Sys Path Exam 1
1/969
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
970 Terms
what are the gross pathology patterns of bone marrow?
decreased/empty/replaced
inflamed
hemorrhagic
extra
how can bone marrow become decreased/empty/replaced?
increased destruction
reduced production
demand exceeds production capacity
replacement (myelophthisis)
what can cause destruction of bone marrow?
radiation
estrogen
chemotherapy
immune mediated
toxins
infection
what can cause reduced production of bone marrow?
deficiencies
when can bone marrow demand exceed production?
overwhelming bacterial infection
what can cause replacement of bone marrow?
myelofibrosis
neoplasia
hyperplasia of bone marrow is due to prolonged…
increased demand
serous atrophy of fat
gelatinous transformation of fat due to cachexia or starvation
thymic involution
physiologic reduction in thymic size that occurs around the onset of puberty
what are the gross pathology patterns for thymus?
absent/small
inflamed
hemorrhagic
large
thymic hemorrhage differentials:
idiopathic hemorrhage
anticoagulant toxicity
traumatic hemorrhage
localized thymic neoplasia is usually…
thymoma
diffuse thymic neoplasia is usually…
lymphoma
what is the pathogenesis for myasthenia gravis secondary to thymoma?
thymoma→develop autoantibodies against thymic myoid cells→antibodies in systemic circulation→bind to AChRs on postsynaptic membrane of neuromuscular junctions→ preventing ACh binding→preventing muscle contraction
what are the gross pathology patterns of spleen
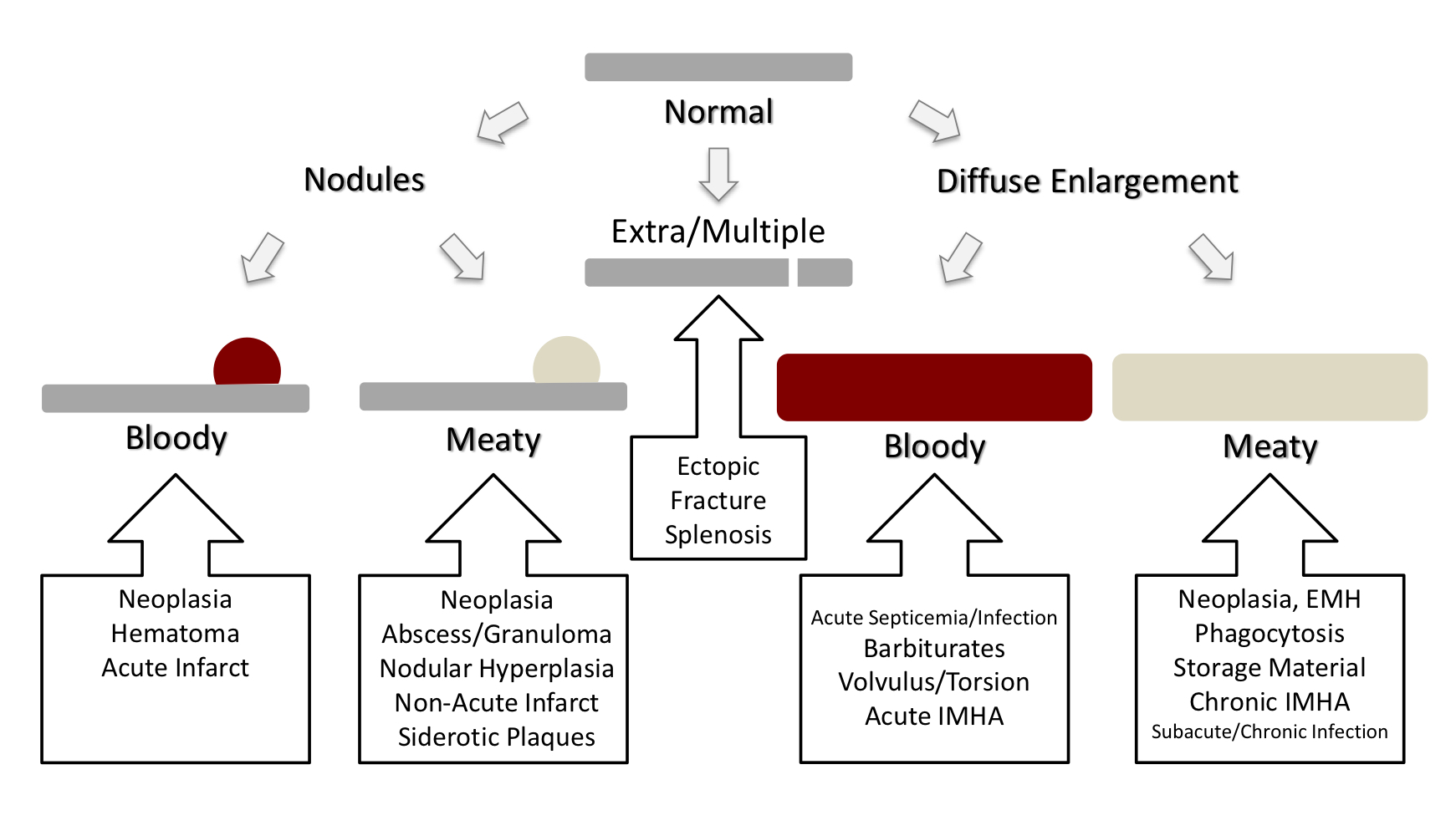
siderotic plaques are benign brown discolorations on the edge of the spleen that are the most common spleen lesion in…
geriatric dogs
macrophage histiocytic sarcoma in the spleen has a _______________ appearance
diffuse meaty
