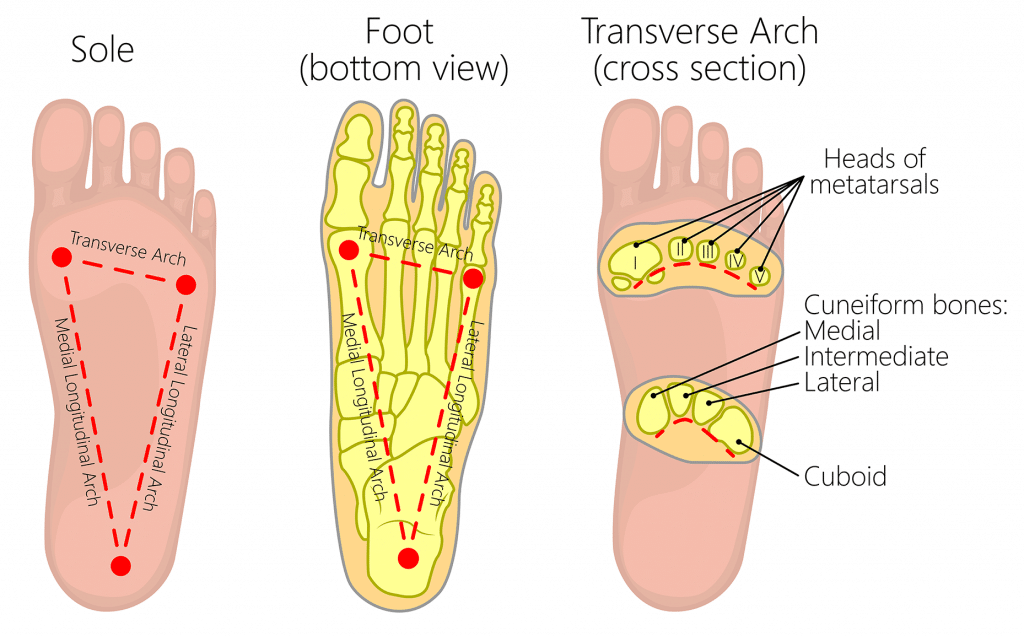
Metatarsal Arch
Front one near the ball of the foot
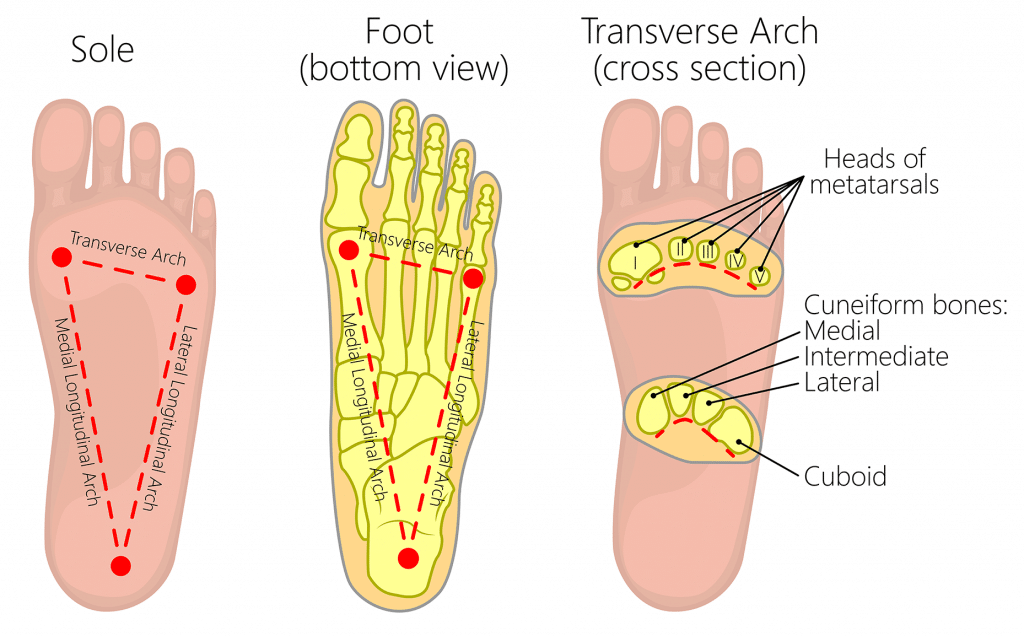
Longitudinal arches
Medial on thumb toe side, distal on pinky toe side
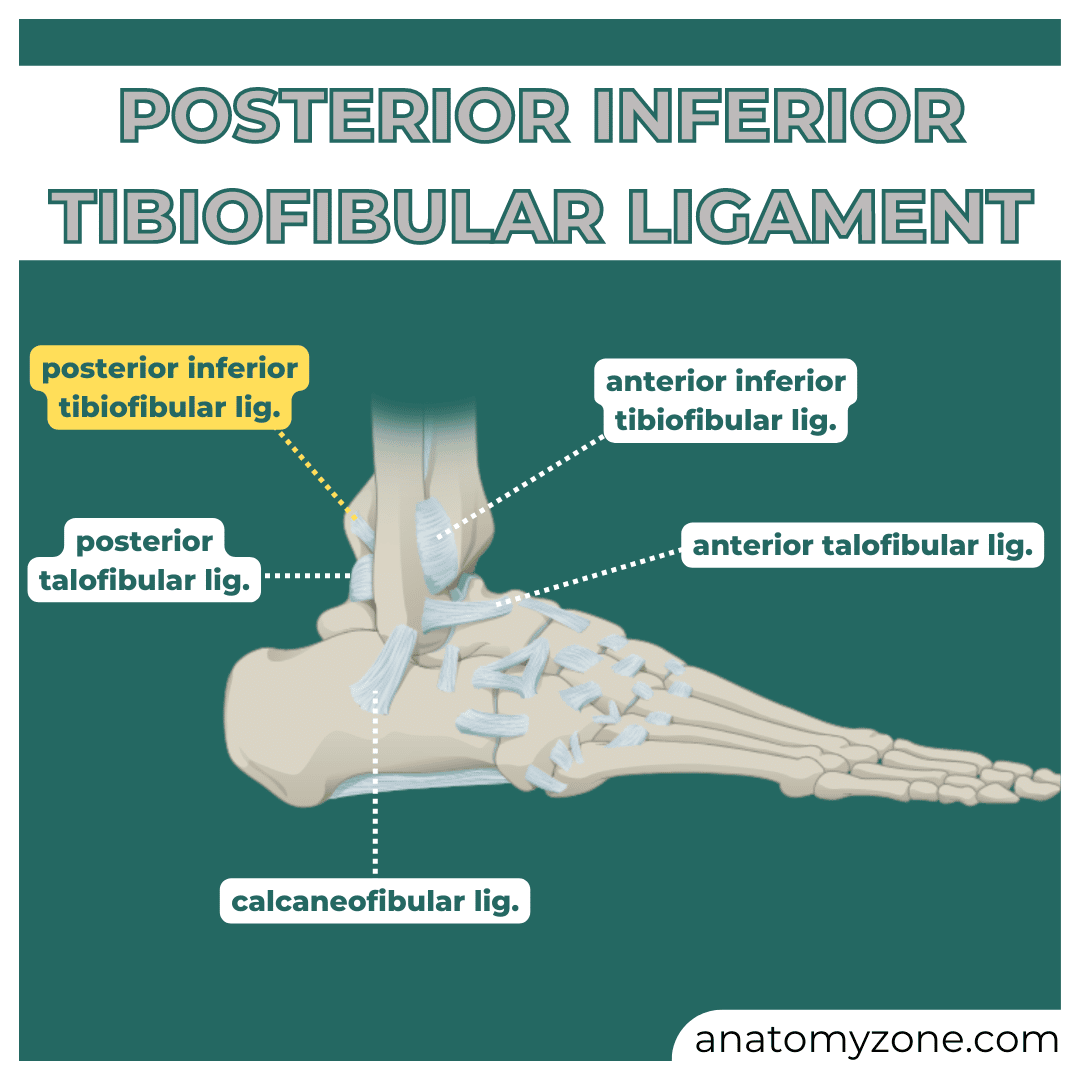
Anterior/Posterior tibiofibular
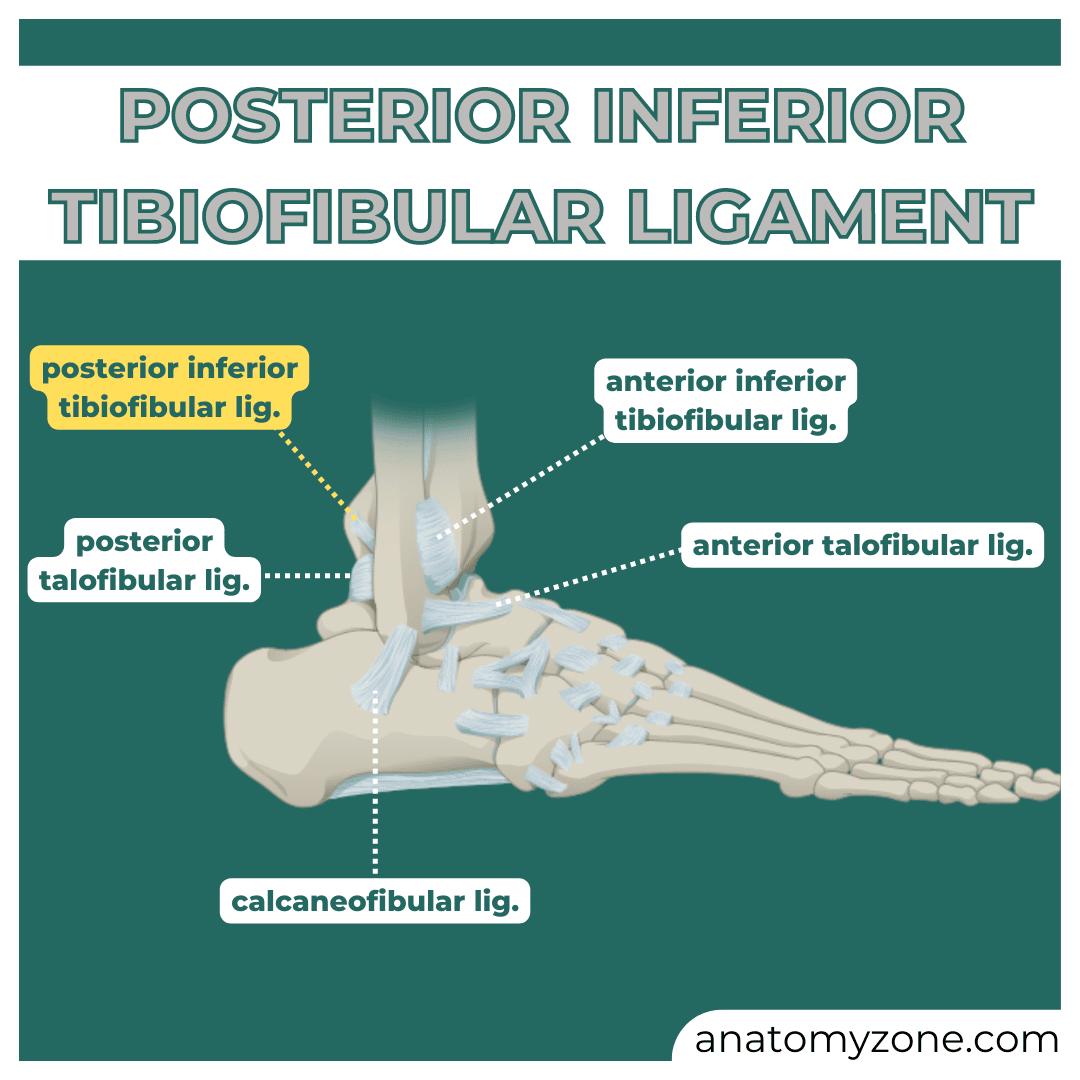
Calcaneofibular
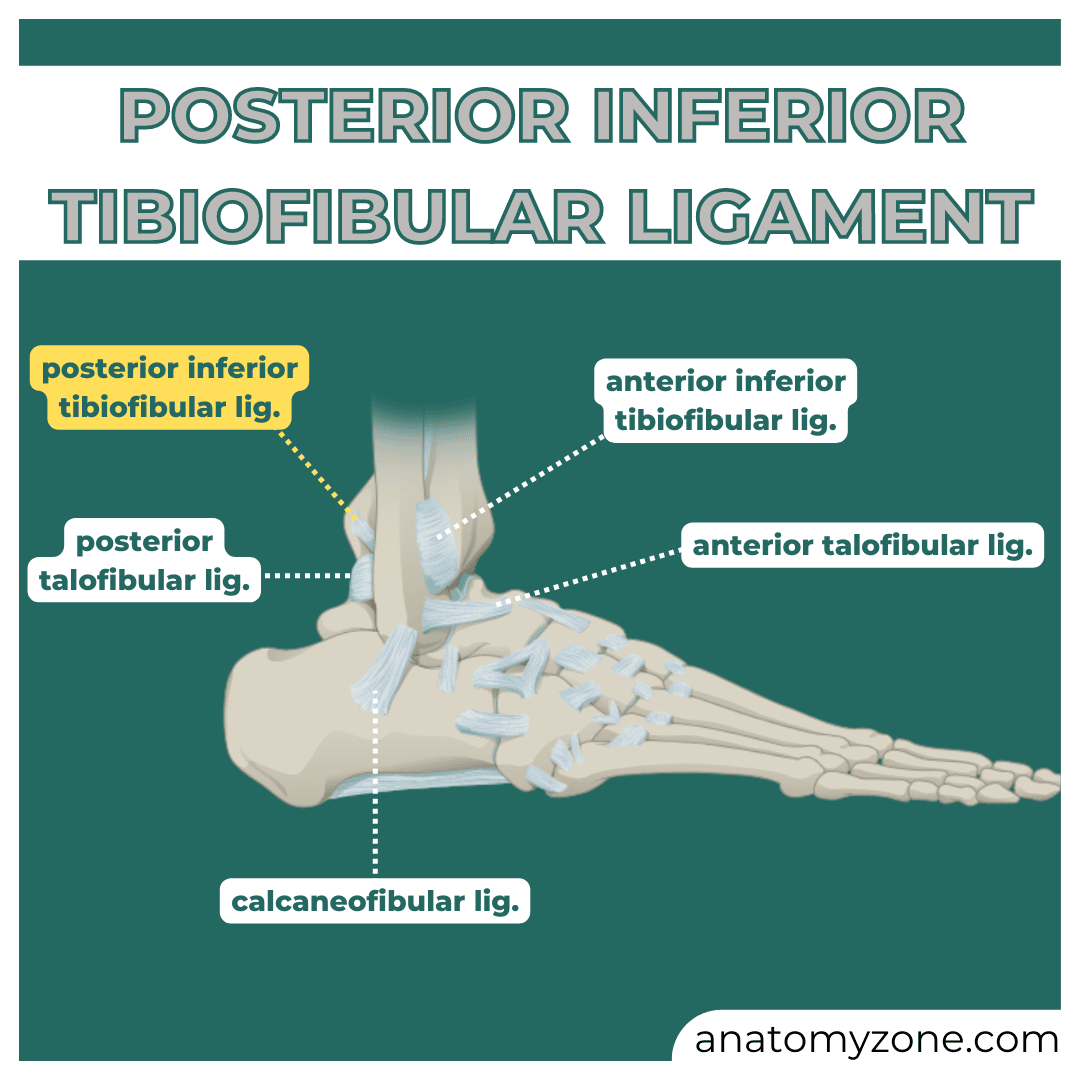
Anterior/Posterior Talofibular
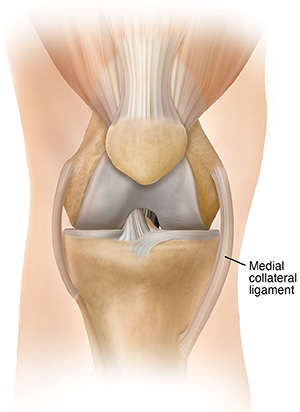
Medial Collateral
inside of knee
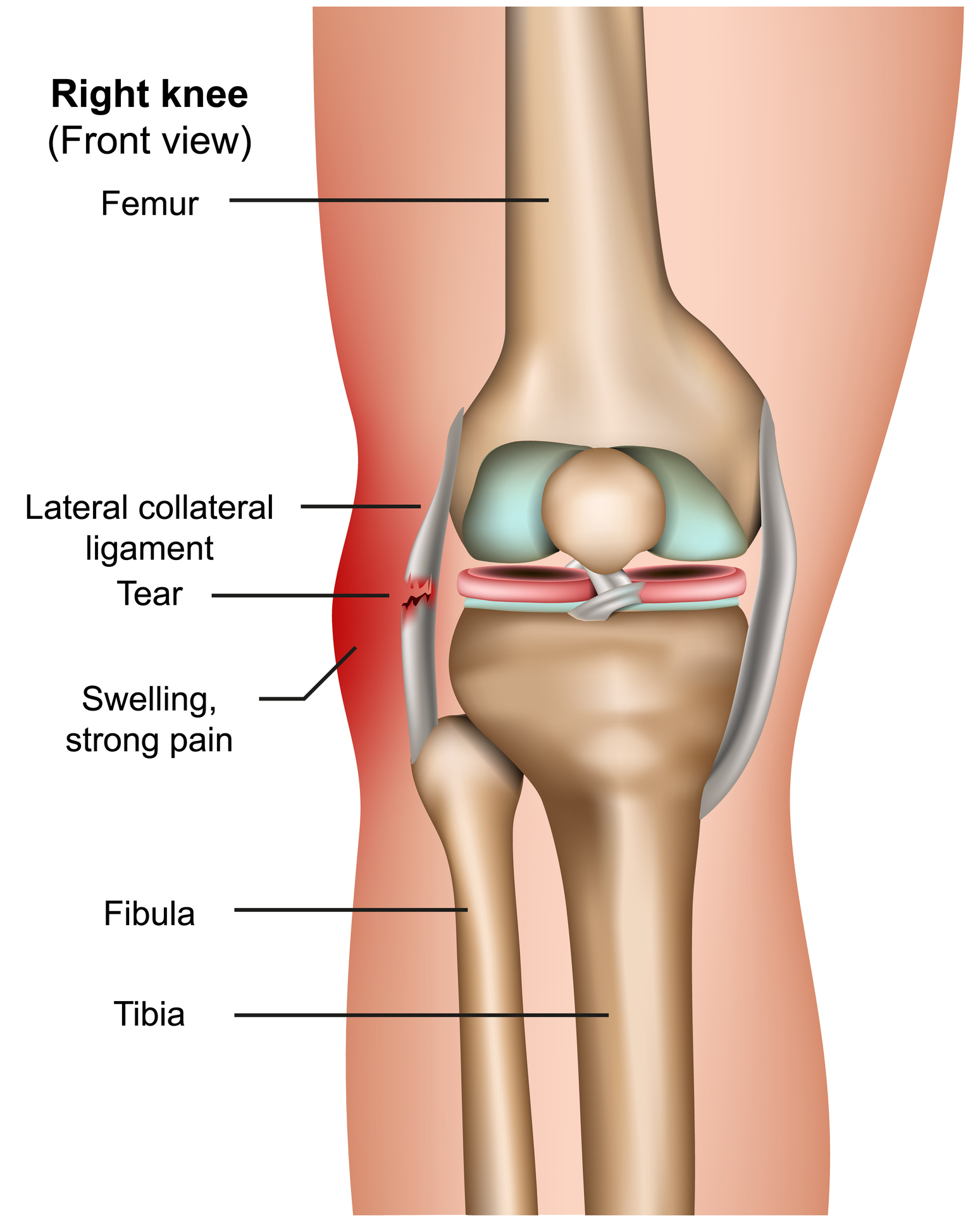
Lateral Collateral
outside of knee
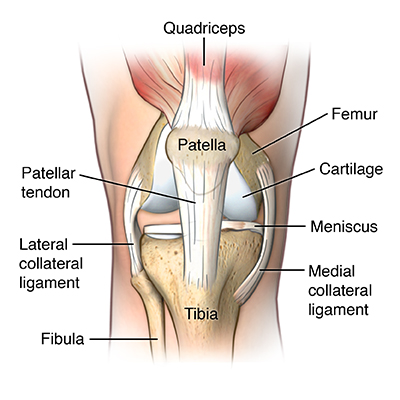
Patellar Ligament/Tendon
