Freshwater fish - NZ
1/186
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
187 Terms
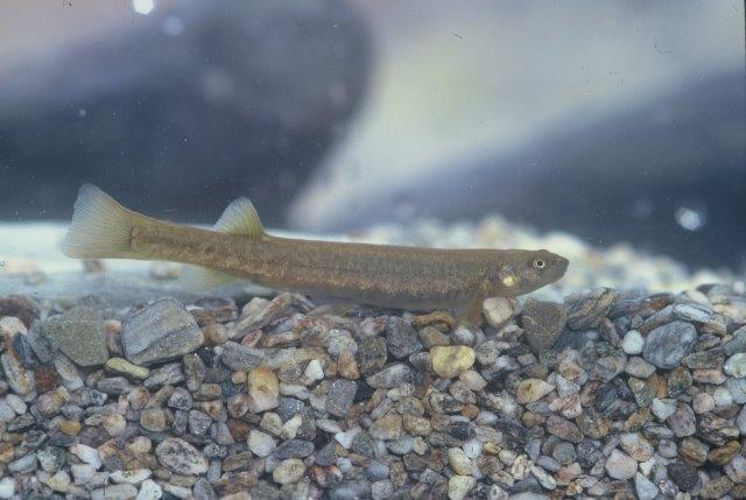

Galaxias paucispondylus
Alpine galaxias
What fin rays differentiate alpine and dusky galaxias?
Caudal and pelvic
Pelvic fin count of alpine galaxias and dusky galaxias
7, 6
Caudal fin count of alpine galaxias and dusky galaxias
16, 15
Alpine galaxias generally live in deeper, swifter water than ________ ________
Longjaw galaxias
Alpine galaxias
_______ ________ have a more slender, elongate shape than canterbury galaxias and koaro
Alpine galaxias
This fish has white chevron-shaped marks in front of its dorsal fin (only in live specimens), which can be used to distinguish them from canterbury galaxias and koaro
Alpine galaxias
Anguilla australis
Shortfin eel
Anguilla dieffenbachii
Longfin eel
Anguilla reinhardtii
Australian longfin eel
Larvae of eels
Leptocephalus
The dorsal fin and anal fin are the same lengths in the _____ eel
Shortfin
Dorsal fin is longer than the anal fin in the _______ eel
Longfin
________ eels are generally found further inland and at greater elevations than their counterpart
Longfin
________ ___ are our most tolerant native fish species
Shortfin eels
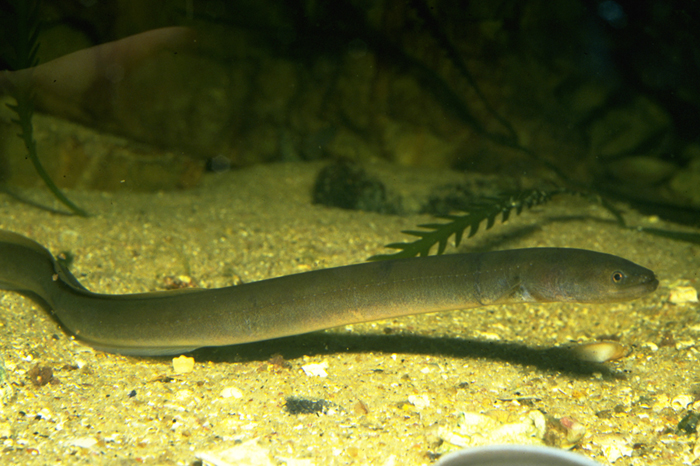

Shortfin eel
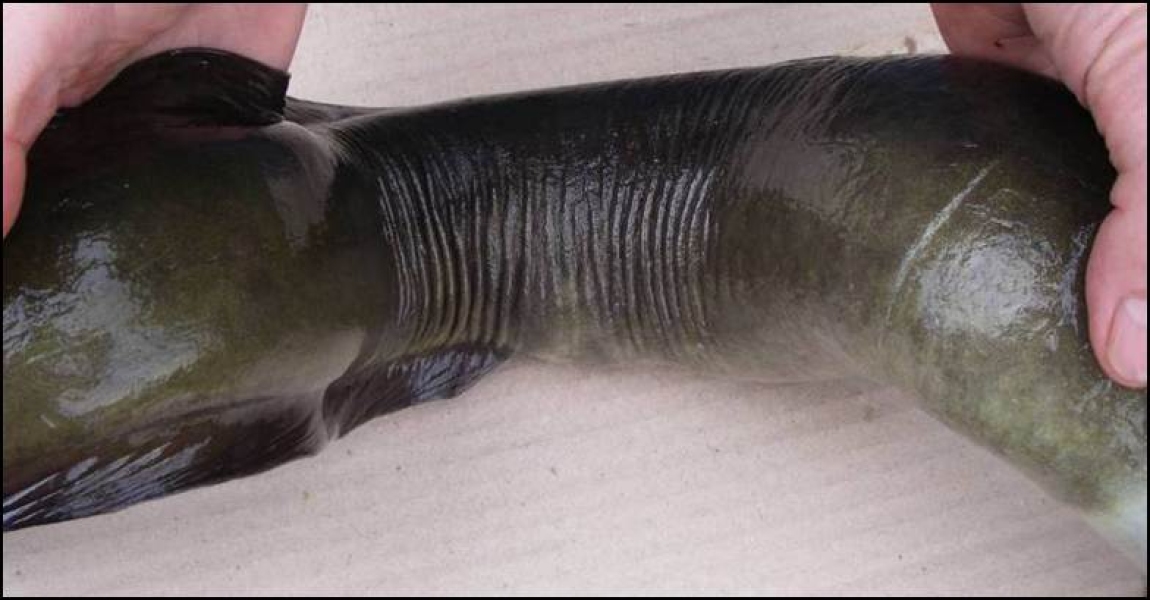

Longfin eel
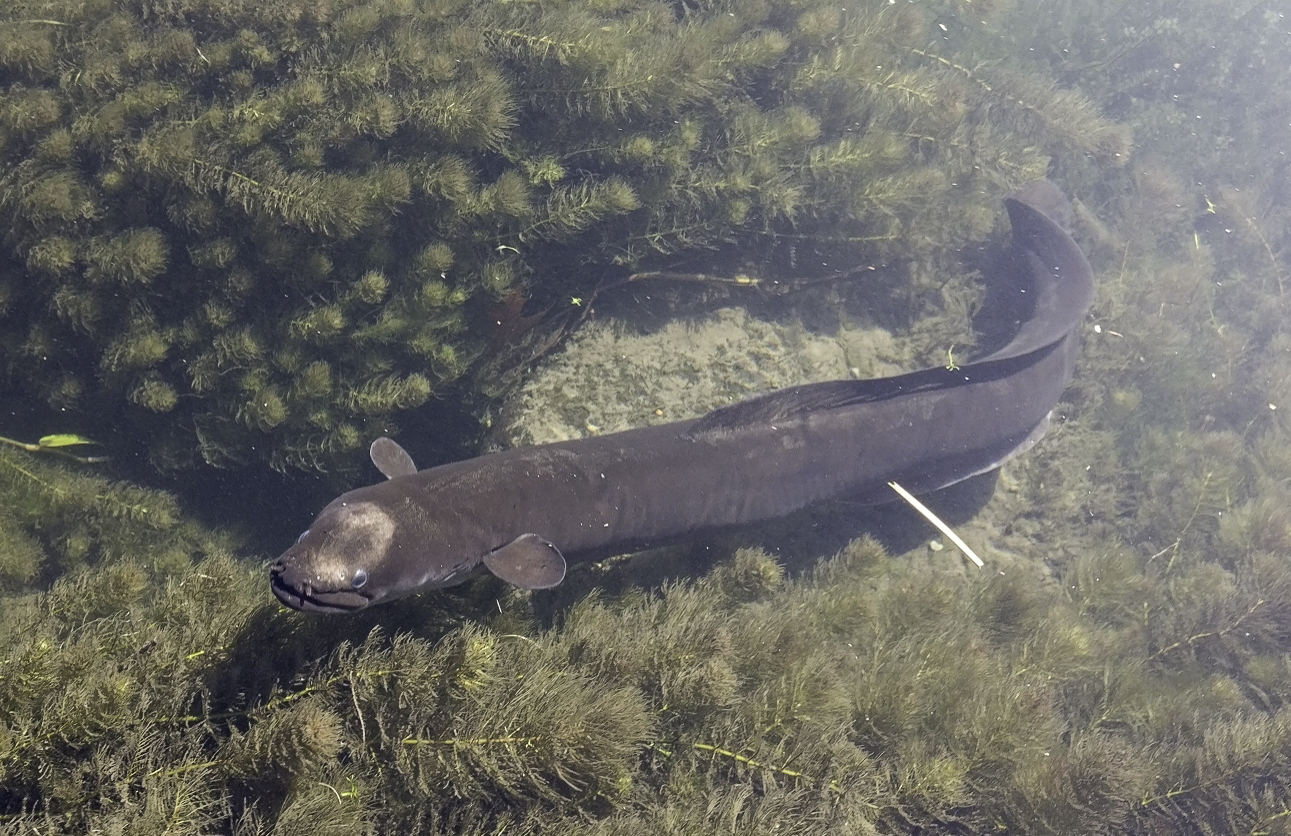

Longfin eel

Leptocephalus
Australian longfin eels can be distinguished from native longfins by the presence of irregular ____ blotches on the back and sides
Black

