L2 Social Perception pt 1
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
The cocktail party effect
Tendency of picking a personally relevant stimulus, eg in a noisy environment you pay attention when your name is said bc its personally relevant to you
Self recognition
Recognizing yourself, humans become capable of this at 18-24 months
How does the brain respond to perceiving info related to the self?
Increase activity when shown stuff related to the self, such as a pic of self, self relevant words, first pov videogame
What is the social self
A sense of who we are forged by others
Self knowledge derived from social relationships
constructed, maintained and negotiated in social environments
ABC aspect of social self
A: Self esteem (Affective) → How ppl evaluate themselves
B: Self presentation (Behavioural) → How people present themselves
C: Self concept (Cognitive) → How ppl come to understand who they are
Explain self esteem
Individual’s positive or negative self evaluations
An attribute that can greatly impact how we think about and present ourselves
A state of mind that fluctuates in respond to life events
Relatively stable
Impacted by environmental events
Typically goes up, peaks then goes down throughout life
Higher self esteem usually predicts success in life
What is trait vs state in self esteem?
Trait is the enduring level of self esteem one possesses across time, relatively stable
State is the dynamic and changable self evaluations that are momentarily experienced
Trait and State are captured differently, eg longitudinal studies for trait self esteem and daily diaries for state self esteem
General vs domain self esteem
General self esteem differs from domain self esteem, as self esteem in different domains tend to not be consistent and vary between individuals much more
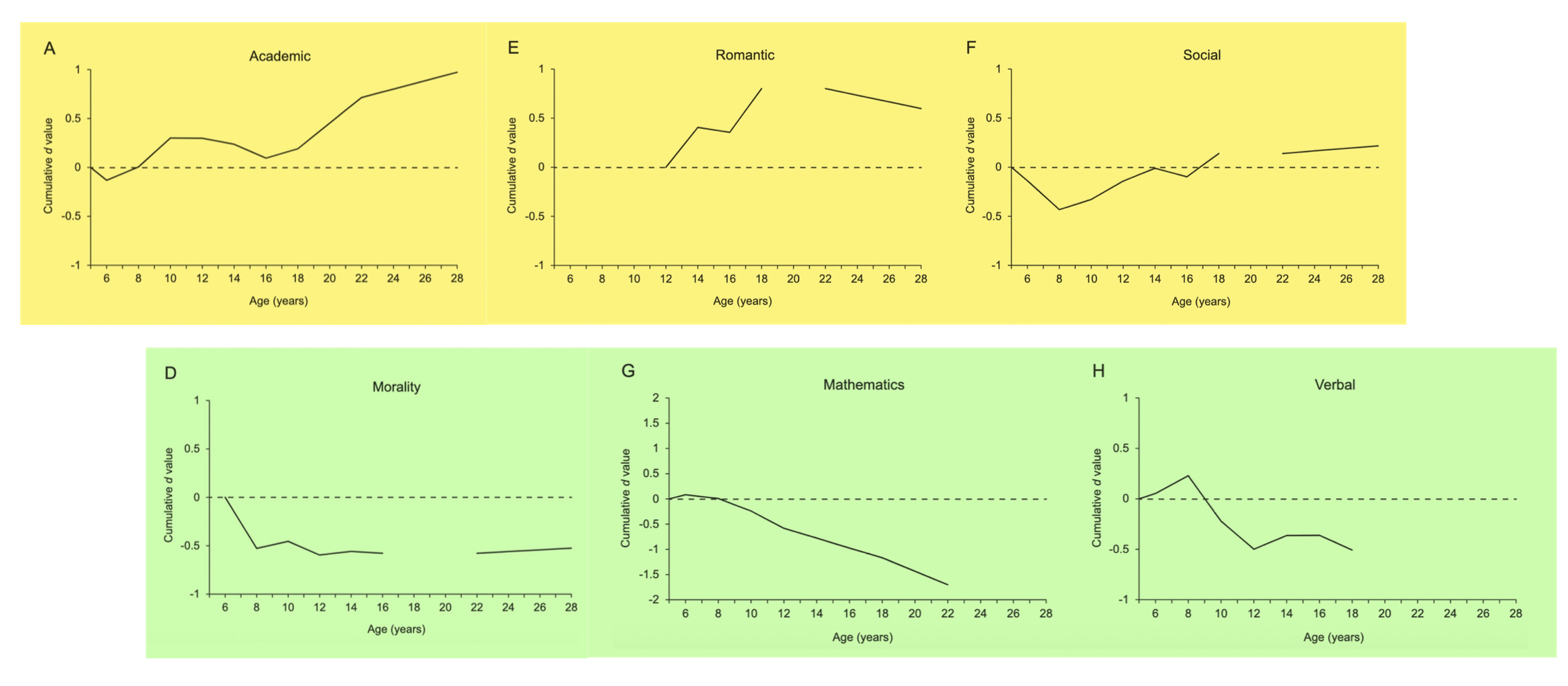
Why do we have self esteem? Explain with reference to a theory (s)
The pursuit of self worth is an aspect of human motivation.
Sociometer theory → Ppl are inherently social animals. A need for self esteem is driven by desire to connect w others and get their approval, this leads to an inner sociometer in some, which detects acceptance and rejection which then translates into hi or low self esteem.
Terror management theory → We r biologically programmed for life and life preservation, since we know of inevitable death, we cope with this by constructing worldviews on how the world was created to give meaning to life, and to give us purpose and a sense of self esteem, also to buffer against anxiety. Self esteem shields from terror.
