Electrolytes (Patho) - EG
1/103
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
104 Terms
Intracellular fluid (ICF)
2/3 of total body fluid
Extracellular fluid (ECF)
interstitial fluid
intravascular fluid
transcellular fluid (TSF)
1/3 total body fluid
Tonicity
isotonic
hypotonic
hypertonic solutions
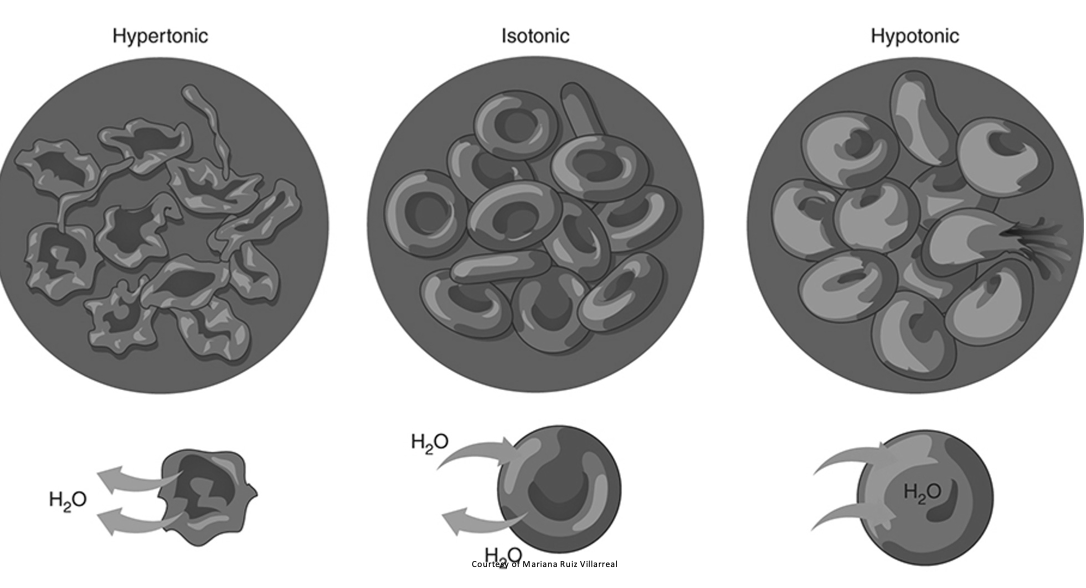
Osmolarity
osmosis
Fluid sources
oral intake
intravenous solutions (iso-, hypo-, or hypertonic)
Fluid losses
urine
feces
insensible losses
Regulatory hormones
antidiuretic hormone (ADH)
aldosterone
atrial natriuretic peptide
Fluid balance
regulation of body’s fluid compartments to maintain a stable internal environment
What functions does fluid affect?
cellular metabolism
temperature regulation
delivery of oxygen and nutrients to cell
Types of fluid excess
third spacing
edema
anasarca
hypervolemia or fluid volume excess
water intoxication
Causes of fluid excess
excessive sodium or water intake
inadequate sodium or water elimination
Filtration
fluid exits capillary since capillary hydrostatic pressure (35 mm Hg) is greater than blood colloidal osmotic pressure (25 mm Hg)
No net movement
no net movement of fluid since capillary hydrostatic pressure (25 mm Hg) = blood colloidal osmotic pressure (25 mm Hg)
Reabsorption
fluid re-enters capillary since capillary hydrostatic pressure (18 mm Hg) is less than blood colloidal osmotic pressure (25 mm Hg)
Pitting edema
indentation in the affected areas
excess fluid mainly composed of water
Non-pitting edema
associated w/ conditions affecting the thyroid or lymphatic system
buildup composed of proteins, salt and water
Common risk factors for edema
medications
obesity
low protein levels
pregnancy
sitting/standing in same position too long
Treatment for edema
mild: resolve on its own / elevate affected limbs
severe: diuretic prescribed to help eliminate excess fluid through urine
chronic: compression socks to promote circulation
Manifestations for fluid excess
edemas: peripheral, periorbital, cerebral and anasarca
dyspnea
tachycardia
hypertension
Diagnosis for fluid excess
through history, physical examination, daily weights, measurement of intake and output
lab results: blood chemistry, urine analysis, complete blood count
Treatment of fluid excess
administering diureticcs
restricting sodium and fluids
maintaining high Fowler’s position
Types of fluid deficits
dehydration
hypovolemia or fluid volume deficit
can occur independently w/o electrolyte defects
Causes of fluid deficit
inadequate fluid intake
excessive fluid or sodium losses
Fluid deficits lead to…
increased level of blood solutes
cell shrinkage
hypotension
Diagnosis for fluid deficit
blood test (CBC and chemistry panels)
urine test (creatinine, urine sodium concentration, urine pH)
X-ray or MRI
daily weights
measurements of intake and output
Manifestations of fluid deficit
altered level of consciousness
hypotension
dry mucous membranes
decreased skin turgor
Treatment for fluid deficit
managing underlying cause
fluid replacement
Electrolyte balance
cations
anions
play a role in muscle and neural activity, and acid-base and fluid balance
Sodium normal range
135-145 mEq/L
most significant cation and prevalent electrolyte of extracellular fluid
mainly acquired through diet
excreted through the kidneys and GI tract
Sodium functions
controls serum osmolality and water balance
plays a role in acid-base balance
facilitates muscles and nerve impulses
Sodium homeostasis
positive ion or “cation” —> Na
most outside cells —> extracellular fluid
concentration: 135 mEq/L —> Na relative to water in body
Hypernatremia
>145 mEq/L
serum osmolarity increases, resulting in fluid shifts
Causes of hypernatremia
excessive sodium
deficient water