dendritic cell histiocytic sarcoma in the spleen has a _______________ appearance
nodular meaty
what are causes of bloody splenic nodules?
hematoma
hemangiosarcoma
acute infarct
what are causes of meaty splenic nodules?
primary neoplasia
benign: myelolipoma, follicular lymphoma
malignant: splenic sarcoma, lymphoma, histiocytic sarcoma
metastatic neoplasia
nodular hyperplasia
granuloma/abscess
non-acute infarct
siderotic plaques
differential diagnoses for splenic congestion:
barbiturates
volvulus
acute septicemia
what are causes of bloody diffuse splenomegaly?
acute septicemia
barbiturates
volvulus or torsion
acute IMHA
acute infectious disease
what are causes of meaty diffuse splenomegaly?
neoplasia
histiocytic sarcoma (macrophage type)
lymphoma
phagocytosis
chronic IMHA
amyloidosis
chronic infectious disease
EMH
which neoplasms can present as nodules or diffuse enlargement in the spleen?
mast cell tumor
lymphoma
histiocytic sarcoma
multiple myeloma
splenosis
acquired, autoimplantation of splenic tissue following trauma
what are the gross pathology patterns of the lymph node?
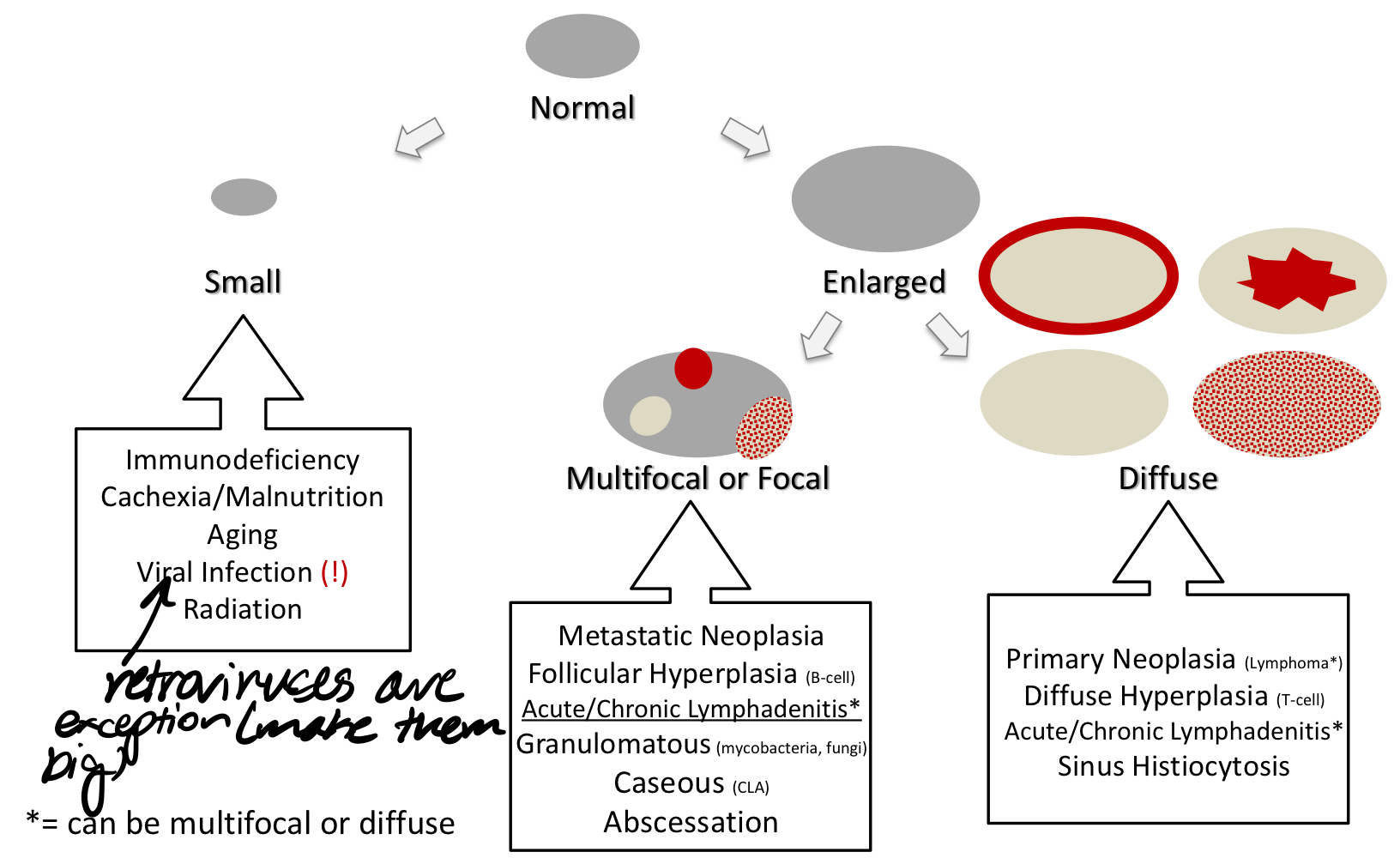
lymphadenomegaly vs lymphadenopathy
lymphadenomegaly- big lymph node
lymphadenopathy- nonphysiologic lymph node change
what are some causes of lymphadenomegaly/ lymphadenopathy
hyperplasia
accumulation
neoplasia
infection
bastard strangles
strep equi infection causes lymph nodes to burst and drain into lungs where it will spread to abdominal lymph nodes
lymphoma
neoplastic lymphocytes form solid tumors and can lead to secondary neoplasia
leukemia
neoplastic lymphocytes in bone marrow and blood can lead to secondary formation of solid tumors in lymph nodes
sporadic bovine lymphoma types:
multicentric (<6 months)
lymph nodes+organs+bone marrow
thymic (6-24 months)