Australian longfin eel

Salmo salar
Atlantic salmon
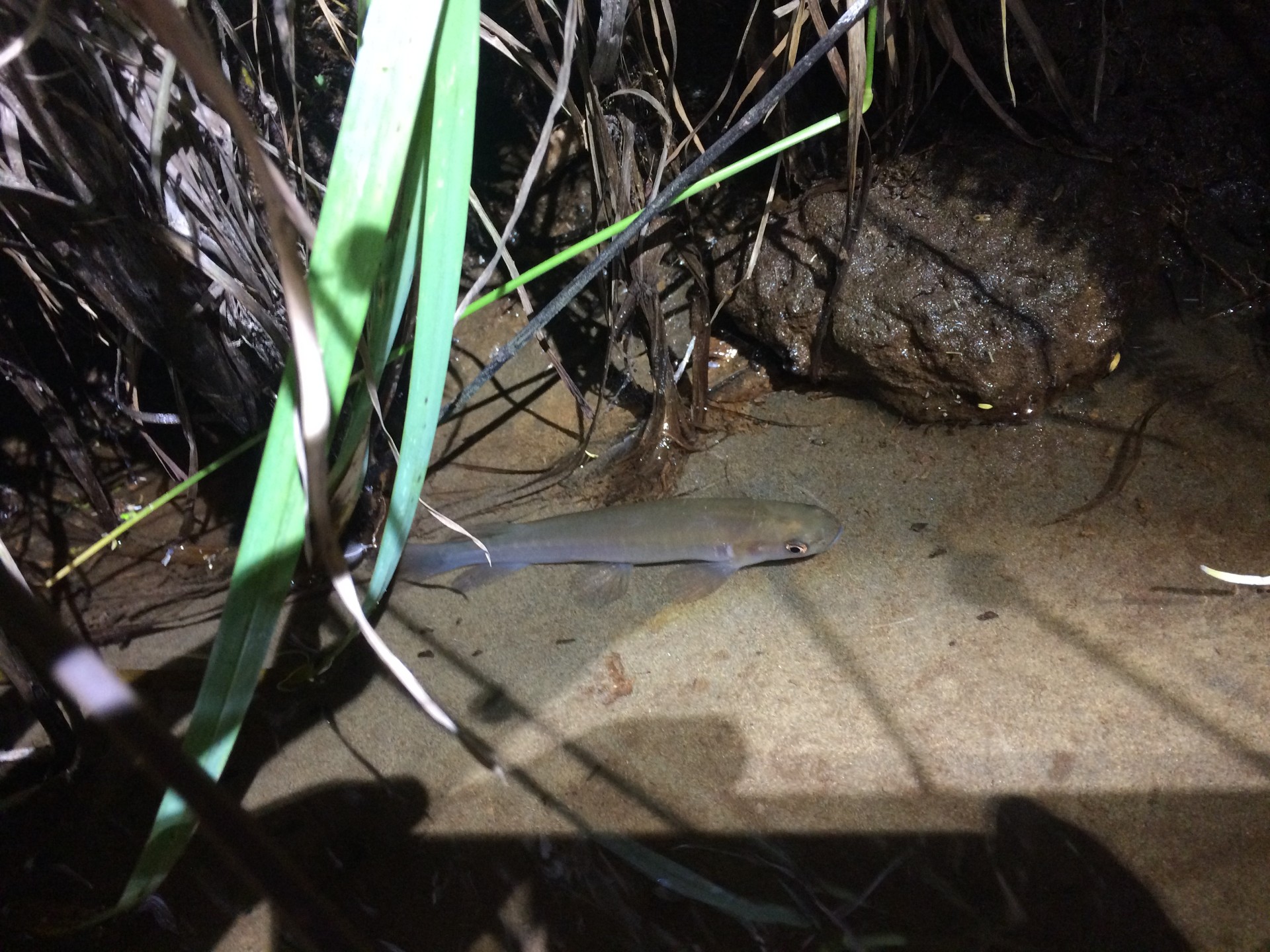

Banded kokopu
Māori name for longfin eel
Tuna
Māori name for shortfin eel
Hao
Māori name for lamprey in North Island
Piharau
Māori name for lamprey in South Island
Kanakana
Māori name for yellow eyed mullet
Aua
Māori name for freshwater mussel
Kakahi
Māori name for whitebait
Mata
Kewai and waikōura
Freshwater crayfish
Māori name for smelt
Paraki
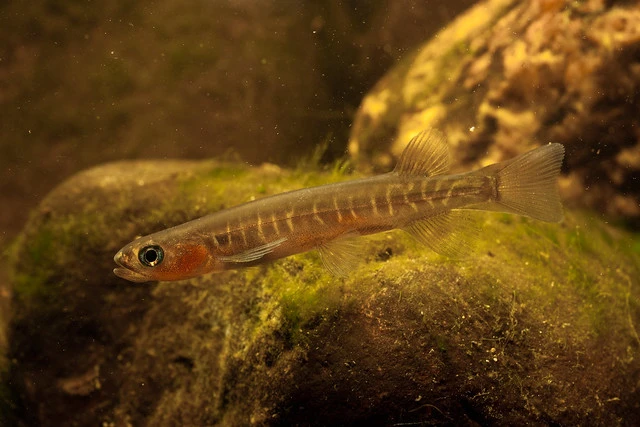

Banded kokopu
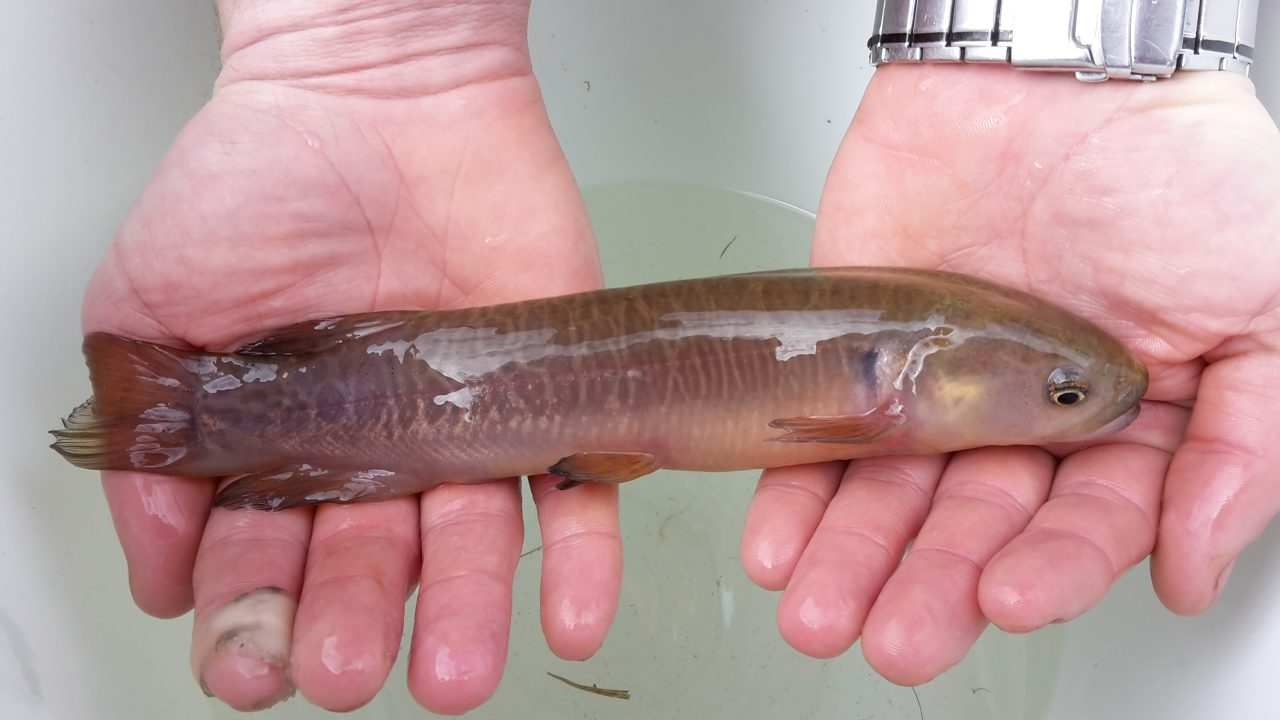

Banded kokopu

Banded kokopu
Distinguishing feature: Thin, pale, vertical bands along the sides and over the back of the fish
Banded kokopu
Adults of what species usually live in the pools of very small tributaries where there is virtually a complete overhead canopy of vegetation.
Banded kokopu
What species are primarily a coastal species and do not venture very far inland?
Banded kokopu
Galaxias fasciatus
Banded kokopu

