Meteorology Exam 1 Mizzou Eric Aldrich
1/122
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
123 Terms
What are the layers of the atmosphere?
-exosphere
-thermosphere
-mesosphere
-stratosphere
-troposphere
how does temperature behave with height?
Temperature decreases with height in the troposphere.
how does pressure behave with height?
Pressure decreases with height in the atmosphere.
Almost all of Earth's weather occurs in the:
Troposphere
Soil dust, salt from ocean waves, forest fire smoke, volcanic ash particles, and pollutants are some of the aerosols found in the atmosphere.
true
The atmospheric layer in which we live is called the:
troposphere
In a volume of air near Earth's surface today, ____ occupies 78 percent and ____ nearly 21 percent.
nitrogen
oxygen
The word "weather" is defined as:
the condition of the atmosphere at a particular time and place.
The rate at which temperature decreases with increasing altitude is known as the
lapse rate
Which weather element ALWAYS decreases as we climb upward in the atmosphere?
pressure
Which atmospheric layer contains the most mixing and overturning of air?
troposphere
Water vapor can best be described as a
gas
Which statement relates to weather rather than climate?
It is cloudy and snowing outside.
In the atmosphere, advection is horizontal and convection is vertical.
true
The total amount of energy stored in an object is called
potential energy
Which of the following is the poorest conductor of heat?
air
When two objects are in direct physical contact, heat is always conducted from the _____ object to the ________ object.
warmer
colder
This is released as sensible heat during the formation of clouds:
latent heat
The temperature of a rising air parcel...
always cools due to expansion.
Sunlight passes through a thicker portion of the atmosphere at:
sunrise and sunset
The amount of heat energy required to bring about a change in temperature in a substance is called the
heat capacity
The ability or capacity to do work on some form of matter is called
energy
The temperature of a rising air parcel
always cools due to expansion.
The greatest variation in daily temperature usually occurs
at the ground.
The lowest temperature is usually observed:
around sunrise
If you are a household gardener concerned about outside flowers and plants during cold weather, you can simply wrap them in plastic or cover each with a paper cup to protect them.
true
