CP - Cell Structures
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
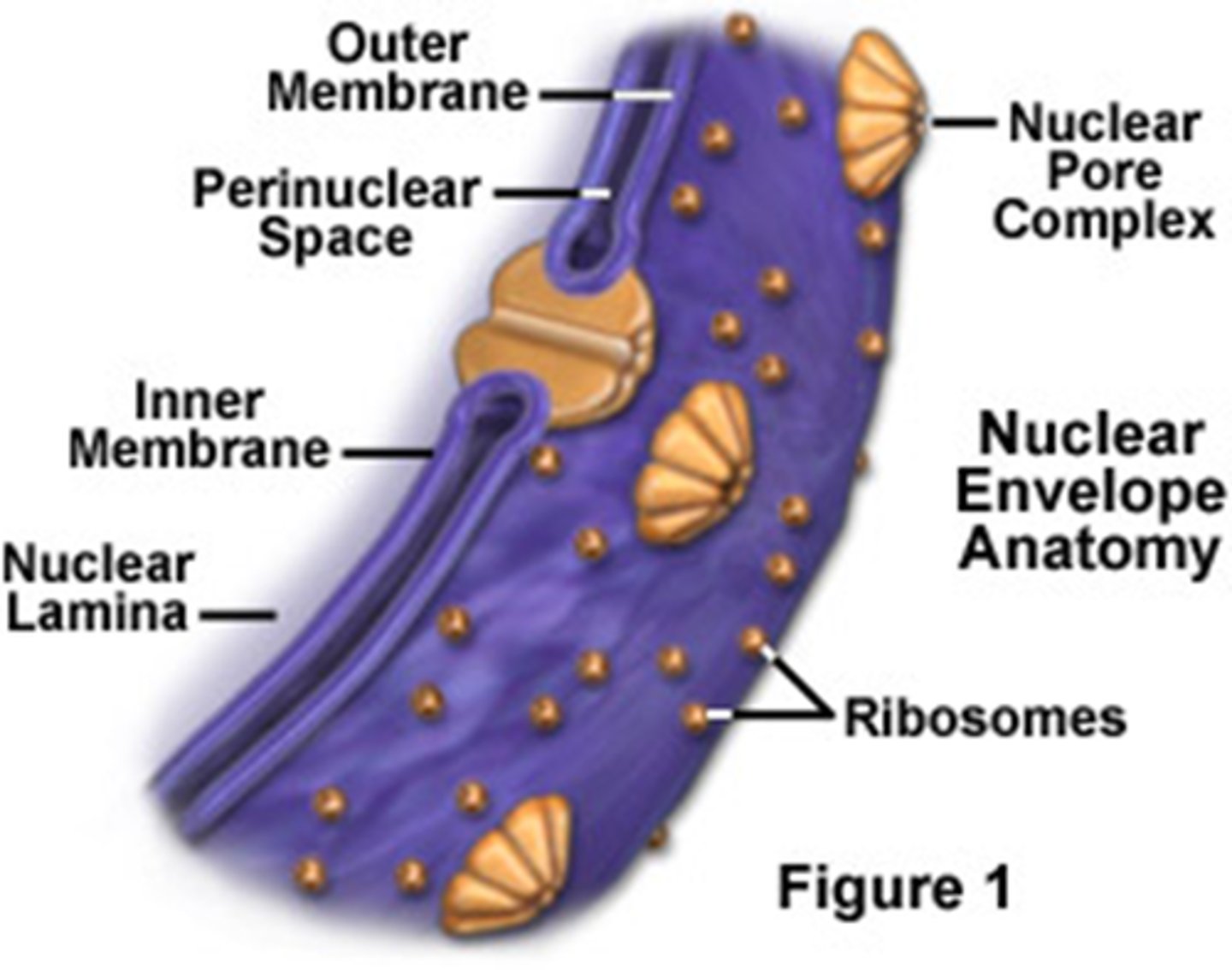
nuclear envelope
double membrane perforated with pores that control the flow of materials in and out of the nucleus
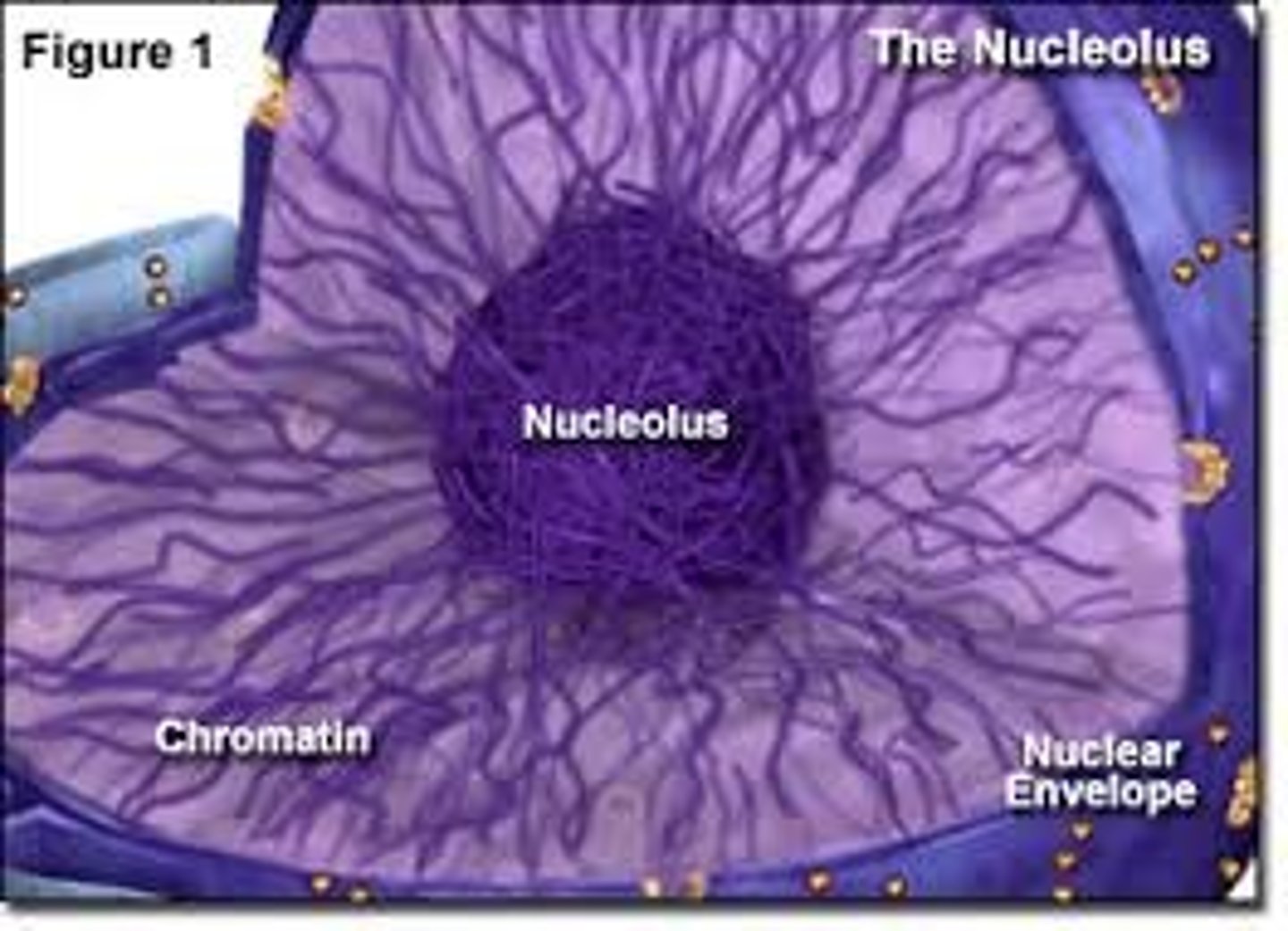
nucleolus
