apo psych 2.2-2.8
1/138
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
139 Terms
Cognition
all forms of knowing and awareness
Metacognition
awareness of one’s own cognitive process (thinking about thinking)
Concept
an idea that represents a class of objects or events or their properties
Prototype
a mental representation of an object or concept
Schema
Mental filters or maps that organize our information about the world
Assimilation
interpreting one’s new experience in terms of one’s existing schema
Accommodation
adapting one’s current understanding to incorporate new information
Algorithm
a methodical
Heuristic
a simple thinking strategy that often allows us to make judgments and solve problems efficiently; usually speedier but also more error-prone than algorithms
Representativeness Heuristic
judging the likelihood of things in terms of how well they seem to represent
Availability Heuristic
estimating the likelihood of events based on their availability in memory
Mental Set
a tendency to approach a problem in one particular way
Priming
the process where exposure to a stimulus influences a subsequent response to a related stimulus without conscious thought.
Framing
the way an issue is posed; how an issue is framed can significantly affect decisions and judgments.
Nudge
altering people's behavior in a predictable way without forbidding any options
Gambler’s Fallacy
a failure to recognize the independence of chance events
Sunk-Cost Fallacy
the tendency for people to continue an endeavor or course of action even when abandoning it would be more beneficial
Functional Fixedness
Inability to perceive a new use for an object associated with a different purpose
Confirmation Bias
A tendency to search for information that confirms one’s preconceptions.
Fixation
the human tendency to approach a given problem in a set way that limits one's ability to shift to a new approach to that problem
Intuition
immediate insight or perception
Overconfidence
the tendency to be more confident than correct - to overestimate the accuracy of our beliefs and judgments
Belief Perseverance
the tendency to hold onto a belief even when there is evidence that proves it wrong
Executive Functions
the set of neurocognitive skills involved in goal-directed problem-solving
Insight
when a solution to a problem presents itself quickly and without warning
Creativity
Ability to produce novel and valuable ideas
Divergent Thinking
expanding the number of possible problem solutions
Convergent Thinking
narrows the available problem solutions to determine the single best solution
Memory
learning that has continued over time
Explicit Memory
memory of facts and experiences that one can consciously know and "declare" (eg jans bday)
Episodic memories
The stories of our lives and experiences that we can recall and tell someone (key word: stories)
Semantic memories
Impersonal memories that are not drawn from personal experience but rather from everyday
Flashbulb memories
refer to emotionally intense events that become “burned in” as a vivid-seeming memory.
Implicit Memory
retention independent of conscious recollection (like procedural memory, conditioning, and priming)
Procedural Memory
long-term memory for the skills involved in particular tasks
Prospective Memory
Remembering to perform actions in the future.
Retrospective Memory
the ability to recall past events, people, facts, and skills, encompassing a wide range of information learned or experienced in the past
Long-term Potentiation
an increase in a cell's firing potential after brief
Neurogenesis
the creation of new neurons in the brain, which happens during both fetal development and throughout adult life
Working Memory
holding short-term (i.e. temporary) information in your mind while using that information to accomplish a task.
Central Executive
a component that manages the activities of the phonological loop and visuospatial sketchpad
Phonological Loop
a part of working memory that handles verbal and auditory information
Visuospatial Sketchpad
a component that is responsible for the brief storage of visual information
Multi-Store Model
describes flow between three permanent storage systems of memory: the sensory register
Sensory memory
processing everything we sense
Iconic memory
fleeting visual images
Echoic memory
auditory signals
Short-term Memory
activated memory that holds a few items briefly before the information is stored or forgotten
Long-term Memory
the relatively permanent and limitless storehouse of the memory system. Includes knowledge
Automatic Processing
unconscious encoding of incidental information (being on autopilot)
Effortful Processing
encoding that requires attention and conscious effort
Deep processing
involves elaborative rehearsal along with meaningful analysis of the ideas and words being learned
Shallow processing
simple memorization of something without attaching meaning to it
Information-processing model
a three-step process: encoding
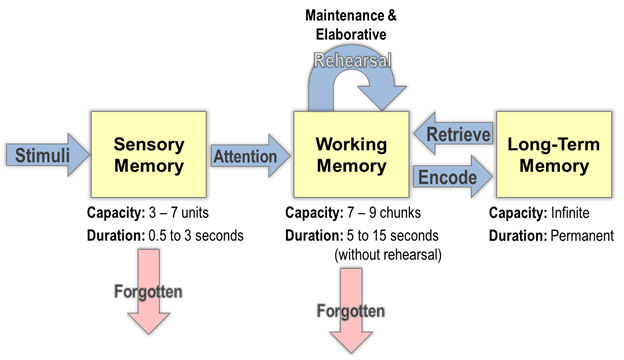
Structural Processing
when we remember only the physical quality of the word
Phonemic Processing
includes remembering the word by the way it sounds
Semantic Processing
the cognitive process of understanding and interpreting the meaning of words, phrases, and sentences.