right below the patella
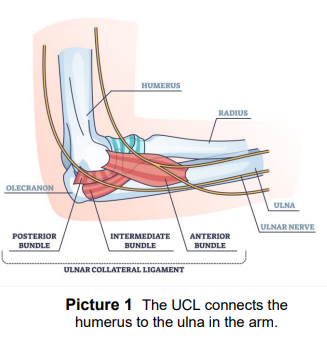
Ulnar Collateral
Made up of the posterior, intermediate, and anterior bundle
Radial Collateral Ligament
on the radius
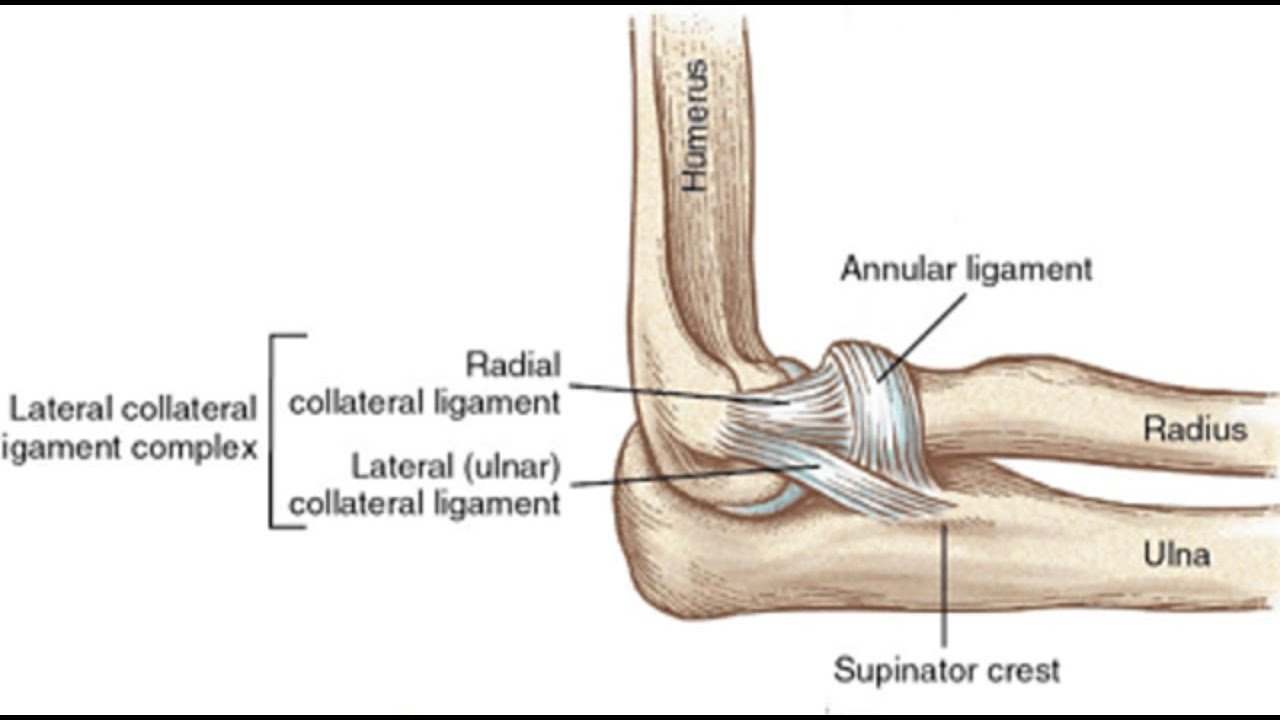
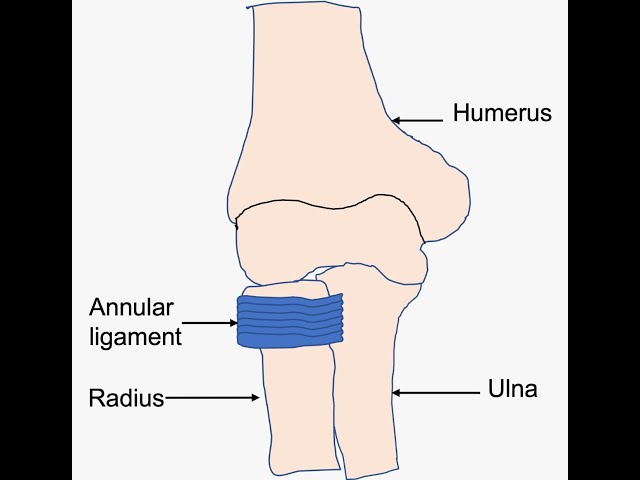
annular collateral ligament
on the beginning of the radius from the elbow
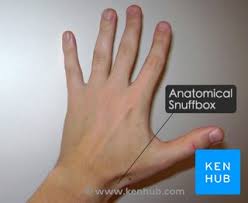
Anatomical Snuffbox
little triangle ahh shape
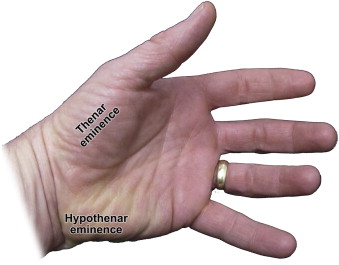
Thenar/Hypothenar Eminence
thenar is on palm, hypothenar near pinky
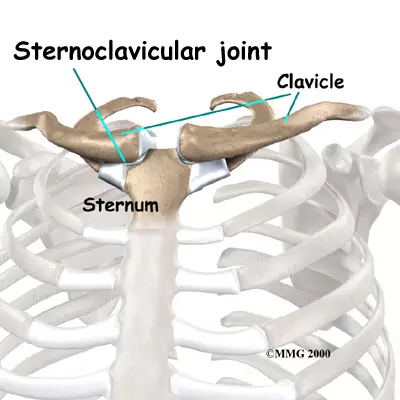
Sternoclavicular
where sternum +clavicle join up
Acromioclavicular