found inside the nucleus and produces ribosomes
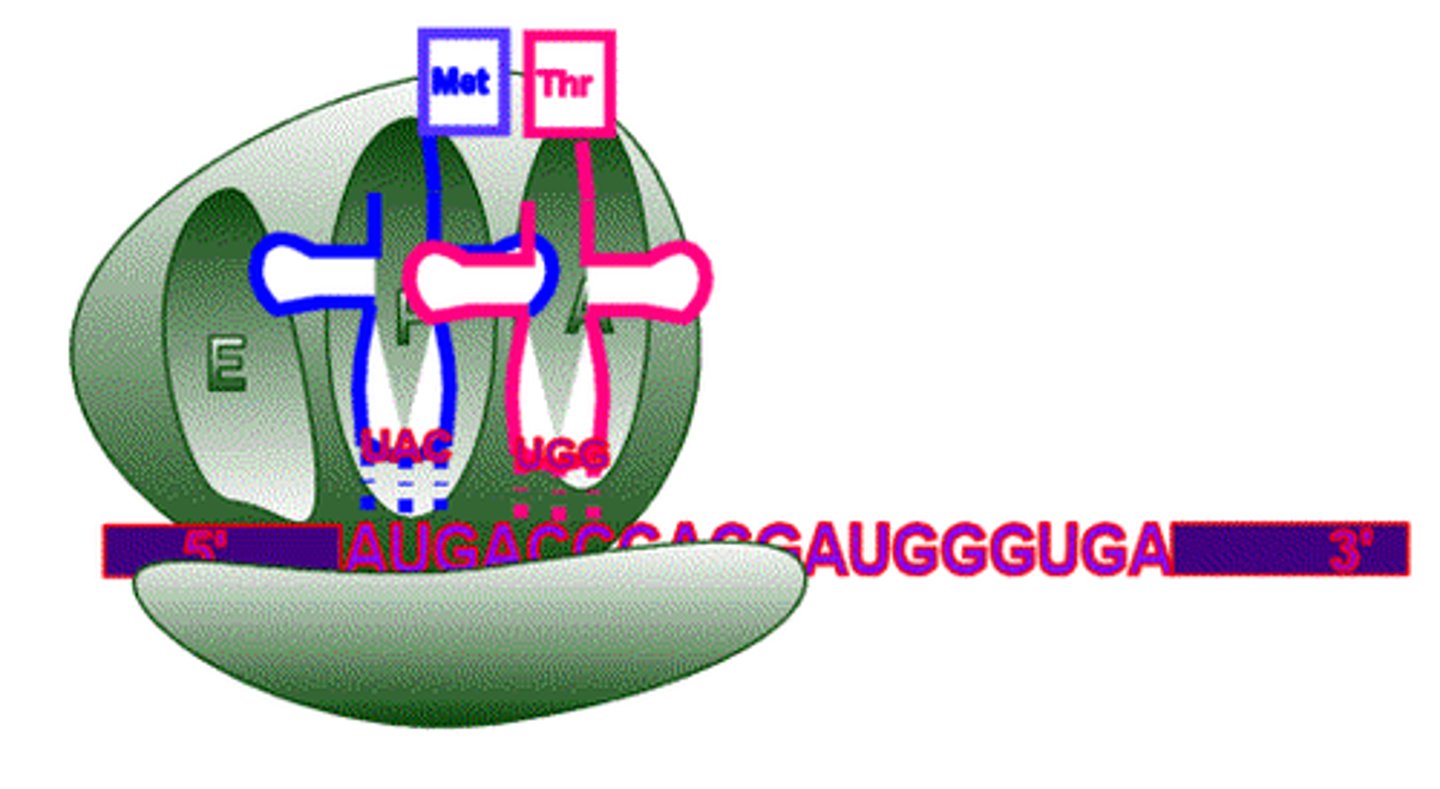
ribosome
cytoplasmic organelles at which proteins are synthesized
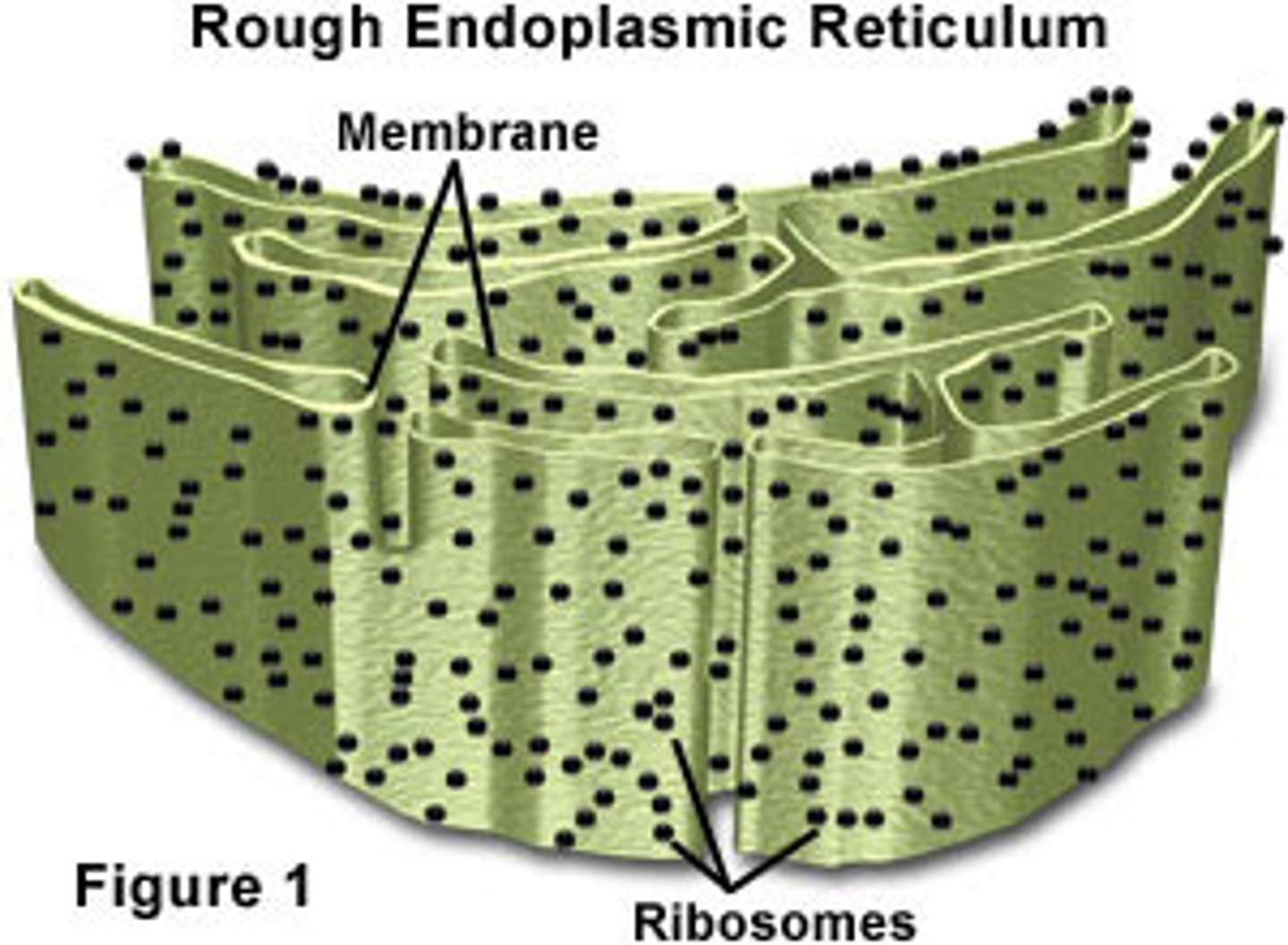
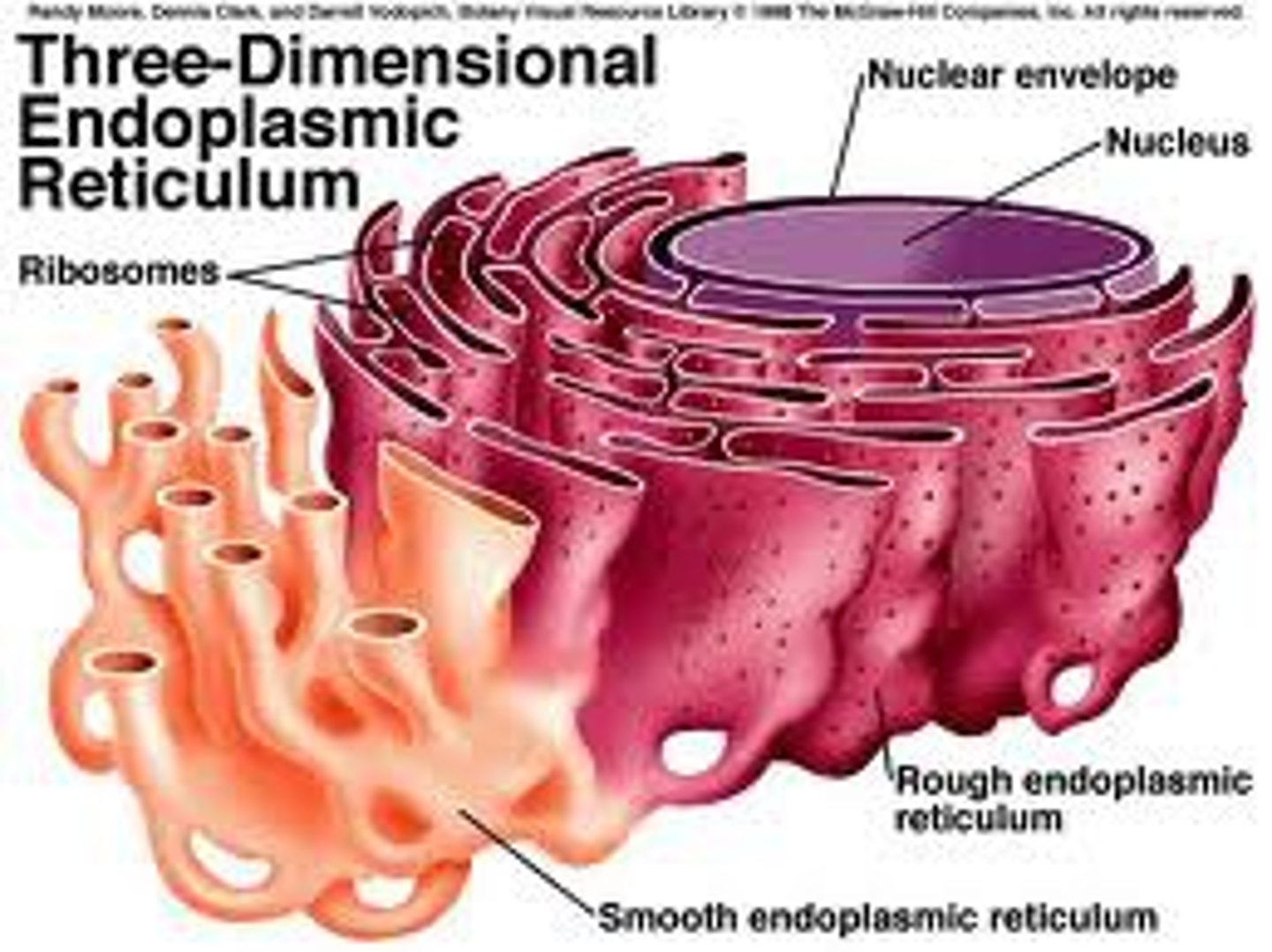
rough endoplasmic reticulum
an endomembrane system covered with ribosomes