bicd 110 — midterm 1 ˚ ౨ৎ ⋆ 。˚ ⋆ (w4)
1/114
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
115 Terms
what is the nucleus the site of? what does it house?
site of transcription
houses DNA in eukaryotic cells
what is the nucleolus? what is it the site of?
a membrane-less compartment within the nucleus
site of ribosomal biogenesis
what is the name of the 2 membranes that encloses the nucleus? what are those two membranes?
nuclear envelope
INM: inner nuclear membrane
ONM: outer nuclear membrane
what is the relationship between the nuclear membrane and the ER membrane?
continuous
what 3 proteins needed to be imported from the cytosol → nucleus?
histones
transcription factos
RNA polymerases
what protein needs to be exported from the nucleus → cytosol?
ribosomal subunits
where do all nuclear proteins need to be synthesized and transported to? when do they transport there?
synthesized = cytosol → transported nucleus
after folding, nuclear proteins transport
what is the NPC? what does it span?
NPC = nuclear pore complex
spans both inner/outer membranes
one of largest macromolecular assemblies in cell
what is the pore/NPC composed of?
structural nucleoporins, membrane nucleoporins, FG-nucleoporins
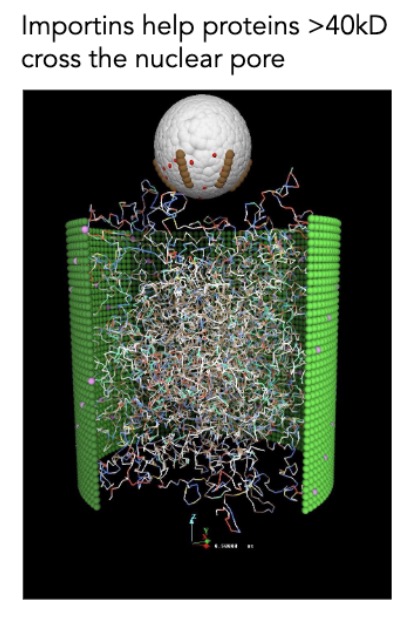
what can pass through the NPC? what can freely diffuse? what needs extra help?
ions and small molecules can freely diffuse thru pore
proteins < 40kDA: freely diffuse
proteins > 40 kDA: need nuclear export signal/nuclear localization
what forms the nuclear pore complex through both the outer and inner nuclear membranes?
membrane nucleoporins (curved regions)
structural nucleoporins (Y-complex)
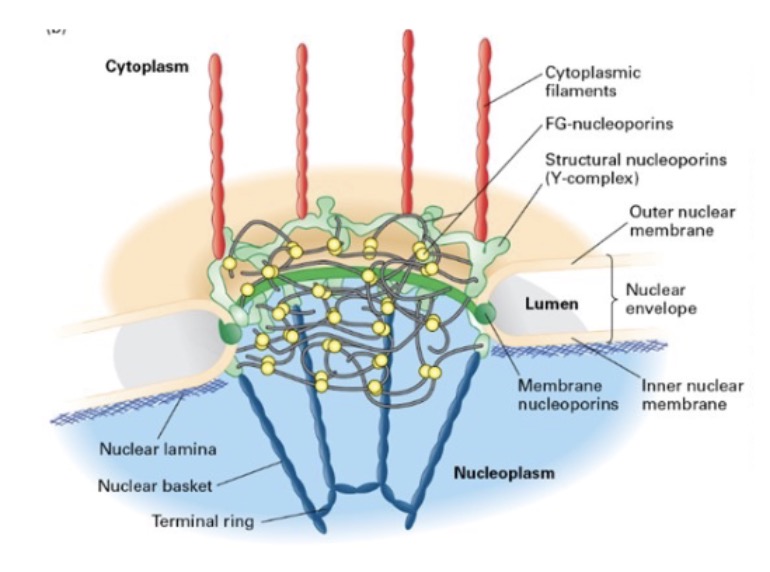
what lines the pore channel? what repeats does it contain?
FG-nucleoporins; contain Phe-Gly (hydrophobic) repeats
seperated by disordered, hydrophilic stretches
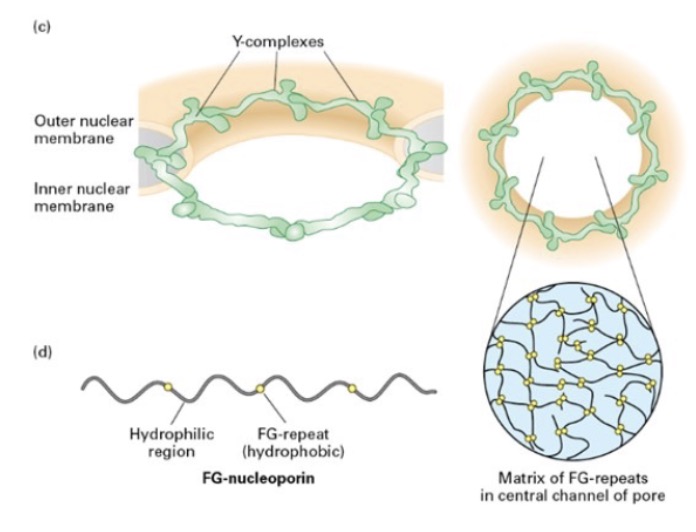
what kind of matrix does FG-nucleoporins form? what is allowed to diffuse? what isn’t?
form gel-like matrix
allows small molecules diffuse
prohibit proteins >40 kDa
what is crucial to the selectivity of NPC (nuclear pore complex)?