Galaxias macronasus
Bignose galaxias
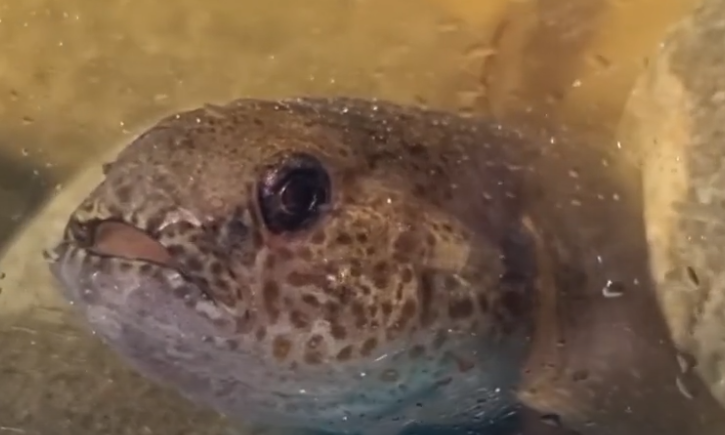

What bully has distinguishing orange spots around its face?
Upland bully
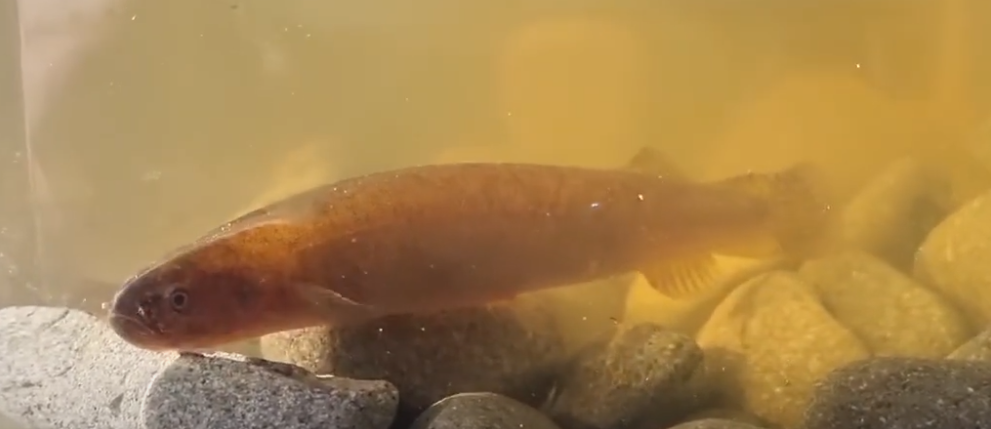

