BIO - unit 1 cells and cell processes
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
New
Card Sorting
1/52
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
53 Terms
1
New cards
what are the 7 characteristics of living organisms?
movement
respiration
sensitivity
growth
reproduction
excretion
nutrition
MRS GREN
respiration
sensitivity
growth
reproduction
excretion
nutrition
MRS GREN
2
New cards
what is movement?
an action by an organism or part of an organism causing a change in position or place
3
New cards
what is respiration?
the chemical reactions that break down nutrient molecules in living cells to release energy for metabolism
4
New cards
what is sensitivity?
the ability to detect or sense stimuli in the internal or external environment and to make appropriate responses
5
New cards
what is growth?
a permanent increase in size and dry mass by an increase in cell number or cell size or both
6
New cards
what is reproduction?
the process that makes more of the same kind of organism
7
New cards
what is excretion?
the removal from organisms of toxic materials, the waste products of metabolism (chemical reactions in cells including respiration) and substances in excess of requirements
8
New cards
what is nutrition
the taking in of materials for energy, growth, and development; plants require light, carbon dioxide, water, and ions; animals need organic compounds, ions, and usually need water
9
New cards
____ and ___ cells are multicellular, contain a nucleus w a distinct membrane.
animal and plant
10
New cards
animal cells do not have a ________
cellulose cell wall
11
New cards
animal cells do not contain _____
chloroplasts
12
New cards
animal cells often store carbohydrates as _____
glycogen
13
New cards
Do animal cells have nervous coordination? (yes or no answer)
yes
14
New cards
are animal cells able to move from place to place? (yes or no answer)
yes
15
New cards
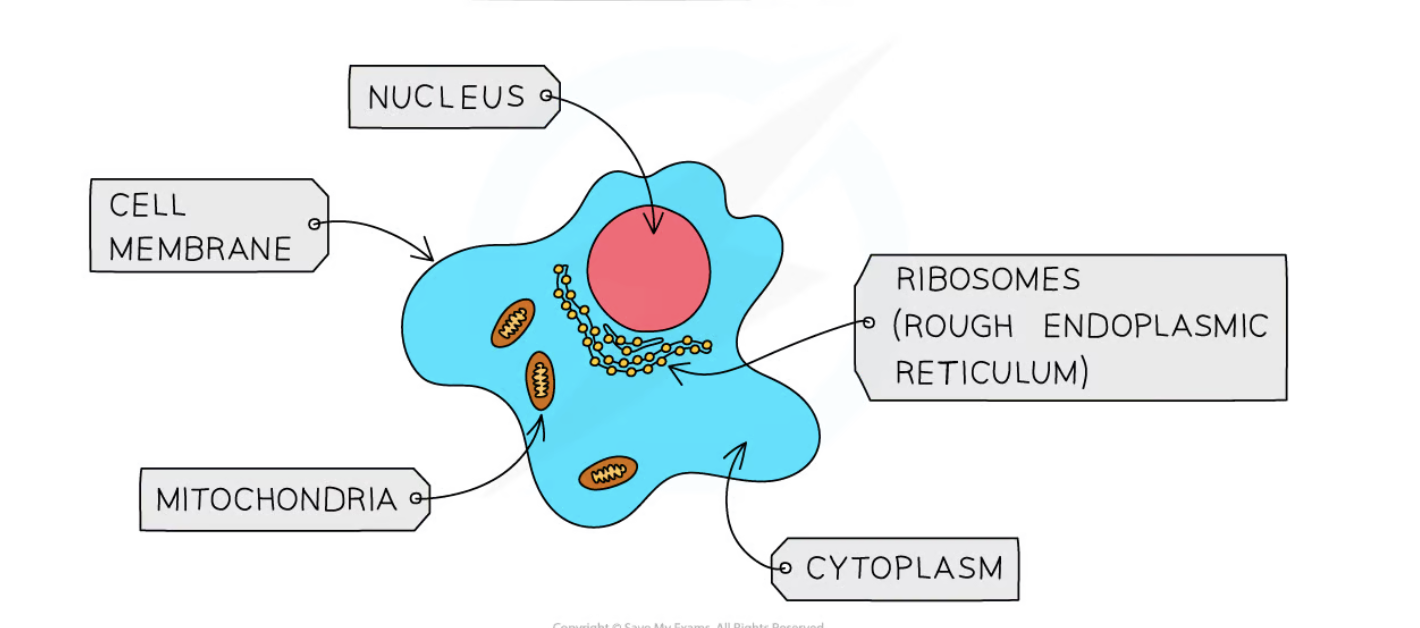
what cell is this?