FG-nucleoporins
what are nuclear localization signals (NLS)? do they have a motif? what are they rich in?
direct proteins → nucleus
no strict motif
rich in basic amino acids
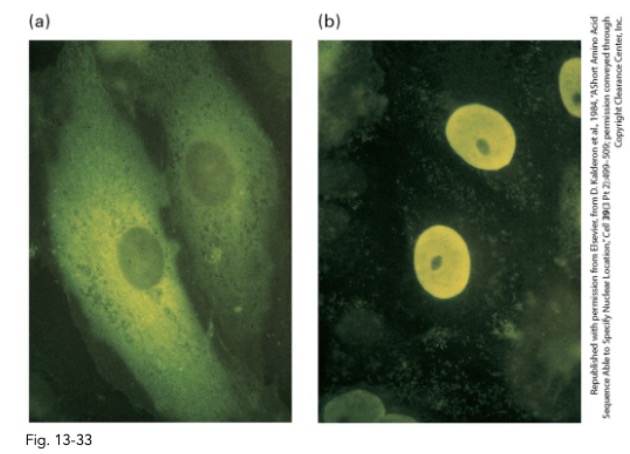
what is the goal of this experiment? what is pictured on the left? on the right?
goal: test if NLS (nuclear localization signal) is sufficient to target protein to nucleus
left: GFP normal pyruvate kinase in cytosol
right: localization of GFP chimeric pyruvate kinase
7-residue NLD drom SV40 T-antigen (P-K-K-K-R-K-V) fused into pyruvate kinase
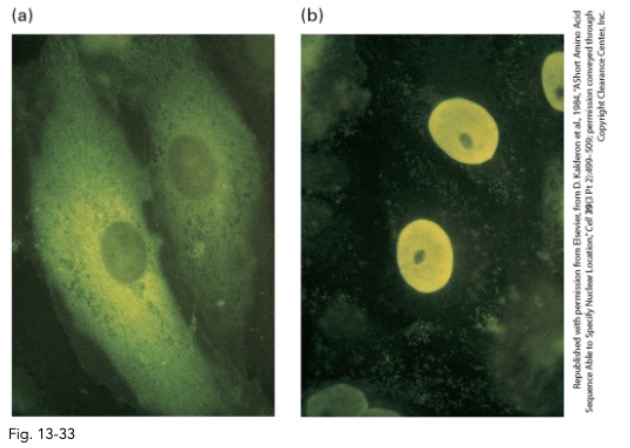
what is the conclusion of this experiment?
NLS is sufficient to target proteins to nucleus
even normal cytosolic ones
what promotes GTP hydrolysis?
GAP (GTPase activating protein)
GTP → GDP
what promotes exchange of GDP for GTP?
GEFs (guanine nucleotide exchange factor)
what is the general mechanism for nuclear import of proteins? (2 steps)
importins recognize NLSs → shuttle cargo into nucleus
Nuclear Ran-GTP interacts w importins → release cargo
in regards to nuclear import of proteins, what does importin bind to? what does it form? what is an importin? where does this occur? (step 1)
importin: soluble nuclear transport receptor
importin binds to NLS(cargo protein) → importin-cargo compelx
cytosol
in nucelar import of proteins, where does the importin-cargo complex diffuse through? what does it interact with to do this? what does it have a high affinity for? where does this occur? (step 2)
importin-cargo complex difffuse thru NPC
by interact w FG-nucleoporins
importins: ↑ affinity for FG-repears
allow movement thru channel
cytosol
what is ran? what is it bound to? how is it found normally in nucleus?
ran: small monomeric G protein
in nucleus = Ran; interacts w Ran-GEF → ran-GTP
what does Ran-GTP interact with? what does this do? where does this occur? (step 3)
interact w importin; displace NLS-containing cargo
nucleus
in terms of nuclear import of proteins, how is importin and Ran recycled?
importin-Ran_GTP complex → diffuse back cytosol (via NPC)
Ran interact w Ran-GTP → (GTP→GDP) ↓ importin affinity
importin free bind another cargo; Ran-GDP → nucleus
what is nuclear import of proteins driving by? where is each thing happening?
Ran-GAP localization (cytosol)
Ran-GEF (nucleus)
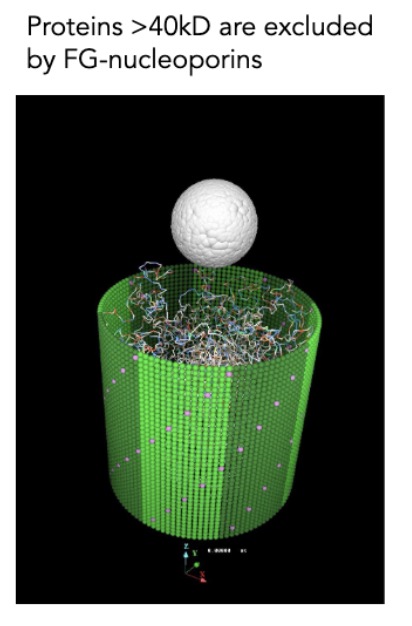
what blocks >40 kD proteins from passing through the NPC?
