Campbell biology Chapter 46
1/81
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
82 Terms
sexual reproduction
the creation of an offspring by fusions of sperm and egg to form a zygote
sperm
male gamete
egg
female gamete
asexual reproduction
creation of offspring without the fusion of egg and sperm
fission
separation of a parent into two or more individuals of about the same size
fragmentation
breaking of the body into pieces, some or all of which develop into adults
regeneration
regrowth of lost body parts
parthenogenesis
the development of a new individual from a unfertilized egg
ovulation
the release of mature eggs at the midpoint of a female cycle
hermaphroditism
each individual has male and female reproductive systems
fertilization
the union of egg and sperm
gonads
organs that produce gametes
spermatheca
where sperm is stored during copulation
accessory glands
secrete products needed for sperm movement
ducts
carry sperm and glandular secretions
testes
highly coiled tubes surrounded by connective tissue
seminiferous tubules
where sperm form
testes location
outside the abdominal cavity in the scrotum, where the temperature is lower than in the abdominal cavity
epididymis
coiled duct that sperm pass through after the seminiferous tubules
ejaculation
sperm are propelled through the muscular vas deferens and the ejaculatory duct, and then exit the penis through the urethra
semen
sperm plus secretions from three sets of accessory glands
two seminal vessicles
contribute 60% of the total volume of semen
prostate gland
secretes its products directly into the urethra
penis
male sex organ composed of three cylinders of spongy erectile tissue
female external reproductive structures
the clitoris, vulva and two sets of labia
female internal reproductive structures
a pair of gonads and a system of ducts and chambers that carry gametes and house the embryo and fetus
ovaries
the female gonads
follicles
each ovary contains these
oocyte
partially developed egg surrounded by support cells
oviduct or fallopian tube
location where the egg travels from the ovary to the uterus
uterus
Location where the cilia in the oviduct convey the egg. Also called the womb
endometrium
uterus lining, many blood vessels