Impact of high and low self esteem
Higher → happier, more confident and successful, can persist longer at difficult tasks and maintain independence under pressure
Lower → more pessimistic, prone to failure, lack confidence and bring a losing attitude that creates a toxic cycle of failure
Costs of pursuing high self esteem
Become anxious, stressed, and neglect needs of others and self
Signs of unrealistically high self esteem
Inflated egotism → Not warranted by obvious facts, actually fragile and insecure
Narcissism → Grandiose perceptions of self, overexaggeration of positive traits
Ppl like this might react aggressively to threats to their self-esteem, resort to violence to assert their feelings of superiority, try to dominate others.
What factors determine how ppl feel about themselves? use a theory to explain
Self discrepancy theory → Self esteem is determined by the match or mismatch of how we see ourselves and how we want to see ourselves that form a relationship in a triangular model
Actual self → contains all info you have of what kind of person you are
Idea self → who you want to be (dreams)
Ought self → who you think you should be (responsibilities)
We compare these selves against each other and often fall short, resulting in emotional reactions like dissapointment. Factors affecting the intensity of emotions are the amount of discrepancy between selves, the importance of the discrepancy and how much we focus on the discrepancies
What does self esteem depend on?
Successes and failures in domains you base your self worth on, ie that r important to you
rises when ur doing well in those domains, vice versa
some parents base their self worth on their children, when their children does bad, they lose face, which is a bad way of parenting
What role does culture play in self esteem?
More independent cultures foster higher self esteem, most likely due to cultural values that promote independence and uniqueness
Explain Self concept
Sum of individuals beliefs about own attributes, made up of cognitive molecules, such as self schemas, that guide processing of self relevant info
Ppl more attuned to info related to their self schemas, and process related info faster
Where do self concepts come from?
Family, other people, introspection, autobio memories and narrated self (stories of self that is told)
Self perception theory
Ppl can learn abt themselves by watching own behaviour. Especially when the situation alone seems insufficient to have caused their behaviour or their internal states are weak or difficult to interpret
People do not infer their own internal states from behaviour that occurred in the presence of compelling situational pressures such as reward or punishment or time pressure.
What are some things that can trigger self perception
Facial expression and body posture, eg if im smiling, i must be happy
Is our knowledge of the self accurate?
Our knowledge of our internal traits are more accurate that others, as only we know who we truly are, want to be and aspire to be. However, others percieve our observable traits more accurately than ourselves bc of our desire to maintain self esteem
We are so motivated to maintain self esteem that we have blind spots in self evaluation to maintain it.
What is social comparison theory?
We evaluate ourselves by comparing us to others. We do it in times of uncertainty, both upwards and downwards
Downward → compare w someone worse than u, uplifting effect and helps us defend from negative perceptions of self and cope
Upward → compare w someone better than u, might result in feelings of envy or insecurity
Super prevalent on social media rn
Self enhancement
Thinking highly of yourself, better than average, especially when it comes to personal traits that are important to u
Processes that serve self enhancement
Implicit egotism → unconscious, subtle expression of self esteem
Self serving bias → Thinking better things will happen to them and showing an optimistic bias towards life, which can result in illusions of control
Self handicapping → Come up with reasons to excuse future performance, purposefully sabotaging ourselves to prevent the damage to self esteem if we fail
Reflected glory → Associating with successful ppl to feel successful as well, may cut off ppl that are not up to standard bc association w them will lower self esteem and reflect faliure
Cultural influence on how self is percieved, evaluated and presented
Differences in cultural dimensions eg individualist and collectivist, some strive for independence and uniqueness while others strive for harmony, in turn influences how u present, evaluate and percieve urself in context of a group
What are the independent and interdependent views of self?
Independent → The self contains a set of psychological qualities that are independent to other people.
The person is a kind of “container” that stores psychological traits that cause the person’s actions.
We have independent rights, such as the right to pursue personal happiness.
Interdependent → Self is influenced by the individual’s roles within family and social relationships and emphasizes responsibilities that accompany these roles.
Behavior is not explained in terms of autonomous mental traits that reside in the person’s head.
People explain behavior in terms of networks of social obligations. It is the person’s location within such social systems that is seen as the cause of behavior.
Explain self presentation
Behavioural expression of the social self, the strats we use to shape other’s perceptions of us, most ppl are at least a little concerned of how they appear to others
Spotlight effect
Tendency to believe we are being paid attention to more than we actually are
Strategic self presentation and its goals
We may present ourselves to others in order to achieve a goal:
Ingratiation → acts motivated by the desire to want to get along w others
Self promotion → acts motivated by the desire to be recognized for our competence
Costs of self presentation
Eating disorders in women, Drug abuse in teens to impress peers, Accidental injury in young men who do risky things to impress peers
Self verification
Desire for others to see us as how we see ourselves so we can confirm our self concepts
Self verification vs self enhancement
Sometimes our need for self verificatoin trumps self enhancement, we will give up looking good or presenting well for others to accept who we really are
Self verification strats
Displaying identity cues thru dress, entering relationships that maintain our sense of self, even if the views of self is toxic
Self monitoring
Regulate behaviour in response to self presentation concerns in a situation, to meet demands of social situations
high self monitors regard themselves as pragmatic, flexible and adaptive
able to cope with the diversity of life’s roles.
willing to change colors like a chameleon just
to fit in
have a repertoire of selves from which to draw.
Low self monitors describe themselves as principled and forthright
always speaking their minds so others know
where they stand
be viewed as stubborn, insensitive to their surroundings
unwilling to compromise in order to get along
self monitoring drops with age, probably bc ppl are more secure about their self image when they get older
Summarize the nature of social self
the self is complex and multifaceted
the cognitive, affective and behavioral components of the self is interrelated
the social self is defined by two truths: malleable and relatively stable