FG-nucleoporins

what helps >40 Kd proteins pass through the NPC?
importins
what is the difference between NES (nuclear export signal) and NLS (nuclear localization signal)?
NESs: proteins nucleus → cytoplasm
NLSs: proteins cytoplasm → nucleus
do NESs have a strict motif? what are they rich in.
NES: nuclear export signals
no strict motif; rich in hydrophobic aa
in nuclear export, what does Ran-GTP in the nucleus bind to? what does it do? what does it increase the affinity for?
Ran-GTP (nucelus) bind to exportin1
conformational change: ↑ affinity for NES-containing cargo
creates exportin-Ran-GTP-cargo
in nucelar export, where does the exportin-Ran-GTP-cargo diffuse to? how does it do this?
diffuses thru NPC → cytosol
exportin 1 interacts w FG repeats; to move cargo thru pore
in nuclear export, what happens in the cytosol to Ran-GAP? where does the produce dissociate from and diffuse to?
in cytosol, Ran-GAP interacts w Ran-GTP: GTP → GDP
Ran-GDP dissociate from cargo; diffuse back → nucleus
Ran-GEF: GDP → Ran-GTP
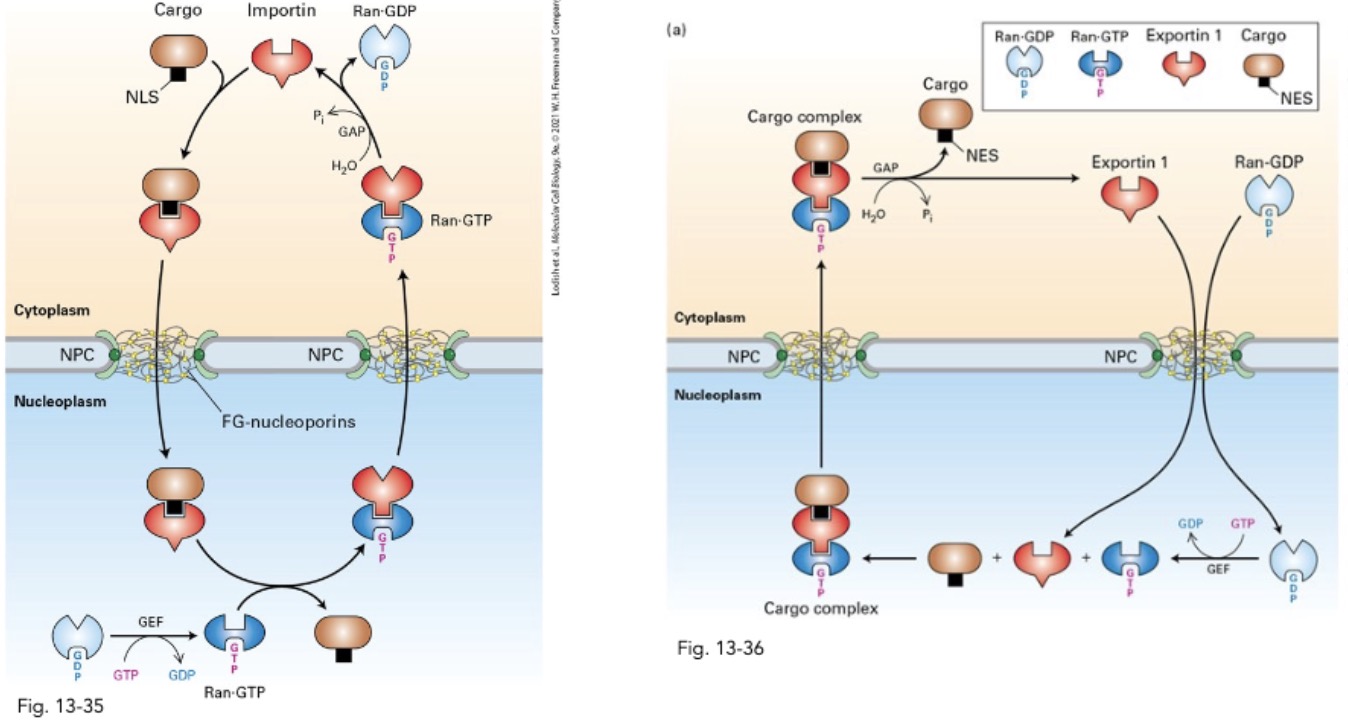
what is the 1 difference between the nuclear import and export pathway?