accromion and clavicle meet here!
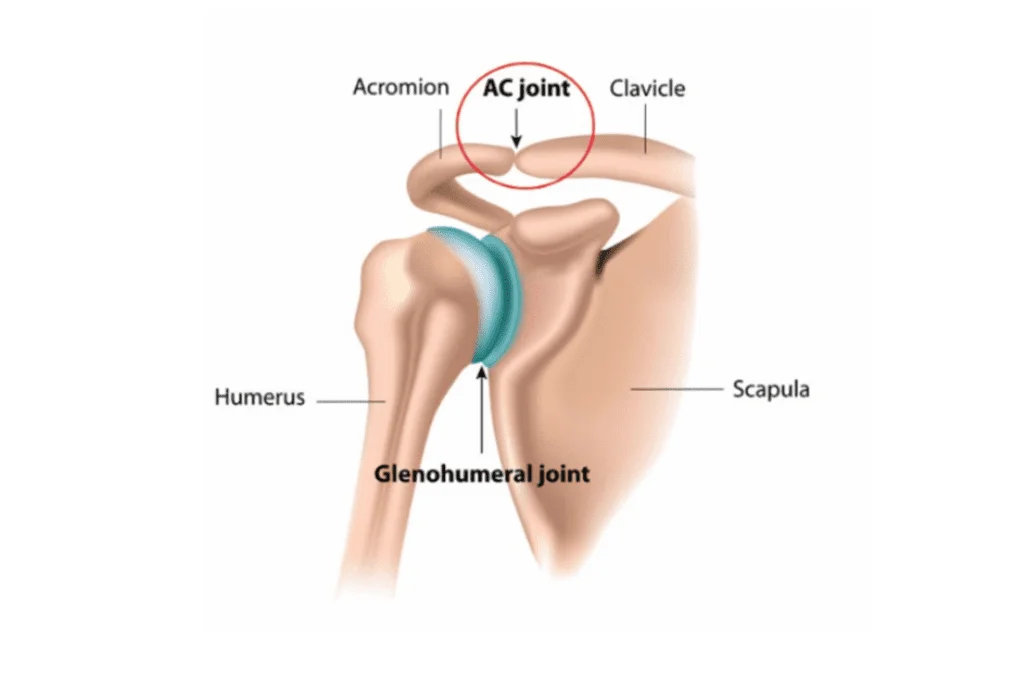
Glenohumeral
shoulder ball and socket joint
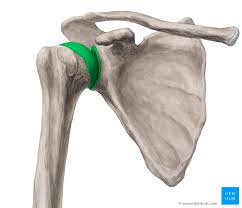
Coracoclavicular
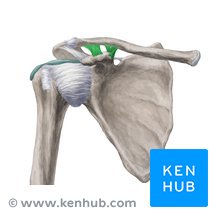
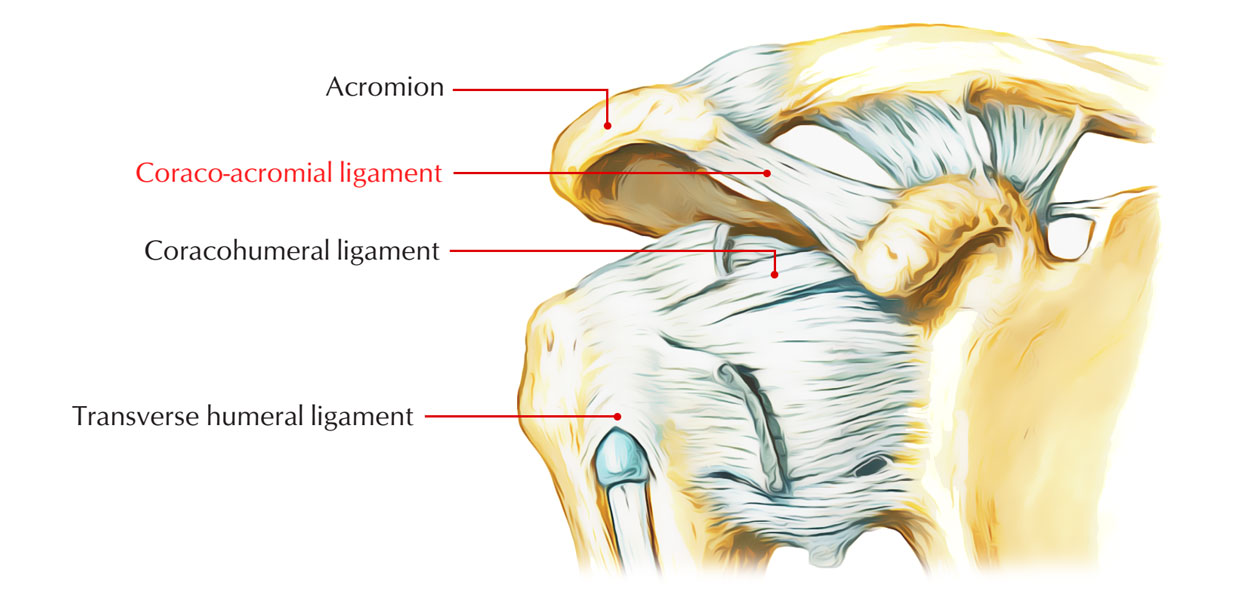
Coracoacromial
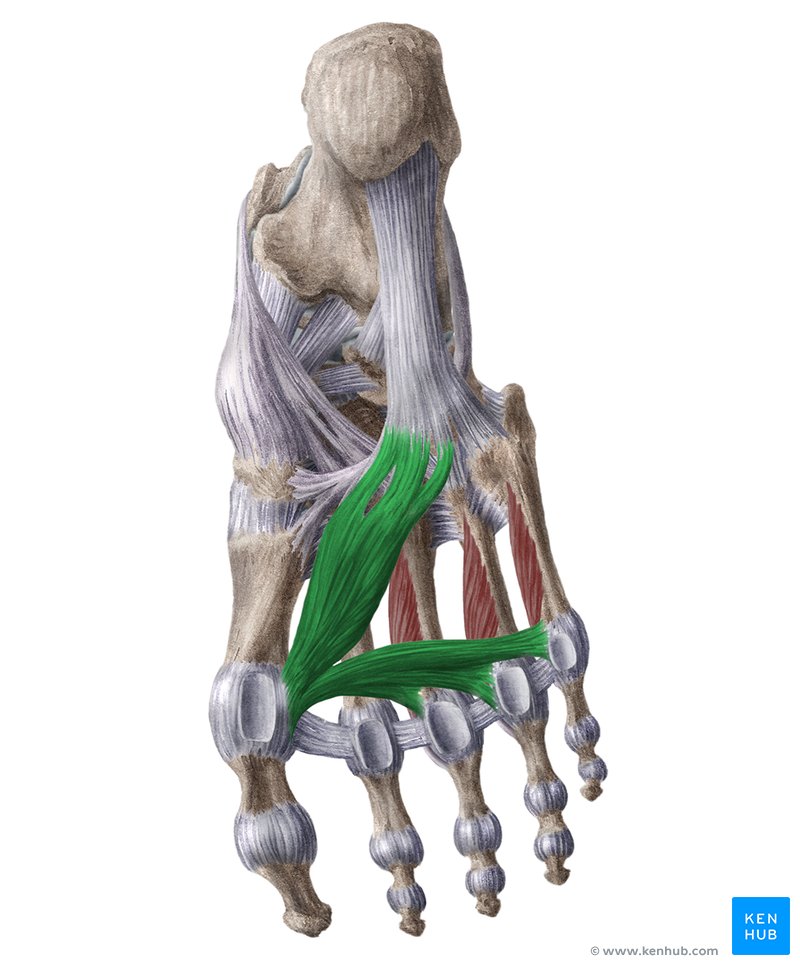
Adductor hallucis
Starts from middle, goes to thumb, and across the rest of the toes
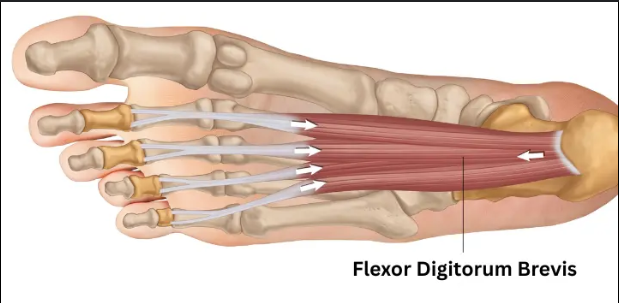
Flexor digitorium (foot)
bottom of feet
extensor digitorium (foot)
top of feet
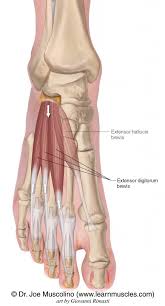
Extensor Hallucis Longus
starts from middle of fibula, ands at distal phalanx of big toe