The combination of heating and cooling degree days gives a practical indication of the energy requirements over the year.
true
The wind-chill factor
relates body heat loss with wind to an equivalent temperature with no wind.
During an equinox, the days and nights are of equal length except at the poles.
true
If clouds arrive at 2 a.m. in the middle of a calm, clear night, it is quite common to see temperatures rise after 2 a.m.
true
Which of the following latitudes is closer to the earth's axis?
90°N
One would expect the lowest temperatures to be found next to the ground on a
clear, dry, calm night
Longer days are generally associated with
more insolation
-warmer weather
The greatest variation in daily temperature usually occurs
at the ground.
The lowest temperature is usually observed:
around sunrise.
If you are a household gardener concerned about outside flowers and plants during cold weather, you can simply wrap them in plastic or cover each with a paper cup to protect them.
true
The combination of heating and cooling degree days gives a practical indication of the energy requirements over the year.
true
The wind-chill factor
relates body heat loss with wind to an equivalent temperature with no wind.
During an equinox, the days and nights are of equal length except at the poles.
true
If clouds arrive at 2 a.m. in the middle of a calm, clear night, it is quite common to see temperatures rise after 2 a.m.
true
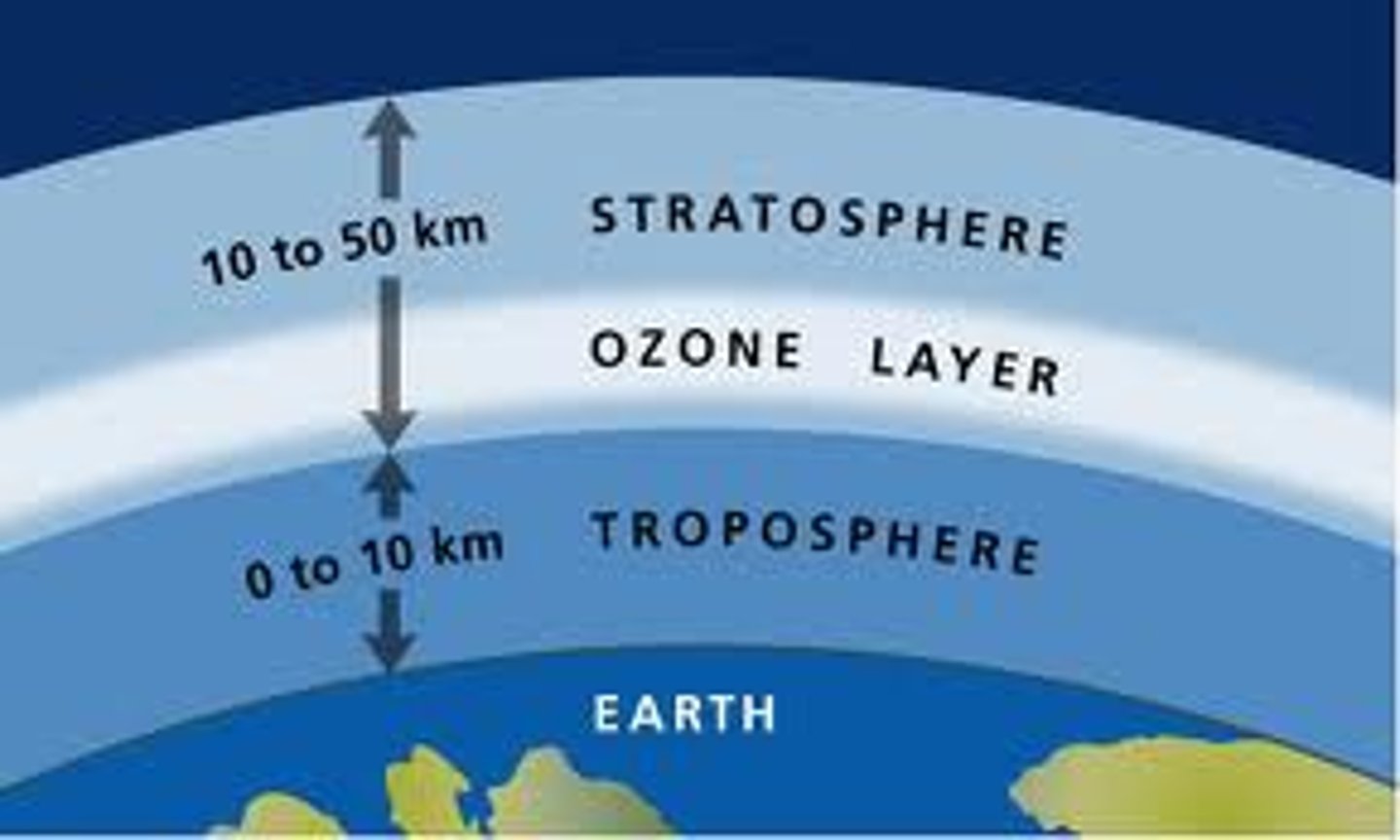
Troposphere
-temperature decreases with height because the troposphere is heated by the surface and notdirectly by sunlight
-From the surface up to about 6-10 miles.
-varies with latitude and season
-higher in the summer and in the
tropics
-Almost all of what we call "weather" occurs in the troposphere
-80% of the atmosphere's mass.
stratosphere
-Temperature increases with height because the ozone layer absorbs ultraviolet light and warms up as a result.
-Lack of mixing and turbulence
-Layered portion of atmosphere ("strata").
-Very little mixing occurs between the stratosphere and troposphere (except with thunderstorms and other strong storms).
-99.9% of the atmospheric mass resides below the stratopause
mesosphere
-temperature decreases with height
-This is layer is often referred to as the cold layer, as the lowest readings in the atmosphere are found here.
thermosphere
-temperature increases increases with height
-The uppermost layer of the atmosphere