where many proteins for transport are assembled
smooth endoplasmic reticulum
an endomembrane system where lipids are synthesized, calcium levels are regulated, and toxic substances are broken down
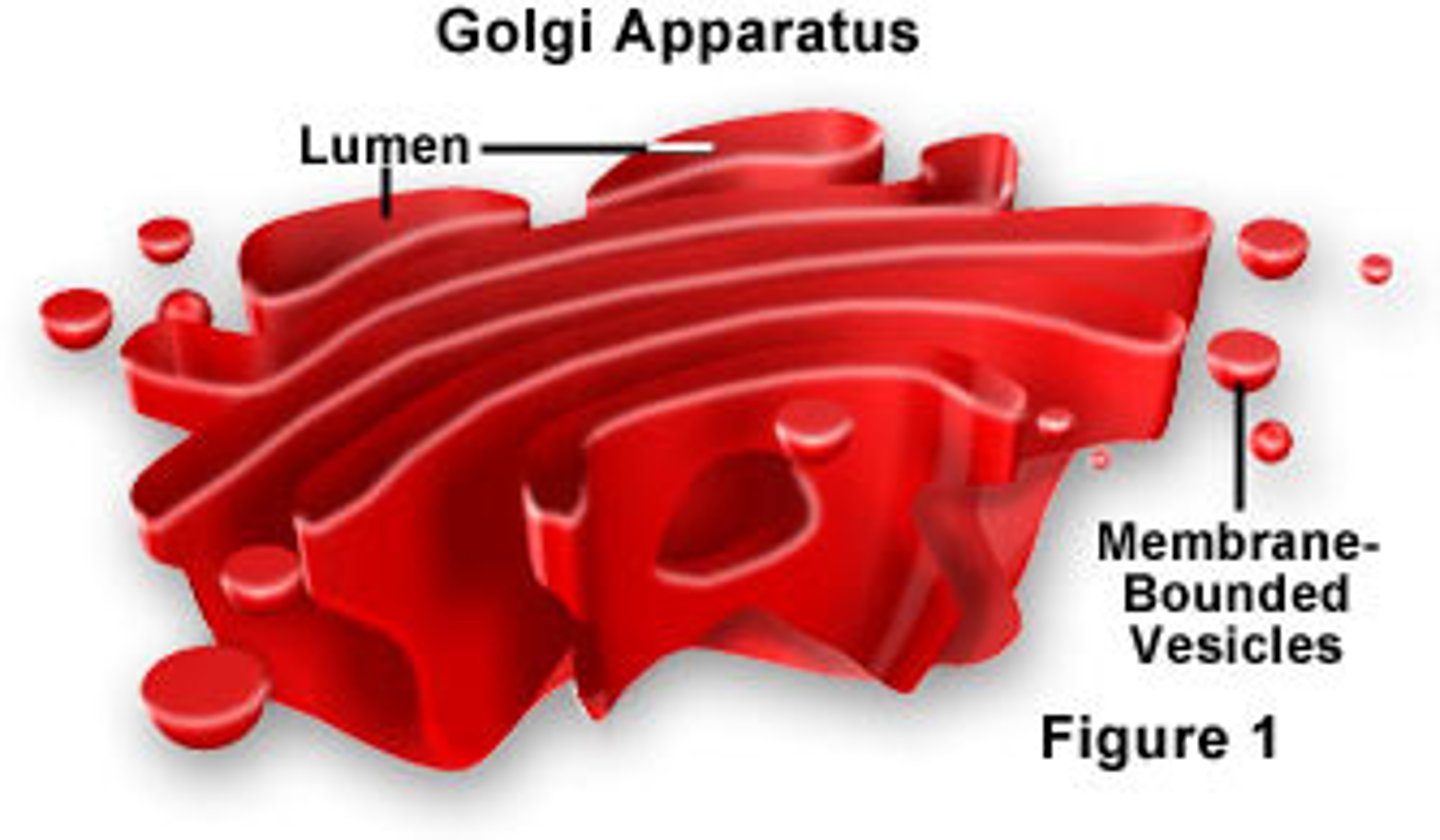
Golgi apparatus
