PATHOGENS TO KNOW
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
Mycobacterium tuberculosis
👩⚕ Patient scenario: A 40-year-old man has had a cough for 3 months, with night sweats, fatigue, weight loss, and bloody sputum. His chest X-ray shows cavitations in the upper lobes. His sputum smear is positive for acid-fast rods.
(A) Classification: Acid-fast bacterium; rod-shaped.
(B) Disease: Causes ? , usually of the lungs but can affect bones, brain, or kidneys.
(C) Identification/Diagnosis: Acid-fast stain, chest X-ray, PCR, sputum culture, Mantoux (PPD) test, IGRA blood test.
(D) Treatment/Prevention: Multi-drug antibiotic therapy (isoniazid, rifampin, pyrazinamide, ethambutol) for months; prevention with BCG vaccine and airborne isolation.
(E) Unique Epidemiology & Lab Safety: Human reservoir only, transmitted by inhaled droplets. Mycolic acids in its cell wall provide drug and disinfectant resistance. Must be handled in BSL-3 labs with respirators and biosafety cabinets.
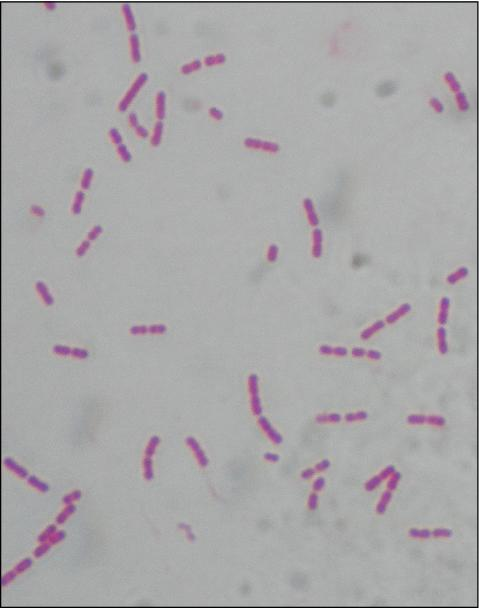
Bacillus anthracis
🧪 Lab differentiation: Gram stain shows large purple rods, often in chains, sometimes with a capsule. On blood agar, colonies are large, gray-white, non-hemolytic, with a “Medusa head” curled edge. Non-motile, catalase-positive.
👩⚕ Patient scenario: A rancher develops a painless black ulcer on his arm after handling animal hides. Culture shows large colonies with Medusa head appearance, and Gram stain reveals purple rods.
(A) Classification: Gram-positive spore-forming bacterium; rod-shaped.
(B) Disease: Causes anthrax, which can be cutaneous, inhalation, or gastrointestinal.
(C) Identification/Diagnosis: Gram stain, colony morphology, PCR for toxin genes, non-motile reaction.
(D) Treatment/Prevention: Ciprofloxacin or doxycycline with antitoxin therapy; vaccine for high-risk individuals (lab workers, military).
(E) Unique Epidemiology & Lab Safety: Spores persist in soil for decades, infect grazing animals, and can spread to humans. Requires BSL-3 precautions; cultures must not be opened outside containment.
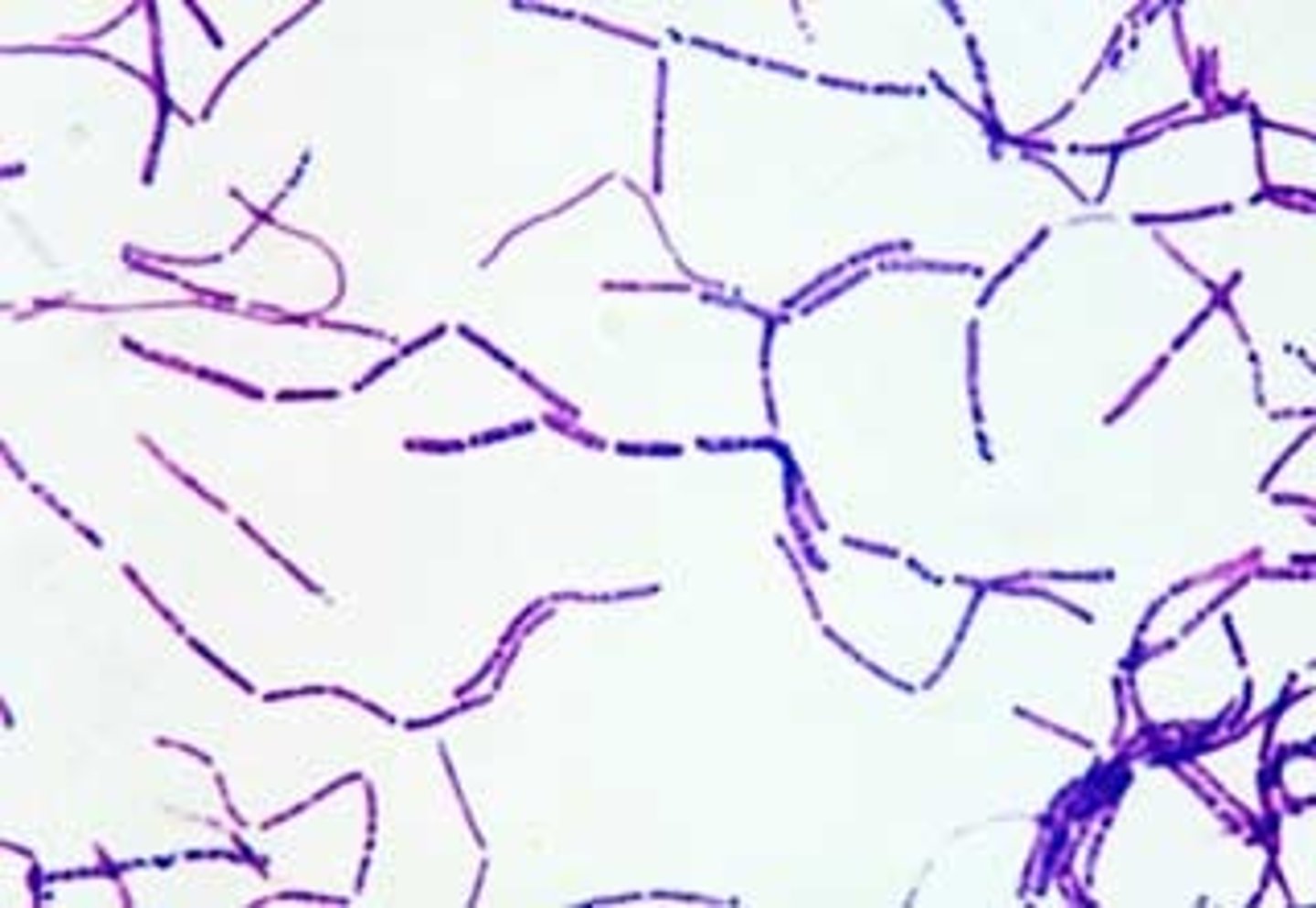
Yersinia pestis
🧪 Lab differentiation:
Gram stain: Gram-negative coccobacillus with bipolar (“safety pin”) staining when viewed with Giemsa or Wright’s stain.
Culture: Grows slowly on blood agar at 28–30 °C, forming small, gray-white, non-hemolytic colonies. On MacConkey agar, colonies appear pale (non-lactose fermenting).
Tests: Oxidase-negative, catalase-positive, urease-negative. Identified by PCR or immunofluorescence for F1 antigen.