-often considered the "hot layer" because it contains the warmest temperatures in the atmosphere.
-because the air is so thin, our bodies would not be able to detect this heat
Ionosphere
(charged gas atoms) that can reflect radio waves is found here, as are the aurora.

exosphere
Upper limit of our atmosphere (space begins here - ~350 miles).
Tropopause separates...
troposphere and stratosphere
Stratopause separates...
stratosphere and mesophere
mesopause separates...
mesosphere and thermosphere
What is the standard Lapse Rate of the troposphere?
6.5°C per 1000m
What is the lapse rate?
The rate at which temperature decreases with height
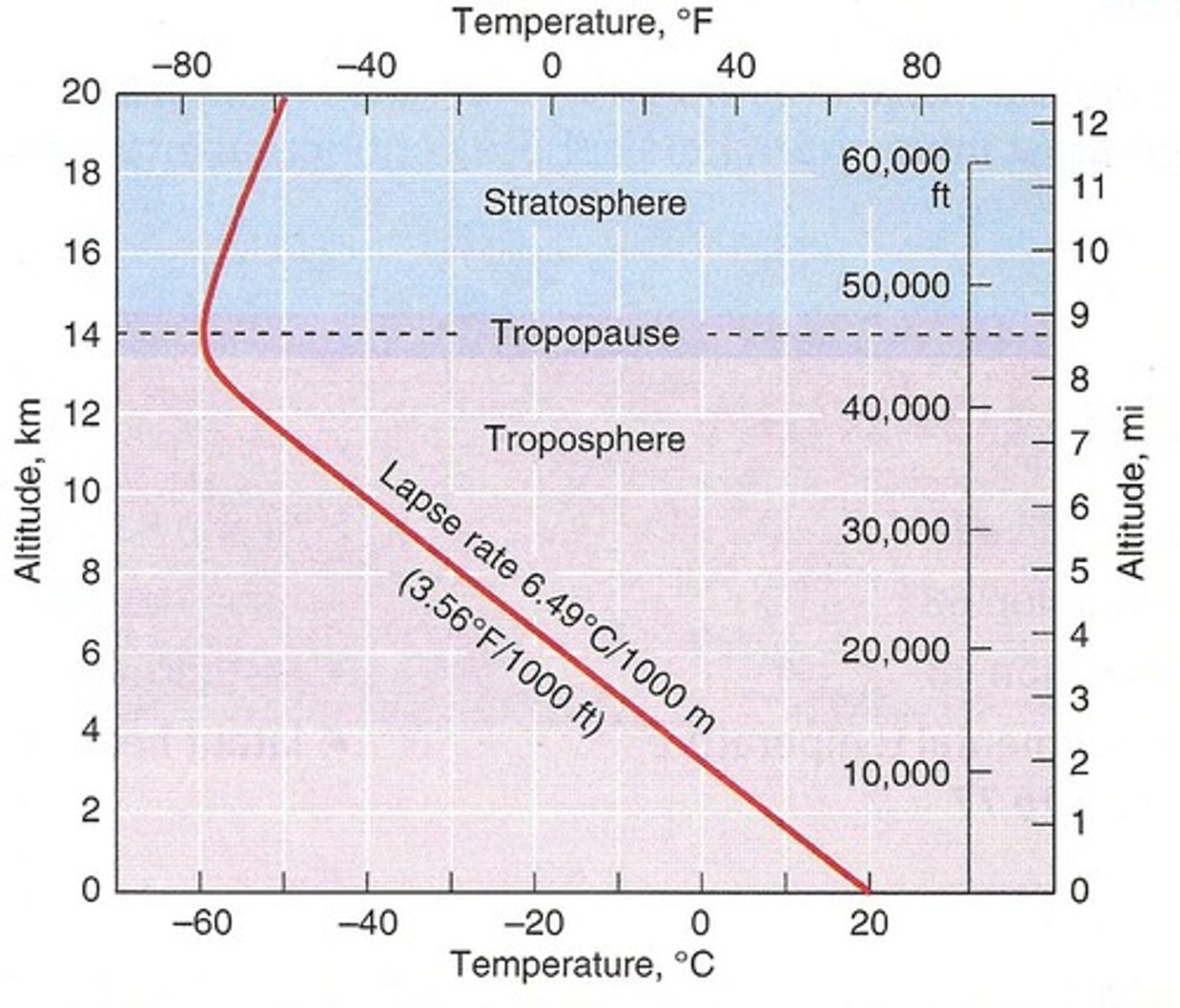
What is inversion?
Where the temperature increases with height
Pressure is...
the force exerted on a given area
Air pressure results when...
air molecules move and collide with objects.
Air pressure is exerted in...
all directions.
Atmospheric pressure always...
decreases with increasing altitude (height).
The pressure, density, and temperature of a gas are...
all related to each other.
The atmosphere can be divided up according to...
pressure (500 mb layer is about halfway up in the atmosphere).
-or temperature (does not follow a simple relationship with height)
meteorology
study of weather
-how weather impacts with life on earth
climatology
study of climate, past climate conditions & future
-how different weather changes over time
weather
the condition of the atmosphere at any particular time and place
-temperature
-humidity
-pressure
-windspeed
-cloud coverage
-visibility
climate
condition of the atmosphere over many years
what makes the northern and southern hemispheres different?
-The Northern Hemisphere lies above the equator
x north of the equator
-summer solstice (usually June 21) until the autumnal equinox (typically Sept. 21).
-Winter takes place from the winter solstice (usually Dec. 22) until the vernal equinox (usually March 20).
-the Southern Hemisphere lies below the equator
x south of equator
-Summer in the Southern Hemisphere typically takes place between Dec. 22 and March 20
-winter season typically lasts between June 21 and Sept. 21.
Why do we have seasons?
tilt of the earth's axis
(not changing distance from the sun)
How does sunlight differ from season to season at certain latitudes?
-The higher latitudes of the middle latitudes will have more of a difference such as 8 hours of sunlight in winter and 16 hours of sunlight in summer.