a complex of vesicles and folded membranes within the cytoplasm of most eukaryotic cells, involved in secretion and intracellular transport
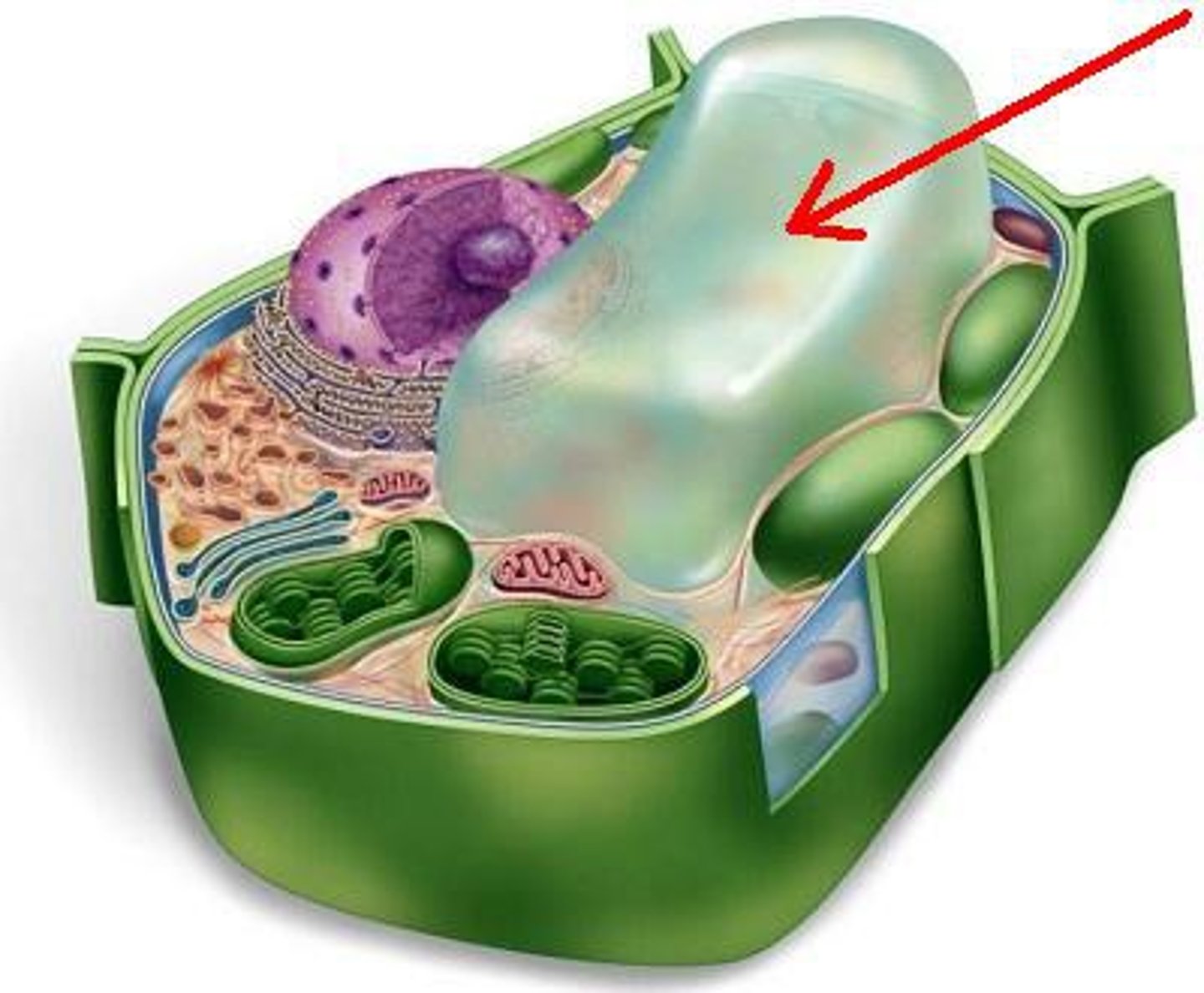
large central vacuole
found in plants, this organelle stores water for the cell
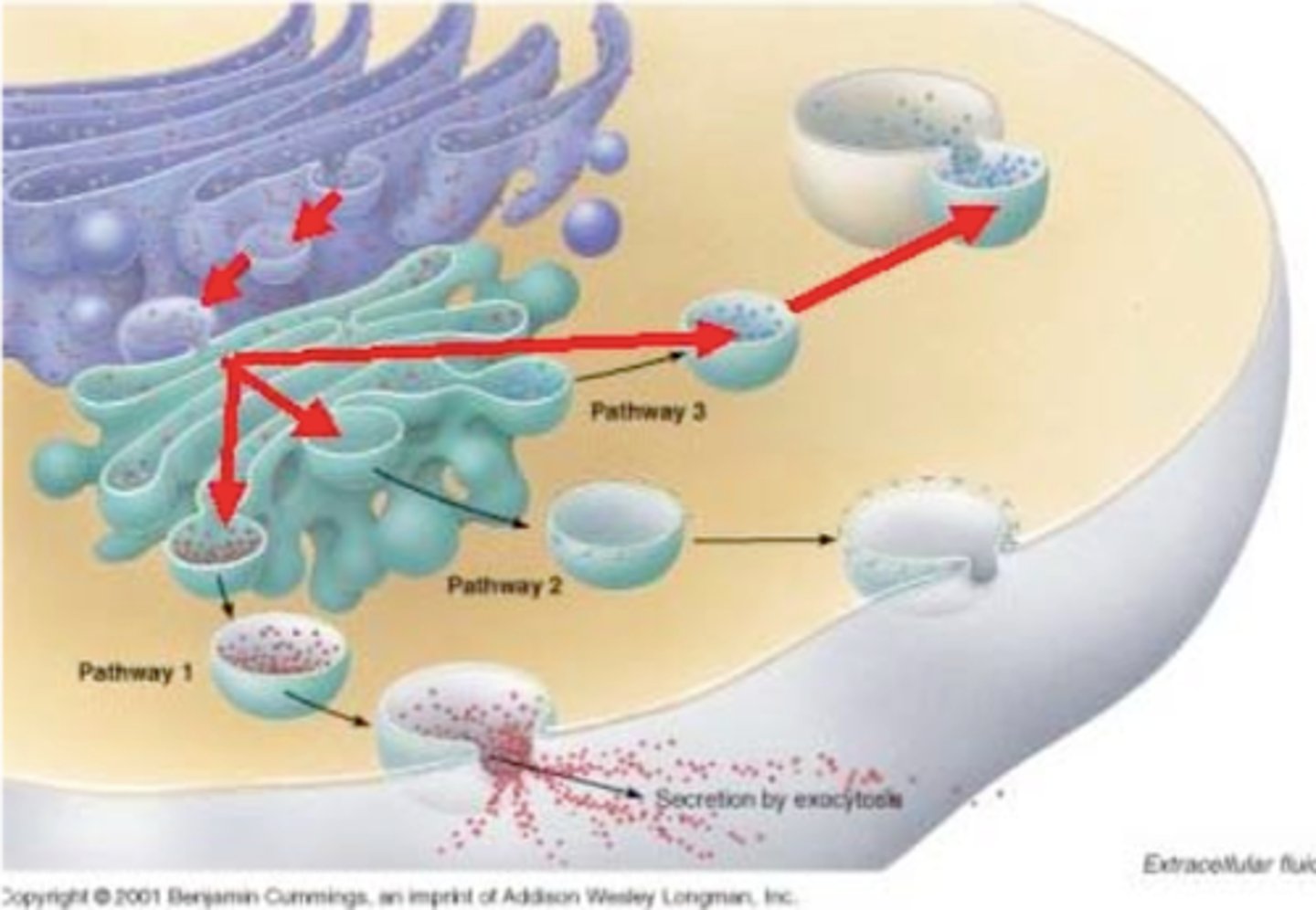
vesicle