(export) Ran-GTP travels w cargo
(import) Ran-GTP doesn’t
where do most proteins start their translation?
cytosol
what are some examples of proteins that use the secretory pathway?
sequence-based targeting to peroxisomes, mitochondria, chloroplasts, nucleus
sequence-based targeting to ER memb and lumen
what is exocytosis? endocytosis?
exocytosis: vesicular transport out of cell
endocytosis: vesicular uptake into cell
what can be used to identify genes that cause a specific phenotype? what are the steps?
forward genetic screens
mutagenize = create random DNA damage
results unique DNA mutated individuals in population
design phenotypic screen to identify gene of interest
figure out which gene is agitated in mutant
what is the secretatory pathway used for?
to transport proteins and lipids fr ER; via vesicles
what % of encoded proteins transit through the secretory pathway?
30%
what is the early secretory pathway responsible for?
packing and processing of cargo
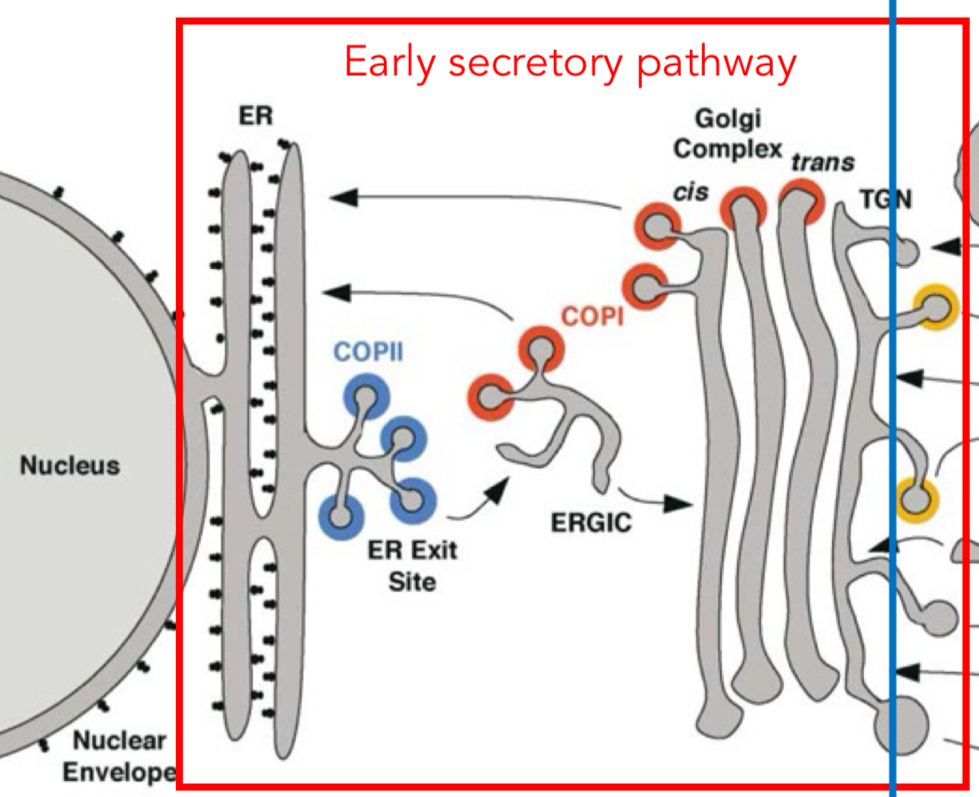
what is the late secretory pathway/trans-golgi network (TGN) responsible for?
transport to final destination
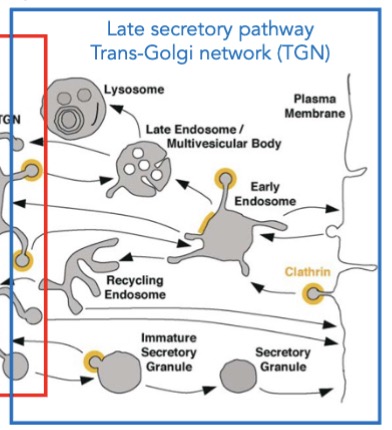
what are the 3 destinations for proteins/lipids traveling through the secretory pathway? name examples if ya can.
lysosme; degrade macromolecules
secretory proteins; digestive enz, antibodies, neurotransmitters
plasma membrane; receptors, channels, cell-adhesion molecules
what was instrumental in decoding the secretory pathway?
temperature-sensitive (ts) alleles
allow to disturb gene function; temperature dependent
basically missense mutation at restirctive temp
how were temperature-sensitive alleles used to decode the secretory pathway? what bacteria was used? what was identified?
created library of S. cerevisiae (budding yeast) where secretion was perturbed
used permissive temp (24°C)
restrictive temp (37⁰C)
identified sec1
what happens at permissive temperature? restrictive temperature?
permissive (24°C) = protein folds normally
restrictive (37°C) = protein x fold, function impaires
are sec genes functionally/biochemically similar?
no
what were the 3 contributions to science of the secretory pathway (randy schekman)?
secretion/assemble = physically/functionally linked via obligate organelle intermediates
polypeptide translocation + vesicular traffic has been conversed thru evolution
COPII coat sorts cargo by recognition of transport signals + deforms ER membrane to create budded vesicles
what are vesicles enclosed by? what do they contain? are the membrane faces conversed during budding and fusion?