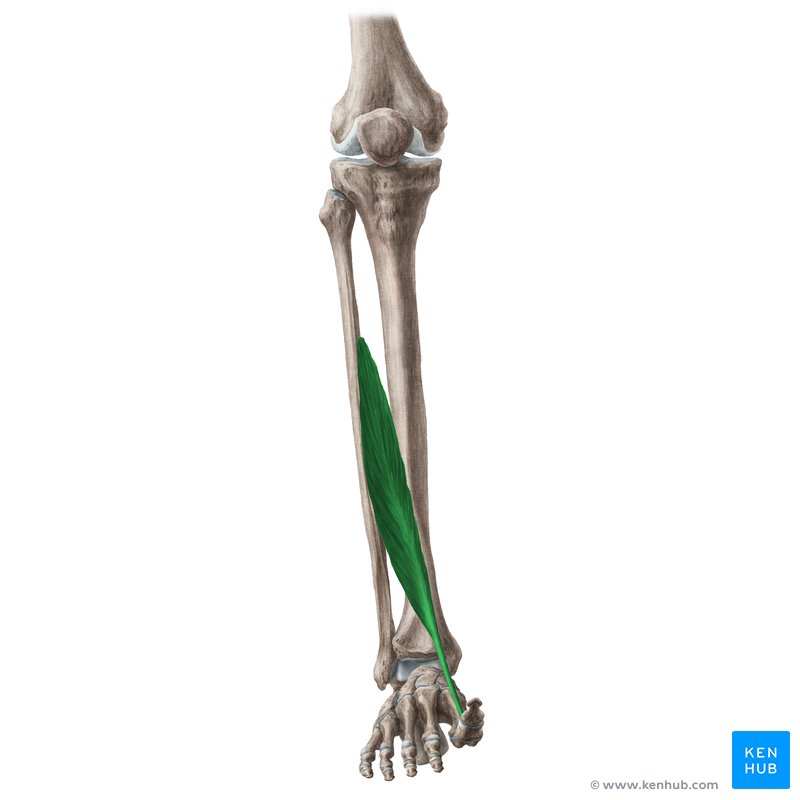
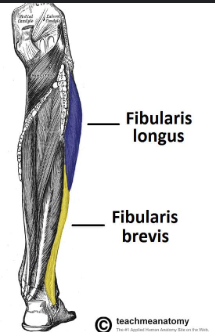
Fibularis(Peroneus) Longus/Brevis
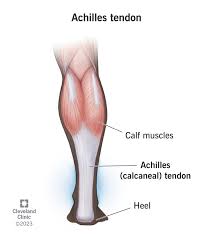
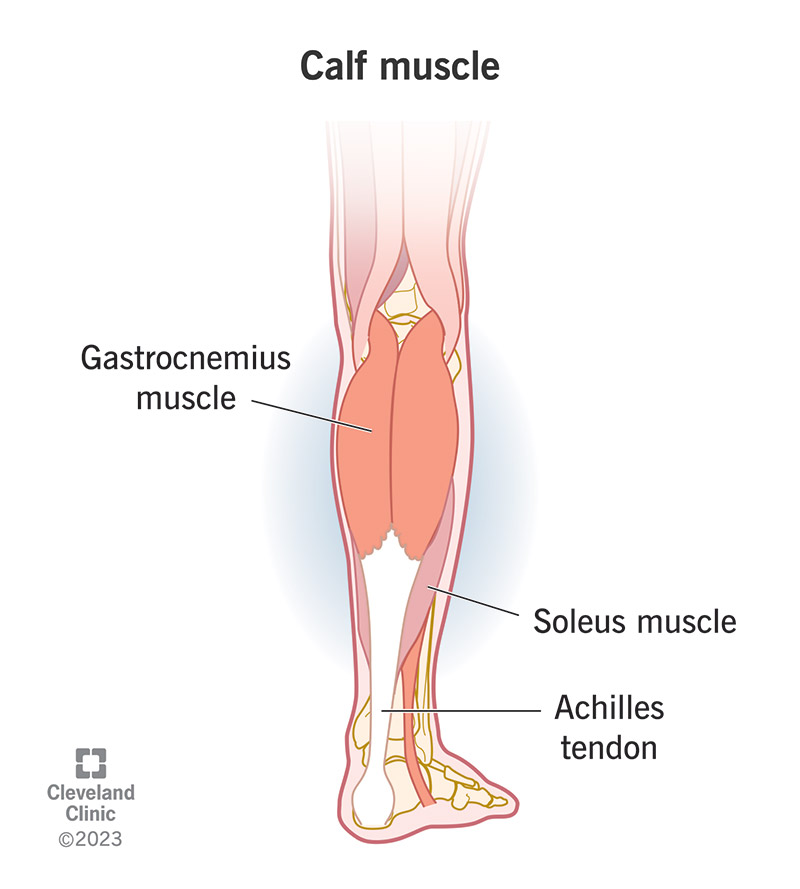
Achilles Tendon
Extensor digitorium longus
on the outside of leg
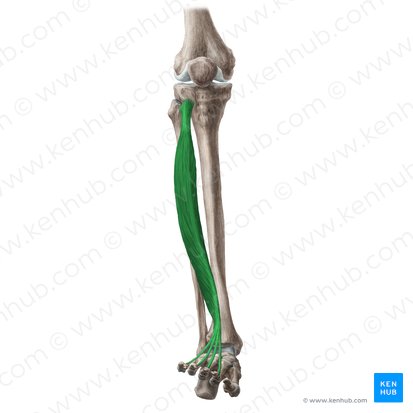
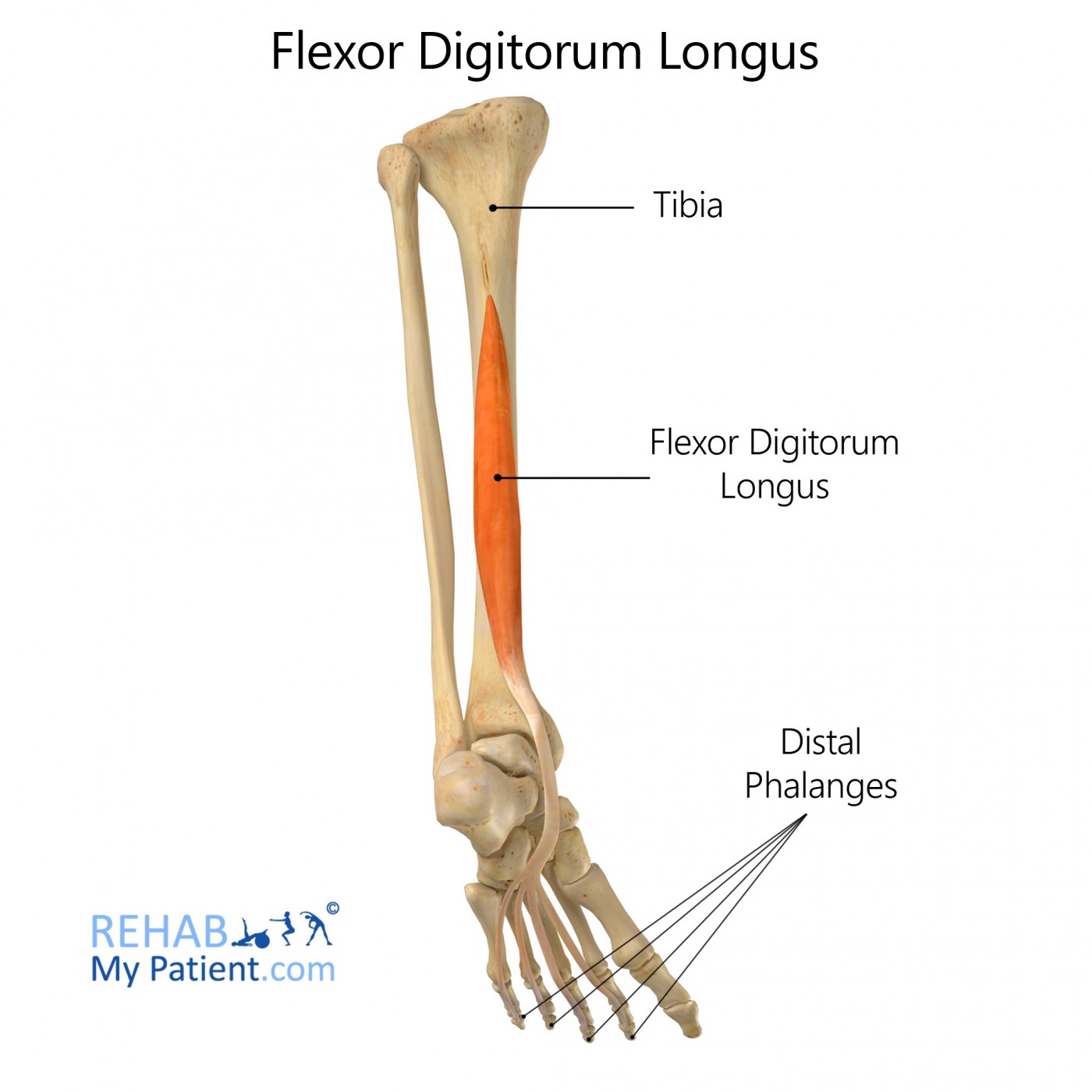
Flexor digitorium longus
goes from mid-tibia to bottom of the foot, to the 4 normal toes
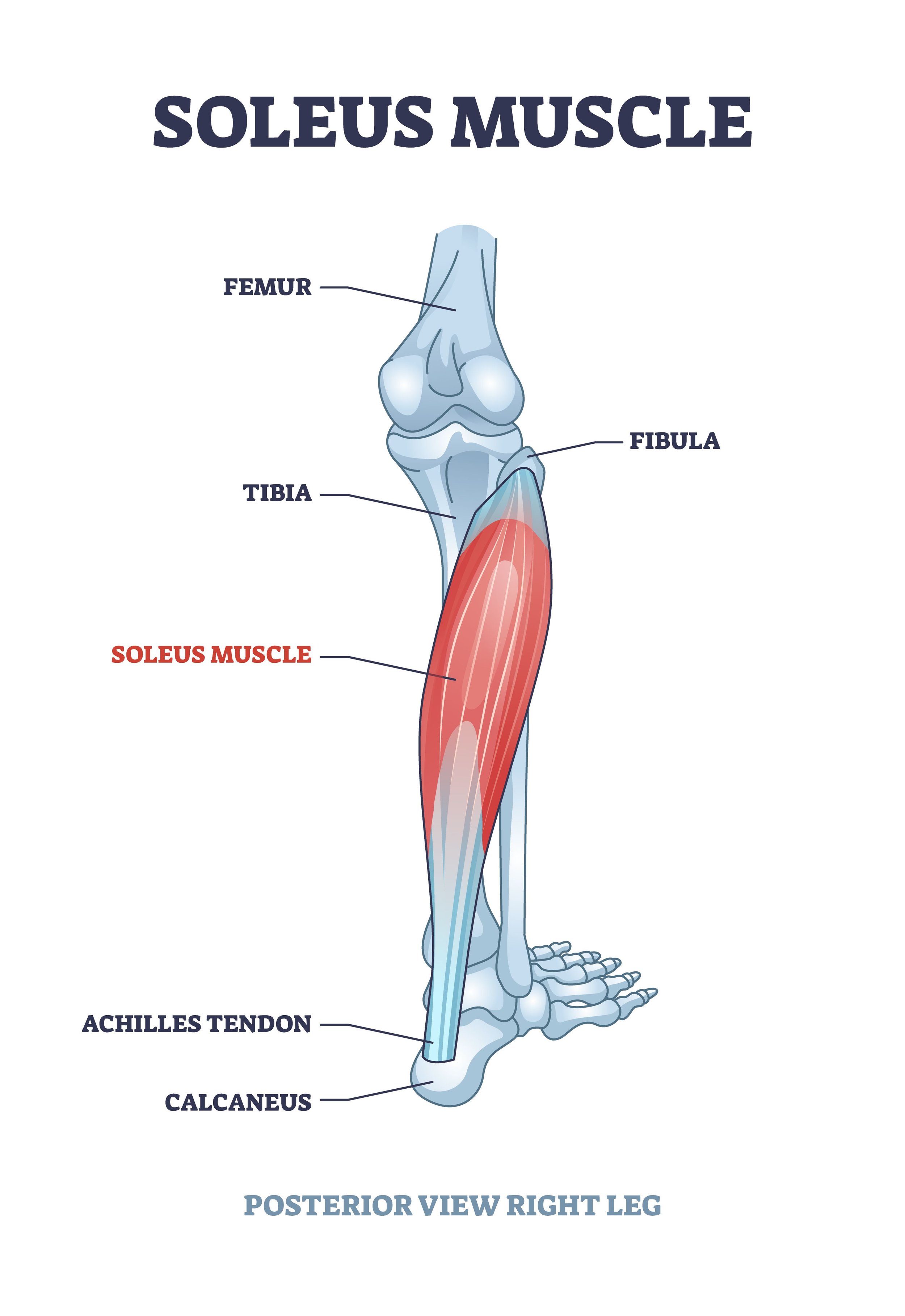
Soleus
on the outside/back of both calves
Tibialis Anterior
in the middle
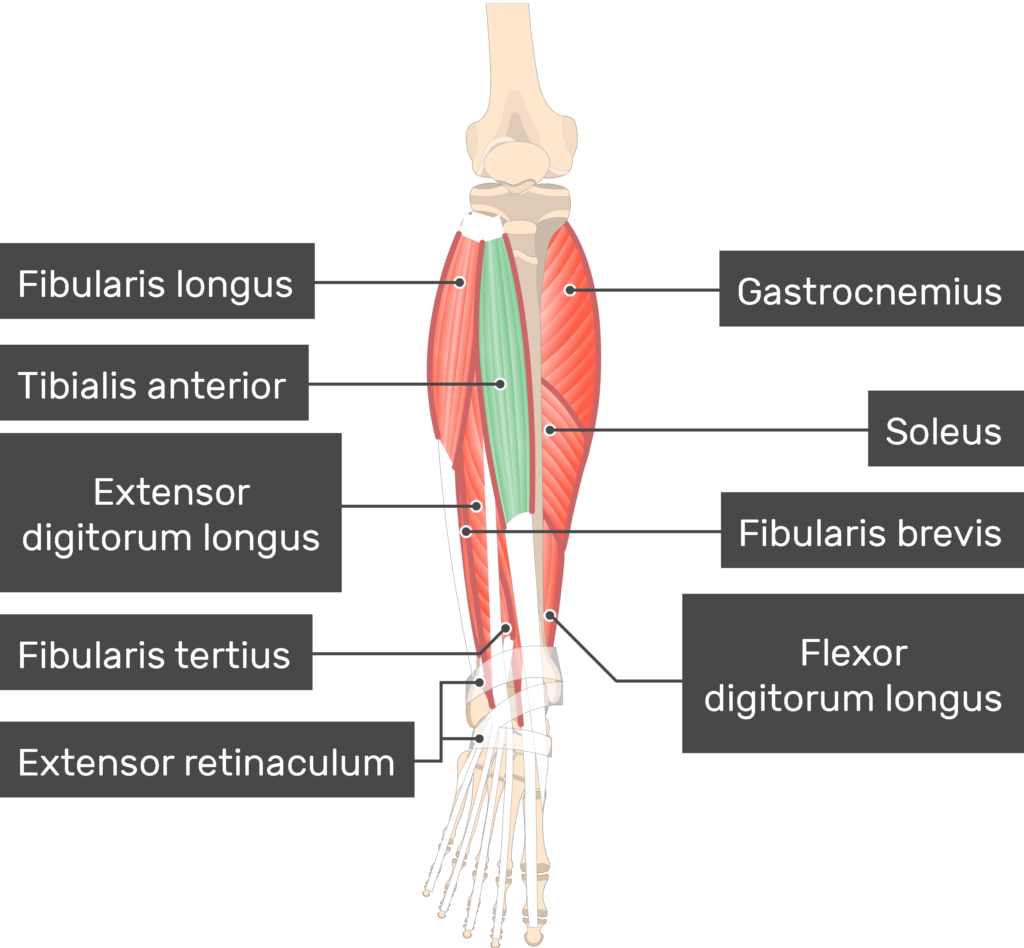
Gastrocnemius
starts from back of knee