small membrane-bound sac that functions in moving products into, out of, and within a cell
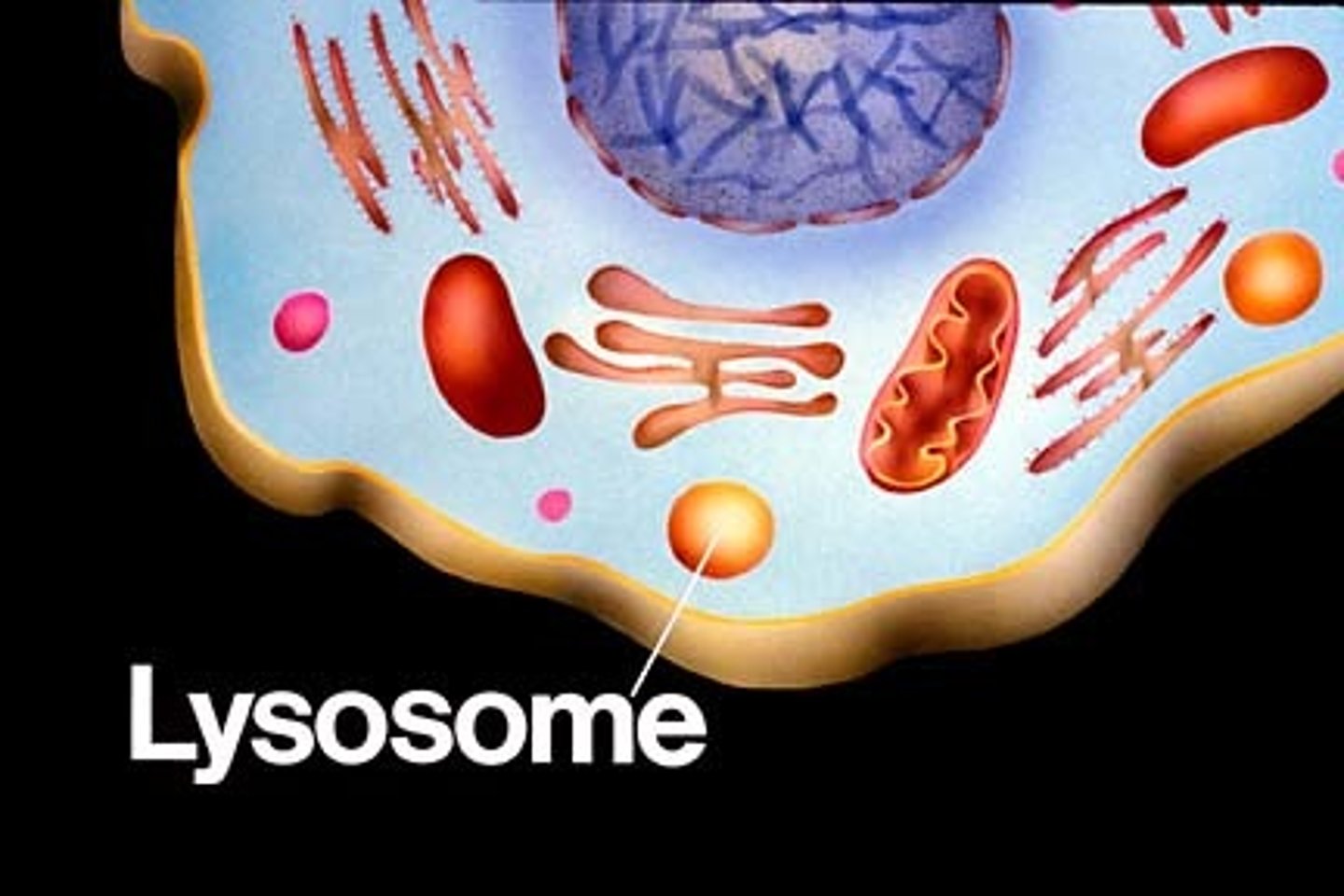
lysosome
cell organelle filled with enzymes needed to break down certain materials in the cell
cytoskeleton
a network of fibers that holds the cell together, helps the cell to keep its shape, and aids in movement