Hypernatremia manifestations
dry and sticky mucous membranes
dysphagia
Hypernatremia diagnosis
through history, physical examination, and lab results
blood chemistry and urine analysis
Hypernatremia treatment
fluid replacement and diuretics
Hyponatremia
sodium <135 mEq/L
serum osmolarity decreases
Causes of hyponatremia
deficient sodium
excessive water
Hyponatremia manifestations
anorexia
GI upset
Hyponatremia diagnosis
through history, physical examination and lab results
blood chemistry and urine analysis
Hyponatremia treatment
limit fluids and increase dietary sodium
Hyponatremia electrolyte disturbance
increase in serum levels of ADH, renal sensitivity to ADH and free water intake
decrease in solute intake

Hyponatremia: SALT LOSS
Stupor/coma
Anorexia
Lethargy
Tendon reflexes
Limp muscles
Orthostatic hypotension
Seizures
Stomach cramping
Electrolyte balance: chloride
normal range: 98-108 mEq/L
mineral electrolyte and major extracellular anion
obtained through dietary intake
excreted through kidneys
plays a role in acid-base balance
Hyperchloremia
chloride > 108 mEq/L
Hyperchloremia causes
increased chloride intake or exchange
decreased chloride excretion
**manifestations reflect underlying cause**
Hyperchloremia diagnosis
through history, physical examination and lab results
blood chemistry, urine analysis and arterial blood gases measurement
SAME AS HYPOCHLOREMIA
Hyperchloremia treatment
identifying and managing underlying cause
diuretics
bicarbonate
Metabolic acidosis
headache
decreased BP
hyperkalemia
muscle twitching
warm, flushed skin
nausea, vomiting, diarrhea
compensatory hyperventilation
Metabolic acidosis causes
DKA
severe diarrhea
renal failure
shock
Hypochloremia
chloride <98 mEq/L
Hypochloremia causes
decreased chloride intake or exchange
increased chloride excretion
**manifestations reflect underlying cause**
Hypochloremia treatment
identifying and managing underlying cause
sodium replacement (oral or intravenous)
ammonium chloride
saline irrigation of gastric tubes
Metabolic alkalosis
restlessness/lethargy
tachycardia
compensatory hypoventilation
confusion
nausea, vomiting, diarrhea
tremors, muscle cramps
Metabolic alkalosis causes
severe vomiting
excessive GI suctioning
diuretics
excessive NaHCO3
Potassium
normal range: 3.5-5 mEq/L
primary intracellular cation
mainly obtained through diet
excreted through the kidneys and GI tract
Potassium plays a role in…
electrical conduction
acid-base balance
metabolism
Hyperkalemia
potassium >5 mEq/L
Hyperkalemia causes
deficient excretion
excessive intake
increased release from cells
acute or chronic kidney disease
tissue breakdown —> crush injury
Hyperkalemia manifestations
paresthesia
muscle weakness
dysrhythmias
Hyperkalemia diagnosis
through history, physical examination and lab results
blood chemistry, 12-lead EKG, arterial blood gas
Hyperkalemia treatment
correcting acidosis (sodium bicarbonate)
calcium glutinate for dysrhythmias
decreased dietary intake
increased excretion (dialysis, IV solutions, meds), insulin
Hypokalemia
potassium <3.5 mEq/L
Hypokalemia causes
excessive loss
deficient intake
increased shift into the cell
abuse of laxatives
metabolic alkalosis
diuretics (loop and thiazides)
Hypokalemia manifestations
paresthesia
leg cramps
cardiac arrest
Hypokalemia diagnosis
through history, physical examination and lab results
blood chemistry, 12-lead EKG, arterial blood gas measurement
Hypokalemia treatment
identifying and managing the underlying cause
potassium replacement (oral or intravenous)
Calcium
normal range: 4-5 mEq/L
mostly found in bone and teeth
has inverse relationship w/ phosphorous
synergistic relationship w/ magnesium
main source = dietary intake
What is calcium regulated by?