Rectus Femoris
Starts from illum, runs down the middle into the knee
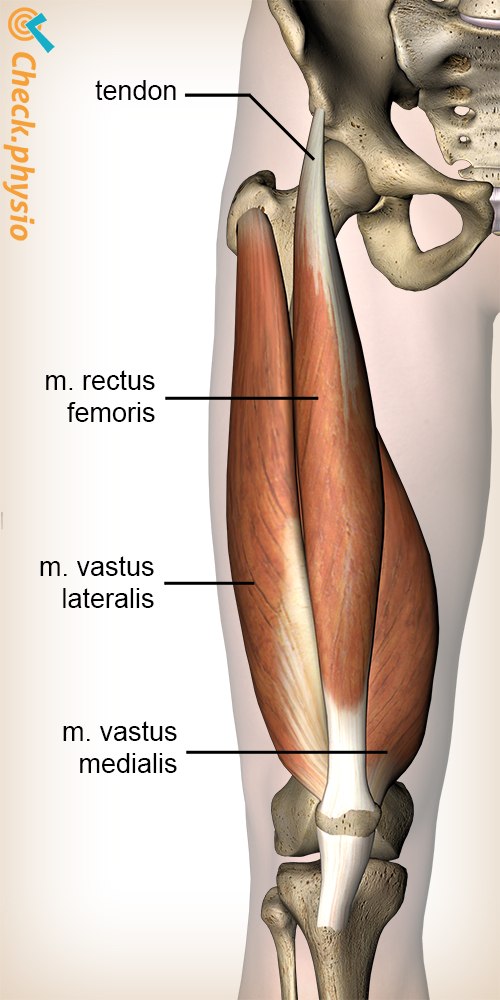
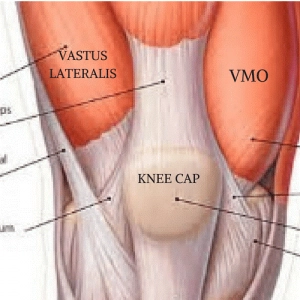
Vastus Lateralis
outside
Vastus Medialis Oblique
thumb side of the leg
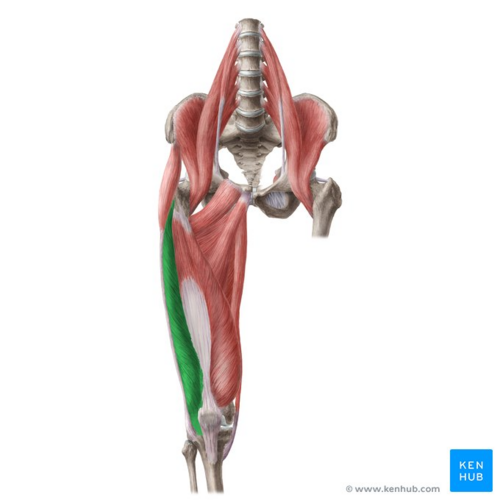
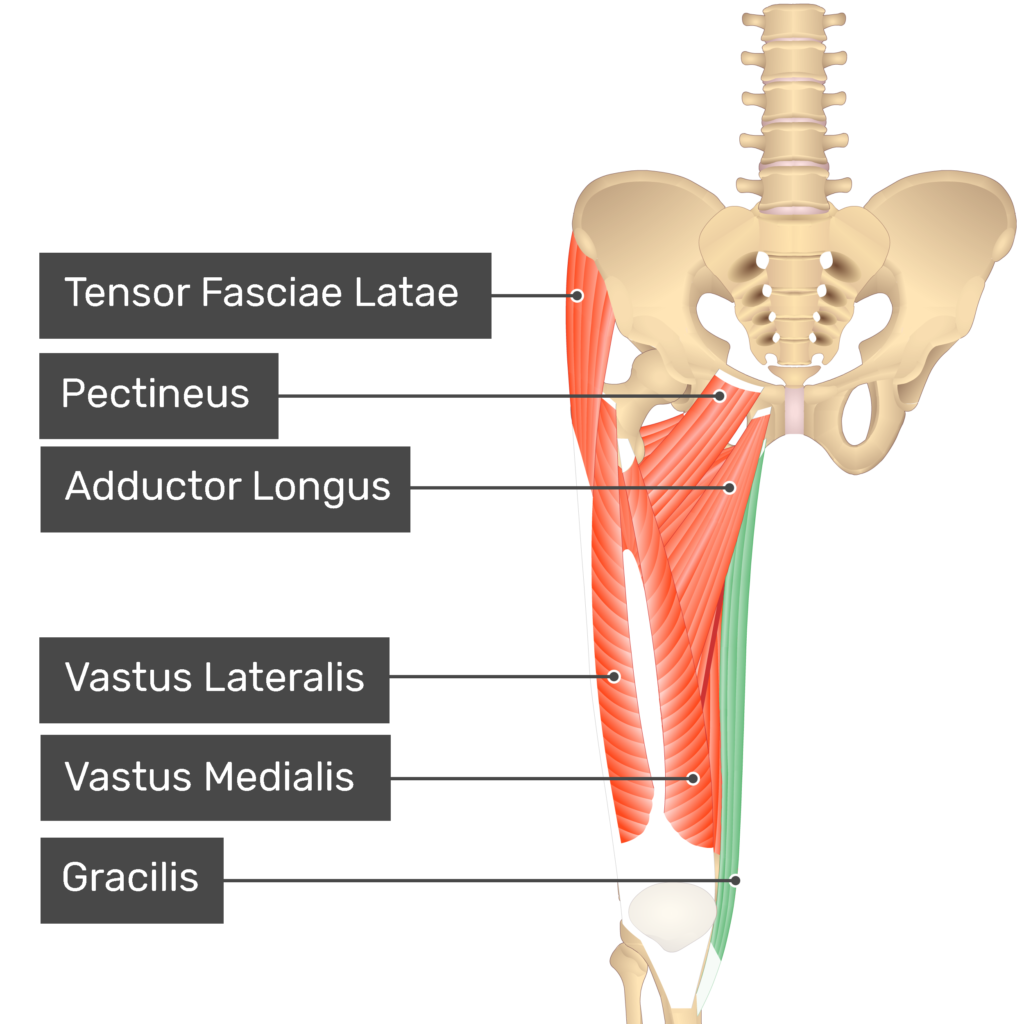
Sartorius
all the way across, ending at the kneecap
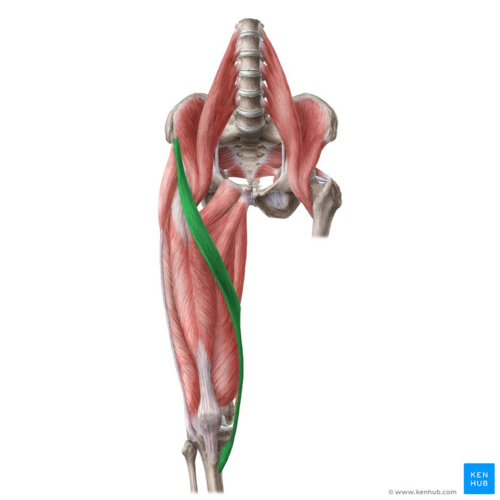
Gracilis
on the insides of ur thighs
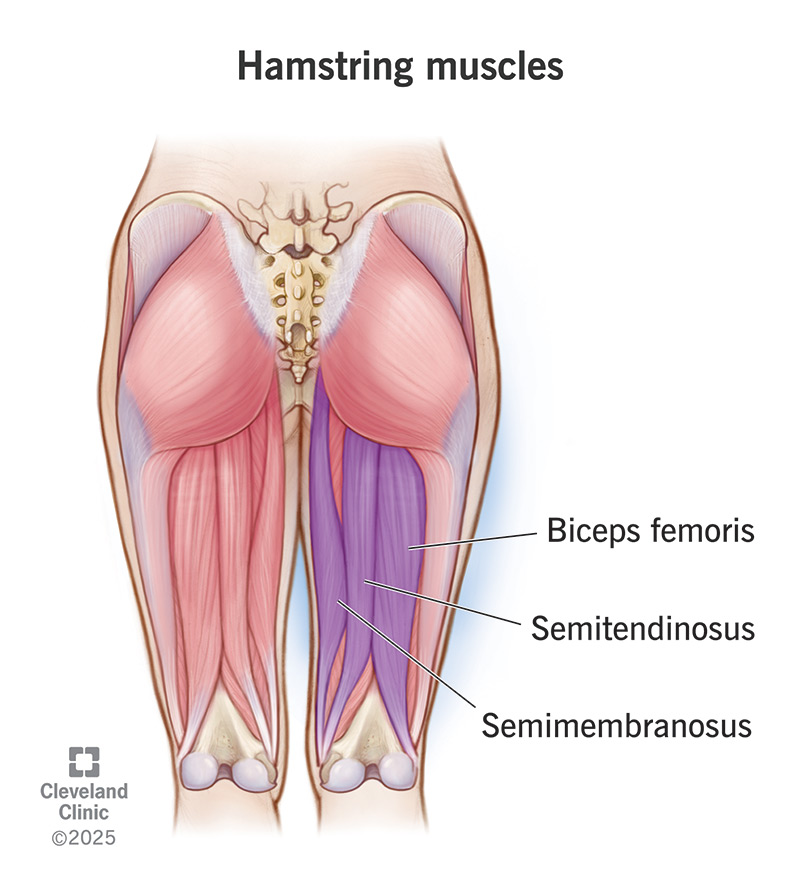
Biceps Femoris
back of leg, lateral side
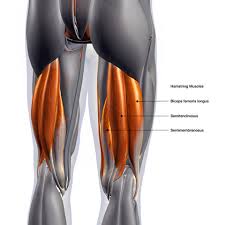
Semitendinosus
middle hamstring
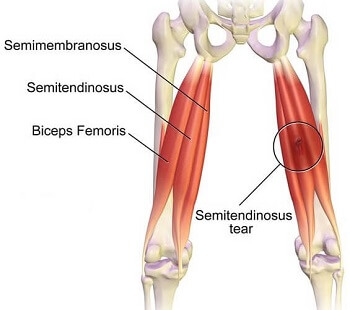