-The lower latitudes of the middle latitudes will have less of a difference such as 11 hours of sunlight in winter and 13 hours of sunlight in summer.
what are the 4 controls of temperature?
-latitude
-land and water distribution
-ocean currents
-elevation
Latitude
-on average, temperatures decrease over land Masses s we move from the equator to the poles
-lower sun angles and shorter days over the poles
Land and Water Distribution
-water has high heat capacity
-water distributes heat through its depth
-areas near coastlines benefit from warm water in winter and cool water in the summer
-water moderates local climate
x sea or lake breeze
oceans act as huge heat reservoirs
Ocean Currents
-transport warmer water near equator
-Ex: Gulf Stream moves warm water near Caribbean toward North
Elevation
-air density decreases with elevation
-fewer air molecules to warmer by conduction
weight
force acting on an object due to gravity
-weight=mass x gravity
Mass
quantity of matter in object
density
amount of mass in a given space (volume)
-density=mass / volume
Carbon Dioxide
-makes up .0038% (by volume) fo earths atmosphere
-enters by: decay of vegetation, volcanic eruptions, exhalation of animals
-removed by: photosynthesis, vegetation, ocean
how do clouds form? ("the 3 C's")
-cool air
-condense air
-cloud forms
ozone
-makes up .01% (by volume) of earths atmosphere
-beneficial: absorb radiation, provides natural shield for living things
-harmful: eye irritation, throat irritation, vegetation damage
methane
-makes up .0001% (by volume) of earths atmosphere
-beneficial: effective absorber of thermal radiation emitted by earths surface
-sources: coal mines, livestock, rice fields, gas pipelines
-methane has been increasing by 1% for the past 20-30 years
Aerosols
-suspended solid and liquid particles in the air
-such as: dust, salt particles, ash (from forest fires and volcanos)
pollutants
-gasses and aerosols in concentration great enough to cause a nuisance/health hazards
-EX: auto & fuel emissions
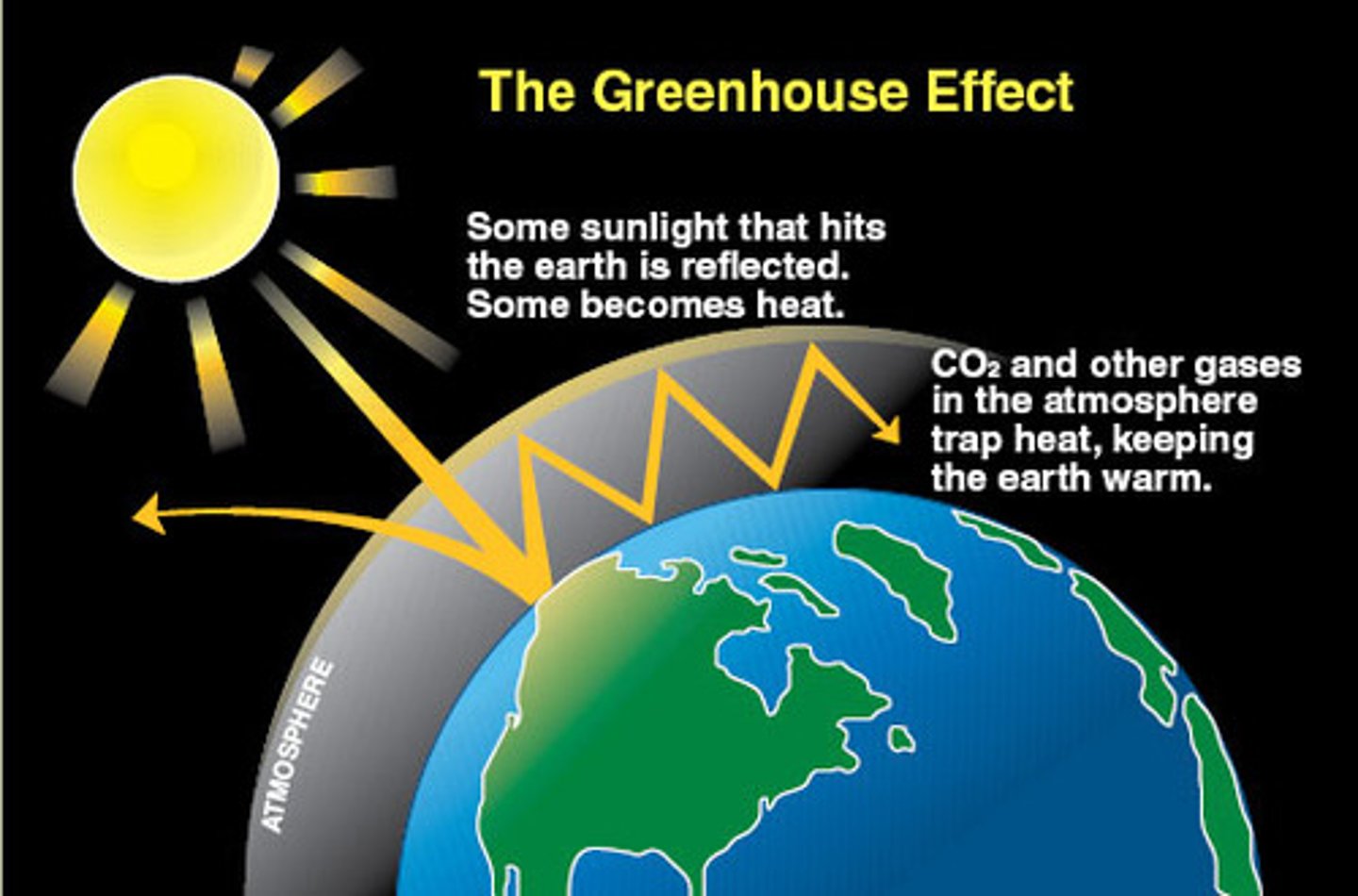
What is the greenhouse effect?
the trapping of the sun's warmth in a planet's lower atmosphere, due to the greater transparency of the atmosphere to visible radiation from the sun than to infrared radiation emitted from the planet's surface.
what are the 3 temperature scales?
-Fahrenheit
-Celsius
-Kelvin
What are the sources of energy for the earth and atmosphere?