vitamin K
parathyroid hormone
calcitonin
What does calcium play a role in?
blood clotting
hormone secretion
receptor functions
nerve transmission
muscular contraction
Hypercalcemia
calcium >5 mEq/L
osteoclastic bone resorption
Hypercalcemia causes
increased intake or release
deficit excretion
Hypercalcemia manifestations
dysrhythmias
lethargy
muscle weakness
SAME AS HYPERMAGNESEMIA
Hypercalcemia diagnosis
through history, physical examination and lab results
blood chemistry and 12-lead EKG
SAME AS HYPOCALCEMIA
Hypercalcemia treatment
identifying/managing underlying cause
managing symptoms
increasing mobility
administering IV fluids
Hypocalcemia
calcium <4 mEq/L
Hypocalcemia causes
excessive losses
deficient intake
hypomagnesemia
hypoparathyroidism
vitamin D deficiency
Hypocalcemia manifestations
dysrhythmias
positive Trousseau’s and Chvostek’s signs
SAME AS HYPOMAGNESEMIA
Hypocalcemia treatment
identifying and managing underlying cause
calcium replacement (oral or intravenous)
decreasing phosphorous
Hypocalcemia symptoms
numbness around mouth
muscle cramps
paresthesias
vomiting
seizures
decreased cardiac function
Hypocalcemia ECG
lengthened ST
lengthened QT
may cause Torsades de pointes
Hypercalcemia ECG
shortened ST
shortened QT
Phosphorous
normal range: 2.5-4.5 mg/dL
mostly found in bones (small amounts in bloodstream)
mainly obtained through diet
excreted through the kidneys
Phosphorous plays a role in…
bone and tooth mineralization
cellular metabolism
acid-base balance
cell membrane formation
Hyperphosphatemia
phosphorous >4.5 mg/dL
Hyperphosphatemia causes
deficient excretion
excessive intake or cellular exchange
Hyperphosphatemia manifestations
rarely seen alone
SAME AS HYPOPHOSPHATEMIA
Hyperphosphatemia diagnosis
through history, physical examination and blood chemistry
Hyperphosphatemia treatment
identifying/managing underlying cause
aluminum hydroxide or aluminum carbonate
treating hypocalcemia
Hypophosphatemia
phosphorous <2.5 mg/dL
Hypophosphatemia causes
excessive excretion or cellular exchange
deficient intake
Hyperphosphatemia diagnosis
through history, physical examination and blood chemistry
Hyperphosphatemia treatment
identifying and managing the underlying cause
phosphorous replacement (oral or intravenous)
Magnesium
normal range: 1.8-2.5 mEq/L
an intracellular cation
mostly stored in the bone and muscle
mainly obtained through diet
excreted through kidneys
Magnesium plays a role in…
muscle and nerve function
cardiac rhythm
immune function
bone strength
blood glucose management
blood pressure
energy metabolism
protein synthesis
Hypermagnesemia
magnesium >2.5 mEq/L
Hypermagnesemia causes
renal failure
excessive laxative and antacid use
Hypermagnesemia diagnosis
through history, physical examination and blood chemistry
SAME AS HYPOMAGNESEMIA
Hypermagnesemia treatment
diuretics
dialysis
intravenous calcium
Hypomagnesemia
magnesium <1.8 mEq/L