Challenges - interviewing Child witnesses
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
13 Terms
Adult Expectations
Children can provide accurate accounts if interviewed properly
Adults, including legal professionals think they can tell truths from lies - particularly children’s accounts
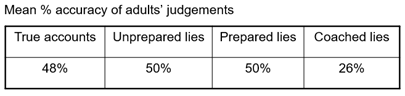
Warrant et al
Children interviewed soon after a serious injury requiring emergency-room treatment (truth teller)
Matched with 3 other children asked to fabricate a similar event
Unprepared lie
Prepared lie
Coached lie
514 students given transcript and asked to judge if they were lying
Controversial Case - McMartin Case
Analysis
Initial denial
Use of suggestive techniques
Leading questions
Conformity pressure
Repeating questions several times
Positive reinforcement
Intonation (stress on certain words
Asking child to imaging the event
Factors effecting reliability of child testimony
Children have limited memory capacities
less communicatively competent
Less information and details reported
Interviewers respond to inappropriate questioning style
Other risks
Interview bias (seeking confirmatory evidence)
Compliance to authority figures
Poor reality monitoring ability
Children have higher risk of being affected by poor interview quality
Poor interviewing victimises children
Stereotype and suggestion – Leichtman & Ceci 1995
Procedure
2 minuet visit from ‘Sam Stone)
5 interviews
Summary
Indirect (stereotype) and direct suggestions negatively influence reliability of children’s report
More for younger children
Some children persistently reported false information even when challenged
Some evidence of embellishment
Follow up study found child protection professionals performed at chance levels when asked to distinguish between the accurate and inaccurate accounts
Information ‘contagion’
Staged a classroom archaeological dig for 3 groups of children 4 years
Conditions
Target group – witnesses
Classmate – classmates of witnesses
Control – did not witness
Summary
Classmate group often falsely claimed they had witnesses the events too
False reported created through interacting with peers
Large percentage claimed to remember the activity
Field stud – highly ecological
Confabulation and imagination inflation
Procedures
Interview one a week for 12 weeks
8 events (4 false )
Told that their mom said it had occurred
Results
For both positive and negative events their was initial rejections but as the interviews went on this number of reports increased
Adults had no better than chance at distinguishing between accurate and inaccurate reports
Imagination paradigm with adults – wade et al
20 participants given 3 interviews over 2 weeks about 3 true photos and one false
False reports increased from 35 in first interview to 50% on final
Results
Imagining an event increases subjective confidence that the event actually happened
Source monitoring
Factors Associated with source monitoring errors
High perceptual semantic and temporal similarity between two sources
Poor encoding conditions – e.g. divided attention
Imagination inflation
Can children monitor the source of their memory
In comparison to adults children are poor at source monitoring
Repeated Interviewing
Problems with particularisation
Children are vulnerable to suggestion when being interviewed about events that happened more than once
Findings
Decline in accuracy, certainty and consistency
High rate of source for each individual event isn’t necessarily correct
Migration of details from other occurrences of the event into the occurrences being recalled
can use evidence to prove this wrong down to a memory error
Lower rate of external intrusion errors (not just making things up)
Details not featured in any occurrence
Implications
Most previous work
Underestimate suggestibility to interview suggestion after repeated experiences
Implications for timeline of interviewing about repeated events
Errors or inconsistencies in a child account of a repeated event reduce the chance of prosecution
Interviewing props and suggestibility
Controversial
Used in high profile cases
Significant animosity between proponents and researchers
Tension between
Justice for child (getting account against abuser)
Justice for defendant (protection against false claims)
Use of props in investigative interviews
Interviewing (play therapy)
Idea that objects help bridge the gap between what children known and what they can explain
Allows them to response without verbalizing
Research suggest that this assumption may be an error
Early observations
Dolls provide affordances (features permitting certain behaviours)
Non-diagnostic of abuse
More controlled research (medical examination )
After physical exam, interviewers presented anatomical dolls
27% of non-touched children falsely claimed doctor touch them (genital area)
51% of touched children denied being touched
Interviewers then asked more suggestive questions
36% of non touched children falsely showed touching
Error include ‘over touching’ responses (finger insertions)
Problem with props
Developmental issues
(don’t understand what they dolls are for, that they are supposed to be them)
(understand the doll is an object but also a symbol of themselves)
Young children find it difficult to understand symbol-referent relations
Younger children suggestible in this context
Body diagrams
5-7 year olds are challenged when asked to report on body diagrams
Practice interview instruction – touched children on elbow and then asked them on diagram where they were touched
54% of children required correction and additional explanation
Body diagrams are also problematic
False Report: Current research
Emerging explanations
Poole et al
Used a Mr science paradigm but also cognitive developmental measures
Found deficient cognitive control – the inability to reliably use internalised rules and representations to guide behaviour was a key predictor of exuberant false allegations