thymic enlargement
cutaneous (6-24 months)
multifocal skin tumors
BLV bovine lymphoma is seen in what organs?
lymph nodes
uterus
abdomen
myocardium
spinal
lymphoid tissue behind eyes
alimentary/internal equine lymphoma is seen in what organs?
GI lymph nodes
liver
spleen
peritoneum
multicentric equine lymphoma is seen in what organs?
peripheral lymph nodes
abdominal lymph nodes
mediastinal mass
lymphedema
accumulation of fluid in tissue secondary to lymphatic blockage/damage
lymphangitis
infection/inflammation of lymph vessels
lymphangiesctasia
abnormally dilated lymph vessels
lymphangiosarcoma
neoplasia of lymphatics
MALT atrophy can be caused by:
viral infection
malnutrition/cachexia
aging
chemotherapy
radiation
toxins
BVDV causes lymphocytolysis and necrosis of germinal centers in…
GALT and Peyer’s patches
MALT hyperplasia is caused by:
antigenic stimulation
conditions affecting the hemolymphatic system;
hypoplasia or atrophy (immunodeficiency)
hyperplasia (immune reactivity)
inflammation (lymphadenitis)
infection
neoplasia
follicular hyperplasia is expansion of __ cells
B
paracortical hyperplasia is expansion of __ cells
T
hyperplastic lymph nodes will have enlarged…
germinal center and lymphoid follicle
what lab parameters are typically changed by a systemic immune response?
increased globulins
how would you clinically distinguish between lymphoid hyperplasia, lymphadenitis, and lymphoid neoplasia?
cytology
anaplasma phagocytophilum infects what cells?
granulocytes
ehrilichia canis infects what cells?
monocytes
ehrilichia ewingii infects what cells?
granulocytes
blood samples capture a snapshot of ________ production and ________ distribution
neutrophil, lymphocyte
how long does it take to increase erythroid or granulocyte production in bone marrow?