Semimembranosus
medial side of thigh (inside hamstring)
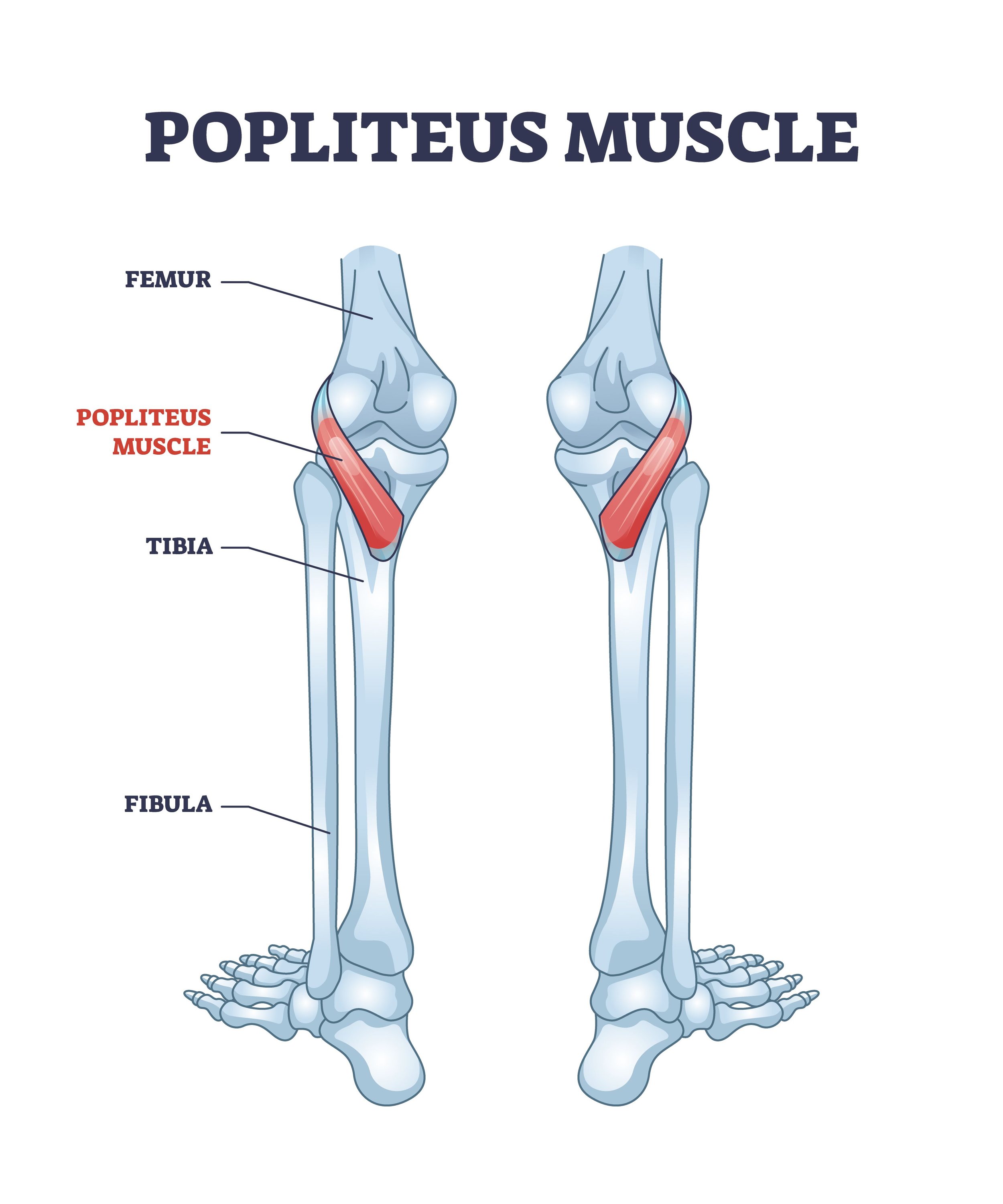
Popliteus
back of knee
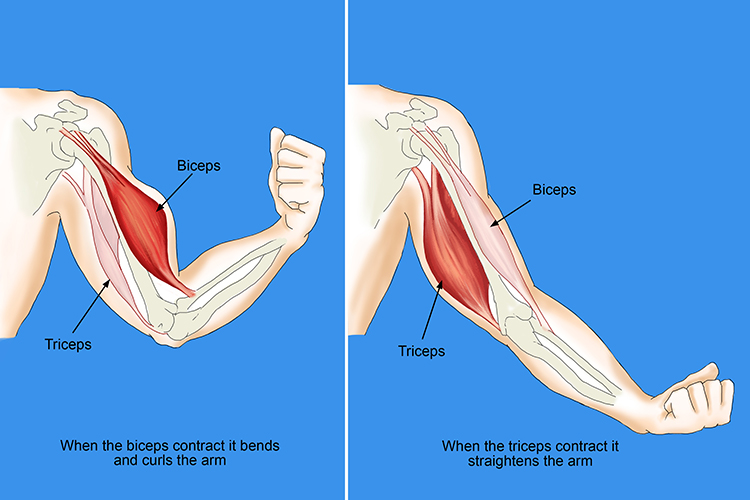
Biceps/Triceps
biceps pop out when arm is contracted, triceps when arm is straightened
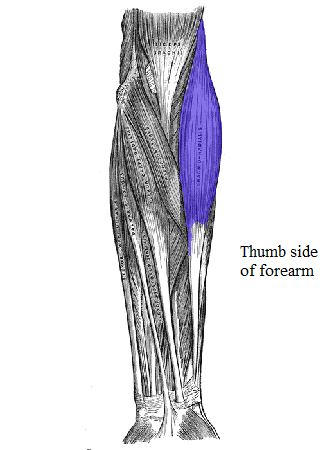
Brachioradialis
thumb side of forearm
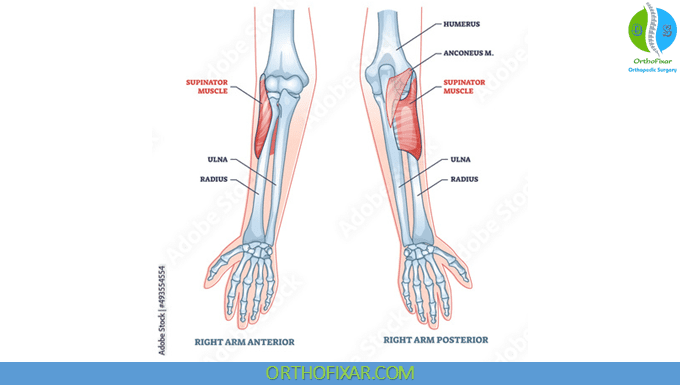
Supinator
back of forearm, still thumb side
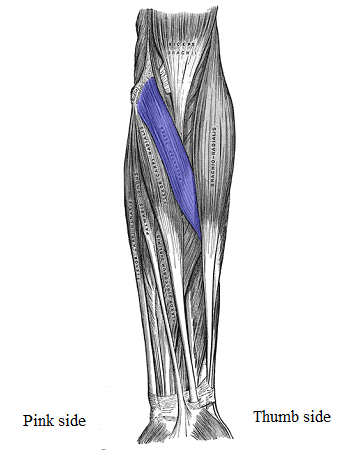
Pronator Teres
anterior (front side of armm)
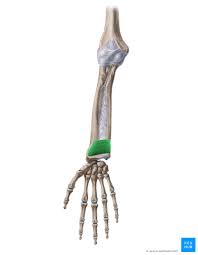
Pronator Quadratus
front of armm
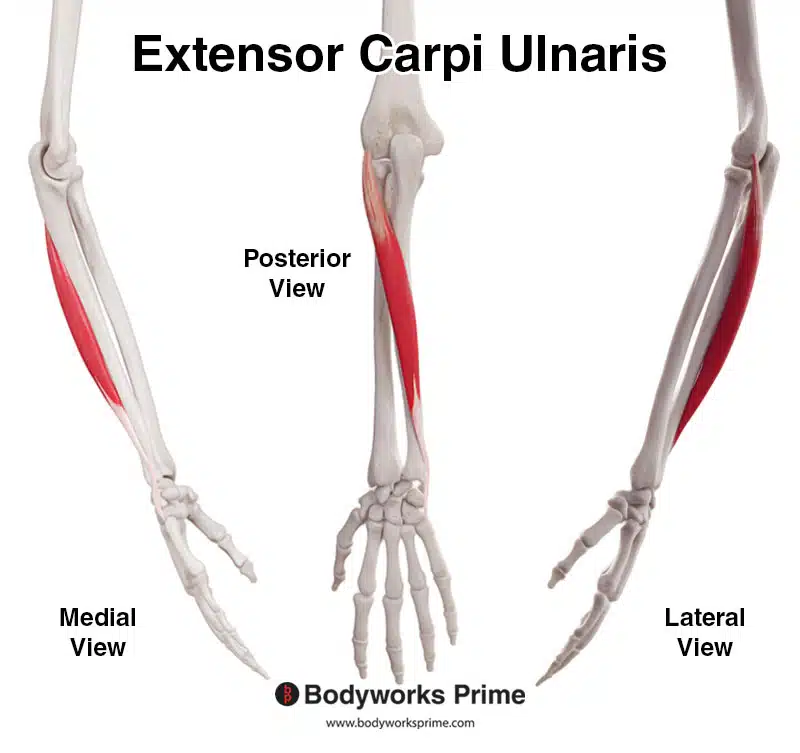
Extensor Carpi Ulnaris