-solar energy
-gravity
-radioactive decay
-the rotation of the Earth
what takes up most of atmosphere
nitrogen
more molecules equals...
greater pressure
fewer molecules equals...
lower pressure
pressure is isotropic---
force exerted equally in all directions
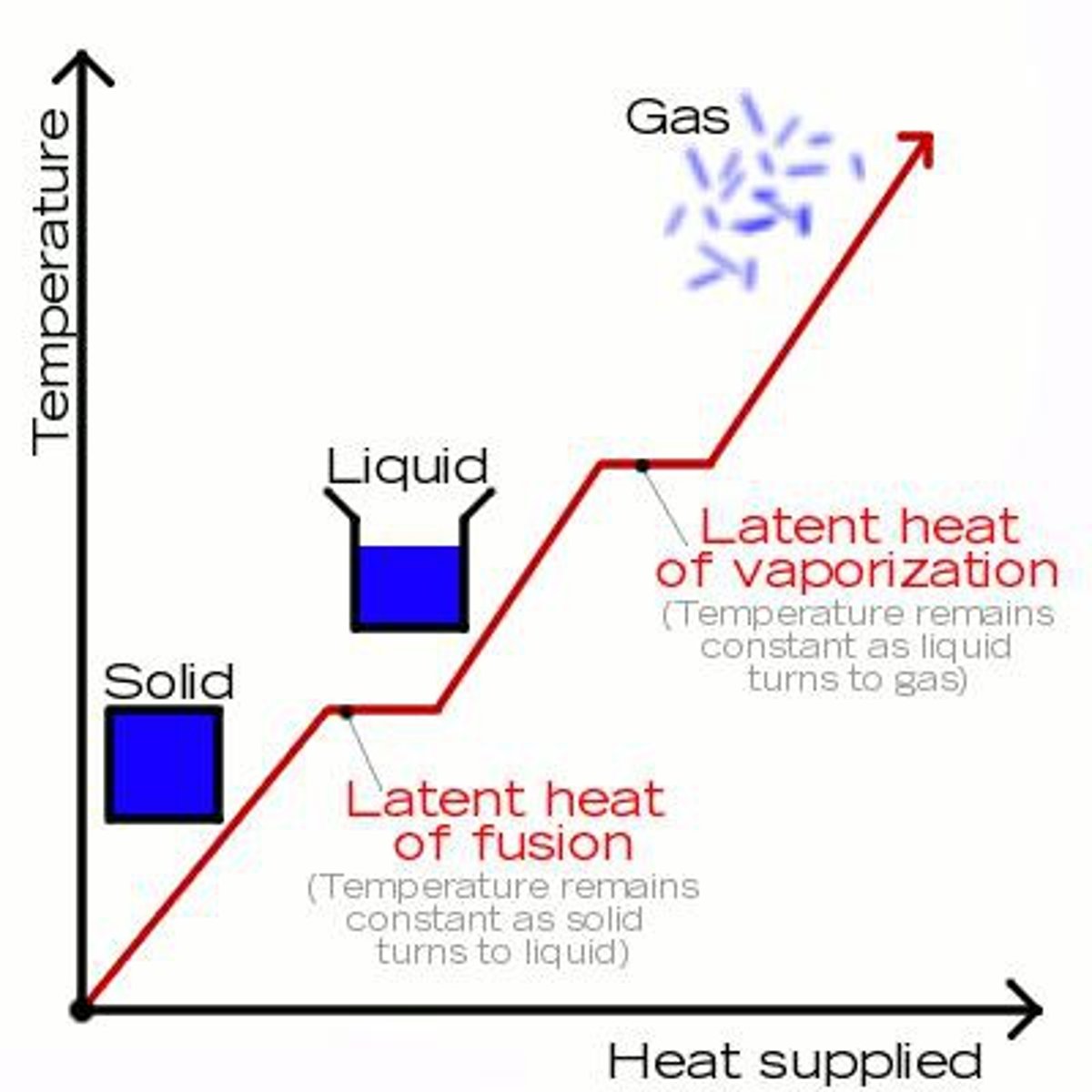
Melting
becoming liquefied by heat.
freezing
-freezing point of water
-below 32°F (0°C).
sublimation
the transition of a substance directly from the solid to the gas phase, without passing through the intermediate liquid phase

deposition
the geological process in which sediments, soil and rocks are added to a landform or land mass.
evaporation
-the process by which water changes from a liquid to a gas or vapor
-takes up heat from environment = cooling process

condensation
-the conversion of a vapor or gas to a liquid.
-gives off heat from environment = warming process

latent heat
-heat energy required to change a substance from one state to another
-water vapor is an invisible gas that becomes visible when changes into liquid/ice particles
-important source of atmospheric energy
specific heat
The heat capacity of a substance per unit mass. The amount of heat required to raise the temperature of
1 g. of that substance 1°C.