enclosed by membrane
contains proteins/small molecules
yes, they are conserved
what are the 5 basic principles of vesicular trafficking? describe them.
specific proteins needed → coat formation/choose cargo
coat proteins; deform membrane, choose which cargo will be in vesicles
protein coat falls off after vesicles budded from membrane; allow vesicle fuse w target membrane
protein needed for fusion; determine where vesicle will b targets, physically pull vesicular + target membrane together → promote fusion
is ER-golgi trafficking unidirectional or bidirectional?
bidirectional
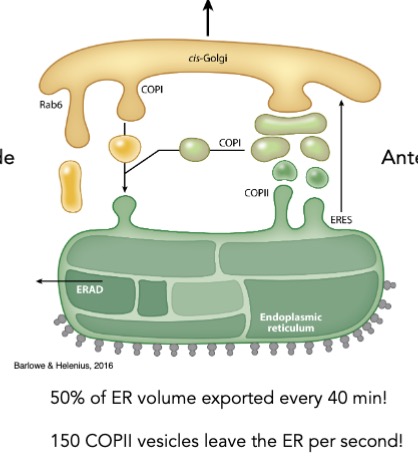
where do proteins/membranes move from in the anterograde transport? what vesicles are used?
membrane/proteins: ER —vesicles→ cis-golgi
COPII vesicles
where do proteins/membranes move from in the retrograde transport? what vesicles are used?
membrane/proteins recycled back to ER
COPI vesicles
where does anterograde and retrograde trafficking occur?
between cisternae of the golgi apparatus (processing center)
what happens at the golgi apparatus?
modification carbohydrate chains on proteins
sorting cargo back to ER
what are the 3 main steps to COPII coat assembly?
protein recruitment (coat) → cytosolic face ER membrane; help deform membrane
cycles of GTP hydrolysis regulate coat dis/assembly
coat formation = tied to cargo sorting
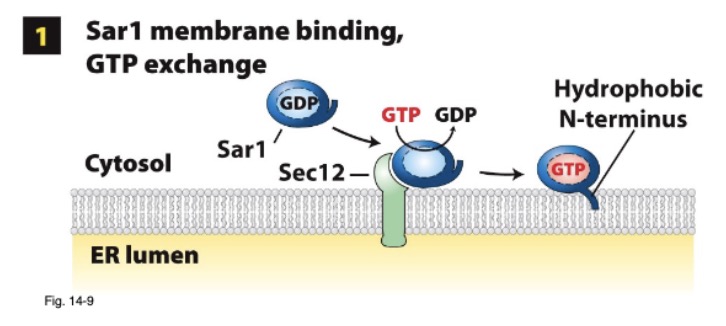
during COPII coat assembly, what is inserted into the ER membrane? how does this do this with GTP? what protein does it interact with?
Sar1-GTP interacts with ER memb protein Sec12
Sec12 GEF activity → stimulated Sar1 GTP → GDP exchange
Sar-GTP → conformational change; integrated N-terminal amphipathic helix → ER memb outer leaflet
during COPII coat assembly, what coat proteins are recruited? what do they bind to? how do they come off the ER membrane?
Sar1-GTP recruit Sec23/Sec24 coat proteins
Sec23/Sec24 binds sorting signals in membrane cargo protein cytosolic domains
Sec13/Sec31 coat complexes assembles into coat; complete coat assembly
after coat assembles: COPII vesicle, w Sec23/Sec24 + v-SNARES, pinches off ER membrane
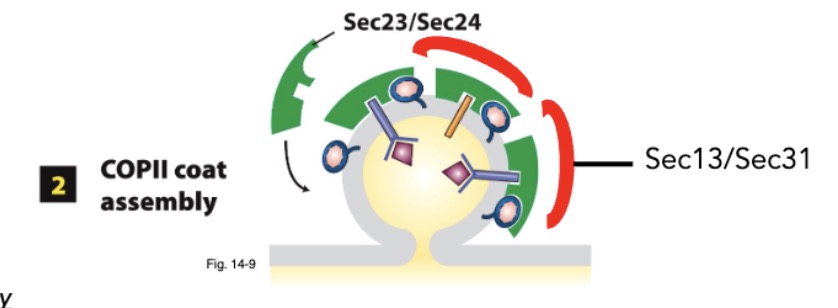
during COPII coat assembly, what are the coat proteins? what are the coat complexes?
Sec23/Sec24 = coat proteins
Sec13/Sec31 = coat complexes
during COPII coat assembly, what happens in GTP hydrolysis? what stimulates it? what is the effect?
Sec23 GAP stimulates Sar1 GTP hyrodolysis
conformation change in Sar1
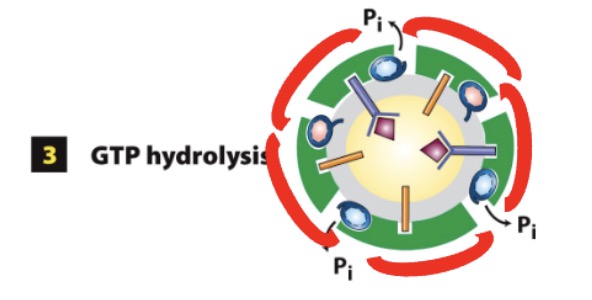
In COPII coat assemble, how does the coat disassemble? what releases from what?
