Chapter 4 - Atomic Physics & Spectra
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
Why do different stars have different colors?
It is because of the temperature they are at; objects at different temperatures will have different colors/brightnesses.
What is a blackbody?
This is a THEORETICAL object that absorbs all electromagnetic radiation that strikes it.
What happens to an objects electromagnetic radiation at all wavelength as it heats up?
It not only gets brighter, but also expels MORE electromagnetic radiation.
What is Wien’s Law?
Wien's Law states that the wavelength of the peak emission of a blackbody is inversely proportional to its temperature, meaning hotter objects emit radiation at shorter wavelengths.
It states that the wavelength of the peak emission of a blackbody is INVERSELY proportional to its temperature. This means that hotter objects emit radiation at shorter wavelenghts.
Formula: gammamax = 2.9 × 10-3/T
What is Stefan-Boltzmann Law?
The Stefan-Boltzmann Law states that the total energy radiated per unit surface area of a blackbody is proportional to the fourth power of its absolute temperature. This means as an object's temperature increases, it emits significantly more energy.
It states that the total radiated energy per unit of a blackbody is proportional to the fourth-power of its absolute temperature. This means that as an object’s temperature increases, it emits signficiantly more energy.
Formula: F = sigma * T4 where sigma = 5.67 × 10-8 J/(m2K4s)
What is Luminosity?
It is the total energy emitted by a sphereical object each second.
Formula: L = F 4pir2 OR L = sigma * T4 * 4pir2
A cool object emits (long/short) wavelength photons that carry little energy.
long
What is Kirchhoff’s 1st Law? What is this also called?
It states that a solid, liquid, or dense gas produces a continuous spectrum of complete rainbow colors when being heated WITHOUT any spectral lines. This is also called a blackbody spectrum.
What is Kichhoff’s 2nd Law?
It states that a rarefied (opposite of dense) gas produces an emottion line spectrum (this is a series of bright spectral lines against a dark background).
What is Kirchhoff’s 3rd Law?
It states that the light from an object with a continuous spectrum that passes through a cool gas will make an absorption line spectrum (this is a series of dark spectral lines among the colors of the rainbow)
What does quantum mechanics explain?
It explains that electrons in atoms can exist in only certain allowed orbits around their nuclei.
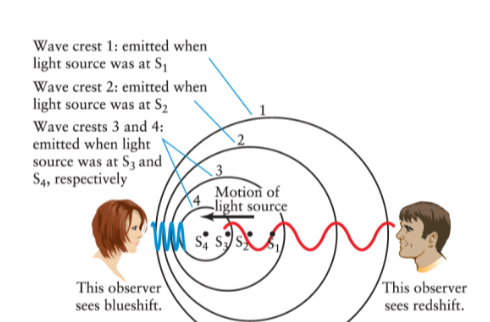
What is the Doppler Shift?
It is the idea that waves are compressed in front of the source but are stretched out behind it.
What is radial velocity?
It is the speed of an object toward or away from us.
What is proper motion?
It’s the actual movement of a star across the sky as observed from Earth, independent of radial velocity effects.
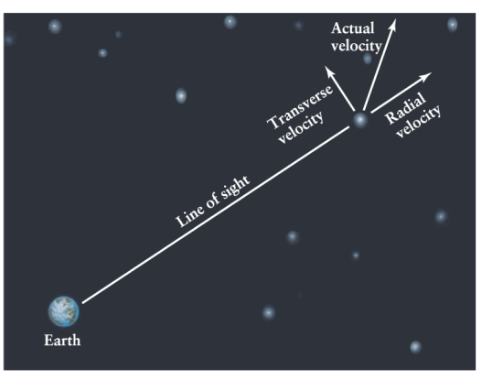
Label them! Oh how you do know?!?!?
Transverse, actual, radial