👩⚕ Patient scenario:
A 28-year-old man develops sudden high fever, painful swollen lymph nodes in the groin (buboes), and chills after skinning rabbits in the Southwest U.S. Blood culture grows small Gram-negative rods with bipolar staining. Diagnosis: plague.
📋 Details:
(A) Classification: Gram-negative, facultative anaerobic coccobacillus.
(B) Disease: Causes plague in three forms—bubonic (swollen lymph nodes), septicemic (sepsis with necrosis), and pneumonic (respiratory spread, highly contagious).
(C) Identification/Diagnosis: Microscopy with bipolar staining, slow growth on routine agar, non-lactose fermentation, antigen detection, and PCR confirmation.
(D) Treatment/Prevention: Streptomycin or gentamicin; alternatives include doxycycline or ciprofloxacin. Prevention through rodent/flea control and protective measures for lab workers.
(E) Unique Epidemiology & Lab Safety: Maintained in rodent reservoirs and transmitted by flea bites; pneumonic form spreads person-to-person via droplets. Requires BSL-3 containment in labs due to high infectivity and bioterrorism risk.
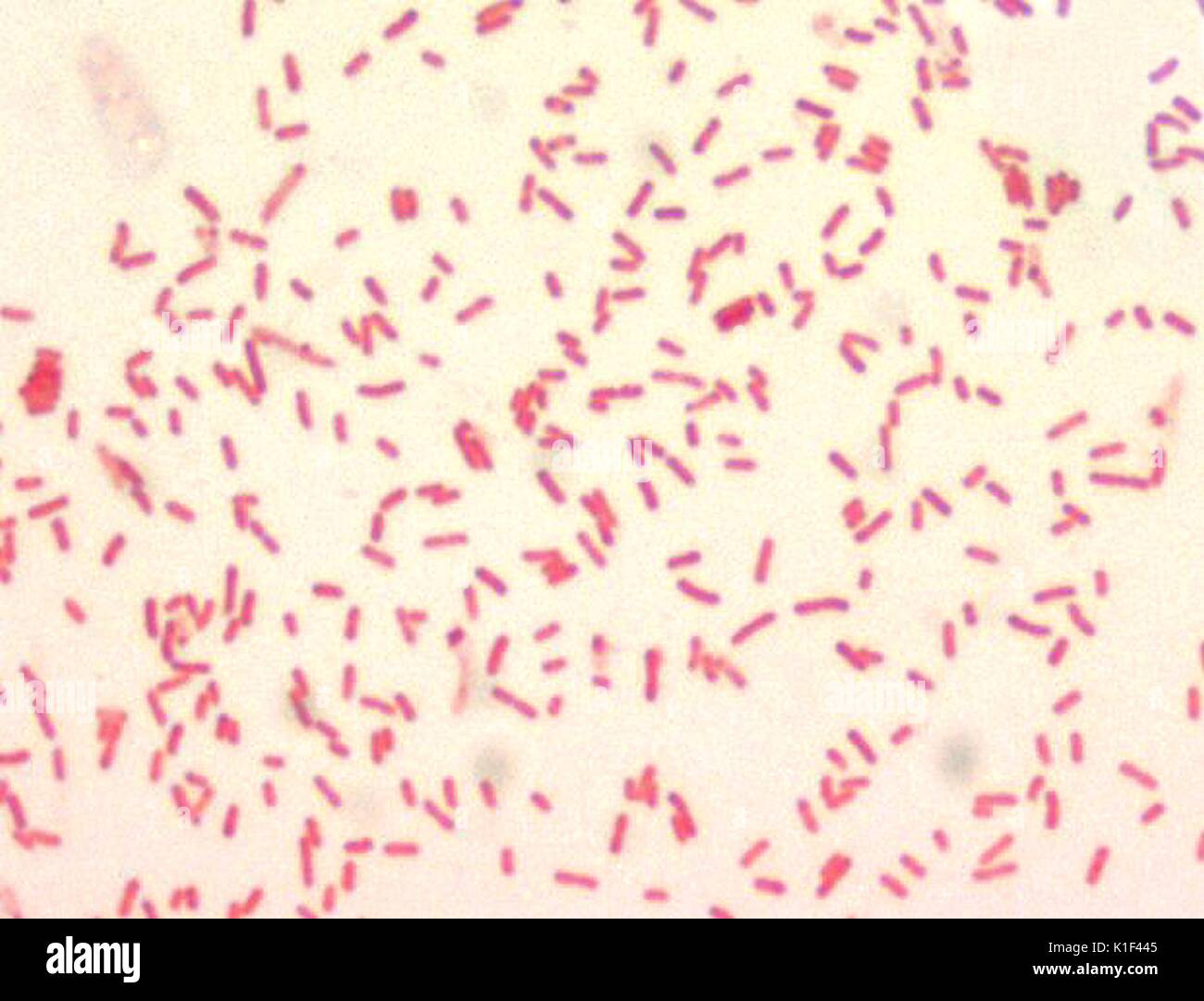
Treponema pallidum
🧪 Lab differentiation:
Gram stain: Not reliable (too thin to visualize).
Microscopy: Best seen with dark-field microscopy of lesion exudate, appearing as thin, tightly coiled spirochetes with corkscrew motility.
Culture: Cannot be cultured on artificial media. Maintained in rabbit testes for research only.
Tests: Serologic testing is standard. Non-treponemal tests (VDRL, RPR) detect antibodies against cardiolipin. Treponemal tests (FTA-ABS, TP-PA) confirm infection. PCR can also be used.
👩⚕ Patient scenario:
A 32-year-old man presents with a painless ulcer on his penis that appeared two weeks after unprotected sex. Dark-field microscopy of the lesion fluid reveals slender, spiraling organisms. VDRL is positive, confirming syphilis.
📋 Details:
(A) Classification: Spirochete bacterium, too thin for Gram stain, visualized by dark-field or silver stains.
(B) Disease: Causes syphilis, which progresses through stages:
Primary: painless chancre.
Secondary: rash (including palms/soles), condylomata lata, fever.
Latent: asymptomatic.
Tertiary: gummas, cardiovascular syphilis, neurosyphilis.
(C) Identification/Diagnosis: Dark-field microscopy of lesion, serologic screening (RPR/VDRL) followed by confirmatory treponemal tests (FTA-ABS).
(D) Treatment/Prevention: Penicillin G is the treatment of choice for all stages; doxycycline can be used if allergic. Prevention: safe sex practices, routine screening in high-risk groups, prenatal testing to prevent congenital syphilis.
(E) Unique Epidemiology & Lab Safety: Only infects humans; transmitted sexually, via blood, or congenitally. In lab, diagnosis relies on serology since culture isn’t possible. Specimens should be handled under BSL-2 conditions with caution due to infectious risk in lesion material.