vagina
a muscular but elastic chamber that is the repository for sperm during copulation and serves as the birth canal
vulva
location where the vagina opens to the outside
labia majora, labia minora, hymen, and clitoris
vulva structures
mammary glands
Not part of the reproductive system but are important to mammalian reproduction
gametogenesis
production of gametes
spermatogenesis
formation of sperm, is continuous and prolific
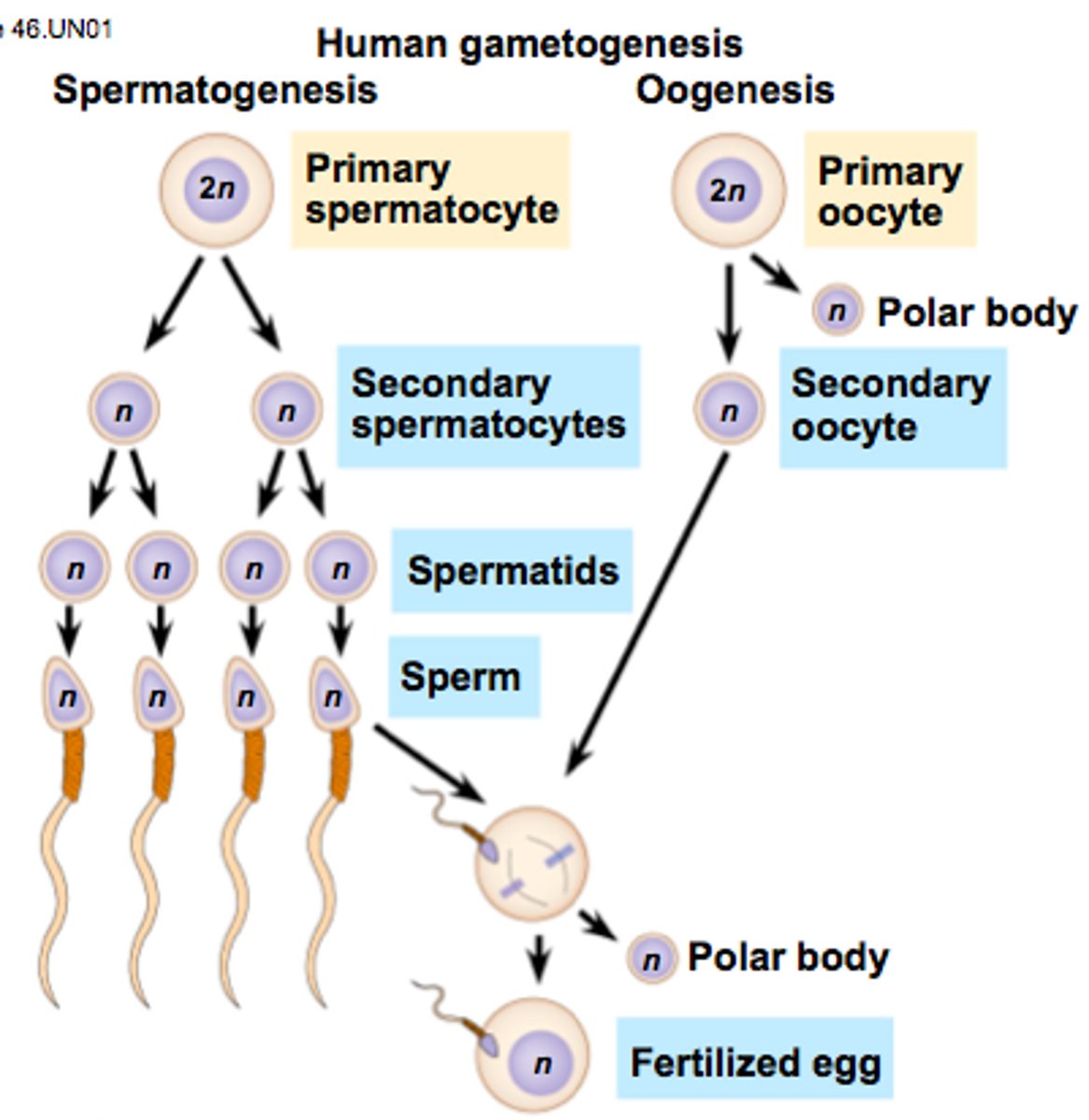
human gametogenesis
spermatogenesis
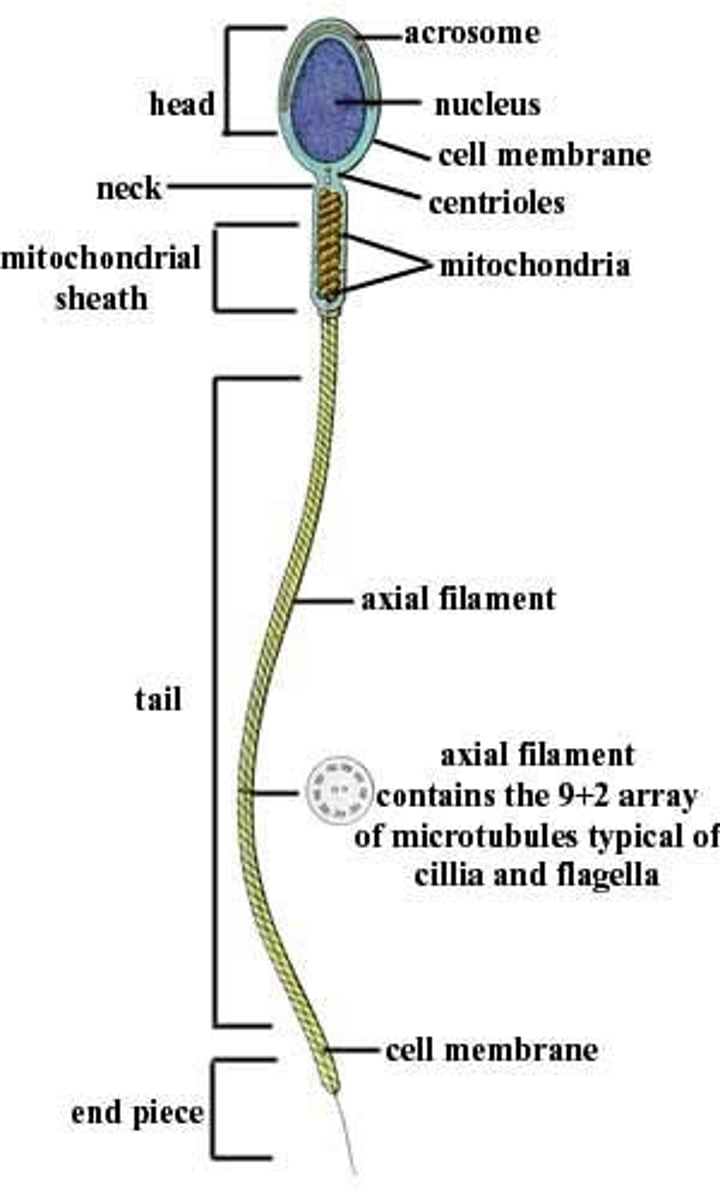
anatomy of sperm
head, acrosome, tail, etc
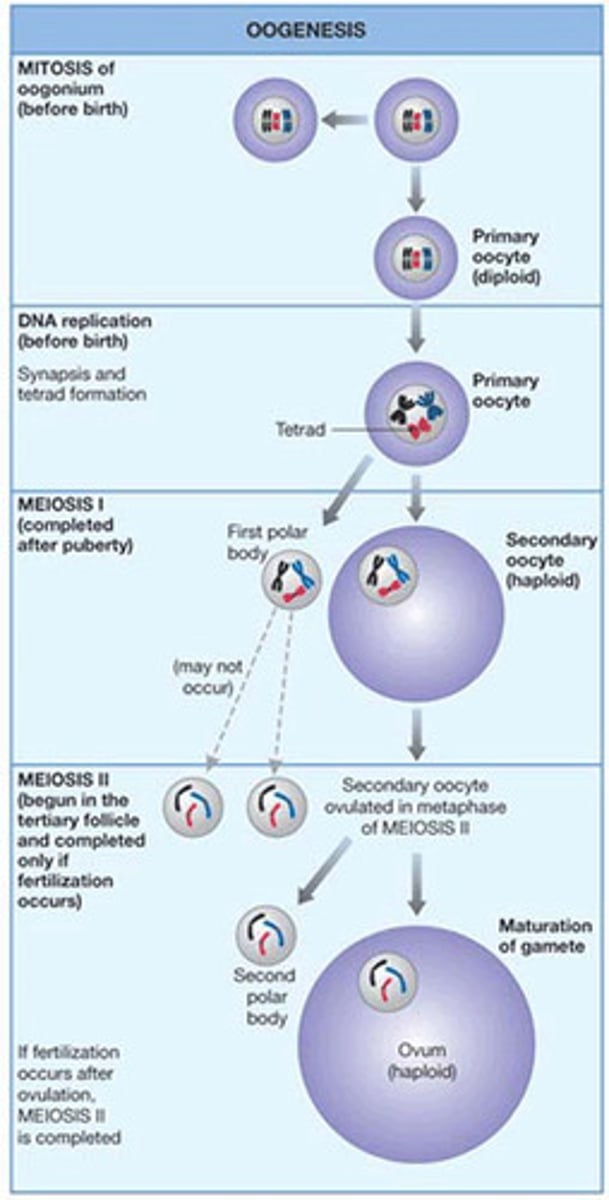
oogenesis defintion
development of mature egg, is a prolonged process
oogenesis diagram