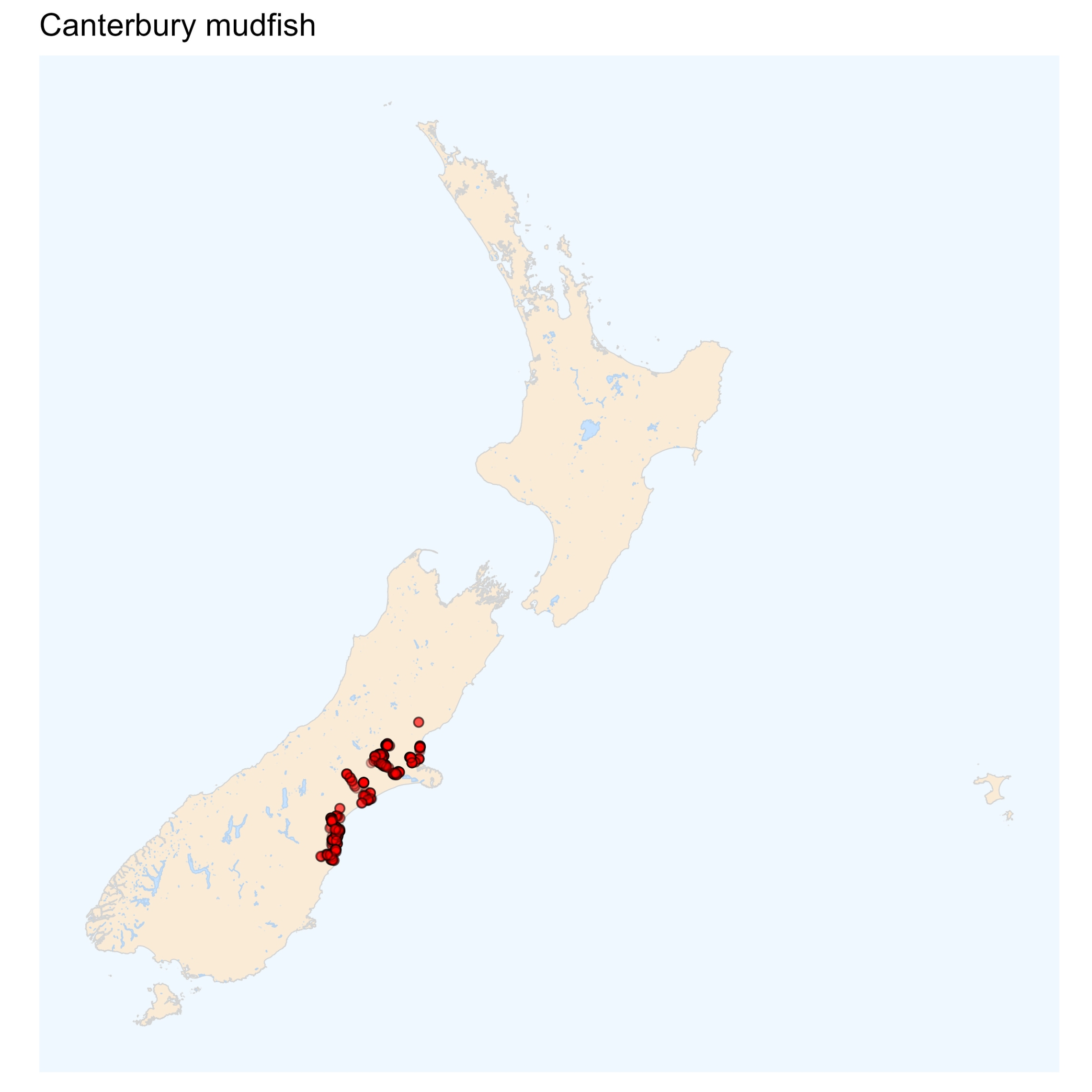
Canterbury mudfish

Giant kokopu

What is this non-migratory bully?
Upland bully

Koaro
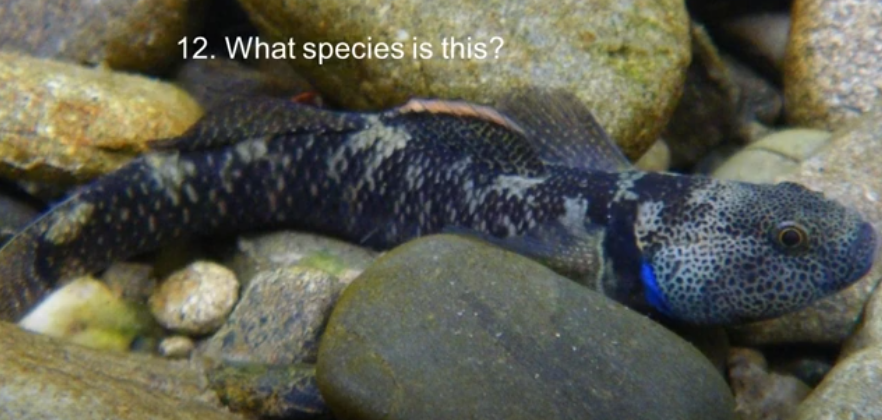

Bluegill bully
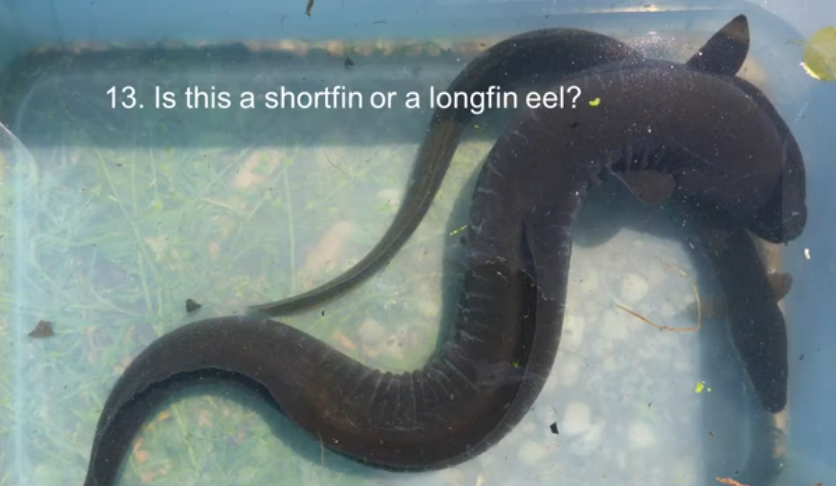

Longfin
How many species of mudfish are there in NZ?
5
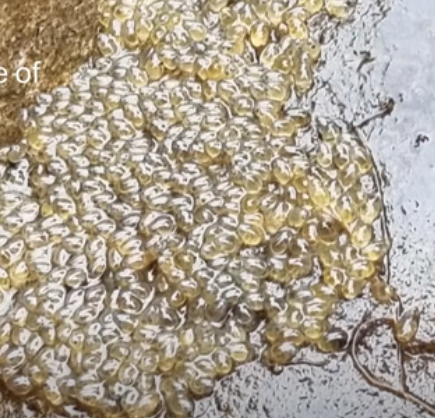

What genera often lay their eggs on the underside of cobbles and boulders in streams?
Gobiomorphus

Shortjaw kokopu
What is a juvenile lamprey called?
Ammocoete
The “pencil galaxias” are small, slender (pencil shaped), non-diadrmous, mainly sub-alpine galaxiids with small fins and long, slender caudal peduncles (G. divergens, G. paucispondylus, G. prognathus and G. cobitinis). What are these four species common names?
Dwarf, alpine, longjaw, lowland longjaw
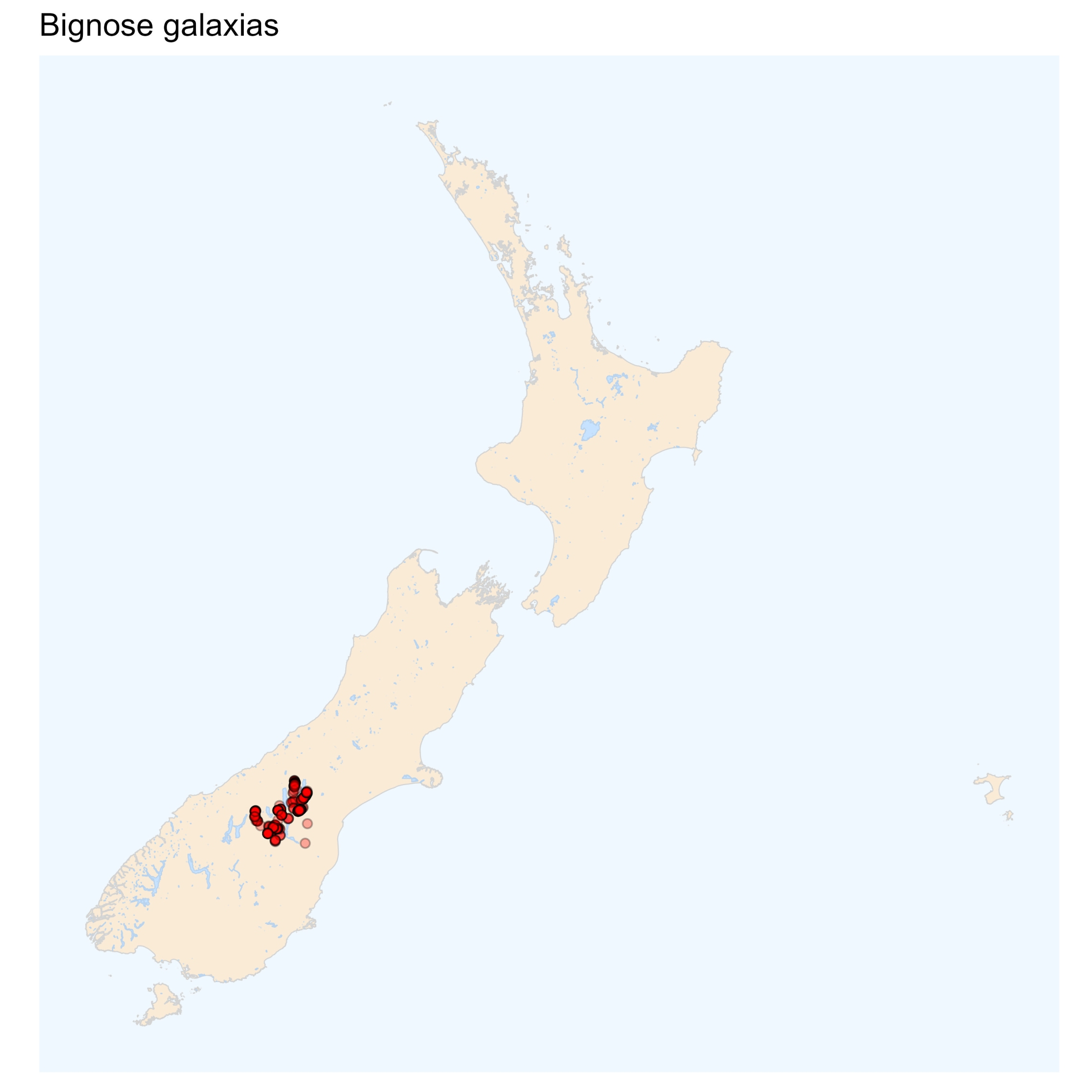
Bignose galaxias are found in several locations in the Mackenzie Basin in the upper Waitaki River catchment. Generally, it is found in small spring or wetland-fed tributaries.
_______ _______ can be distinguished from the ‘pencil galaxias’ because it has only 4–6 pelvic fin rays (usually only 5) and only 11–14 caudal rays.
Bignose galaxias
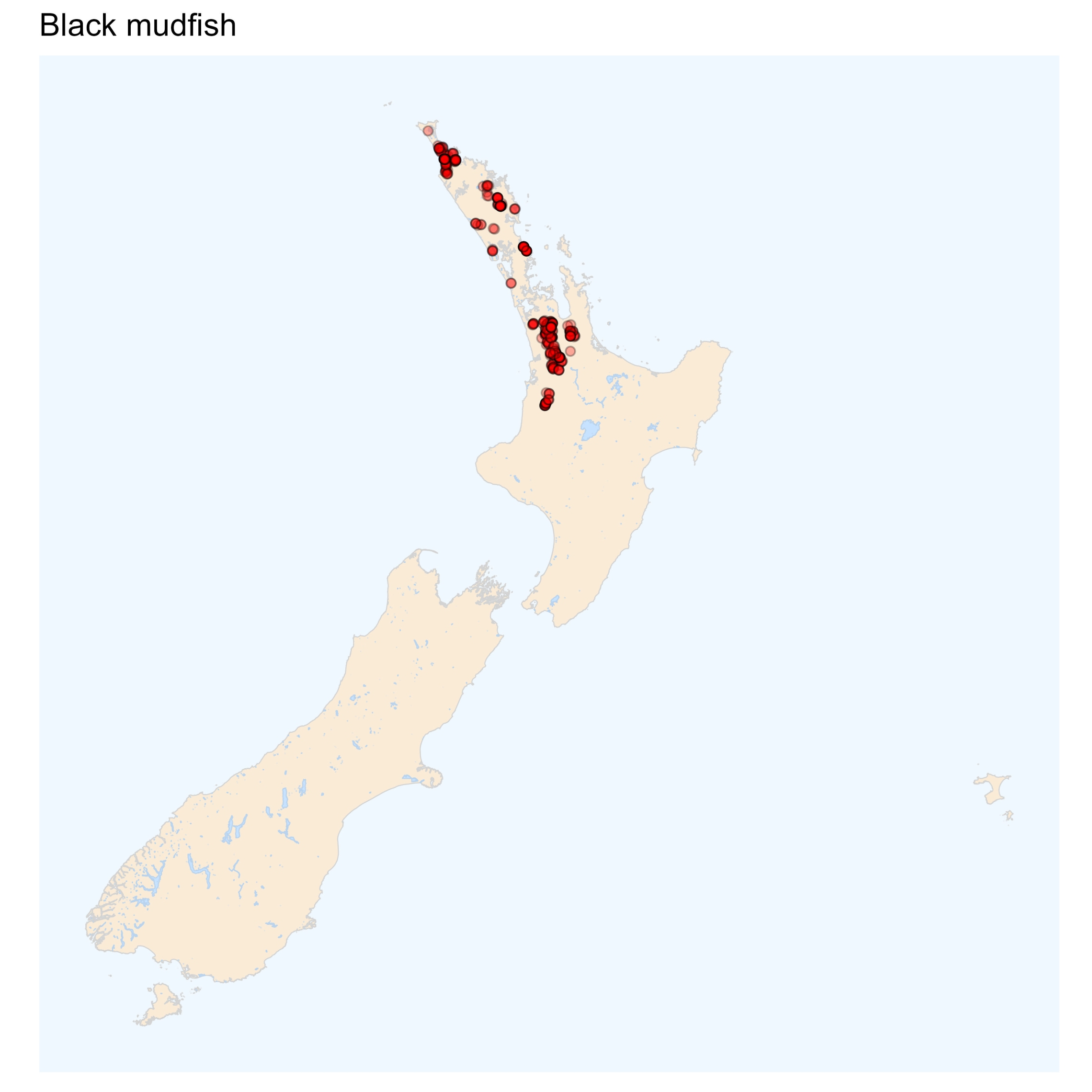
Distribution can be used to differentiate brown and black mudfish.
Black mudfish can be distinguished from the Northland mudfish by the number of caudal fin rays; the Northland mudfish has only 13 or fewer rays whereas the other mudfish usually have 14 or more.