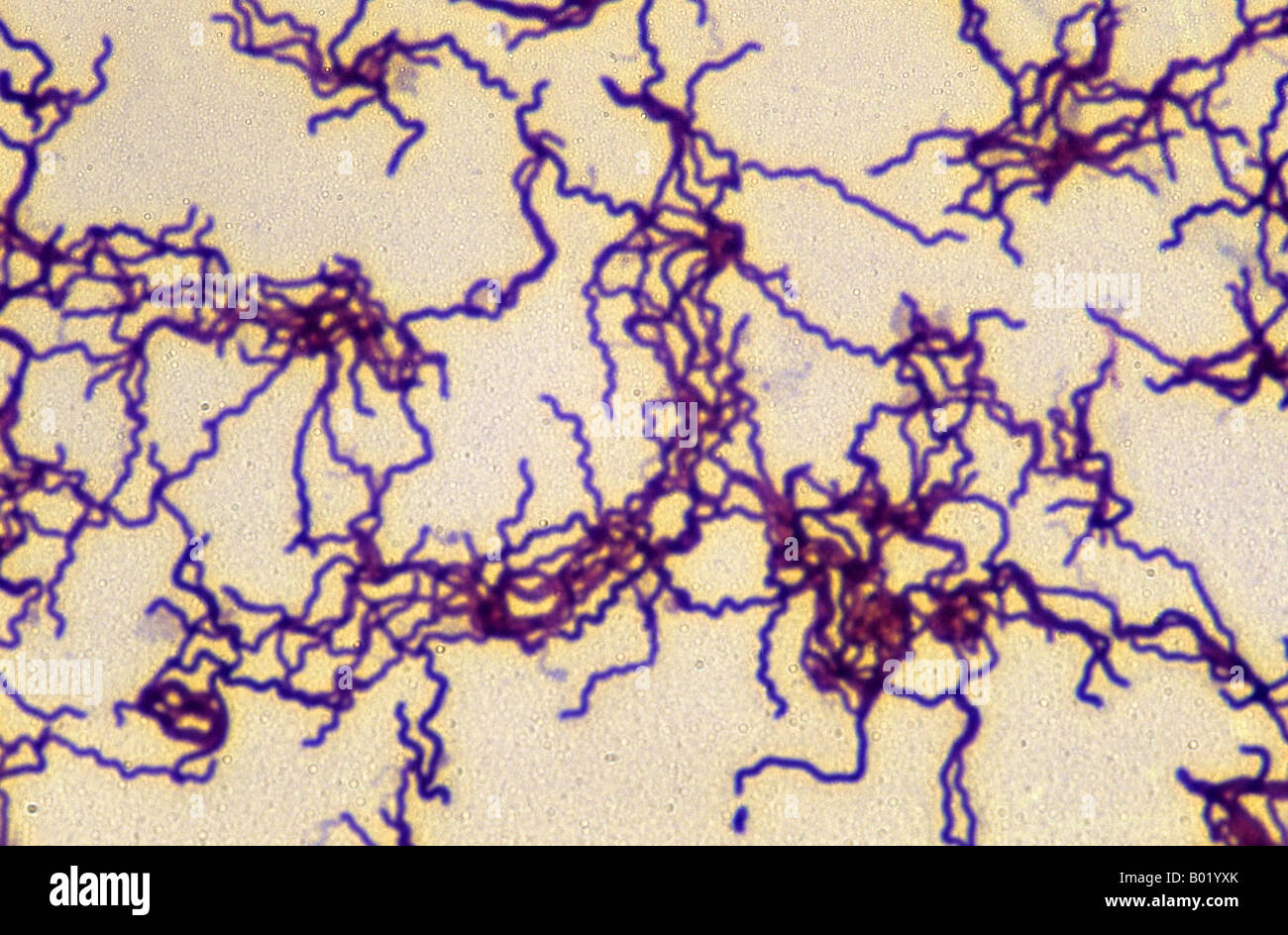
Rickettsia rickettsii
Lab differentiation:
Gram stain: Not useful (tiny, intracellular).
Microscopy: Weakly Gram-negative coccobacilli, best seen with Giemsa or Giménez stains inside endothelial cells.
Culture: Requires living host cells (e.g., tissue culture, embryonated eggs); not grown on routine agar.
Tests: Indirect immunofluorescence assay (IFA) is gold standard. PCR can detect DNA. Weil-Felix test (historical, not specific).
👩⚕ Patient scenario:
A 12-year-old boy presents in summer with fever, severe headache, and a rash that begins on wrists and ankles then spreads to trunk, palms, and soles. He recalls a recent tick bite during a camping trip. PCR of blood confirms Rickettsia rickettsii infection, consistent with Rocky Mountain spotted fever (RMSF).
📋 Details:
(A) Classification: Obligate intracellular, Gram-negative bacterium; infects endothelial cells.
(B) Disease: Causes Rocky Mountain spotted fever, characterized by fever, headache, myalgia, rash, and possible organ failure if untreated.
(C) Identification/Diagnosis: Clinical suspicion is critical (tick exposure, rash). Confirm with serology (IFA), PCR, or tissue biopsy stained for rickettsiae.
(D) Treatment/Prevention: Doxycycline is the treatment of choice, even for children. Prevention: tick avoidance (repellents, protective clothing, tick checks).
(E) Unique Epidemiology & Lab Safety: Transmitted by tick vectors (Dermacentor species). Not spread person-to-person. Work with cultures requires BSL-3 precautions due to high risk of aerosol transmission.
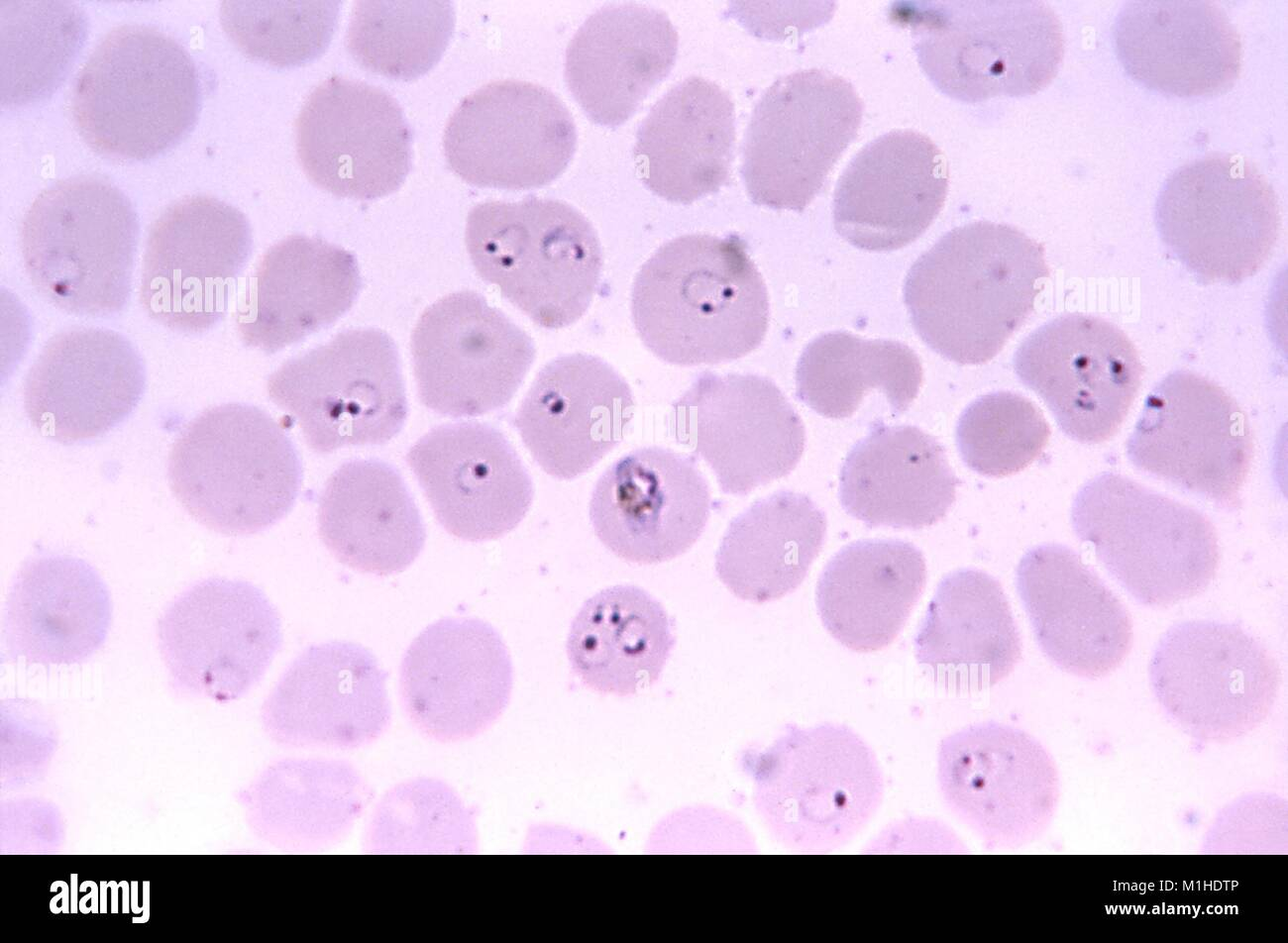
Plasmodium falciparum
Lab differentiation:
Microscopy: Seen in thin and thick blood smears stained with Giemsa. Rings, trophozoites, schizonts, and sometimes crescent-shaped gametocytes are visible inside red blood cells. Parasitemia can be high.