Spermatogenesis differs from oogenesis in three ways.
1) All four products of meiosis develop into a sperm while only one of the four becomes an egg
2) Sprematogenesis occurs throughout adolescence and adulthood
3) Sperm are produced continuously without the prolonged interruptions in oogenesis
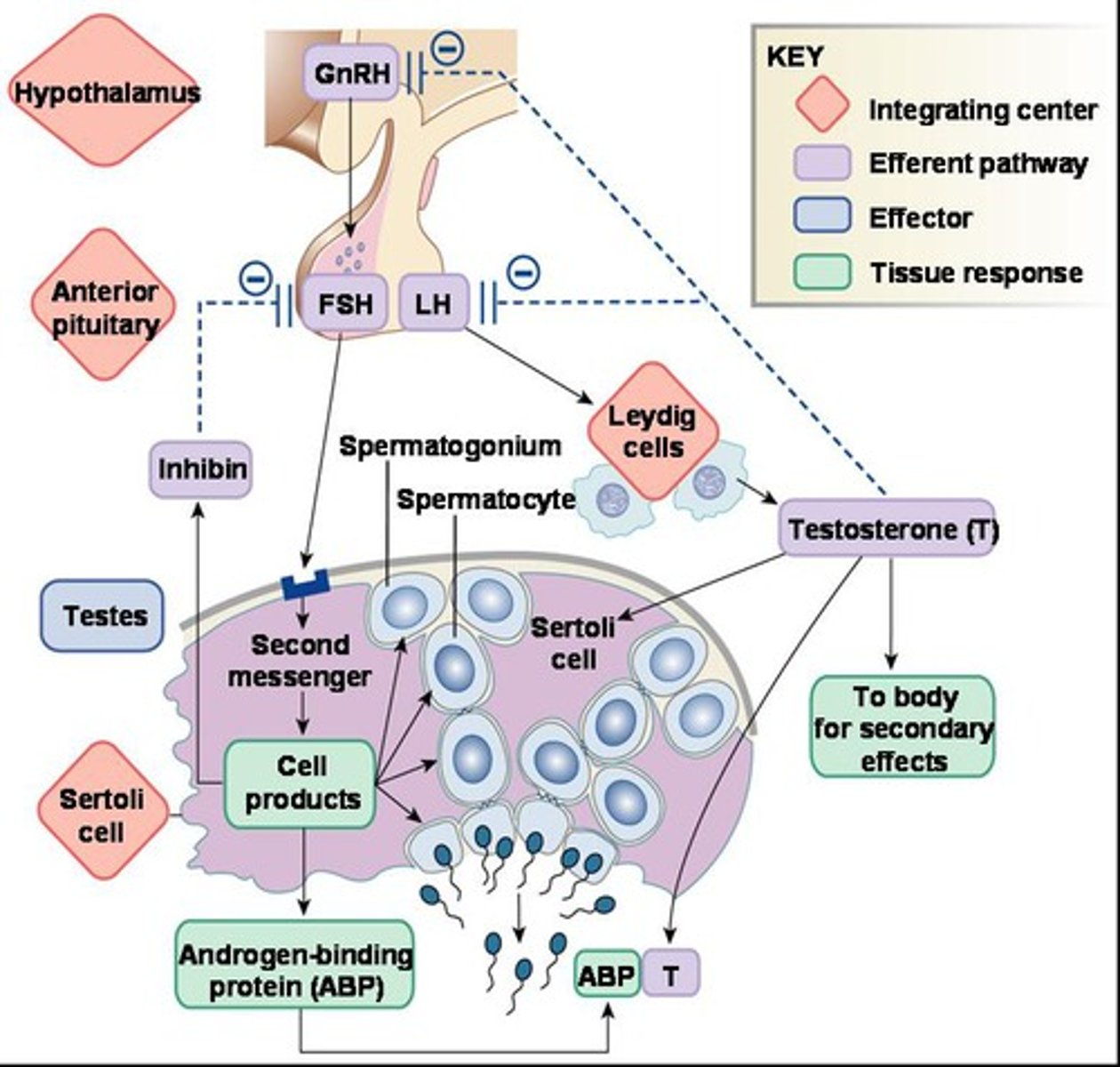
testosterone
the main androgen
progesterone and estradiol
The main estrogens
Sertoli cells
nourish developing sperm
leydig cells regulated by
LH
hormonal control of the testes
menstruation
process that occurs if an embryo does not implant in the endometrium, the endometrium is shed
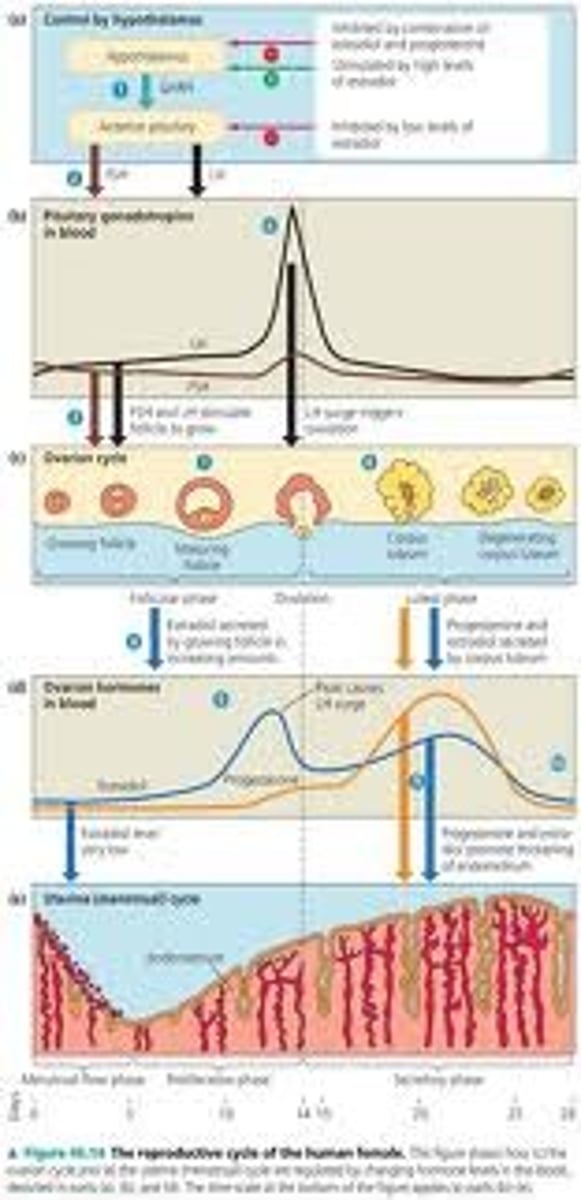
hormones closely link the two cycles of female reporduction
