Mass transport in plants (xylem)
1/11
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
12 Terms
What are the two parts of a plant involved in mass transport of substances and what do they transport?
Xylem → transport of water and mineral ions from the roots up to the leaves.
Phloem → transport of food substances (sugars) from where they are produced in the leaves by photosynthesis to parts of the plant that need it for respiration (all cells).
What functions does water have in plants?
Cell turgidity
Metabolite in photosynthesis
Hydrolysis reactions
Transporting inorganic ions
How is water and mineral ions absorbed in the roots?
Through root hair cells, water moves in by osmosis down a water potential gradient.
Mineral ions are taken in by active transport.
What are some features of root hair cells?
They’re extensions on some of the root epidermal cells and have a thin cell wall (short diffusion pathway), large SA and lots of mitochondria (release ATP which provides energy for active transport of mineral ions).
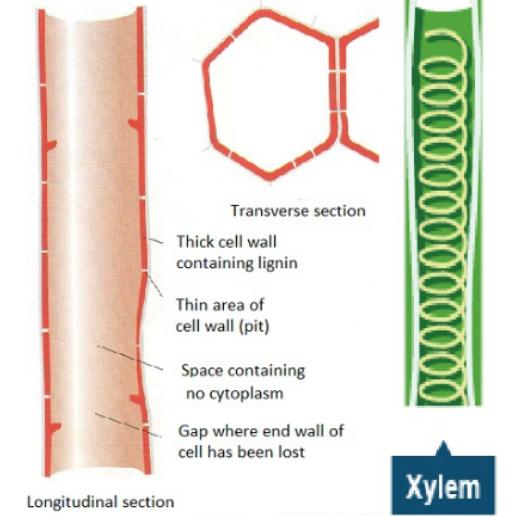
Describe the structure of a xylem vessel.
Hollow/continuous because the cells have no end walls.
Lignified as the cells that make up the xylem mature, a substance called lignin builds up in their cell walls;
This causes the cells to die and lose their end walls, cytoplasm and organelles making it a long continuous tube.
The lignin often forms in rings or spirals/helices and makes the xylem very rigid.
Describe how water moves through the xylem.
Pulling force (transpiration stream)- bulk transport of water up the stem of a plant through the xylem vessels, due to evaporation of water from the leaves (negative force).
Root pressure- water taken into the roots by osmosis providing a pushing force (positive force.
Capillary action- assisting in the xylem vessels, combination of adhesion and cohesion, aids upward movement of water.
Describe capillary action.
Water is polar- uneven distribution of charge - one side is slightly positive and one slightly negative;
This causes extensive hydrogen bonding which makes water cohesive → as well as water molecules sticking to each other, they also stick to xylem walls (adhesion).
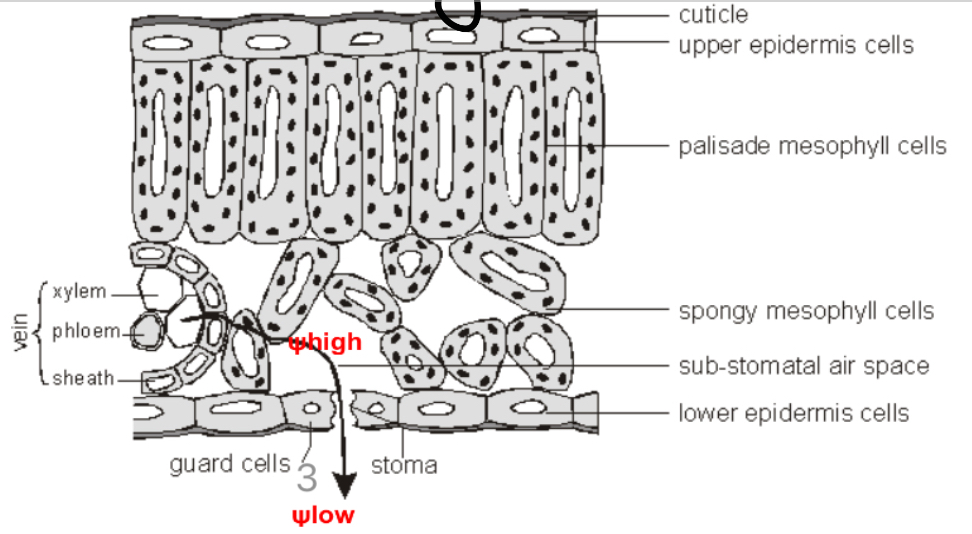
How does water moves out of the stomata?
There’s a water potential gradient between the inside of the leaf and the outside (higher in substomatal air spaces and lower in the atmosphere).
Moves down its water potential gradient- evaporating out the stomata (due to thermal energy from the sun).
As one water molecule moves forward and evaporates out, this pulls the whole continuous column if water up.
What’s the cohesion-tension theory?
That water being pulled up the plant (sucked up-transpiration pull), causes tension in the xylem vessels- slightly pulls in the xylem walls and reduces diameter of the stem/trunk.
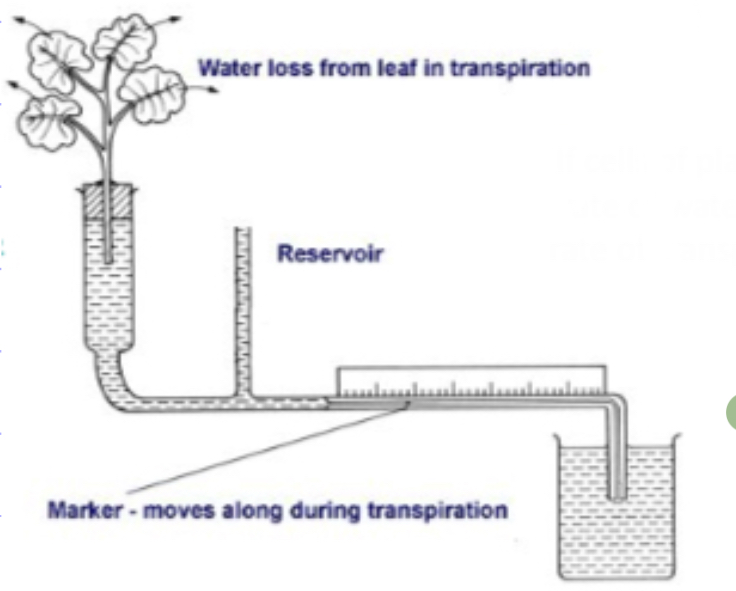
What equipment can be used to measure the rate of transpiration?
Potometer
How do potometers work?
If cells of a plant are fully turgid, then the rate of water uptake/absorption + rate of transpiration are roughly the same.
By introducing a bubble, you can watch the bubble move along and time how much water is taken up in a set amount of time.
What factors affect the rate of transpiration?
Temperature (increase)
Light (increase)
Air movement (increase)
Humidity (decrease)
If you change one factor, the others must be kept constant.