Rapid diagnostic tests (RDTs): Detect antigens such as HRP2 or pLDH.
Culture: Not routinely cultured in standard labs; maintained in specialized in vitro cultures for research.
👩⚕ Patient scenario:
A 25-year-old traveler returns from sub-Saharan Africa with high fever, chills, and sweating every 48 hours, along with fatigue and headache. Blood smear shows numerous ring-shaped parasites inside red blood cells, some with crescent-shaped gametocytes. Diagnosis: severe falciparum malaria.
📋 Details:
(A) Classification: Protozoan parasite, apicomplexan, infects human red blood cells.
(B) Disease: Causes malaria, which may present as cyclical fever, anemia, splenomegaly, and in severe cases, cerebral malaria or multi-organ failure.
(C) Identification/Diagnosis: Thick and thin blood smears with Giemsa stain; RDTs for rapid antigen detection; PCR for confirmation in specialized labs.
(D) Treatment/Prevention: Artemisinin-based combination therapy (ACT) is first-line. Prevention includes mosquito control, insecticide-treated bed nets, prophylactic antimalarials, and vaccines (RTS,S in endemic regions).
(E) Unique Epidemiology & Lab Safety: Transmitted by Anopheles mosquitoes; humans are primary host. Parasite exhibits antigenic variation to evade immunity. Laboratory work should follow BSL-2 procedures, using standard precautions to avoid handling infected blood.
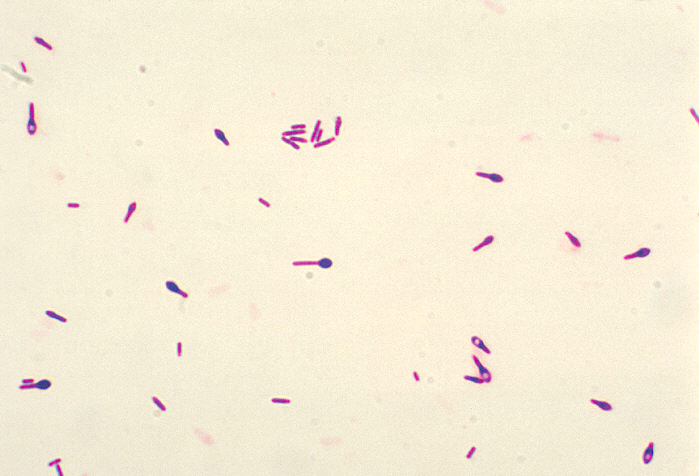
Clostridium botulinum
Lab differentiation:
Gram stain: Gram-positive, rod-shaped, often with terminal spores giving a “drumstick” appearance.
Culture: Obligate anaerobe; grows on anaerobic blood agar or reinforced clostridial medium forming large, grayish, irregular colonies.
Tests: Anaerobic growth required, catalase-negative, toxin production confirmed by mouse bioassay or PCR for botulinum toxin genes.
👩⚕ Patient scenario:
A 1-year-old infant presents with constipation, poor feeding, weak cry, and hypotonia (“floppy baby”). History reveals ingestion of honey. Stool and serum test positive for botulinum toxin. Diagnosis: infant botulism.
📋 Details:
(A) Classification: Gram-positive, spore-forming, obligate anaerobic rod.
(B) Disease: Causes botulism, leading to flaccid paralysis. Forms include foodborne, infant, wound, and iatrogenic botulism.
(C) Identification/Diagnosis: Clinical signs (descending flaccid paralysis, cranial nerve involvement), toxin detection in serum, stool, or food, and anaerobic culture.
(D) Treatment/Prevention: Supportive care (mechanical ventilation if needed), botulinum antitoxin, and antibiotics for wound botulism. Prevention: proper food preservation, avoiding honey in infants under 1 year.
(E) Unique Epidemiology & Lab Safety: Found in soil and improperly canned foods; spores are heat-resistant. Work in BSL-2/3 conditions when handling cultures or toxin; toxin is highly potent.
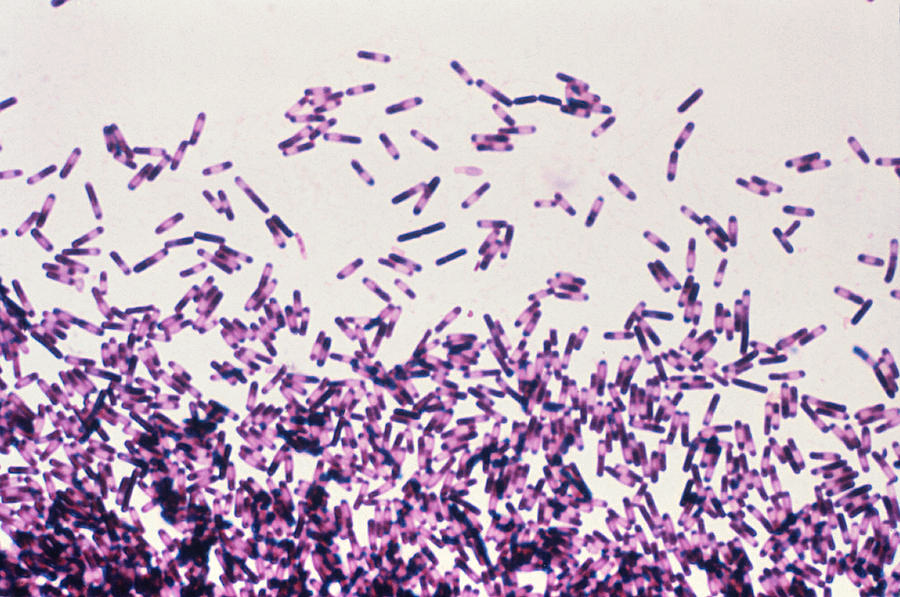
Clostridium difficile
Gram stain: Gram-positive, rod-shaped, spore-forming; often seen as single or short chains.
Culture: Anaerobic growth on CCFA (cycloserine-cefoxitin-fructose agar) or blood agar, producing yellow-green fluorescing colonies under UV light.
Tests: Toxin detection is key—toxin A and B ELISA or PCR for toxin genes. Catalase-negative.
👩⚕ Patient scenario:
A 68-year-old woman recently treated with broad-spectrum antibiotics develops watery diarrhea, abdominal cramping, and fever. Stool tests positive for C. difficile toxins A and B. Colonoscopy shows pseudomembranous colitis. Diagnosis: C. difficile infection.