changes in the uterus and changes in the ovaries. uterine cycle and ovarian cycle
ovulation
stage where the follicular phase ends, and the secondary oocyte is released
reproductive cycles of the human female
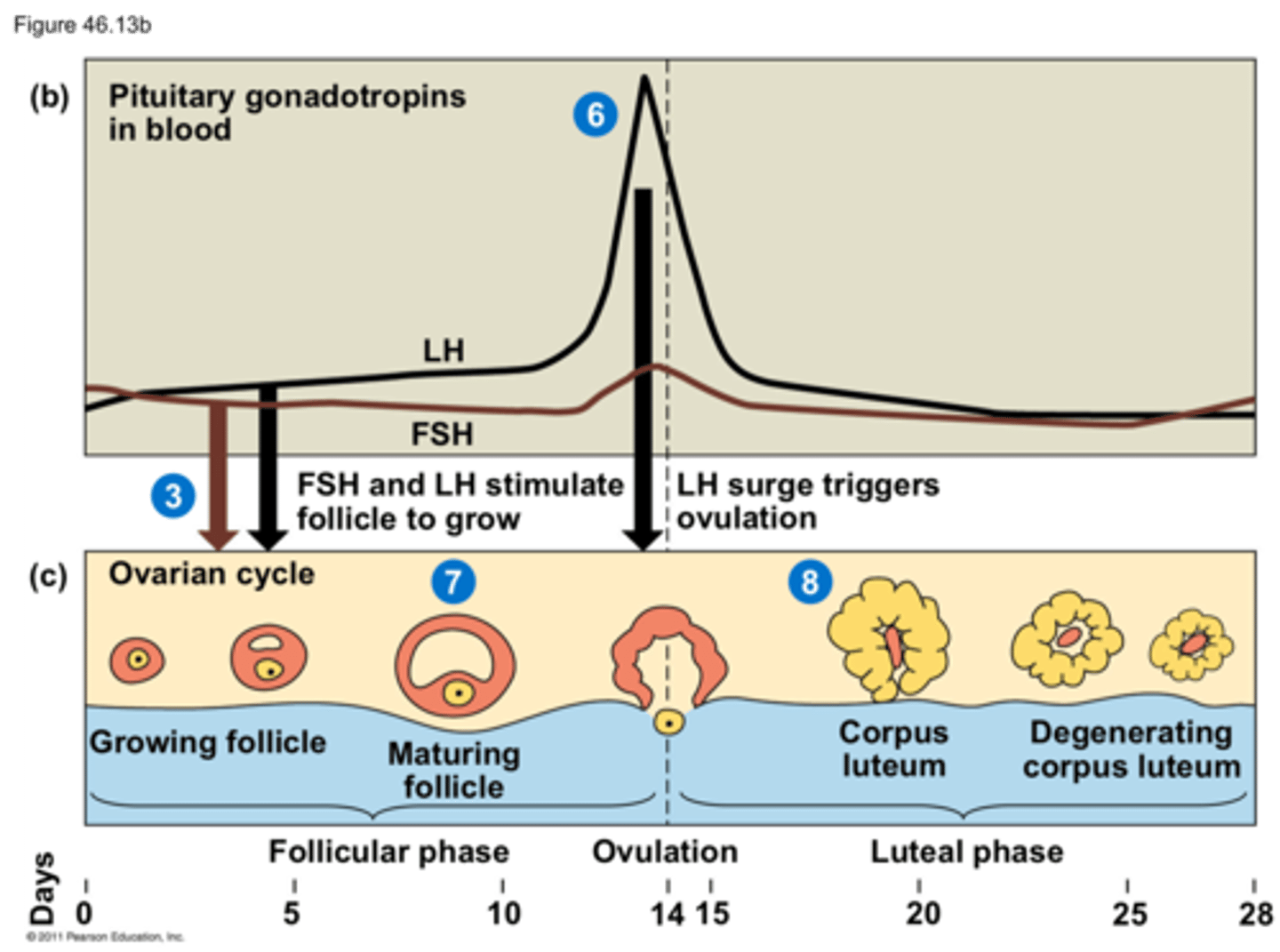
uterine cycle
ectopoic
abnormal location that cells of the uterine lining can sometimes migrate to
endometriosis
Swelling of cells in response to hormone stimulation results in a disorder called
menopause
the cessation of ovulation and menstruation
estrous cycles
cycles that are characteristic of most mammals
estrous cycles characteristics
endometrium reabsorbed by the uterus, sexual receptivity is limited to a heat period caleld estrus, the length and freuency of estrous cycles vary from species to species
conception