heat capacity
Ratio of the amount of heat energy absorbed by a substance to its corresponding temperature rise
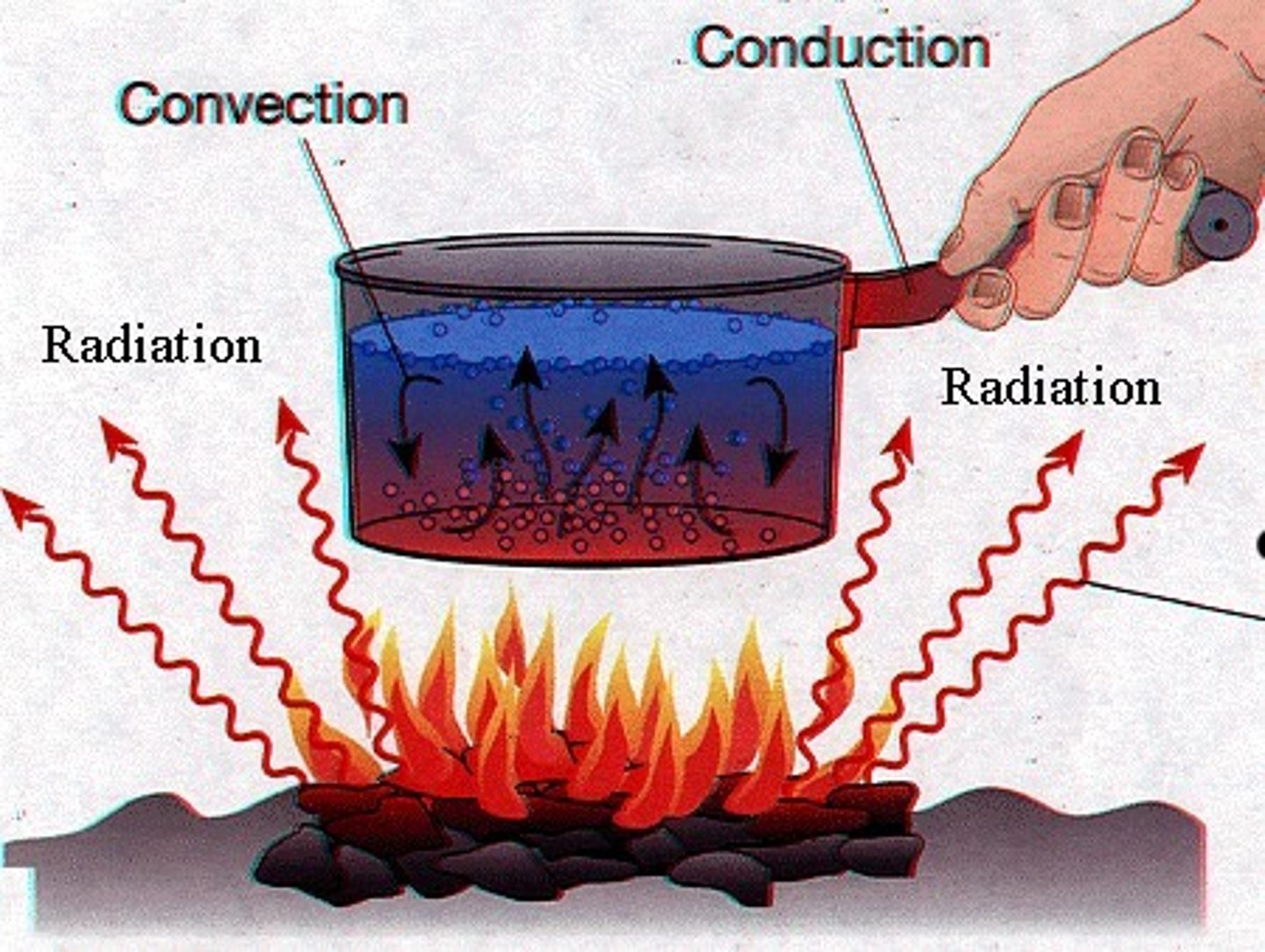
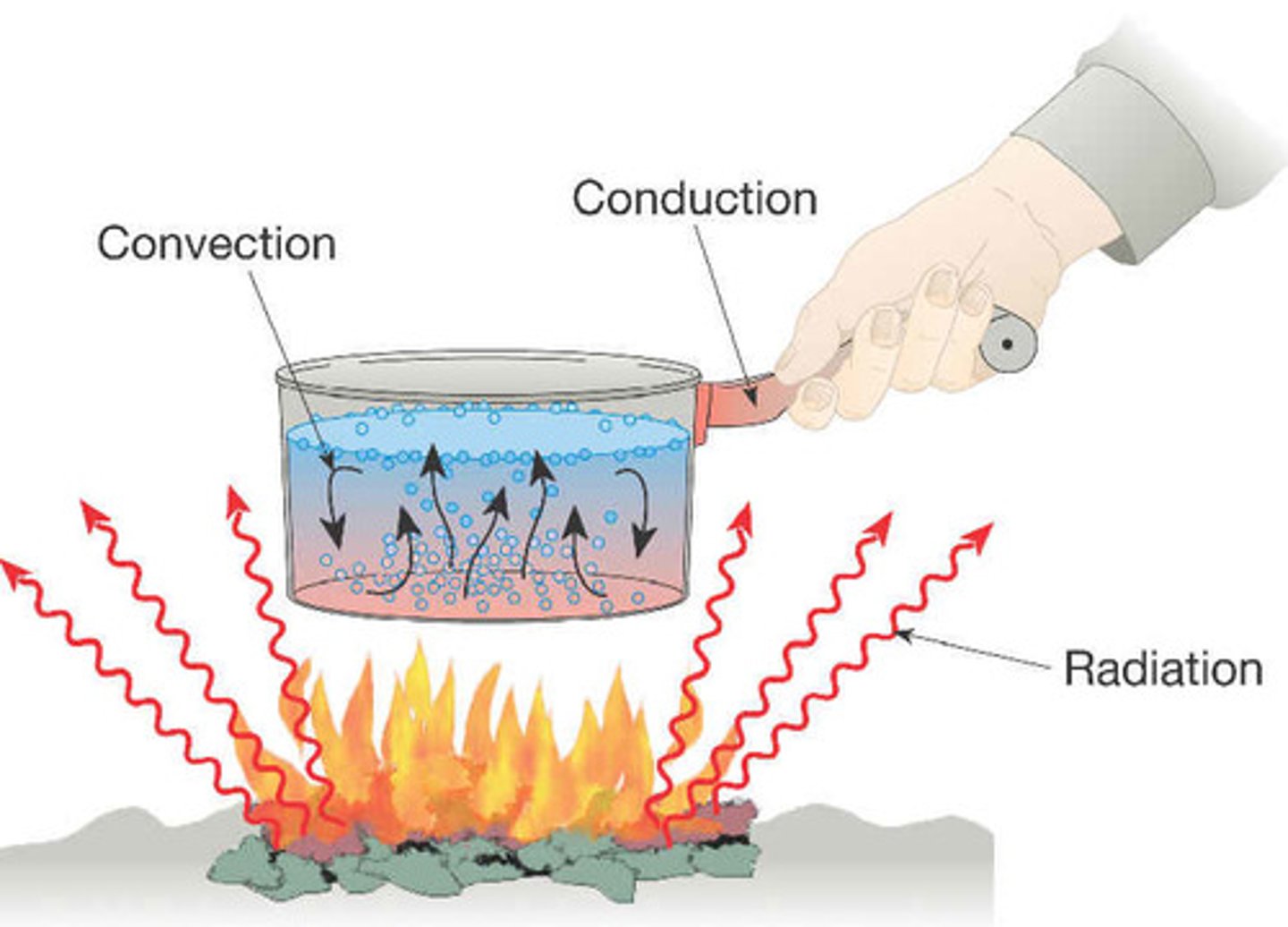
conduction
-requires two objects to touch
-Not important in the atmosphere except near the ground.
-The air is not heated directly by the sun, but it gets its energy from the heated ground below (and gets the energy by conduction).