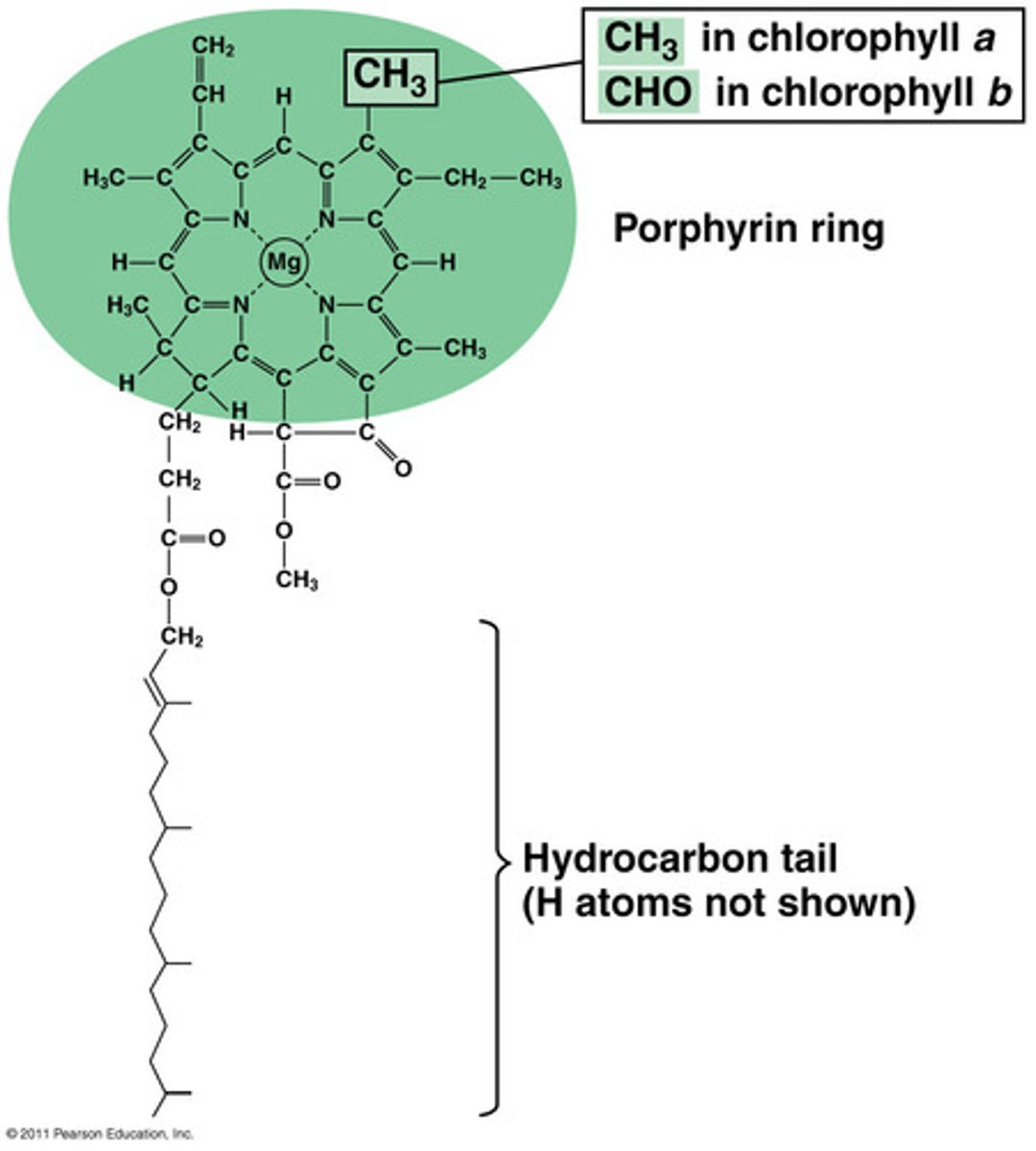
chlorophyll
a green pigment found in the chloroplasts of plants, algae, and some bacteria
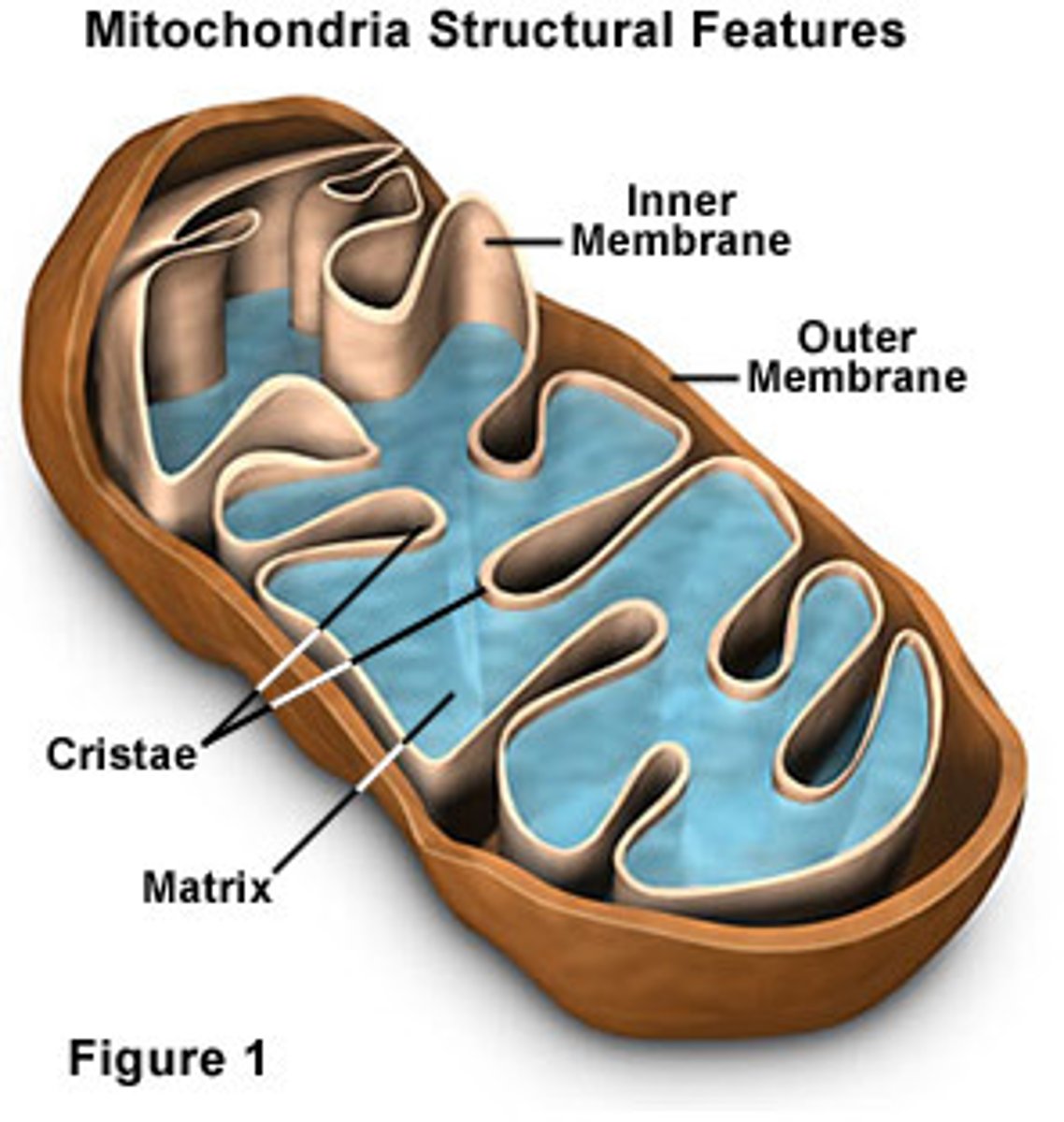
mitochondria
an organelle found in large numbers in most cells, in which the biochemical processes of respiration and energy production occur