fertilization of an egg by a sperm, occurs in the oviduct
blastocyst
a ball of cells with central cavity
formation of a human zygote
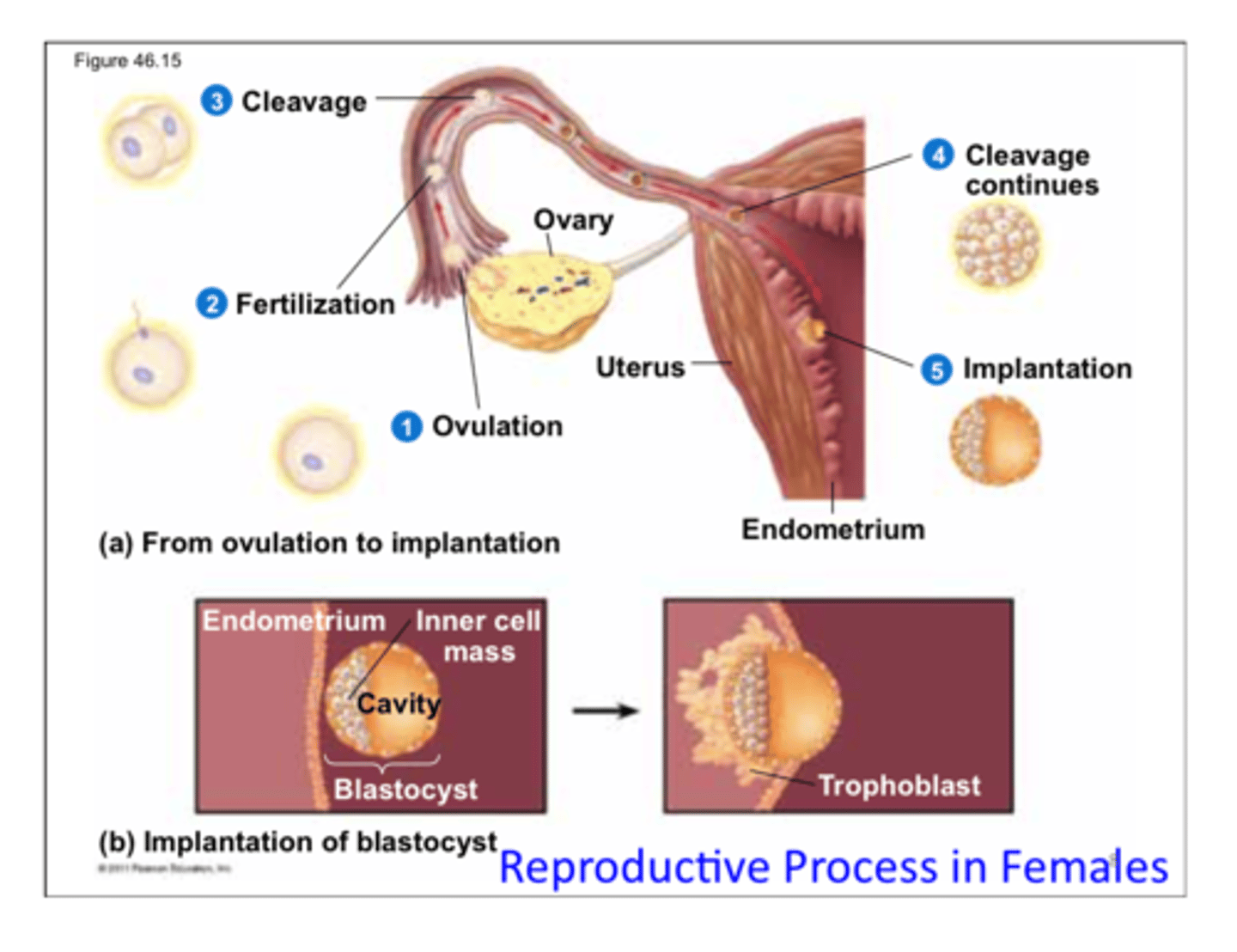
pregnancy or gestation
the condition of carrying one or more embryos in the uterus
trophoblast
the outer layer of the blastocyst
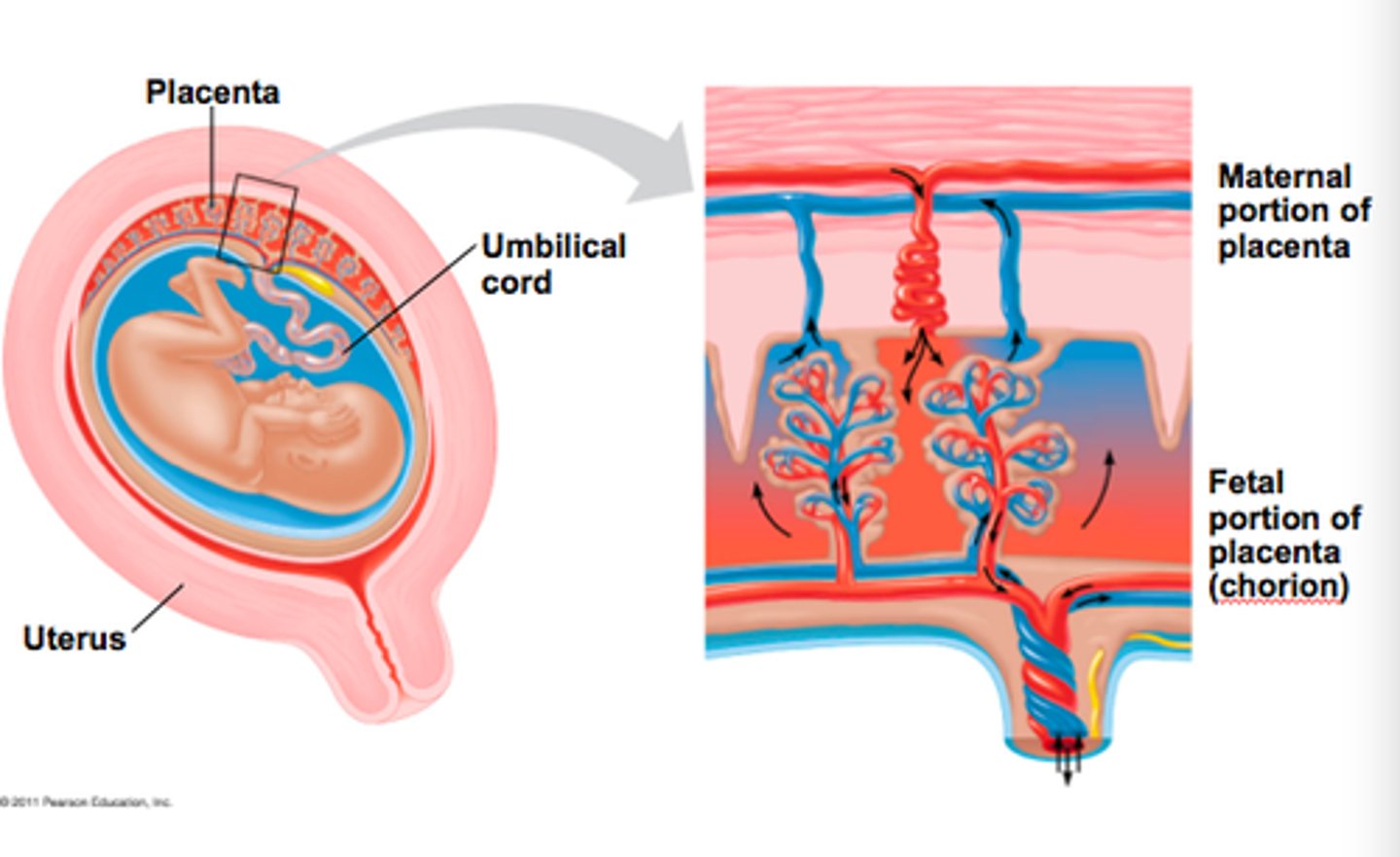
placenta
What forms after the endometrium and trophoblast mingle
placental circulation
organogenesis
development of the body organs
fetus
what the embryo is called after 8 weeks
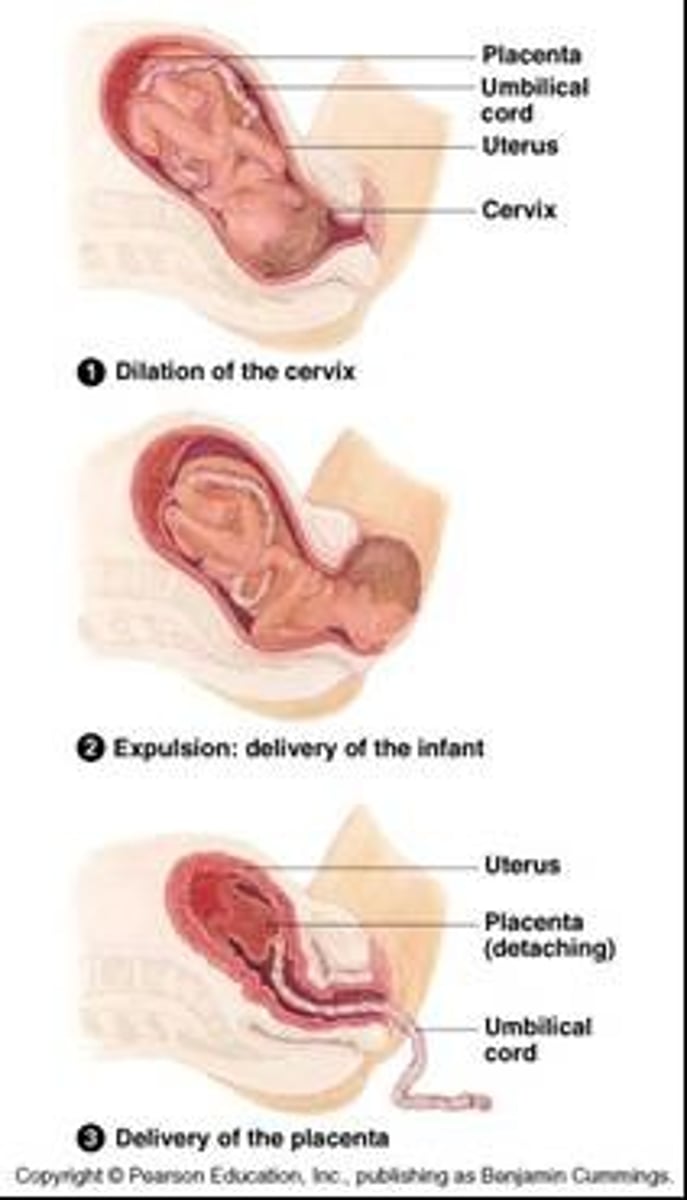
labor
a series of strong rhythmic uterine contractions that push the fetus and placenta out of the body
three stages of labor
dilation, explusion, and delivery of the placenta
dilation