animal cell
16
New cards
____ have a cell wall made out of XXX
plant cells
cellulose
cellulose
17
New cards
plant cells contain ____ so that they can carry out photosynthesis
chloroplasts
18
New cards
plant cells store carbohydrates as what?
starch or sucrose
19
New cards
do plant cells have nervous coordination?
no
20
New cards
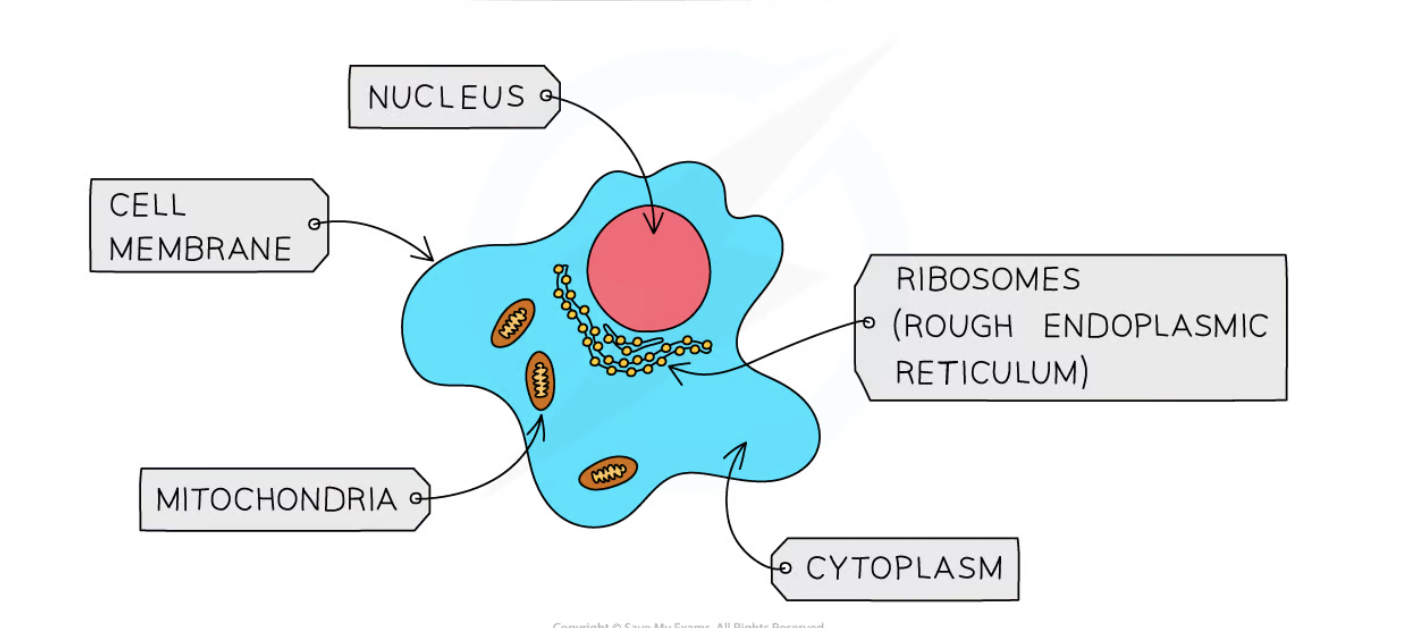
what cell is this?
plant cell
21
New cards
what is the function of the nucleus?
contains the DNA which controls the activities of the cell
22
New cards
what is the function of the cytoplasm?
its a gel like substance that supports the internal cell structures. Its also the site of many chemical reactions
23
New cards
what is the function of the cell membrane?
it holds the cell together as well as controls which substances can enter and leave the cell
24
New cards
what is the function of the ribosomes?
they are the sites of protein synthesis
25
New cards
what is the function of the mitochondria?
it is the site of most of the chemical reactions involved in respiration, where energy is released to fuel cellular processes.