-amount of heat transferred depends on:
-temperature difference between 2 objects
-thermal conductivity between 2 objects
-water is a good conductor
-air is a poor conductor
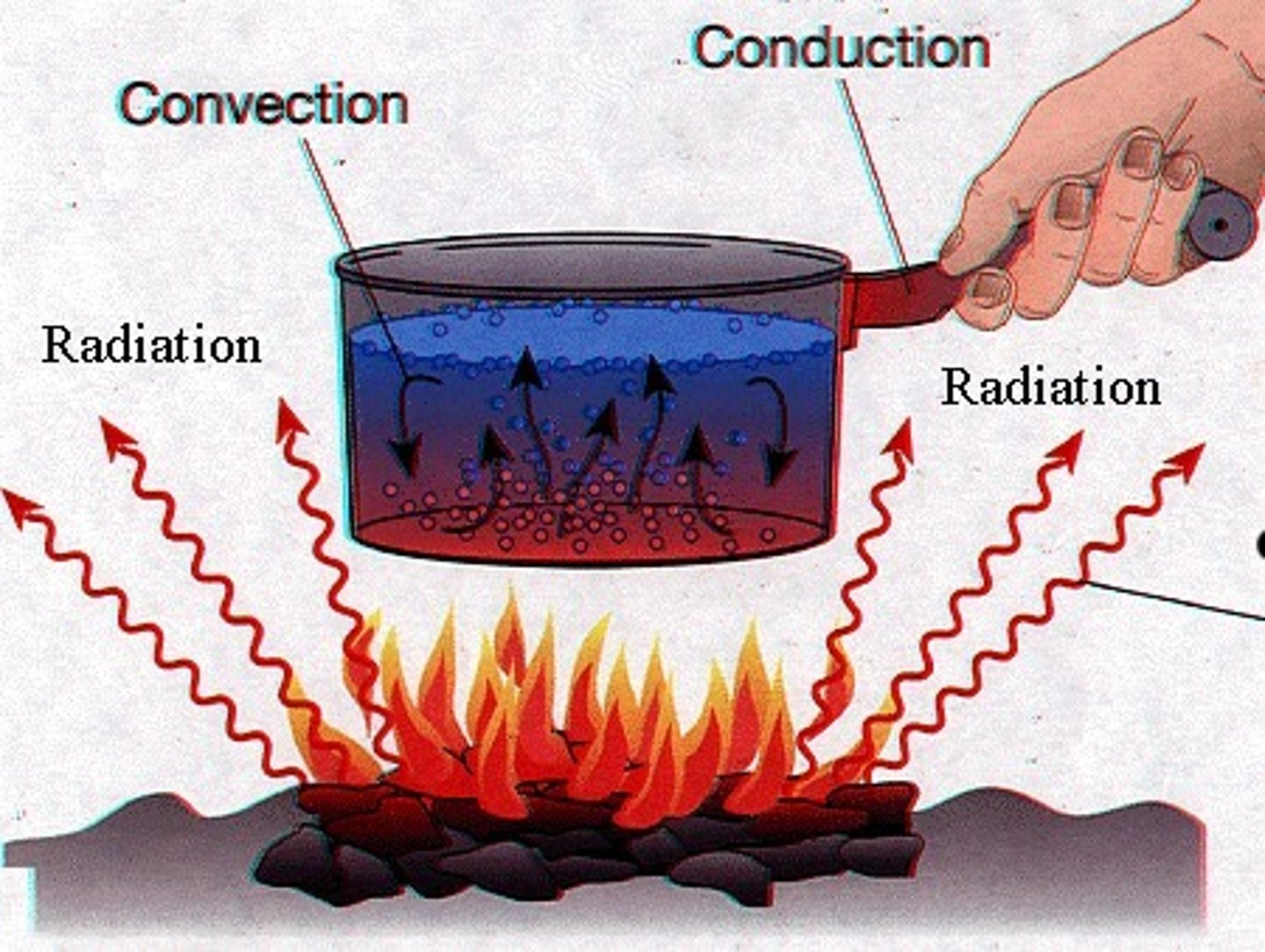
Convection
-VERTICAL transfer of heat by movement of a fluid
-Air is heated at the surface by conduction.