back of arm, pinky side
Flexor Carpi Ulnaris
front of arm, pinky side
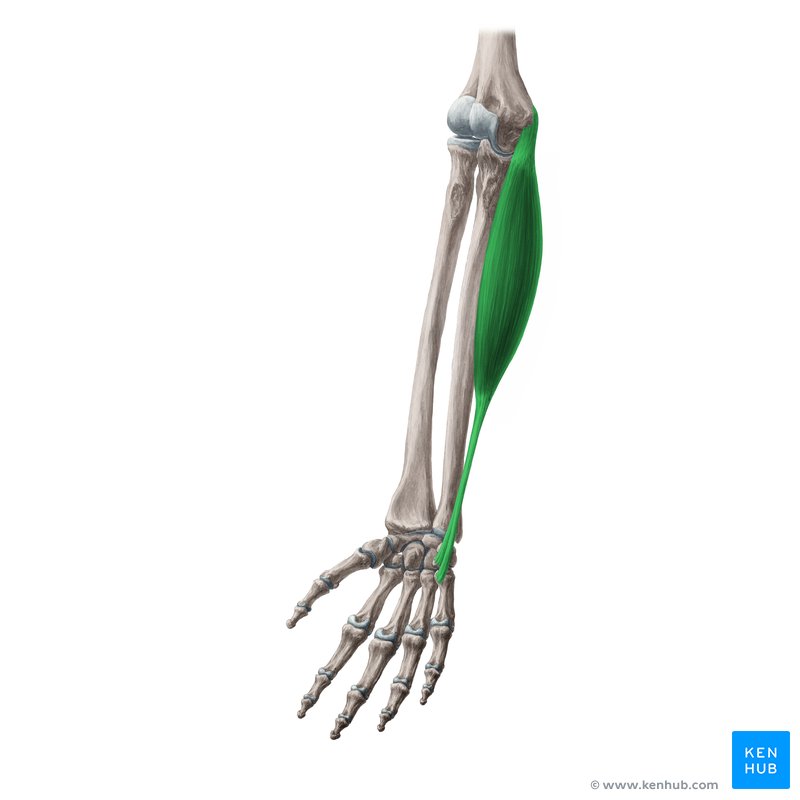
Flexor Carpi Radialis
front of arm, thumb side
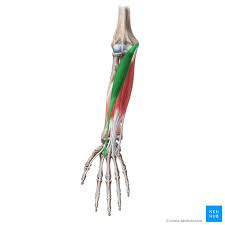
Extensor Carpi radialis
back of arm, thumb side
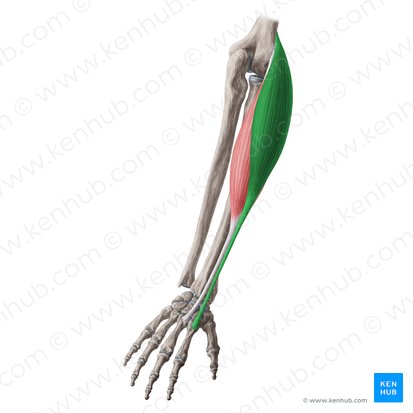
Flexor digiti Minimi
front of hand
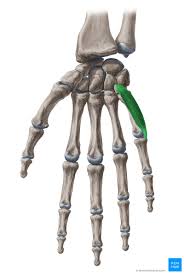
Extensor digiti Minimi
back, starting from arm
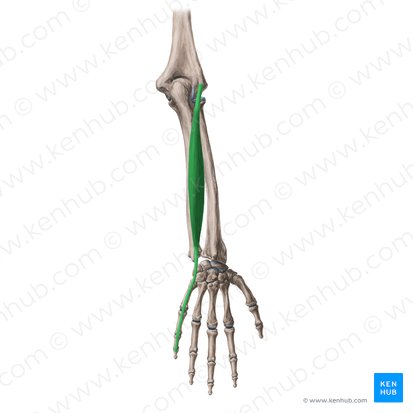
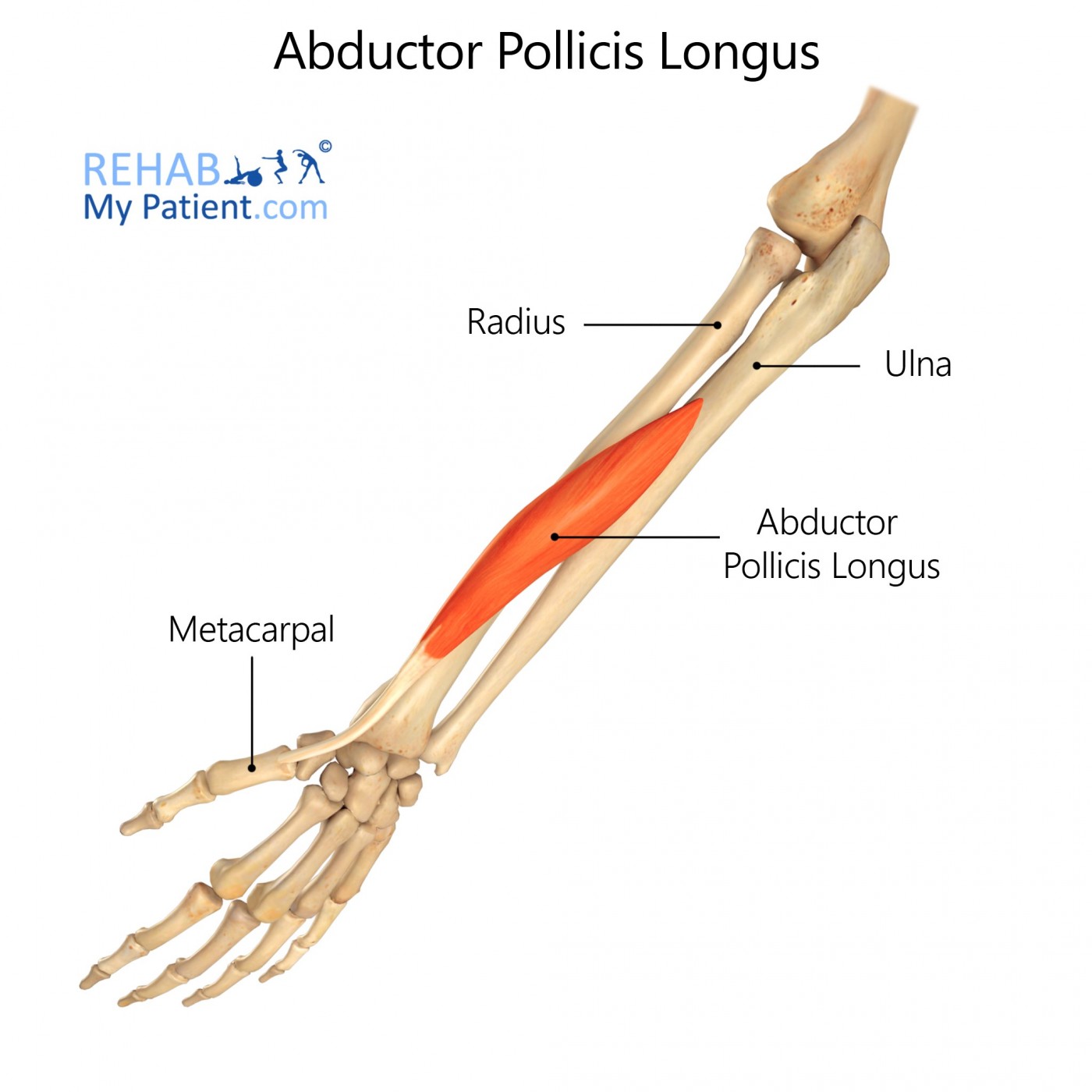
Abductor Policis longus
kind of in the middle of radius and ulna
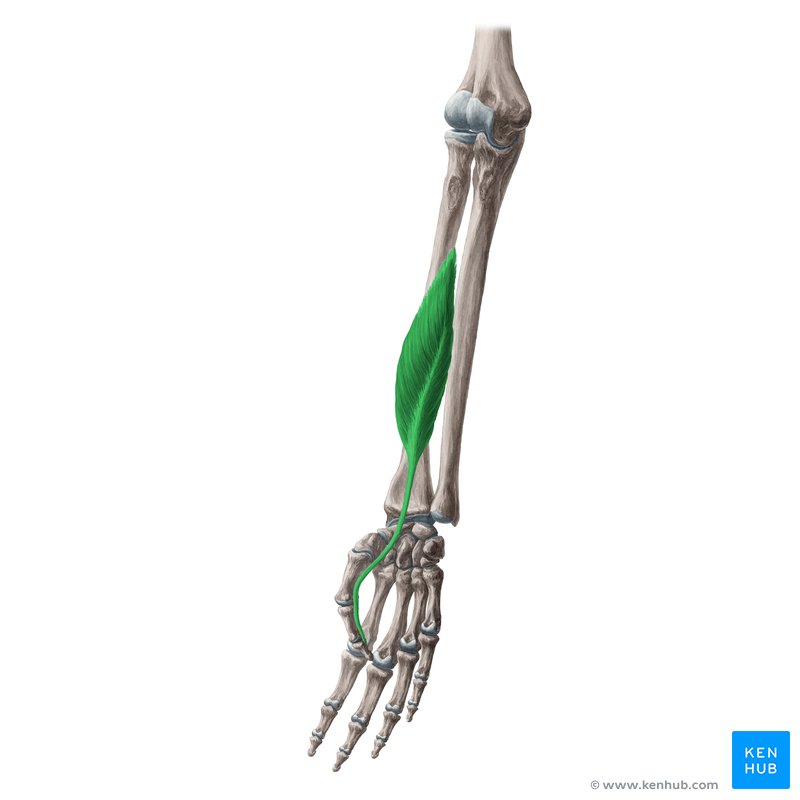
Flexor Pollicis