26
New cards
what is the function of the cell wall?
it gives the cell extra support, defining its shape
27
New cards
what is the function of the chloroplasts?
it contains chlorophyll and the enzymes needed for photosynthesis
28
New cards
what is the function of the vacuole?
it is used for storage of certain materials and it also helps support the shape of the cell
29
New cards
do animal cells have a cell wall?
no
30
New cards
how are new cells produced?
through the division of existing cells
31
New cards
what are specialised cells?
they are cells which have developed certain characteristics in order to perform particular functions.
32
New cards
what is differentiation?
it is when cells develop the structure and characteristics needed to carry out their functions
33
New cards
what is the function of a ciliated cell?
to move the mucus in the trachea and bronchi
34
New cards
what is the adaptation of a ciliated cell?
extension of the cytoplasm at the surface of the cell to form hair-like structure called cilia which beat to move mucus up to the throat
35
New cards
what is the function of a nerve cell?
the conduction of impulses
36
New cards
what are the adaptations of a nerve cell? (3)
* long so that nerves can run to and from diff places of the body to the CNS
* has extensions and branches so that it can communicate w other nerve cells
* the axon is covered w a fatty sheath which insulated the nerve and speeds up the nerve impulse
* has extensions and branches so that it can communicate w other nerve cells
* the axon is covered w a fatty sheath which insulated the nerve and speeds up the nerve impulse
37
New cards
what is the axon?
it is an extension of cytoplasm away from the cell body
38
New cards
what is the function of a red blood cell?
to transport oxygen
39
New cards
what are the adaptations of the red blood cell? (3)
* biconcave disc shape increases the surface area for more efficient diffusion of oxygen
* contains haemoglobin which joins w oxygen to transport it
* contains no nucleus to increase amount of space available for haemoglobin
* contains haemoglobin which joins w oxygen to transport it
* contains no nucleus to increase amount of space available for haemoglobin
40
New cards
what is the function of the sperm cell?
reproduction
41
New cards
what are the adaptations of the sperm cell? (4)
* the head contains genetic materials for fertilisation in a haploid nucleus.
* the acrosome in the head contains digestive enzymes so that a sperm can penetrate the egg
* the mid-piece is packed w mitochondria to release energy needed to swim and fertilise the egg
* the tail enables to sperm to swim
* the acrosome in the head contains digestive enzymes so that a sperm can penetrate the egg
* the mid-piece is packed w mitochondria to release energy needed to swim and fertilise the egg
* the tail enables to sperm to swim
42
New cards
how many chromosomes are in a haploid nucleus?
23
43
New cards
what is the function of the egg cell?
reproduction
44
New cards
what are the adaptations of the egg cell? (3)
* contains a lot of cytoplasm which has nutrients for the growth of the early embryo
* haploid nucleus contains the genetic material for fertilisation
* cell membrane changes after fertilisation by a single sperm so that no more sperm can enter
* haploid nucleus contains the genetic material for fertilisation
* cell membrane changes after fertilisation by a single sperm so that no more sperm can enter
45
New cards
what is the function of a root hair cell?
absorption of water and mineral ions from soil
46
New cards
what are the adaptations of a root hair cell? (3)
* root hair increases surface area of cell to ensure maximum absorption of water and mineral ions
* walls are thin to ensure water moves through quickly
* no chloroplasts present
* walls are thin to ensure water moves through quickly
* no chloroplasts present
47
New cards
what is the function of a xylem vessel?
conduction of water through the plant; support of the plant
48
New cards
what are the adaptations of a xylem vessel? (3)
* no top and bottom walls between xylem vessels so there is a continuous column of water running through them
* cells are dead w/o organelles or cytoplasm to allow free passage of water
* their wall become thickened w a substance called lignin when means they are able to help support the plant
* cells are dead w/o organelles or cytoplasm to allow free passage of water
* their wall become thickened w a substance called lignin when means they are able to help support the plant
49
New cards
what is he function of the palisade mesophyll cell?
photosynthesis
50
New cards
what are the adaptations of the palisade mesophyll cell? (2)
* column shaped to maximise absorption of sunlight and fit as many in a layer under the upper epidermis of the leaf as possible
* contains many chloroplasts for maximum photosynthesis
* contains many chloroplasts for maximum photosynthesis
51
New cards
what is the formula for magnification?
Magnification = image size x actual size
52
New cards
what is the formula for actual size?
Actual size = Image size / magnification
53
New cards
what is the formula for image size?
Image size = actual size x magnification