📋 Details:
(A) Classification: Gram-positive, spore-forming, obligate anaerobic rod.
(B) Disease: Causes antibiotic-associated diarrhea and pseudomembranous colitis.
(C) Identification/Diagnosis: Stool toxin detection (ELISA or PCR), anaerobic culture, endoscopic visualization of pseudomembranes in severe cases.
(D) Treatment/Prevention: Discontinue inciting antibiotics if possible. Treat with oral vancomycin or fidaxomicin. Fecal microbiota transplant for recurrent infections. Prevention: strict infection control, hand hygiene, and contact precautions in hospitals.
(E) Unique Epidemiology & Lab Safety: Endospores resist disinfectants, persist in healthcare environments. Transmission is fecal–oral. Handwashing with soap (not just alcohol) is essential. Handle cultures under BSL-2 precautions.
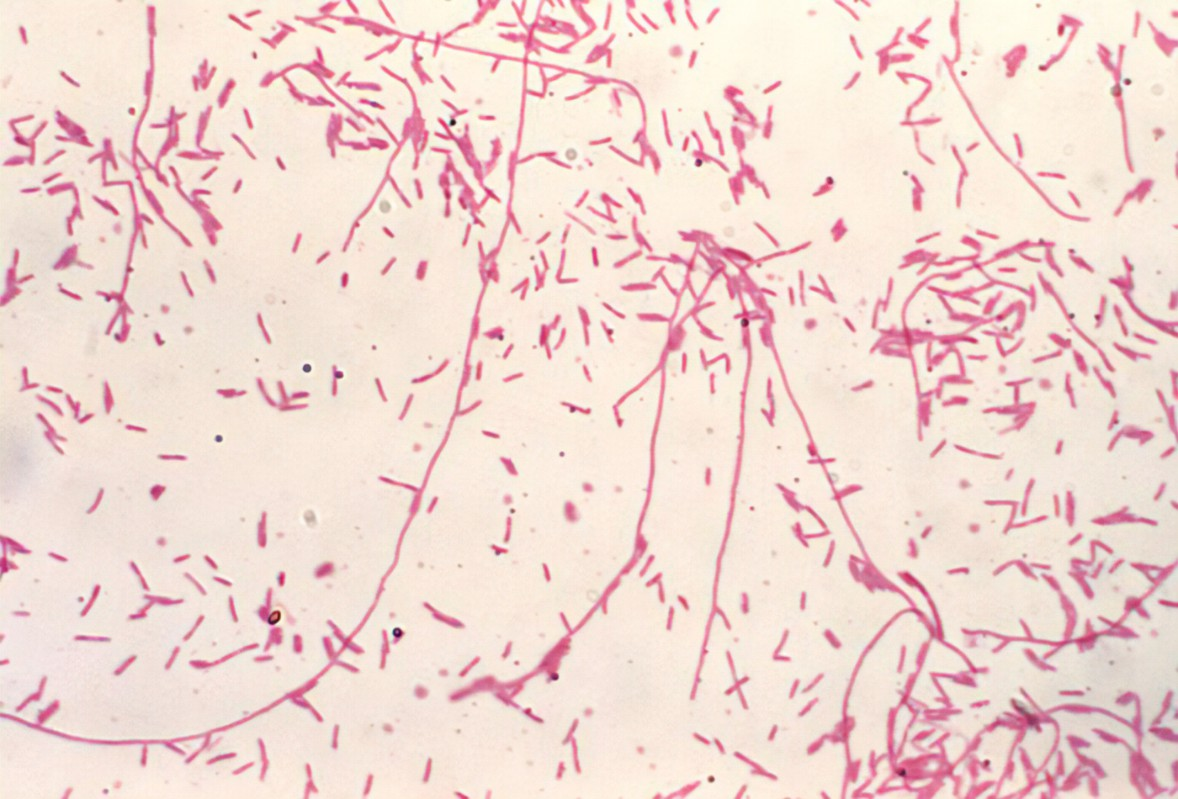
Legionella pneumophila
Lab differentiation:
Gram stain: Poorly stains with Gram; thin, faintly staining Gram-negative rods.
Culture: Requires BCYE (Buffered Charcoal Yeast Extract) agar with cysteine and iron; colonies appear gray-white, glistening, and may take 3–5 days to grow.
Tests: Urinary antigen test for rapid detection of serogroup 1; PCR can detect DNA; serology can be used for confirmation.
👩⚕ Patient scenario:
A 55-year-old man presents with high fever, cough, shortness of breath, and confusion after staying at a hotel with a contaminated hot water system. Chest X-ray shows patchy infiltrates. Urinary antigen test is positive for Legionella. Diagnosis: Legionnaires’ disease.
📋 Details:
(A) Classification: Gram-negative, facultative intracellular rod.
(B) Disease: Causes Legionnaires’ disease (severe pneumonia) and Pontiac fever (mild flu-like illness).
(C) Identification/Diagnosis: Culture on BCYE agar, urinary antigen test (rapid), PCR, and serology.
(D) Treatment/Prevention: Treated with macrolides (azithromycin) or fluoroquinolones (levofloxacin). Prevention includes maintaining and disinfecting water systems in hospitals and buildings.
(E) Unique Epidemiology & Lab Safety: Found in freshwater environments; spreads via inhalation of contaminated aerosols, not person-to-person. Survives inside amoebae. Work with cultures under BSL-2 conditions, avoiding aerosol generation.
Vibrio cholerae
Lab differentiation:
Gram stain: Gram-negative, curved rod (comma-shaped).
Culture: Grows on TCBS (Thiosulfate-Citrate-Bile-Sucrose) agar, producing yellow colonies (sucrose fermenters). Non-lactose fermenting on MacConkey.
Tests: Oxidase-positive, motile, fermentative metabolism. PCR can detect cholera toxin gene.
👩⚕ Patient scenario:
A 35-year-old man presents with profuse watery diarrhea (“rice-water stools”), severe dehydration, and vomiting after drinking contaminated water while traveling abroad. Stool culture on TCBS agar produces yellow colonies. Diagnosis: cholera.
📋 Details:
(A) Classification: Gram-negative, facultative anaerobic curved rod.
(B) Disease: Causes cholera, characterized by massive watery diarrhea and dehydration.
(C) Identification/Diagnosis: Stool culture, Gram stain, TCBS agar growth, PCR for cholera toxin.
(D) Treatment/Prevention: Oral rehydration therapy, antibiotics (doxycycline, azithromycin) in severe cases. Prevention: clean water, sanitation, hygiene, and vaccination in endemic areas.
(E) Unique Epidemiology & Lab Safety: Humans are main host; transmitted via contaminated water or food. Produces cholera toxin causing massive fluid loss. Handle under BSL-2 with standard precautions.
Salmonella enterica
Lab differentiation:
Gram stain: Gram-negative rod.
Culture: Non-lactose fermenting on MacConkey agar (colorless colonies). On Hektoen enteric agar, colonies appear green with black centers if H₂S-positive.
Tests: Oxidase-negative, motile, urease-negative, H₂S-positive. Serotyping distinguishes strains.
👩⚕ Patient scenario:
A 7-year-old child develops diarrhea, fever, and abdominal cramps after eating undercooked chicken. Stool culture shows colorless colonies on MacConkey and black-centered colonies on Hektoen agar. Diagnosis: non-typhoidal ? gastroenteritis.
📋 Details:
(A) Classification: Gram-negative, facultative anaerobic rod.