runs down onto the thumb
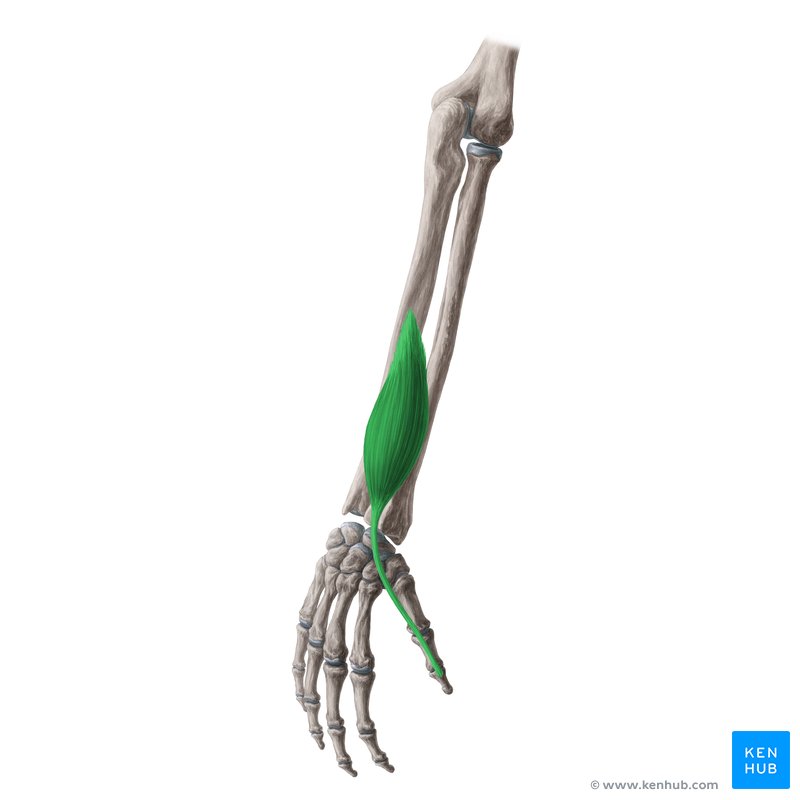
Extensor Pollicis
back side
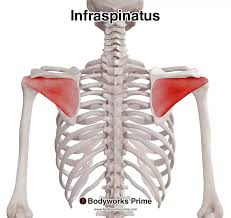
Infraspinatus
back
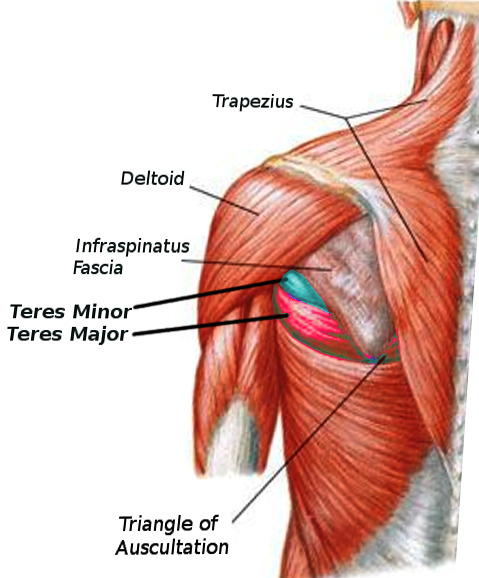
Teres Minor
Above the major
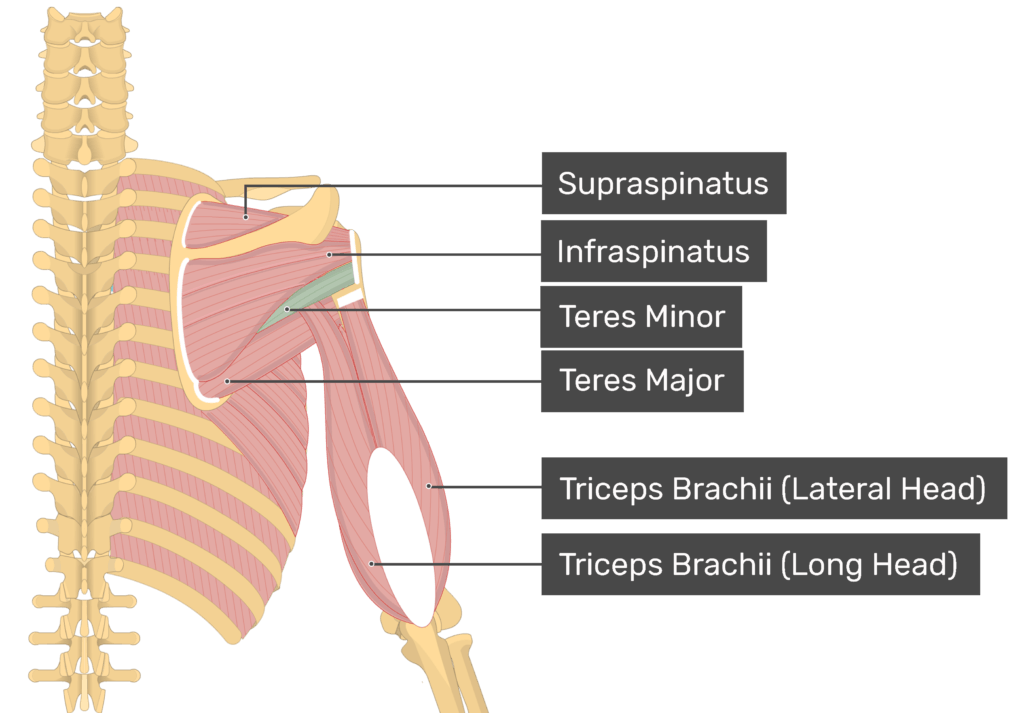
Teres Major
below the minor
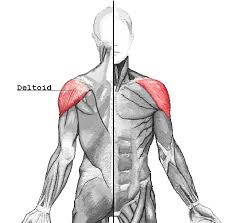
Deltoid
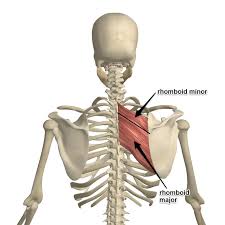
Rhomboids Major/Minor
Minor above major
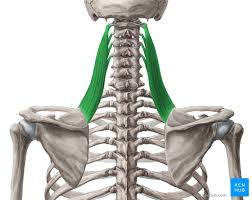
Levator Scapula
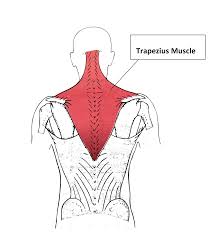
Trapezius
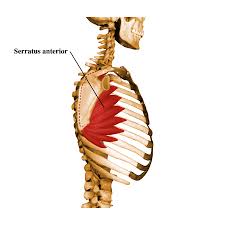
Serratus Anterior
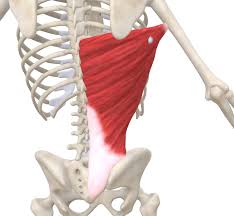
Latissimus Dorsi