Sar1-GDP releases from vesicle membrane
triggers disassembly
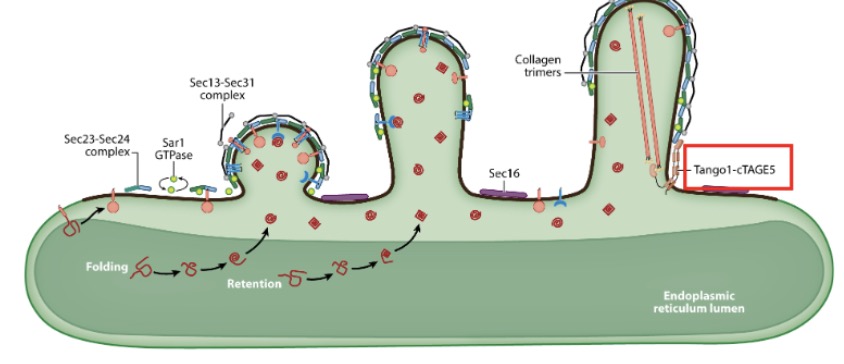
what location does COPII coat assembly prefer? what happens here? where are they distributed? where do they form?
ERES: ER exit sites
major sites of cargo packing + COPII vesicle formation
distributed throughout cell
form at regions of high membrane curvature
for COPII vesicles, what is recognized that allows for sorting of internal membrane proteins? what recognizes them?
sorting signals; Sec24 subunit of COPII
what are the 2 things COPII vesicles are mediated by? what recognizes them?
diacidic sorting signal: Asp-x-Glu (GxE)
dihydrophobic signal: Phe-Phe (FF)
Sec24 subunit of COPII coat binds to sorting signal
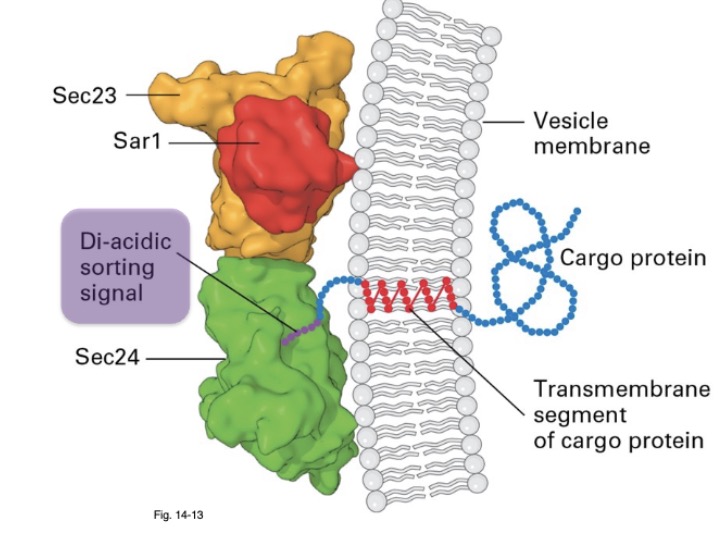
where are Sec 24 sorting signals found
found on cytosolic side of integral membrane proteins
in terms of COPII vesicles, what allows the packing of luminal cargo/ER lumen proteins? what does this do?
interactions w transmembrane proteins that are also being sorted
sorts proteins into COPII vesicles
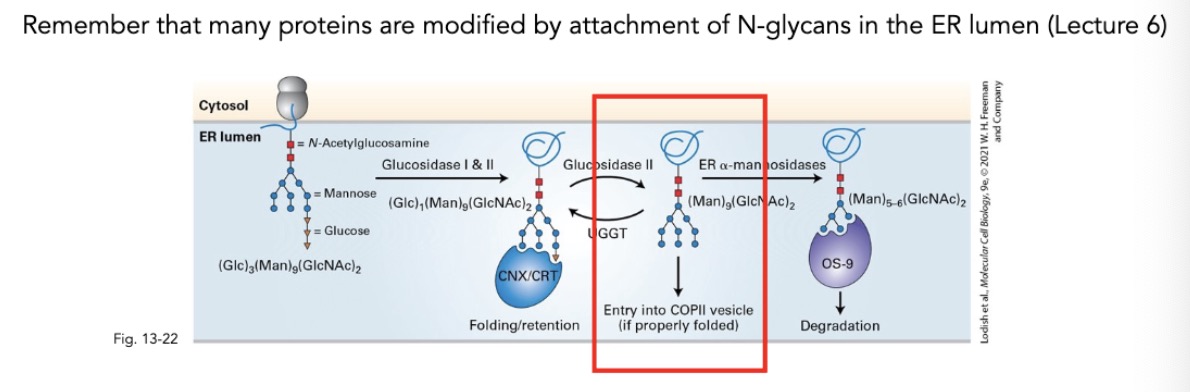
in terms of COPII vesicles and sorting ER lumen proteins in into COPII vesicles, what protein modifications are recognized? what are they bounded by?