(B) Disease: Causes gastroenteritis, often self-limiting; may cause bacteremia in immunocompromised patients.
(C) Identification/Diagnosis: Stool culture, H₂S production on selective agar, serotyping.
(D) Treatment/Prevention: Supportive care; antibiotics reserved for severe cases (fluoroquinolones, ceftriaxone). Prevent by proper cooking, hand hygiene, and food safety.
(E) Unique Epidemiology & Lab Safety: Transmitted via contaminated food or water; animal reservoirs (poultry, reptiles). Handle cultures under BSL-2 precautions.
Salmonella typhi
Lab differentiation:
Gram stain: Gram-negative rod.
Culture: Non-lactose fermenting on MacConkey (colorless). On Hektoen agar, colonies may be green without black center (H₂S may be weak).
Tests: Motile, urease-negative, H₂S variable; blood culture during acute infection is diagnostic.
👩⚕ Patient scenario:
A 24-year-old traveler returns from South Asia with prolonged fever, abdominal pain, and rose-colored spots on the trunk. Blood culture grows colorless Gram-negative rods identified as S. typhi. Diagnosis: typhoid fever.
📋 Details:
(A) Classification: Gram-negative, facultative anaerobic rod.
(B) Disease: Causes typhoid fever, systemic illness with fever, abdominal pain, and potential complications (intestinal perforation).
(C) Identification/Diagnosis: Blood cultures in first week, stool or urine cultures later, PCR for confirmation.
(D) Treatment/Prevention: Treated with ceftriaxone, azithromycin, or fluoroquinolones. Prevention: safe food and water, typhoid vaccines.
(E) Unique Epidemiology & Lab Safety: Humans are only reservoir; transmitted fecal–oral. Chronic carriers can shed bacteria. Handle under BSL-2 precautions.
Neisseria gonorrhoeae
Lab differentiation:
Gram stain: Gram-negative diplococci, often seen inside polymorphonuclear leukocytes from urethral or cervical specimens.
Culture: Grows on Thayer-Martin agar (chocolate agar with antibiotics), forming small, gray-white, smooth colonies in 24–48 hours.
Tests: Oxidase-positive, carbohydrate utilization (ferments glucose only), NAATs for rapid molecular detection.
👩⚕ Patient scenario:
A 22-year-old woman presents with dysuria and purulent vaginal discharge. Urethral swab shows Gram-negative diplococci inside neutrophils. Culture on Thayer-Martin agar grows small gray-white colonies. Diagnosis: gonorrhea.
📋 Details:
(A) Classification: Gram-negative diplococcus.
(B) Disease: Causes gonorrhea, a sexually transmitted infection affecting urethra, cervix, rectum, throat, and eyes in newborns.
(C) Identification/Diagnosis: Clinical symptoms, Gram stain, culture on selective media, or NAAT.
(D) Treatment/Prevention: Ceftriaxone single dose; use condoms to prevent transmission. Screening and partner treatment critical.
(E) Unique Epidemiology & Lab Safety: Humans are the only host; high antigenic variation enables immune evasion; increasing antibiotic resistance. BSL-2 precautions for lab work.
Borrelia burgdorferi
Microscopy: Spirochetes are too thin for Gram stain; best seen with dark-field microscopy or silver staining.
Culture: Very slow and difficult in specialized Barbour-Stoenner-Kelly (BSK) medium. Not routine.
Tests: Serology (ELISA, confirmed by Western blot), PCR for bacterial DNA.
👩⚕ Patient scenario:
A 10-year-old boy develops a bull’s-eye rash, joint pain, and fatigue 3 weeks after a tick bite while hiking in the northeastern U.S. ELISA and Western blot are positive for antibodies to B. burgdorferi. Diagnosis: early Lyme disease.
📋 Details:
(A) Classification: Spirochete bacterium.
(B) Disease: Causes Lyme disease, affecting skin, joints, heart, and nervous system.
(C) Identification/Diagnosis: Clinical presentation (erythema migrans), serology, PCR.
(D) Treatment/Prevention: Early disease treated with doxycycline or amoxicillin; severe cases may require IV ceftriaxone. Prevention: tick avoidance, protective clothing, and repellents.
(E) Unique Epidemiology & Lab Safety: Transmitted by Ixodes ticks; mice serve as reservoirs, deer as tick hosts; antigenic variation helps evade immunity. BSL-2 precautions for lab work.
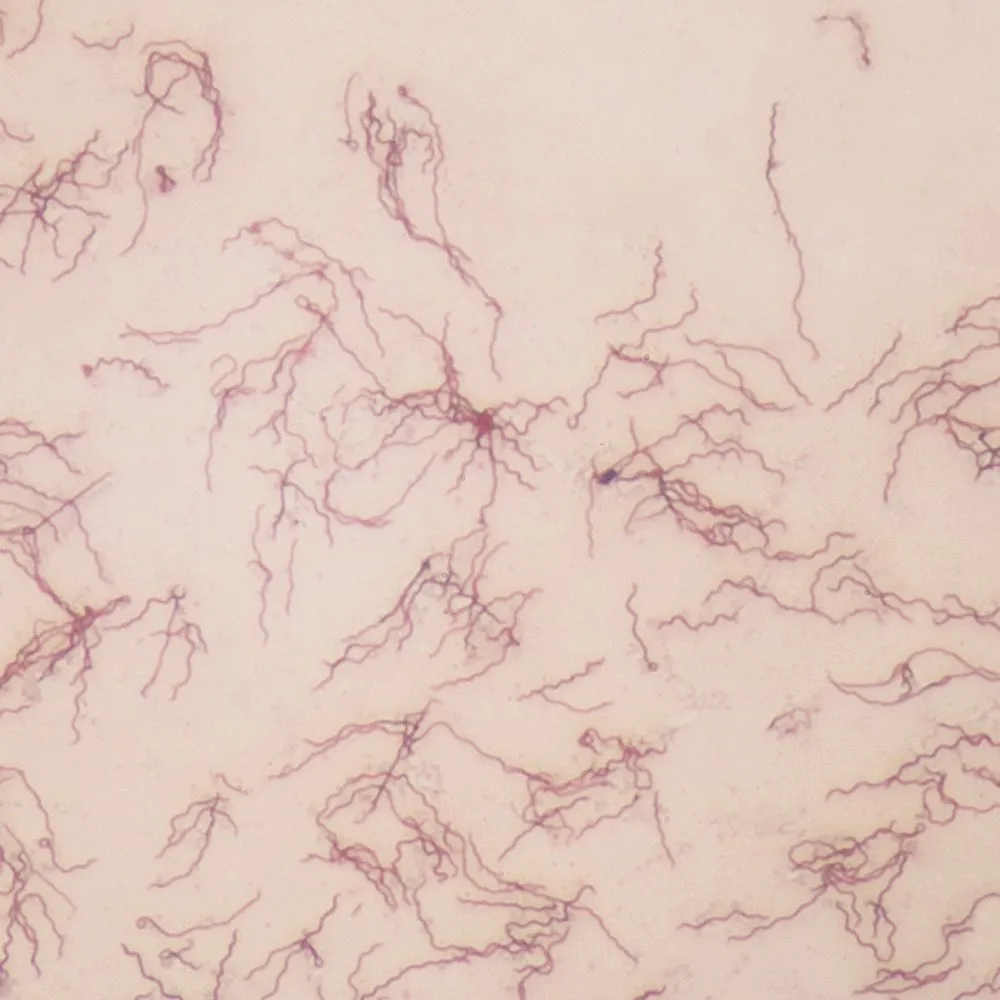
Mycobacterium leprae
Lab differentiation:
Microscopy: Acid-fast rods using Ziehl-Neelsen stain; often clustered in skin or nerve tissue biopsies.