Black mudfish

Blue gill cover and small dark spots that cover their cheeks
Bluegill bully
Bluegill bullies inhabit similar habitat to torrentfish - swift broken water in open rivers and streams.

Brown mudfish
Three of the five mudfish species lack pelvic fins, and this is the easiest way to distinguish them from other members of the Galaxiidae family.
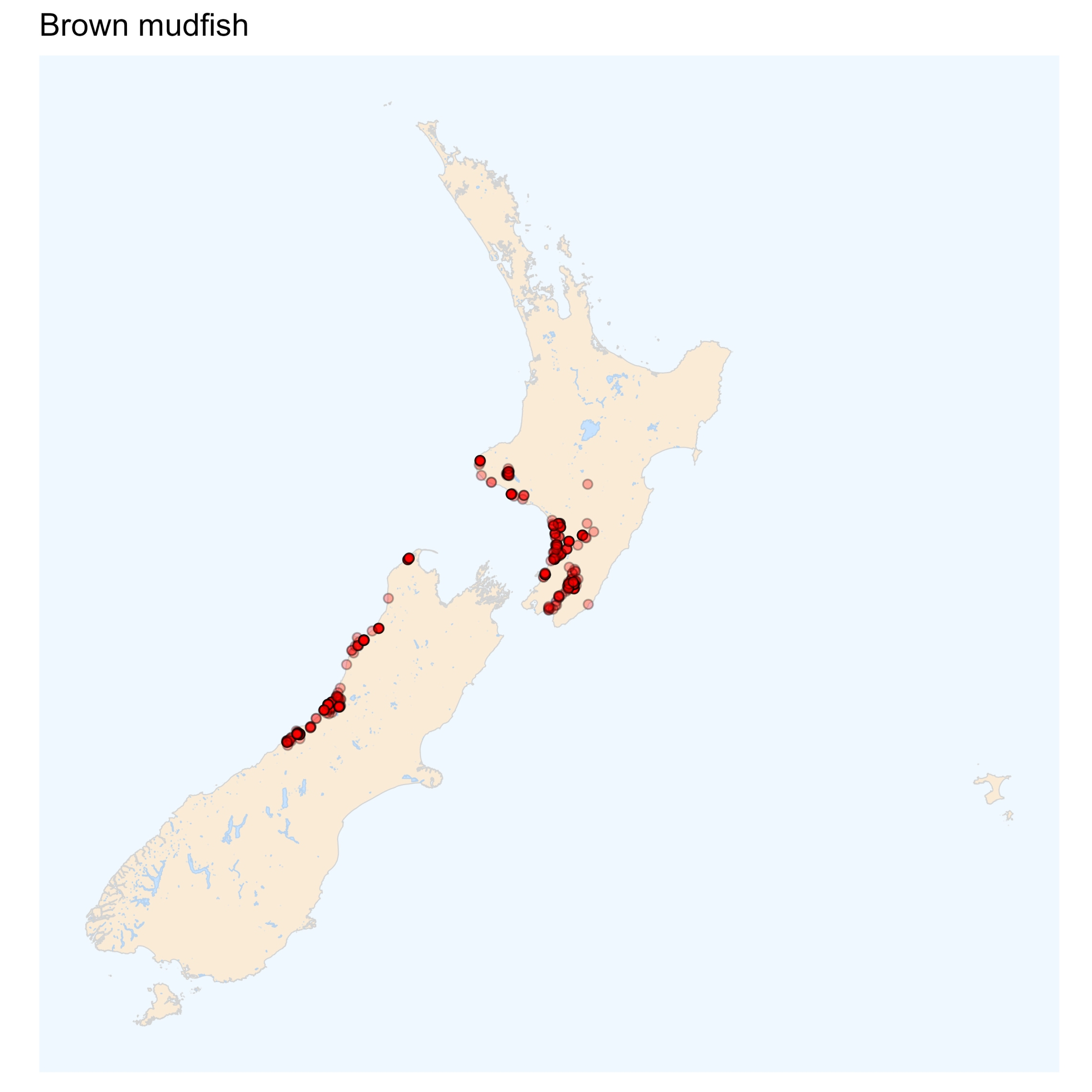
Brown mudfish doesn’t overlap with any other mudfish
Brown trout seldom have any spots on their tails, a feature that distinguishes them from rainbow trout.