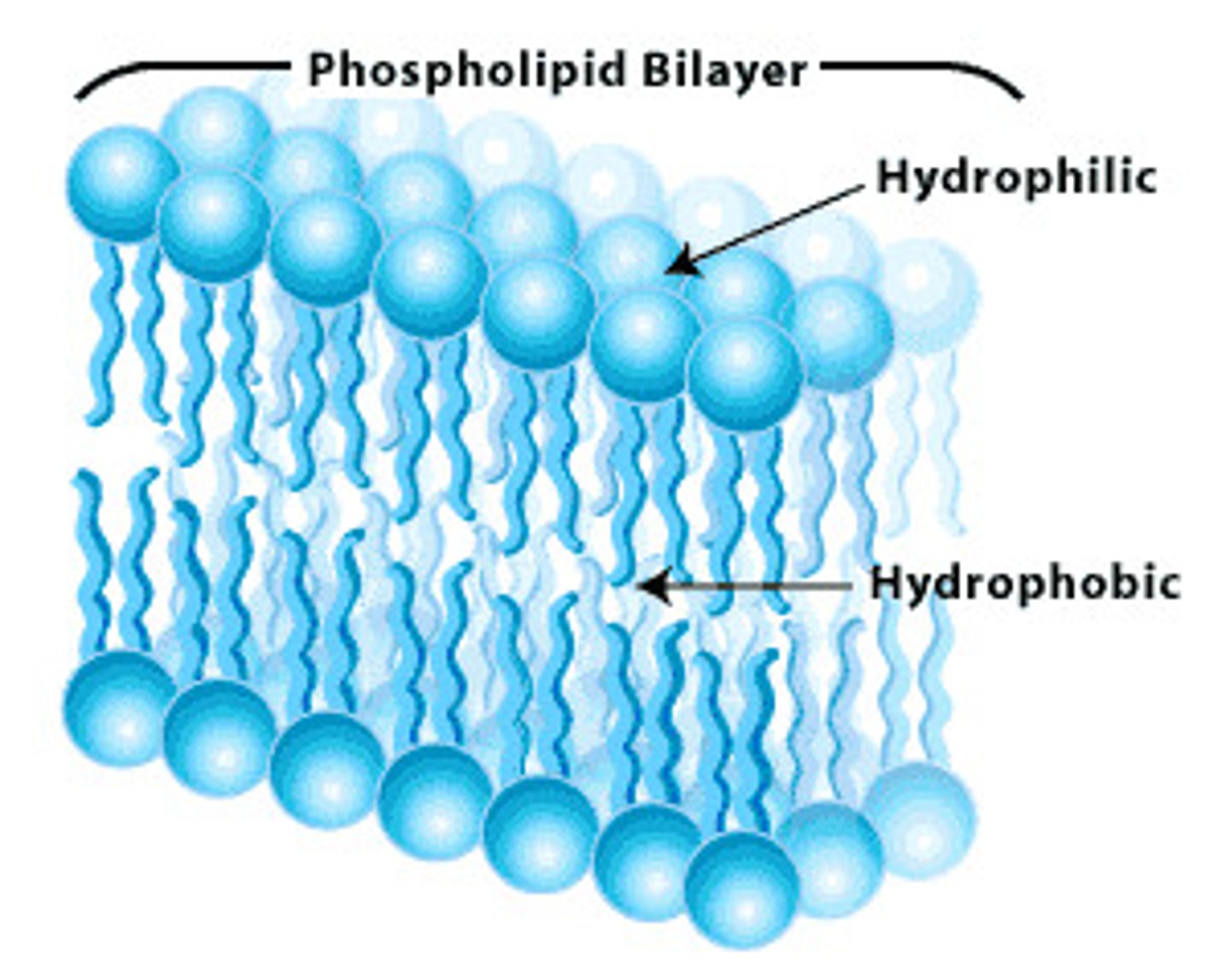
phospholipid bilayer
a two-layered arrangement of phosphate and lipid molecules that form a cell membrane, the hydrophobic lipid ends facing inward and the hydrophilic phosphate ends facing outward
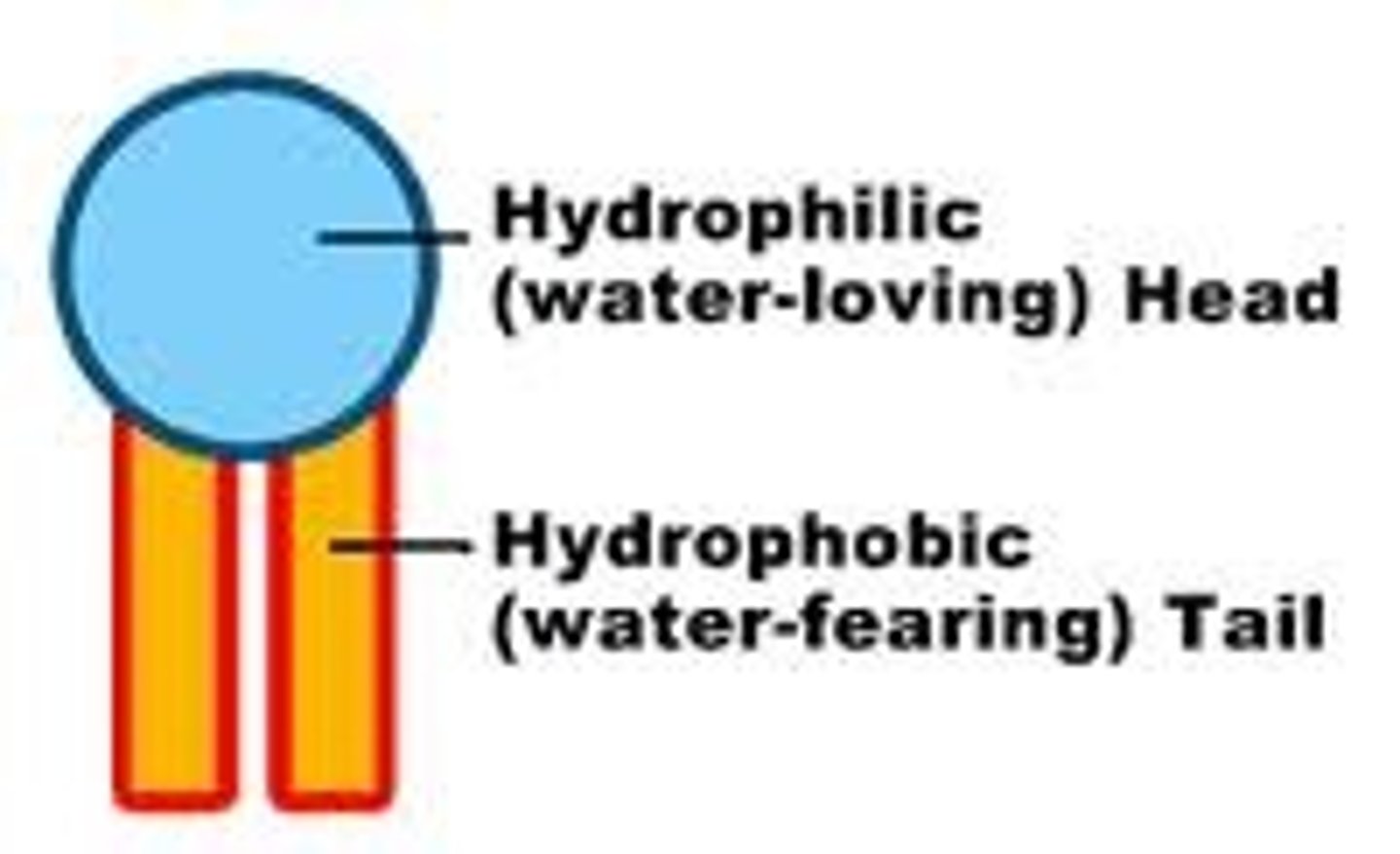