Encoding
the conversion of a sensory input into a form capable of being processed and deposited in memory.
Mnemonic Devices
memory aids
Method of loci
Using a familiar environment to recall memories
Peg word system
a mnemonic device that is used to memorize lists that need to be in order.
Chunking
combining grouping bits or related information
Categories
the way we sort objects into groups that help us organize knowledge
Hierarchies
systems where individuals or concepts are ranked one above another based on specific criteria
Spacing Effect
the tendency for distributed study or practice to yield better long-term retention than is achieved through massed study or practice
Massed Practice
a learning procedure in which practice trials occur close together in time
Serial Position Effect
refers to the tendency, when learning information in a long list, to more likely recall the first items (primacy effect) and the last items (recency effect).
Autobiographical Memory
a person’s memory for episodes or experiences that occurred in their own life
Memory Consolidation
the neurobiological processes by which a permanent memory is formed following a learning experience
Maintenance Rehearsal
repeating items over and over to maintain them in short-term memory
Elaborative Rehearsal
linking new information with existing memories and knowledge
example:remembering the name "Cliff" by visualizing a steep rock face or "Sandy" by imagining a beach
Basal Ganglia
Plays an important role in memory retrieval and procedural memory
Amygdala
Primary processor of emotional reactions and social and sexual behavior
Hippocampus
Most associated with emotions and transfer of information from STM to LTM
Cerebellum
Responsible for procedural memories
Retrograde Amnesia
You can’t remember information previously stored in memory
Anterograde Amnesia
The inability to form memories from new material
Alzheimer’s Disease
a brain disorder that gets worse over time
Infantile Amnesia
the commonly experienced inability to recall events from early childhood
Retrieval
the act of getting information out of memory storage and back into conscious awareness
Recall
direct retrieval of facts or information
Recognition
correct identification of previously learned material
Relearning
a measure of memory that assesses the amount of time saved when learning material again
Retrieval Cues
stimuli that help people retrieve memories
Encoding Specificity Principle
the principle that retrieval of memory is optimal when the retrieval conditions duplicate the conditions that were present when the memory was formed
Context-Dependent Memory
the phenomenon of how much easier it is to retrieve certain memories when the context is the same for both encoding and retrieval.
Mood-Congruent Memory
information can be retrieved while in a mood similar to when it was acquired
State-Dependent Memory
a person may be alert, tired, happy, sad, drunk, or sober when the information was encoded and may recall that information better when in the same state.
Testing Effect
enhanced memory after retrieving
Interleaving
a process where students mix multiple subjects or topics while they study in order to improve their learning
The Forgetting Curve
a graphic depiction of the amount of forgetting over time after learning has taken place
Hermann Ebbinghaus
guy that discovered the forgetting curve and the spacing effect.
Encoding Failure
inability to recall something because it was never properly stored in memory.
Proactive Interference
the disruptive effect of prior learning on the recall of new information
Retroactive Interference
the disruptive effect of new learning on the recall of old information
Tip-of-the-Tongue Phenomenon
when information is retained in the memory store but cannot be accessed
Ego
The largely conscious
Repression
banishing anxiety arousing thoughts
Reconsolidation
the process of replacing or disrupting a stored memory with a new version of the memory
Misinformation Effect
incorporating misleading information into one's memory of an event