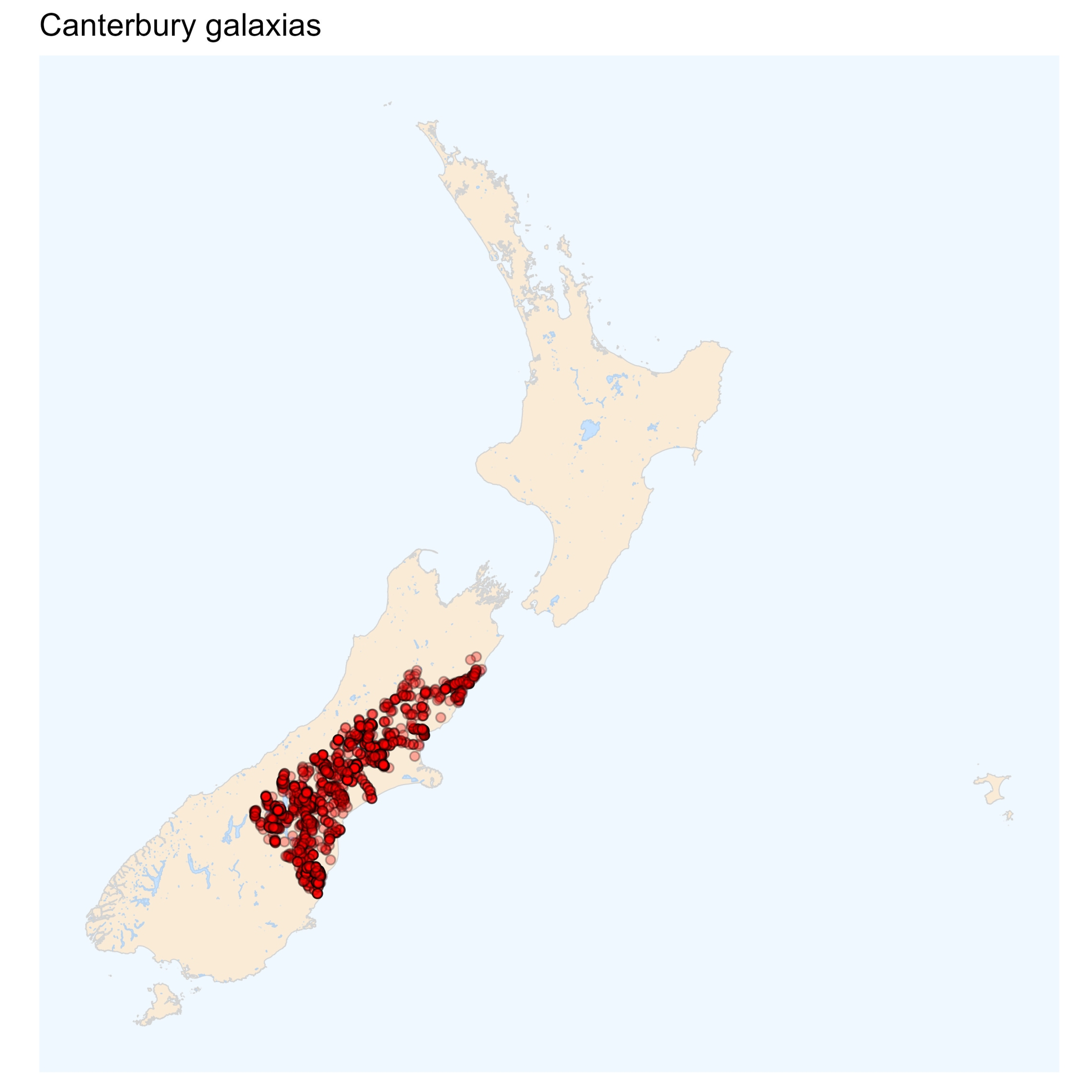
Canterbury galaxias
There are three galaxiid species that co-exist with the Canterbury galaxias and that might be confused with this species. Alpine and longjaw galaxias are relatively easy to distinguish, but the koaro is more difficult. Both the alpine and longjaw galaxias are very slender fish, and when alive, the alpine galaxias has distinct white chevron-shaped marks at the front of the dorsal fin. The long, protruding jaw of the longjaw galaxias is unmistakable. In koaro, the lower jaw is obviously shorter than the upper jaw, and this feature can be used to tell it apart from the Canterbury galaxias. Koaro also have a bolder colour pattern with sparkling gold highlights whereas the colouration of the Canterbury galaxias tends to be more subdued. However, colour can vary so much in individual fish that this is not an infallible characteristic to use for identification.

Canterbury mudfish
this mudfish species is restricted to the Canterbury region. This is the best feature for distinguishing it from the other mudfish, but the presence of pelvic fins on the Canterbury mudfish is also a unique feature of the mainland mudfish species. The Canterbury mudfish can be distinguished from other members of the Galaxiidae family by the presence of fewer rays in the pelvic fins (4 or 5 rays for Canterbury mudfish compared to 7 in the other galaxids). They also have comparatively small eyes.

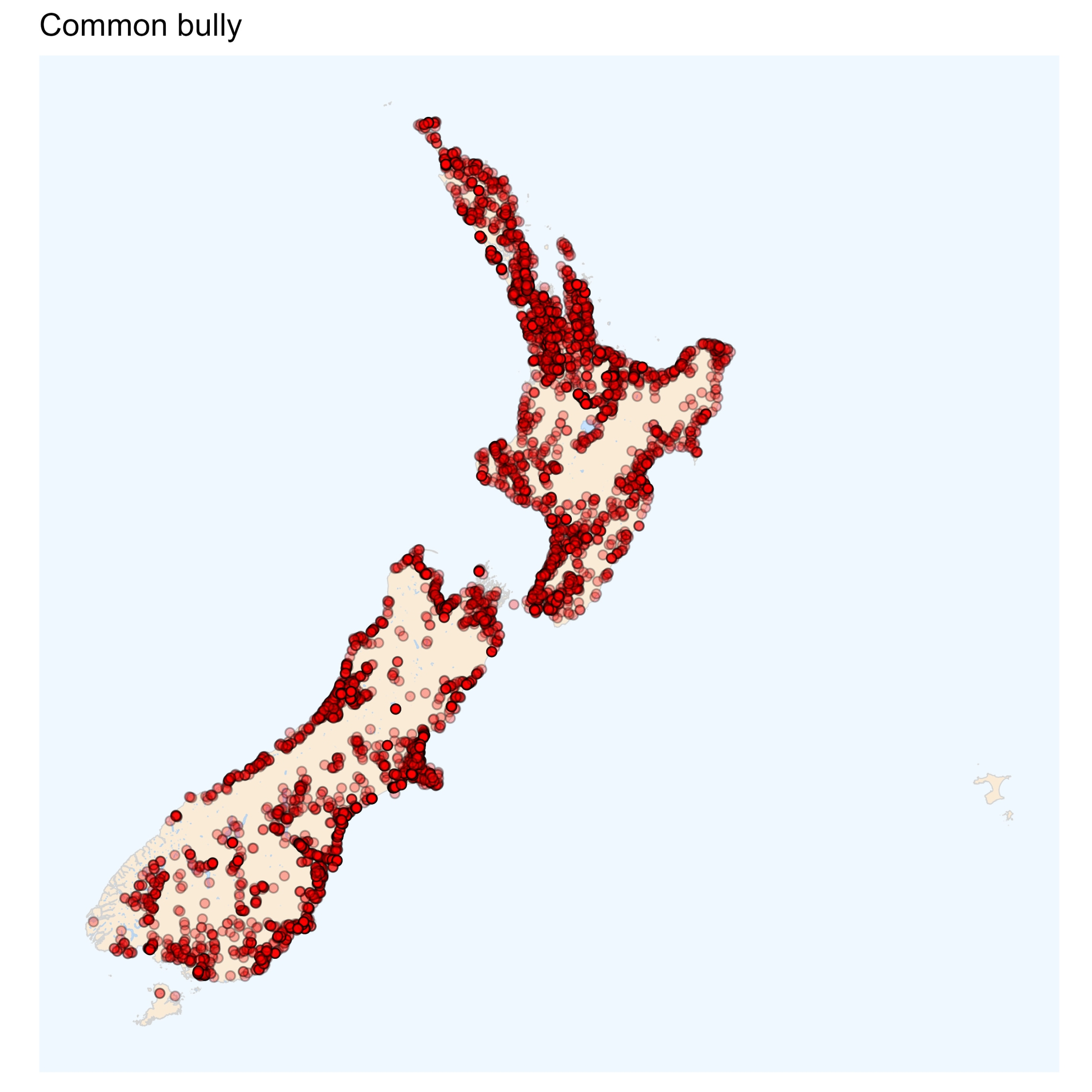
Common bully
The location of head pores and the scale pattern on the head are used to distinguish common bullies from Crans and upland bullies, whereas the number of spines in the first dorsal fin distinguishes common from giant bullies.