-A heated air parcel rises vertically upward.
-Cooler parcels replace the rising parcel.
-rising thermals and thunderstorms are 2 examples of convection in atmosphere
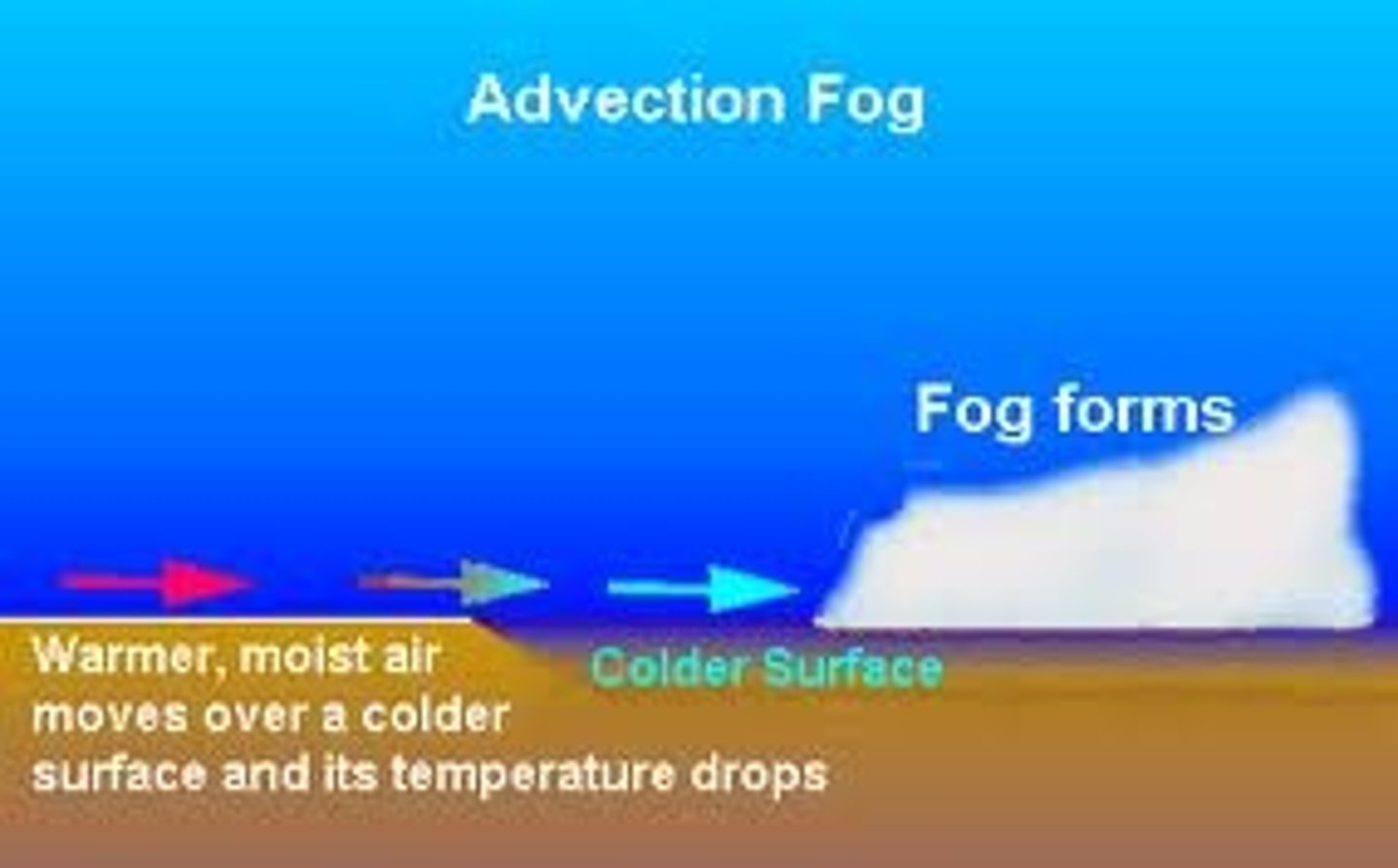
advection
-HORIZONTAL transfer of heat via mass movement of a fluid
-heating by wind
-Example:
Wind blowing across a body of water will "pick-up" water vapor and transport it. If the air cools, the water vapor may condense into cloud droplets and release latent heat.
Radiation
-Energy which travels in the form of waves, and is released when the waves are absorbed by an object
electromagnetic waves
means by which radiation is transmitted