proteins w/ (Man)8(GIcNAc)2 modification are recognizes
bonded by ERGIC-53
what is ERGIC-53? what type of protein is it? what is on the tail?
lectin = carbohydrate-binding protein
type I transmembrane protein w/ dihydrophobic motif (FF) in cytoplasmic tail
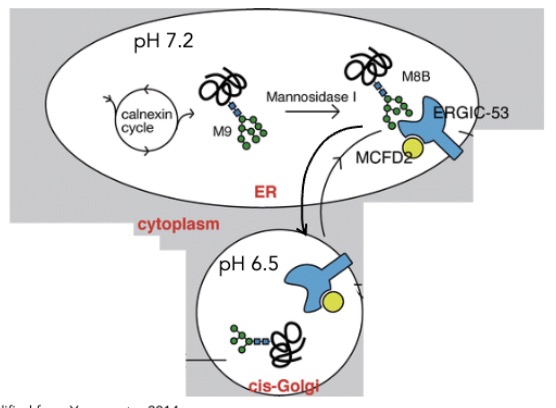
in the ER lumen (pH 7.3) what ix the relationship of binding btwn ERGIC-53 and bound cargo?
enhanced
in the cis-golgi (pH 6.5) what is the relationship of binfing btwn the ERGIC-53 and cargo? what does this allow?
reduced
after vesicles fuse at cis-golgi → allow cargo release
in terms of COPII vesicles, are all cargos the same size? give an ex
no; collagen (larger than typical COPII vesicle)
what is the additional component of the COPII coat that makes vesicles for large cargo?
Tango1
how are uncoated vesicles target to a specific membrane? what is attached? how?
cytosolic Rab-GDP is attached to uncoated vesicle membrane
via lipid anchor
rab = prenylated; covalent attachment of lipid
in COPII vesicle targeting and fusion, are Rabs specific? what does this provide for the vesicle types?
yes, Rabs are specific
provide code for vesicles to be defines by bound Rab
what converts Rab-GDP (inactive) → Rab-GTP (active)?
GEF in vesicle membrane
what is COPII vesicle targeting and fusion done by?
Rab-GTP mediated targeting
in COPII vesicle targeting and fusion, what does Rab-GTP recognize and bind? where is it located? where does it dock?
Rab-GTP recognized/binds to Rab effector (target membrane)
docks vesicle to membrane
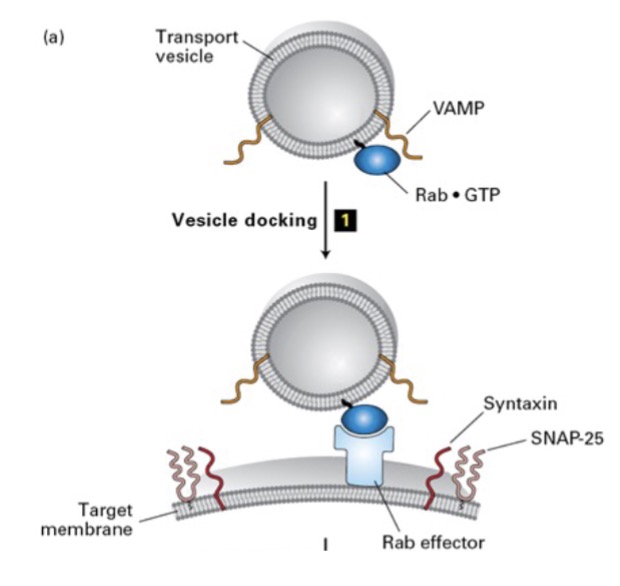
in COPII vesicle targeting and fusion, what SNARE proteins form stable coiled-coil interactions? what does this do?
v-SNARE and t-SNARE
after vesicle docked, v/t-SNAREs form coiled interactions
brings membrane closer to fuse
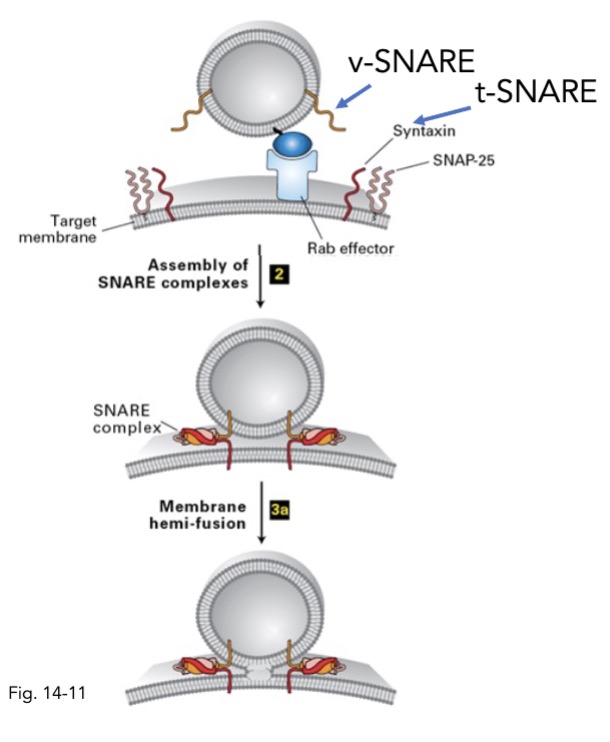
what is v-SNARE and t-SNARE?
