L1 Blood as a Tissue
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
What type of tissue is blood?
Specialized connective tissue
Cell suspended within tissue specific extracellular matrix: plasma
What are the components of blood?
~50% plasma
90% water, 10% dissolved substance (protein, waste, etc)
45% RBC
1% buffy coat
White blood cell
platelets
What is serum?
The remaining liquid when the clotting factors moves to the blood which clots naturally,
What is plasma?
Contains clotting factors (fibrinogen)
Anticoagulant is added to it to prevent clotting
RBC
What?
Function?
Appearance?
Red blood cell aka erythrocytes
Mature in bone marrow, starts out as reticulocytes (immature RBC, larger than RBC and contains less hemoglobin)
Function:
Contains hemoglobin (Hb)
Protein that carries molecules of oxygen
Appearance:
Central pallor: dived in the center
Anucleate: no nucleus
Due to evolution reasons
Also means they cannot replicate bc they have nowhere to store DNA/RNA
Biconcave disc (shaped)
What are reticulocytes?
Immature RBC in the bone marrow (less hemoglobin but bigger)
What is central pallor?
Dip center of RBC
RBC
What are the increase and decrease of RBC?
Erythrocytosis (increase): can be caused by 2 things
Overproduction in the bone marrow
Compensation such as chronic hypoxia (low oxygen levels), high altitudes
Anemia (decrease): Making of new red blood cells
Regenerative anemia:
Bone marrow is intact: not due to its inability to make enough/malfunctioning in its production
Can see the reticulocytes (to overcompensate the lost somewhere)
Usually bc of blood lost
Non-regenerative anemia:
issue with the bone marrow
Does not have enough, and cannot make new ones
What are white blood cells?
Leukocytes
Classified into granulocytes and agranulocytes
What is the increase and decrease of white blood cells?
Leukocytosis (increase)
Leukopenia (decrease)
What are the Granulocytes
3 types
“BEN”
Basophil
Eosinophil
Neutrophil (most abundant)
What is a neutrophil?
Function?
Appearance?
Increase decrease?
Most abundant leukocytes
First responders (cuts invasion)
Function:
Fight diseases by migrating into blood vessels and perform phagocytosis: engulfing the invading bacteria, cellular debris etc.
Appearance:
Lobulated nucleus
Mature: segmented neutrophil
Immature: band neutrophil, more unified
Neutrophilia (increase)
Neutropenia (decrease)
Increase in band neutrophil: left shift
neutrophils
What are eosinophils?
Function?
Appearance?
Increase decrease?
Function:
Defend against parasites
Regulate w allergic reactions
Enzymes that will inactivate histamine
Appearance: (like a raspberry)
Lobulated nucleus
Eosinophilic (pink) granules
Eosinophilia (increase)
Eosinopenia (decrease)
Eosinophil
What are basophils?
Function?
Appearance?
Increase decrease?
Function:
Parasite defense
Regulate allergic reactions
Release histamine (responsible for allergic reactions: runny nose, itchy eyes, hives)
Proinflammatory/signals inflammatory cells to go to sites of inflammatory
Appearance:
Lobulated nucleus
Granules are much more purple/blue
Basophilia (increase)
Basopenia (decrease)
basophils
What the the types of agranulocytes?
2 types
Monocyte (largest of all leukocytes)
Lymphocyte (2nd most common of all leukocytes)
What are monocytes?
Function?
Appearance?
Increase decrease?
Function:
Phagocytic, kills anything that’s too big, kills microorganism, ingests foreign material, remove dead cells
Appearance:
BIGGEST leukocytes
Variable morphology (shape)
Dog: horseshoe shape
Can sometimes see vacuoles like bubbles in cytoplasm
When they migrate into tissues, they mature into macrophages or dendritic cells
Monocytosis (increase)
Monocytopenia (decrease)
monocyte
What are Lymphocytes?
Function?
Appearance?
Increase decrease?
Second most common leukocytes
Function:
Main cell type of immune system (B and T cells)
B cell: mature into plasma cells and produces antibodies (protein that tags bacteria, virus)
T cell:
Cytotoxic T cell: kill infected cells
Helper T cells: antibodies that recognize infected cells & recruitment of inflammatory
Appearance:
Overmall small, round nucleus, little cytoplasm
Lymphocytosis (increase): sometimes just mean its stressed
Lymphopenia (decrease)
Lymphocyte
What are the types of lymphocytes?
B cell: mature into plasma cells and produces antibodies (protein that tags bacteria, virus)
T cell:
Cytotoxic T cell: kill infected cells
Helper T cells: antibodies that recognize infected cells & recruitment of inflammatory
What are Platelets?
Function?
Appearance?
Increase decrease?
Aka thrombocytes
Produced in bone marrow (fragments of cells)
Function:
Forming blood clots
Prevents bleeding after vessel injury
Form “platelet plug” at site of injury
Appearance:
Very small compared to red blood cells
Disc shape
Anucleate (like RBC)
Thrombocytosis (increase)
Thrombocytopenia (decrease)
Can lead to increased bleeding and bruising
What are thrombocytes?
Platelets!
Blood clot
Platelets (thrombocytes)
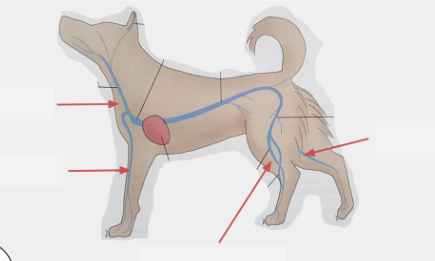
Identify sites of blood collection:
Jugular vein (neck): catheter and site with good blood pressure
Cephalic vein (front limb): catheters mainly done for dog and cat
Lateral saphenous vein/Medial saphenous vein: used for smaller animals/sacred animal
Purple blood tube:
Contains EDTA (anticoagulant: prevent blood clot)
Used for CBC (complete blood count)
Analyse the # & type of blood cell
Green blood tube:
Contains Heparin (anticoagulant)
Chemistry panel
analyze the non-cellular components (plasma, serum: protein, electrolyte, minerals)
Blue blood tube:
Citrate (anticoagulant)
Coagulation panels
Red blood tube:
No additives
Clot and form serum
Used for chem panel
What is a blood smear?
morphology(form) of blood cells
What is the anticoagulant?
Substance that prevents blood from clotting