Culture: Cannot be grown on artificial media; maintained in armadillo models or mouse footpads.
Tests: Skin smears, biopsy, PCR for bacterial DNA.
👩⚕ Patient scenario:
A 35-year-old man presents with hypopigmented skin patches with loss of sensation and thickened peripheral nerves. Skin biopsy shows acid-fast rods. Diagnosis: leprosy (Hansen’s disease).
📋 Details:
(A) Classification: Acid-fast rod-shaped bacterium.
(B) Disease: Causes leprosy, affecting skin, peripheral nerves, and sometimes eyes.
(C) Identification/Diagnosis: Clinical signs, skin smear/biopsy with acid-fast staining, PCR.
(D) Treatment/Prevention: Multidrug therapy with dapsone, rifampicin, and clofazimine for months to years. Prevention: early detection, prolonged close contact is usually required for transmission.
(E) Unique Epidemiology & Lab Safety: Very slow-growing; cannot be cultured in vitro; long incubation period. Humans are main reservoir; spreads mainly via prolonged respiratory contact. BSL-2 precautions when handling specimens.
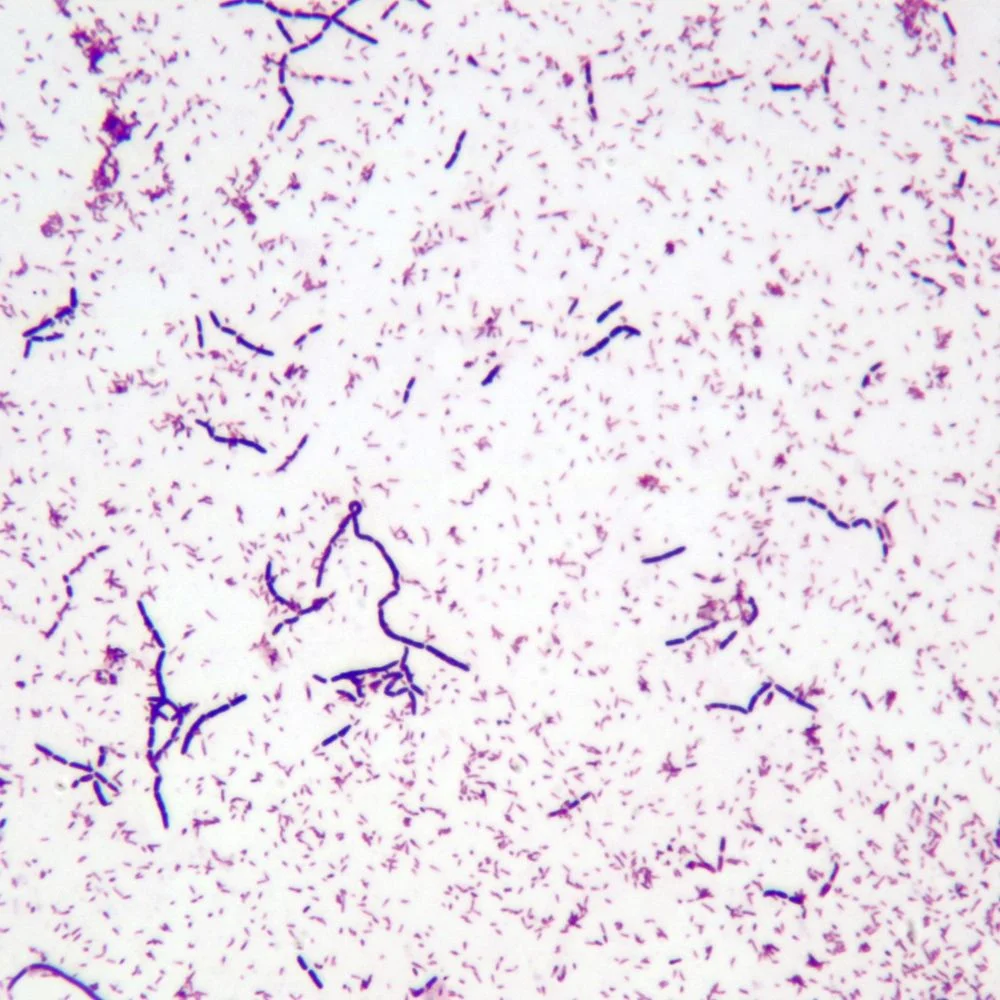
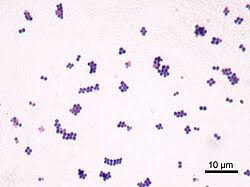
Staphylococcus aureus
🧪 Lab differentiation: Gram stain shows purple grape-like cocci clusters. On blood agar, colonies are golden-yellow and beta-hemolytic. On Mannitol Salt Agar, ferments mannitol turning media yellow. Catalase- and coagulase-positive.
👩⚕ Patient scenario: A college wrestler develops a pus-filled boil on his thigh. Swab culture grows golden-yellow colonies, Gram stain shows clusters, and coagulase test is positive.
(A) Classification: Gram-positive bacterium; cocci in clusters.
(B) Disease: Abscesses, pneumonia, food poisoning, toxic shock syndrome.
(C) Identification/Diagnosis: Gram stain, mannitol fermentation, coagulase test.
(D) Treatment/Prevention: Nafcillin (MSSA) or vancomycin/linezolid (MRSA). Abscess drainage. Hygiene prevents spread.
(E) Unique Epidemiology & Lab Safety: Found in nose/skin of ~30% of people. Virulence: Protein A, toxins. BSL-2 organism.
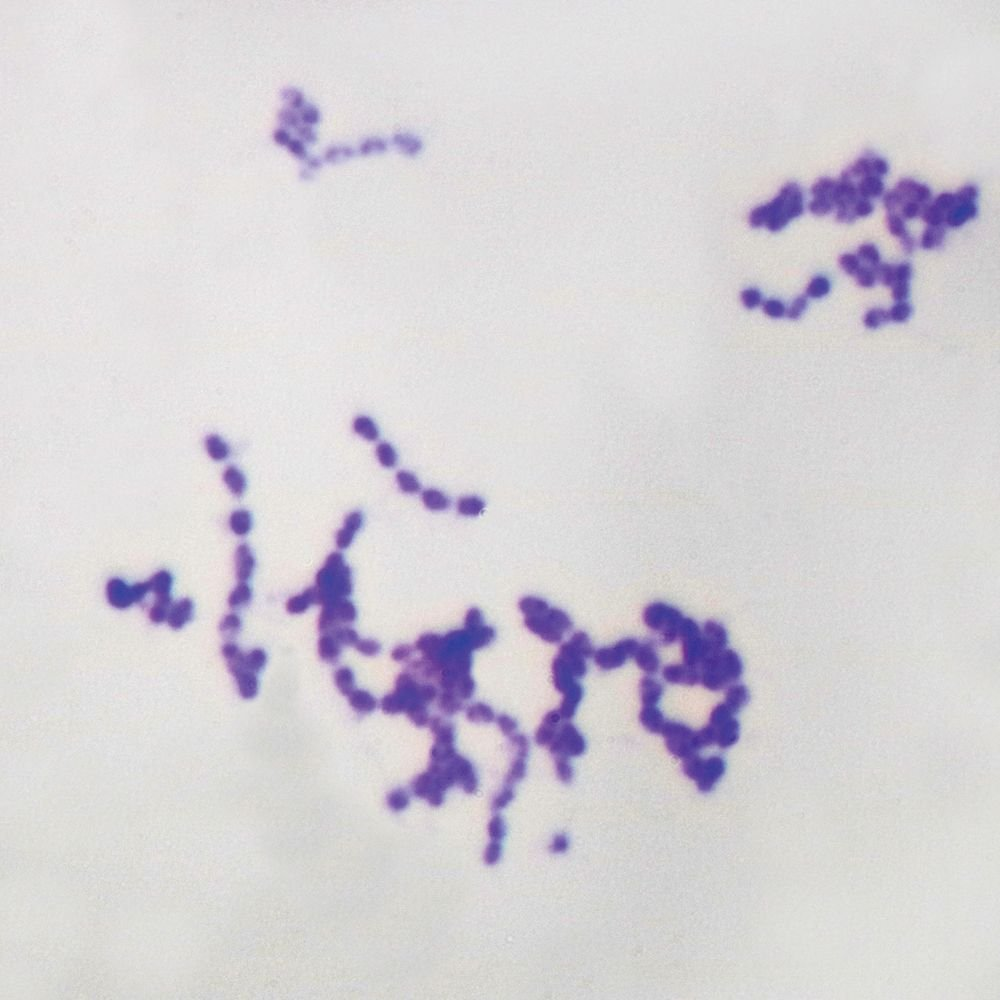
Streptococcus pneumoniae
🧪 Lab differentiation: Gram stain shows purple lancet-shaped diplococci. Colonies on blood agar are alpha-hemolytic and mucoid due to capsule. Optochin-sensitive, bile soluble.