2-3 days depending on age of animal, illness and nutrition status
how long does it take to produce new neutrophils from undifferentiated precursors into blood?
about 6 days
what is the proportion of granulocyte to erythroid precursors in bone marrow?
about 1:1 in dogs and cats, 1:2 or 1:3 in large animals
myelofibrosis
overgrowth of bone marrow cavity by fibroblasts
what are causes of myelofibrosis?
aberrant cytokine production by chronically stimulated bone marrow cells
leukemia
idiopathic
acute leukemia characteristics:
undifferentiated cells
marked cytopenia
sick animal
rapidly progressive and fatal
myelodysplastic syndromes characteristics:
production of abnormal cells
chronic cytopenia
not very ill
progresses slowly
chronic leukemia characteristics:
fairly normal cells in blood
slow progression
organ infiltration
leukemia diagnosis:
abnormal cells in peripheral blood and/or bone marrow + cytopenia
bone marrow cytology and/or histo
occasional splenic disease
lymphoma and lymphosarcoma are _____________ terms
interchangeable
nodal lymphoma
tumor occurs inside lymph node
extranodal lymphoma
tumor occurs outside lymph node (anywhere else where there is lymphatic tissue)
indolent lymphoma
slowly progessive
lymphoma in dogs age of onset is usually…
middle ages
most dog lymphomas are indolent/aggressive
aggressive
majority of of nodal lymphomas in dogs are of what cell origen?
B cells
all mediastinal lymphomas in dogs are of what cell origin?
T cell
how can T cell lymphomas lead to hypercalcemia?
tumors produce PTH-like molecule that causes increased bone resorption, intestinal calcium absorption, and renal calcium preservation
hypercalcemia from T cell lymphoma can lead to…
kidney mineralization
what kind of nodular lymphoma is most common in dogs?
diffuse
most dogs with lymphoma do/don’t have lymphocytosis
don’t (will have normal or reduced lymphocytes)
20-50% of dogs with lymphoma also have _______
mild anemia
T/F secondary leukemia is seen in some types of lymphomas in dogs
T
cat lymphomas are frequently nodal/extranodal
extranodal
how does lymphoma most commonly present in cats?
solitary intestinal mass in older cats
what is the common cell type making up cat intestinal lymphoma?
T cell
mediastinal lymphomas in cats are almost always of what cell origin?
T cell
how can feline leukemia virus cause lymphoma?
can activate cellular proto-oncogenes, and the gene product can be overexpressed
what location is lymphoma common in FeLV infected young cats?
mediastinum
how can FIV cause aggressive extranodal lymphomas in cats?
loss of CD4+ cells→chronic immune stimulation, lack of immunosurveillance, proliferation of other viral agents
lymphomas of what cell origin are most common in horses?
T cell
horse lymphomas are often associated with ______ and ______ likely due to production of cytokines that recruit other cells
inflammation; anemia
peripheral lymph nodes are commonly/rarely involved in horse lymphoma
commonly
cutaneous lymphomas in horses can change in response to…
estrogen and progesterone
horse mesenteric or intestinal lymphoma is often associated with…
IMHA
mediastinal lymphomas in horses are of what cell origin?
T cell
________________ is more common in horses with lymphoma than in other species
gammopathy (increased globulins)
lymphoma due to what infection is common in older dairy cattle?
BLV
what percent of cattle infected with BLV get lymphoma?
2-5%
methods to classify lymphoma:
histopathology
diffuse vs follicular
high, medium, or low grade
immunophenotype (flow cytometry or IHC)
cytogenetics, molecular genetics
laboratory quality assurance program
procedures and strategies to ensure that lab reports trustworthy results (assure precision and accuracy)
Pre-analytical variables:
test selection
history
fasting
tube selection
order of tube filled
volume
collection technique
tube labeling
requisition form
time lapsed before analysis
storage/transport
disadvantages of in house tests:
records legally required
reference intervals needed
in house result will be different from lab result
advantages of vet labs:
gold standard
properly validated reference intervals
clinical pathologist
what is the ideal and minimum number of healthy animals needed to create a reference interval?
ideal: >100
minimum: 40
isoenzymes
occur in one or multiple tissues
increased enzymes enter plasma due to:
injury
increased production
decreased excretion
enzyme activity decreases with…
time and temperature