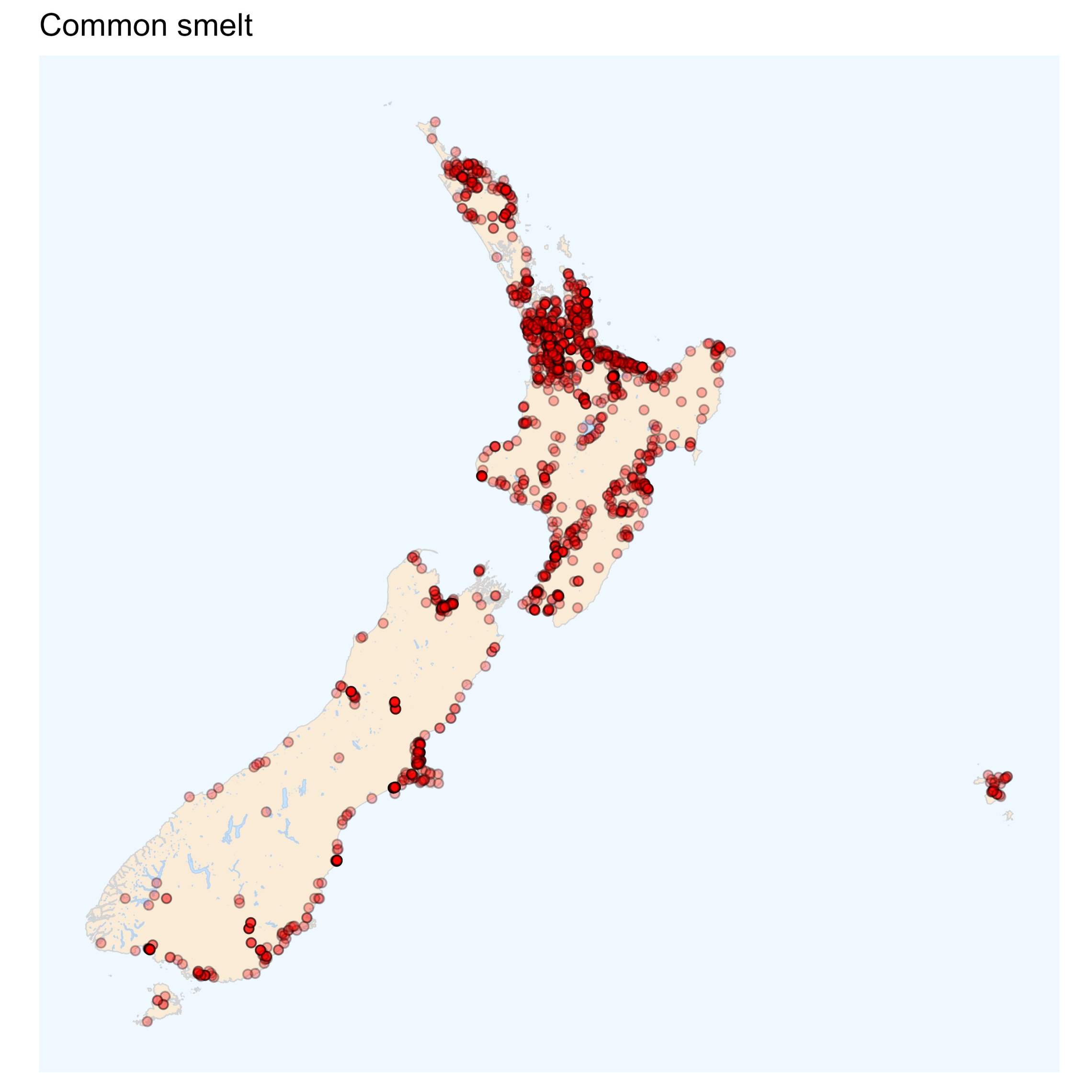
Common smelt
Smelt can be distinguished from other species by the presence of the adipose fin, a small fleshy lobe on their back between the dorsal fin and the tail. They also have scales, a distinctly forked tail, and a cucumber-like smell. The two species that live in New Zealand are very difficult to tell apart, and positive identification depends primarily on the size and number of the scales.
Of the freshwater fish that live in New Zealand, smelt are one of the most sensitive to pollutants like ammonia and stressors such as high water temperature. In some cases, they are as intolerant as the salmonids, which are often used as a benchmark species overseas for establishing water quality guidelines to ensure fish are protected from human activities. Smelt are therefore an appropriate native species for establishing guidelines for New Zealand waterways and usually their presence indicates that the water quality is suitable for most other fish.
What bully is Gobiomorphus mataraerore?
Kaharore bully
What bully is Gobiomorphus breviceps?
Upland bully
The genetic split is around Blenheim, is the upland or kaharore bully found above this split?
Kaharore bully
What bully is Gobiomorphus basalis?
Crans bully
What bully is Gobiomorphus dinae?
Dinahs bully
The genetic spit is around north waikato and only in the North Island. Is Crans or Dinahs bully found in Wellington region?
Dinahs bully
As _____ bully has no marine phase, their ability to colonize new river systems is limited, and once they are gone from an area it is unlikely they will re-colonize on their own.
Crans

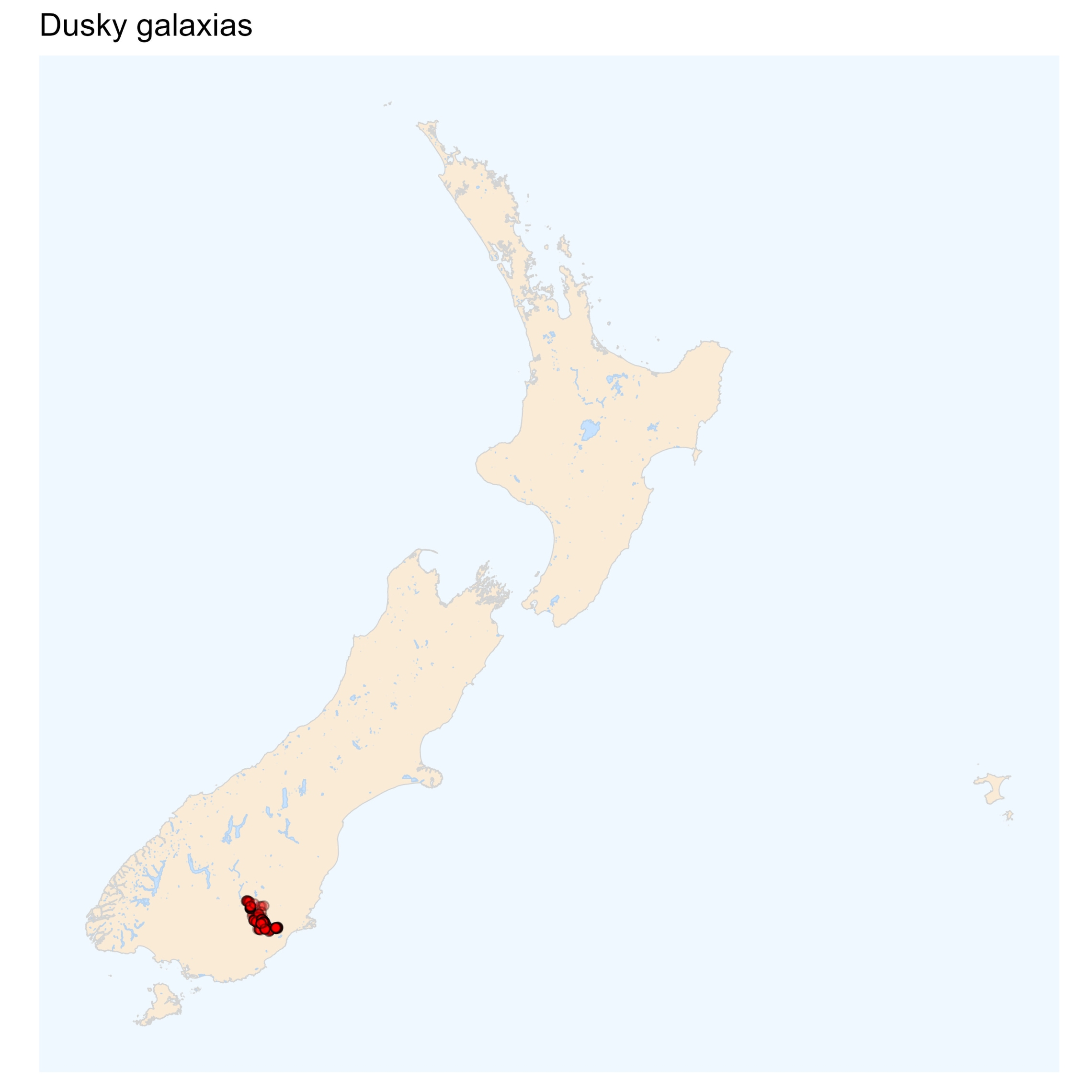
Galaxias pullus
Dusky galaxias
The _____ galaxias differs from the other galaxiids in having only 14 caudal fin rays compared to 15 for Eldons and dwarf galaxias and 16 for the others. It is generally a brown colour, but with a distinct dark and light colour pattern. It also has darker blotches behind the gill openings that are more characteristic of the diadromous banded and shortjaw kokopu.
dusky