👩⚕ Patient scenario: An elderly man develops fever, cough, and rusty sputum. Blood agar shows alpha-hemolytic mucoid colonies. Gram stain shows lancet diplococci.
(A) Classification: Gram-positive diplococcus.
(B) Disease: Pneumonia, meningitis, otitis media.
(C) Identification/Diagnosis: Gram stain, alpha-hemolysis, optochin sensitivity, antigen detection.
(D) Treatment/Prevention: Penicillin (if susceptible), ceftriaxone. Vaccine available (PCV13, PPSV23).
(E) Unique Epidemiology & Lab Safety: Leading cause of bacterial pneumonia. Capsule = major virulence factor.
Corynebacterium diphtheriae
🧪 Lab differentiation:
Gram stain: Gram-positive, slender club-shaped rods that may form V- or L-shaped arrangements (“Chinese letters”).
Culture: On Löffler’s medium, colonies appear small, gray-white; on cystine-tellurite blood agar, colonies are black or brown due to tellurite reduction.
Tests: Catalase-positive, urease-negative, non-motile. Elek’s test (immunodiffusion) detects toxin production. PCR can detect the tox gene.
👩⚕ Patient scenario:
A 7-year-old child presents with fever, sore throat, and difficulty swallowing. On examination, a thick gray pseudomembrane is covering the tonsils and pharynx. Throat swab culture on tellurite agar produces black colonies. Toxin confirmed by Elek’s test. Diagnosis: diphtheria.
📋 Details:
(A) Classification: Gram-positive, non-spore-forming, pleomorphic rod.
(B) Disease: Causes diphtheria, which affects the throat (respiratory diphtheria) or skin (cutaneous diphtheria).
(C) Identification/Diagnosis: Gram stain morphology, growth on selective media (tellurite agar, Löffler’s medium), Elek test or PCR for toxin.
(D) Treatment/Prevention: Antitoxin (diphtheria antiserum) plus antibiotics (erythromycin or penicillin). Prevention via DTaP/Tdap vaccine.
(E) Unique Epidemiology & Lab Safety: Spread by respiratory droplets. Carriers may harbor it asymptomatically. Only toxigenic strains cause severe disease. Handled at BSL-2 with caution when working with suspected toxin-producing isolates.
Haemophilus influenzae
Lab differentiation:
Gram stain: Small Gram-negative coccobacilli.
Culture: Requires chocolate agar with both X factor (hemin) and V factor (NAD⁺) for growth. Won’t grow on standard blood agar unless “satelliting” near Staphylococcus aureus (which provides V factor).
Tests: Catalase-positive, oxidase-positive. Serotyped by capsule polysaccharides (type b is most virulent).
👩⚕ Patient scenario:
A 3-year-old unvaccinated child develops fever, drooling, and difficulty breathing. Examination shows inspiratory stridor, and lateral neck X-ray reveals a “thumb sign” suggesting epiglottitis. Throat culture on chocolate agar confirms the pathogen.
📋 Details:
(A) Classification: Gram-negative coccobacillus.
(B) Disease: Causes meningitis, epiglottitis, pneumonia, otitis media, and sinusitis.
(C) Identification/Diagnosis: Chocolate agar growth, requirement for X and V factors, serotyping for capsule, PCR or antigen detection in CSF.
(D) Treatment/Prevention: Ceftriaxone for serious infections; rifampin prophylaxis for close contacts. Prevention with Hib conjugate vaccine.
(E) Unique Epidemiology & Lab Safety: Spread by respiratory droplets. Encapsulated strains (especially type b) cause invasive disease. BSL-2 handling in labs.
Escherichia coli
Lab differentiation:👩⚕ Patient scenario:
A 22-year-old woman presents with dysuria, frequency, and suprapubic pain. Urine culture shows pink colonies on MacConkey agar, oxidase-negative, and indole-positive. Diagnosis: urinary tract infection caused by this bacterium.
📋 Details:
(A) Classification: Gram-negative, facultative anaerobic rod.
(B) Disease: UTIs, neonatal meningitis, gastroenteritis (traveler’s diarrhea, hemorrhagic colitis).
(C) Identification/Diagnosis: Gram stain, lactose fermentation on MacConkey agar, biochemical tests, PCR for virulence genes.
(D) Treatment/Prevention: UTIs treated with TMP-SMX, nitrofurantoin, or fluoroquinolones. Most diarrheal illnesses are self-limiting; avoid antibiotics in Shiga toxin strains (to prevent HUS). Prevention: hand hygiene, cook meat thoroughly.
(E) Unique Epidemiology & Lab Safety: Normal gut flora, but some strains acquire toxins (e.g., Shiga toxin). BSL-2 organism in labs; stool and urine cultures commonly used for identification.
Pseudomonas aeruginosa
👩⚕ Patient scenario:
A burn patient in the ICU develops fever and wound infection with a blue-green pus and sweet odor. Culture shows oxidase-positive, non-lactose-fermenting colonies on MacConkey agar, confirming the organism.
📋 Details:
(A) Classification: Gram-negative, aerobic rod.
(B) Disease: Causes pneumonia (esp. in cystic fibrosis), burn wound infections, UTIs, bacteremia, otitis externa (“swimmer’s ear”).
(C) Identification/Diagnosis: Pigment production, oxidase positivity, growth as non-lactose fermenter on MacConkey.
(D) Treatment/Prevention: Resistant to many antibiotics; treated with antipseudomonal drugs (piperacillin-tazobactam, ceftazidime, meropenem, or combination with aminoglycosides/fluoroquinolones). Prevention with strict infection control in hospitals.
Endotoxin
A lipopolysaccharide found in the outer membrane of Gram-negative bacteria. It is released when the bacteria die and can cause systemic effects.
Exotoxin
A broad category of toxins released by both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria into their surroundings.
These toxins target specific tissues or organs, such as the nervous system (neurotoxins), blood cells (hemotoxins), or general tissues (cytotoxins).
Example: Clostridium botulinum releases botulinum toxin, a neurotoxin that causes paralysis.