hydrophilic
having an attraction to water
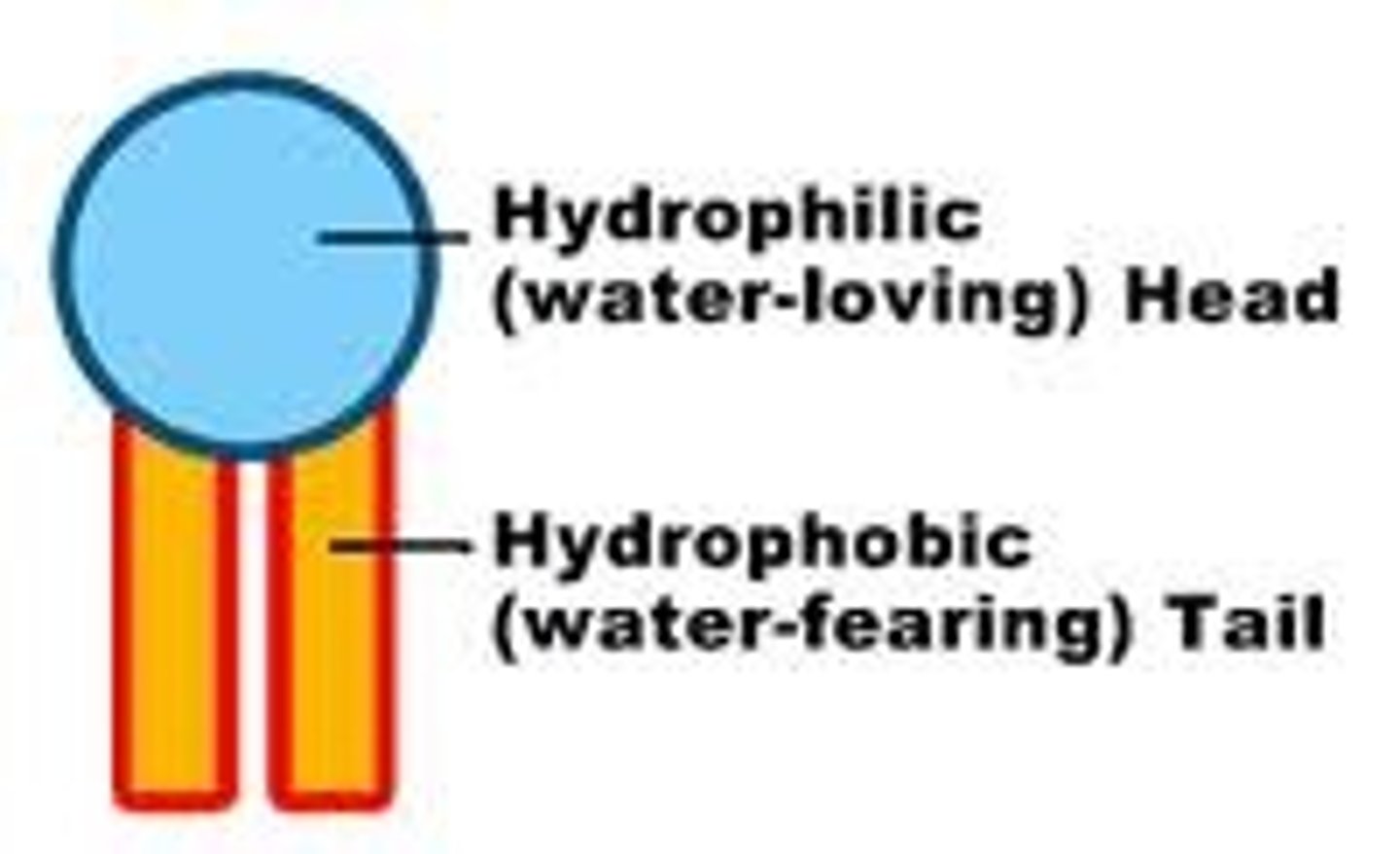
hydrophobic
having an aversion to water
selectively permeable
property of biological membranes that allows some substances to pass across it while others cannot; also called semipermeable membrane