Dwarf galaxias
The number of caudal fin rays (15) of this species is also different from most other galaxiids, except for Eldons galaxias. However, ____ and Eldons galaxias do not co-exist, with Eldons galaxias being confined to Otago.
Dwarf
The ____ galaxias is amber to olive green in colour with dark brown blotches on the sides and back. The belly is silvery. It has only 6 pelvic fin rays compared to the more usual 7 for the other galaxiids.
Dwarf
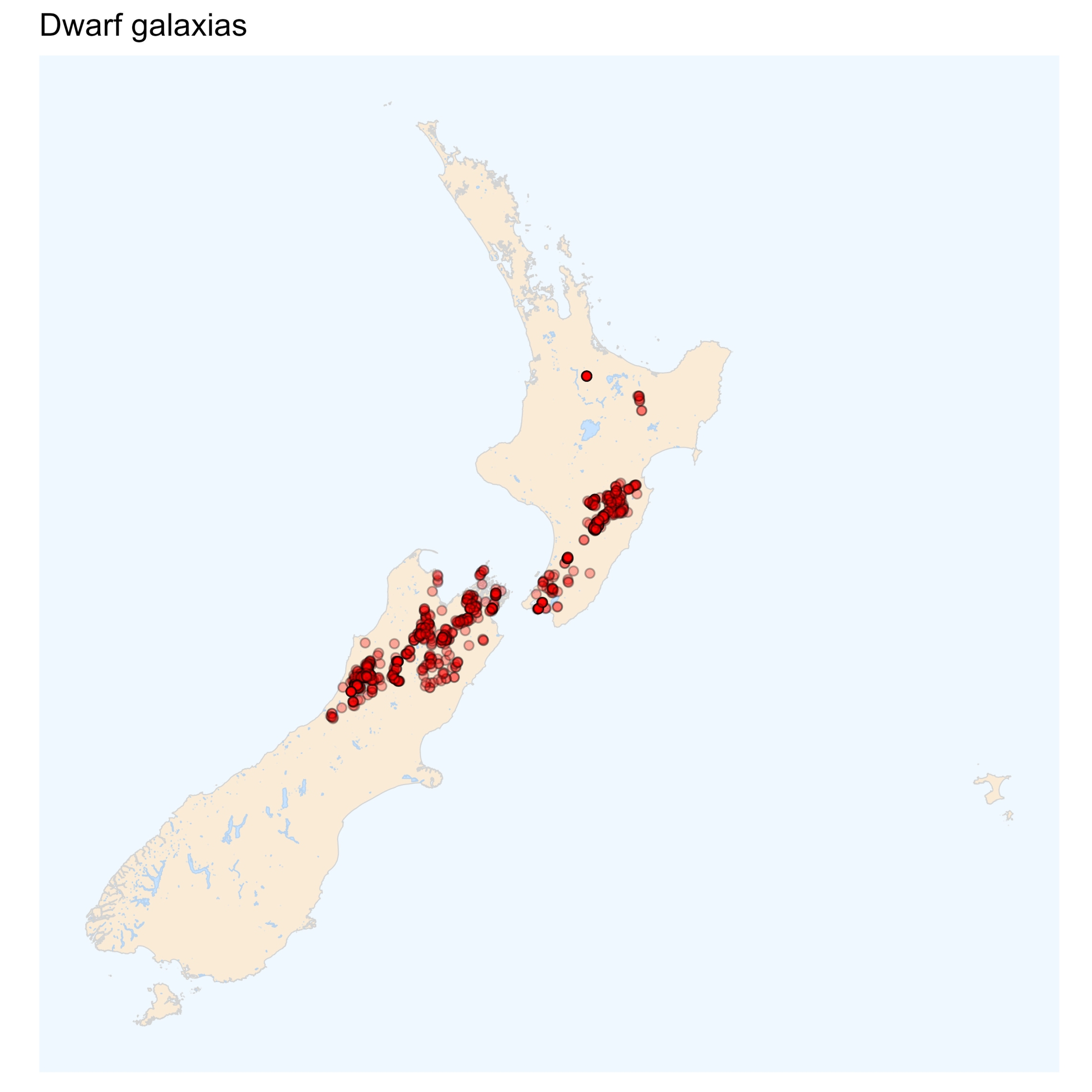
What is the non-migratory galaxiid that can be found in the Wellington region?
Dwarf galaxias

Dwarf inanga
What region are dwarf inanga found?
Northland

Eldons galaxias
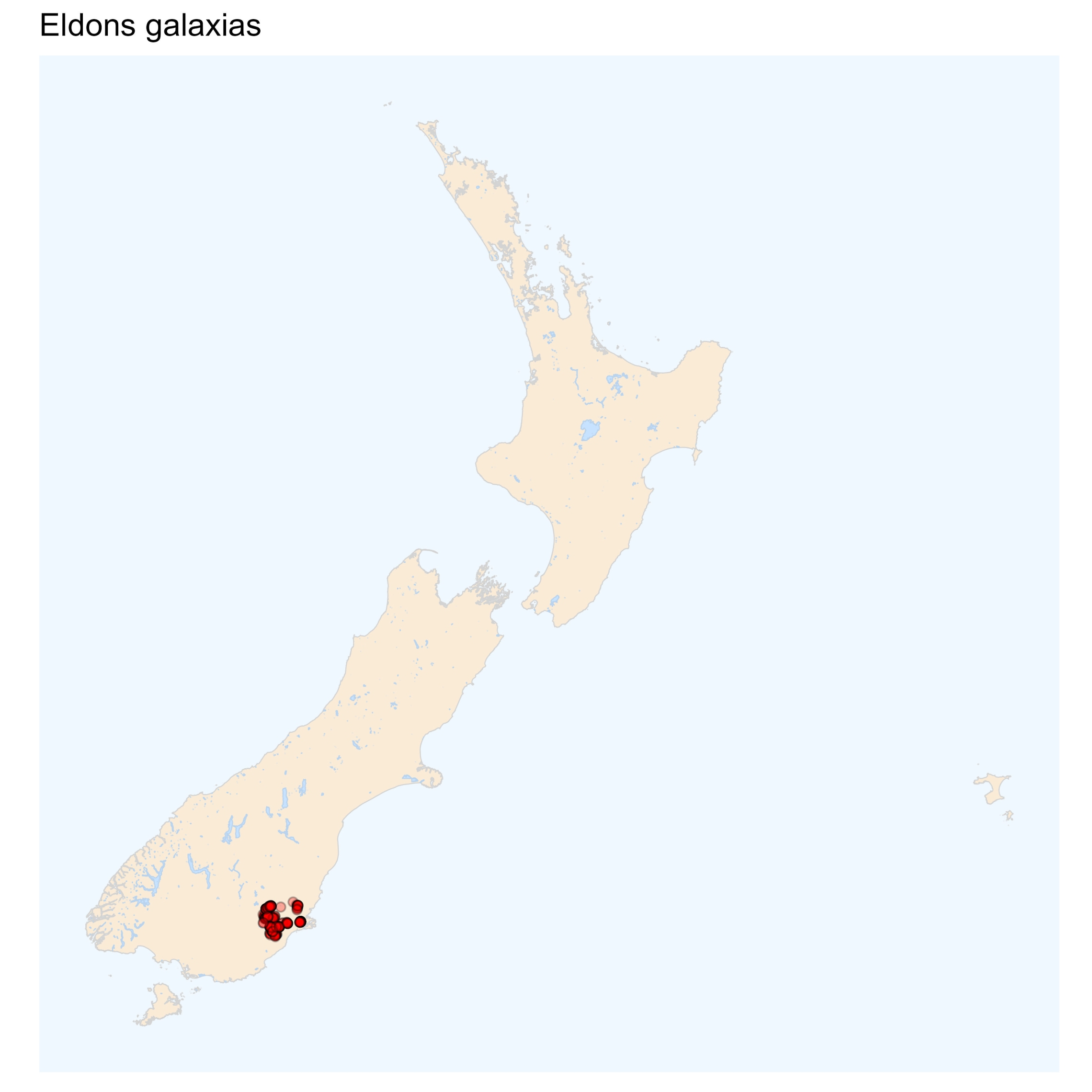
_____ galaxias closely resembles the flathead galaxias, but it has a deeper body and darker colouration, especially in large individuals. Its can also be distinguished from the flathead and other galaxiids by the number of caudal rays (15 in Eldons, 16 in the flathead, and 14 in the dusky galaxias). It shares this characteristic of 15 caudal rays with the dwarf galaxias, but their distributions do not overlap
Eldons
Of the seven species of Gobiomorphus found in New Zealand, three are strictly diadromous (bluegill, redfin, and giant bullies), while three are non-diadromous (Crans, upland, and Tarndale bullies). The _____ bully can be either.
Common