thinning and opening of the cervix
expulsion
delivery of the baby
lactation
production of mother's milk
three stages of labor picture
contraception
deliberate prevention of pregnancy
3 categories of contraception
preventing release of egg and sperm, keeping sperm and egg apart, and preventing implantation of an embryo
mechanisms of contraception
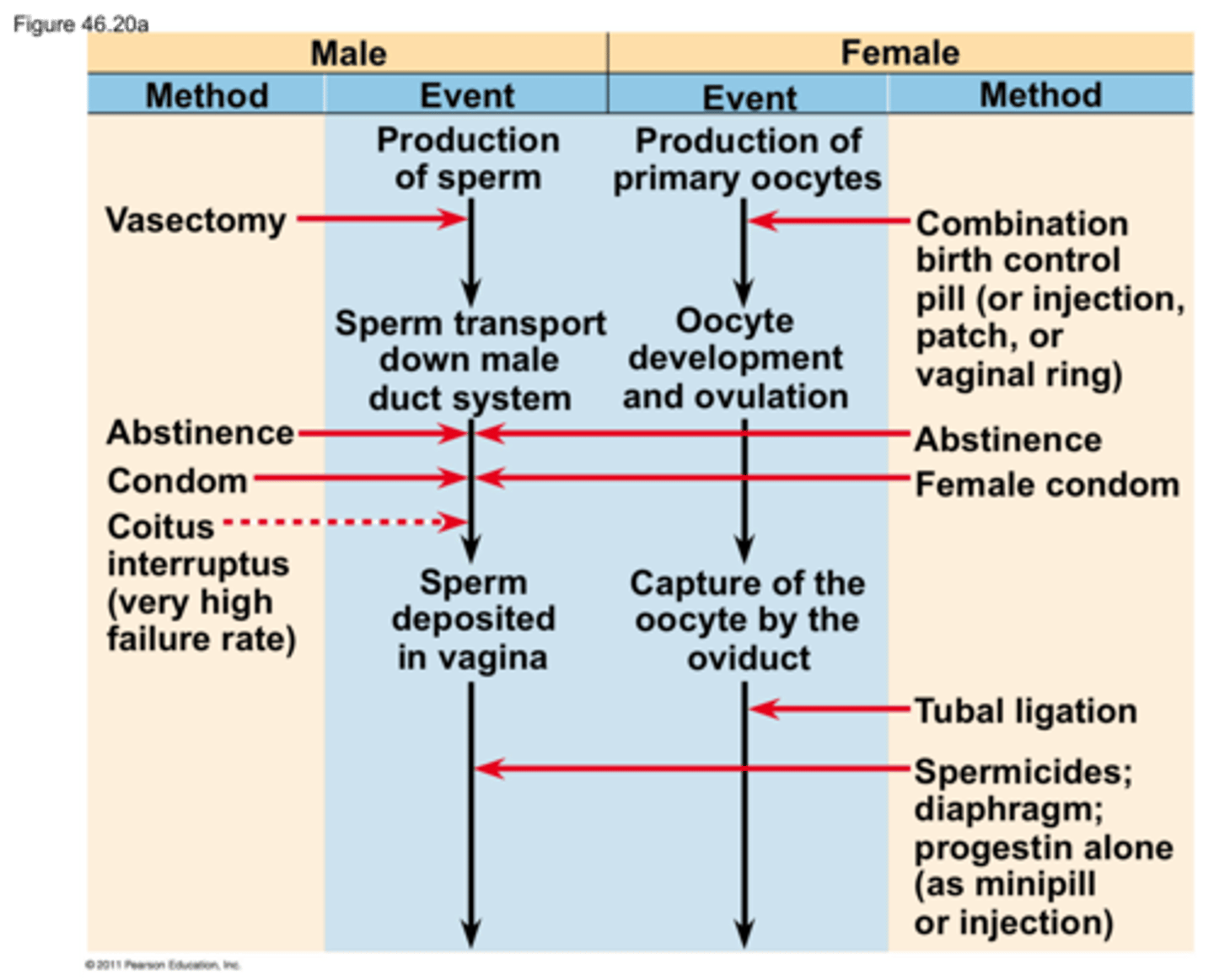
birth control pills
hormonal contraceptives with a pregnancy rate of less than 1%
tubal ligation
ties off the oviducts
vasectomy
ties off the vas deferens
abortion
termination of a pregnancy
spontaneous abortion
miscarriage
in vitro fertilization (IVF)
mixes eggs with sperm in culture dishes and return the embryo to the uterus at the eight-cell stage