v-SNARE = SNAREs on vesicle membrane
t-SNARE = SNAREs on target membrane
in COPII vesicle targeting and fusion, how is the SNARE complex disassembles?
after fusion, NSP and alpha-SNAP + ATP → seperate SNARE complex
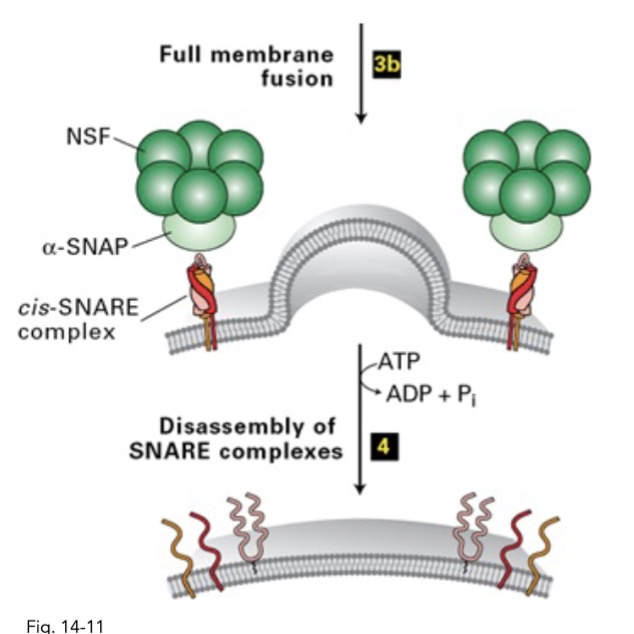
what are the 3 general steps of COPI coat assembly at the cis-golgi that initiates retrograde trafficking?
coat recruitment → cytosolic face of cis-membrane; helps defrom membrane
GTP hydrolysis cycles regulate coat dis/assembly
coat formation and cargo sorting is tied
in COPI coat assemble, what is inserted into the outer leaflet of the cis-golgi membrane? how does it reach this activated state? what proteins do this? (step 1)
Arf1-GTP inserts → outer leaflet of cis-golgi membrane
Arf1-GDP + p23/p24 (cis-Golgi type I transmemb proteins) interact
GBF1 GEF stimulate Arf1 (GDP —> GTP)
Arf1-GTP → conformational change
integrated N-termin amphipathic helic → membrane outer leaflet
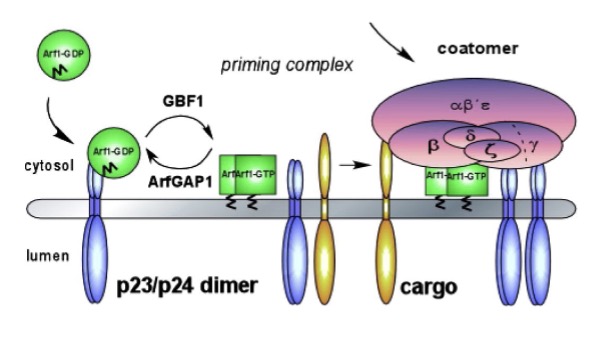
in COPI coat assemble, how is the coat assembles and the cargo sorted?what does Arf1-GTP recruit? what does that bind to? what 2 things happens as the coat assembles? (step 2)
Arf1-GTP recruit heptameric coatomer coat protein complex
coatomer protein binds to sorting signals (cytosolic domain of transmembrane protein)
as coat assembles, membrane curves + pinches off as COPI vesicle (w/ cargo proteins + v-SNAREs)
in COPI vesicle cargo sorting, what is inside the COPI vesicle after the membrane curves and the vesicle is pinches off?
cargo proteins
v-SNAREs
in COPI coat assembly, when does GTP hydrolysis occur? (step 3)
after vesicle pinch off; ArFGAP → Arf1 GTP hyodrolysis
in COPI coat assembly, what happens when the coat is released? (step 4)
Arf1-GDP falls off from vesicle memb
cause disassembly of coat
what allows proteins to be recyled back to the ER? what vesicles do they use?
retrograde trafficking (COPI)
what is the KDEL sorting signal? what does it do? why is it important?
KDEL sorting signal = Lys-Asp-Glu-Leu sorting signal on c-terminal target proteins on ER back
targets proteins → ER
KDEL-containing proteins must be returned to ER to prevent depletion of profile folding proteins in ER lumen
what problem caused for KDEL sorting signals to exist?
ER resident proteins = nonspecifically pack → COPII vesicles bc ↑ amnts in ER lumen
how to KDEL sorting signals target proteins to ER? what pH environments are needed? what sorting signal is used? what vesicle is used?
KDEL R (cis-golgi memb) beinds to KDEL sequences in acidic (6.5 pH)
KDEL R has KXX (Lys-Lys-X-X) sorting signal that binds to COPI coatomer subunit
or di-arginine sorting signal
KDEL R dissociates from KDEL sequences in neutral environment (pH 7.2)