Axial Muscles
1/52
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Head & Torso
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
53 Terms
Belly (Made of dense irregular CT)
Part of the muscle that contracts
What attaches the bone to belly
tendon and aponeurosis
Insertion
Bone moves when belly contracts
Synergist
(Muscles with )Same action of same body parts
Antagonist
(muscles with) opposite action
Why are skeletal musklces multinucleic
Stem cells fuse
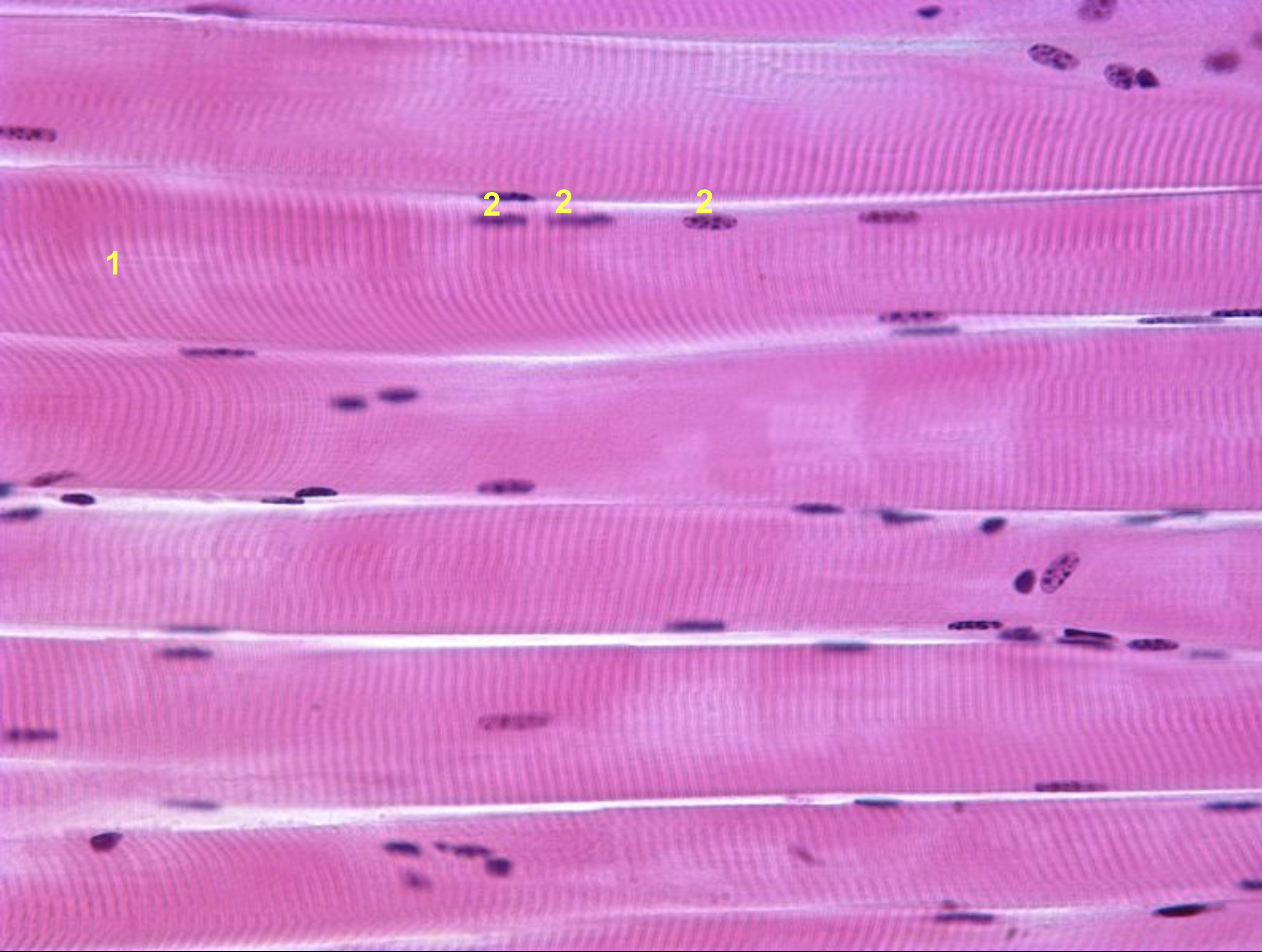
Characteristics of skeletal muscle (location, function, control mode, shape)
Location: Bone
Function: Move bone
Control mode: Voluntary
Shape: Cylindrical, striated, multinuclear
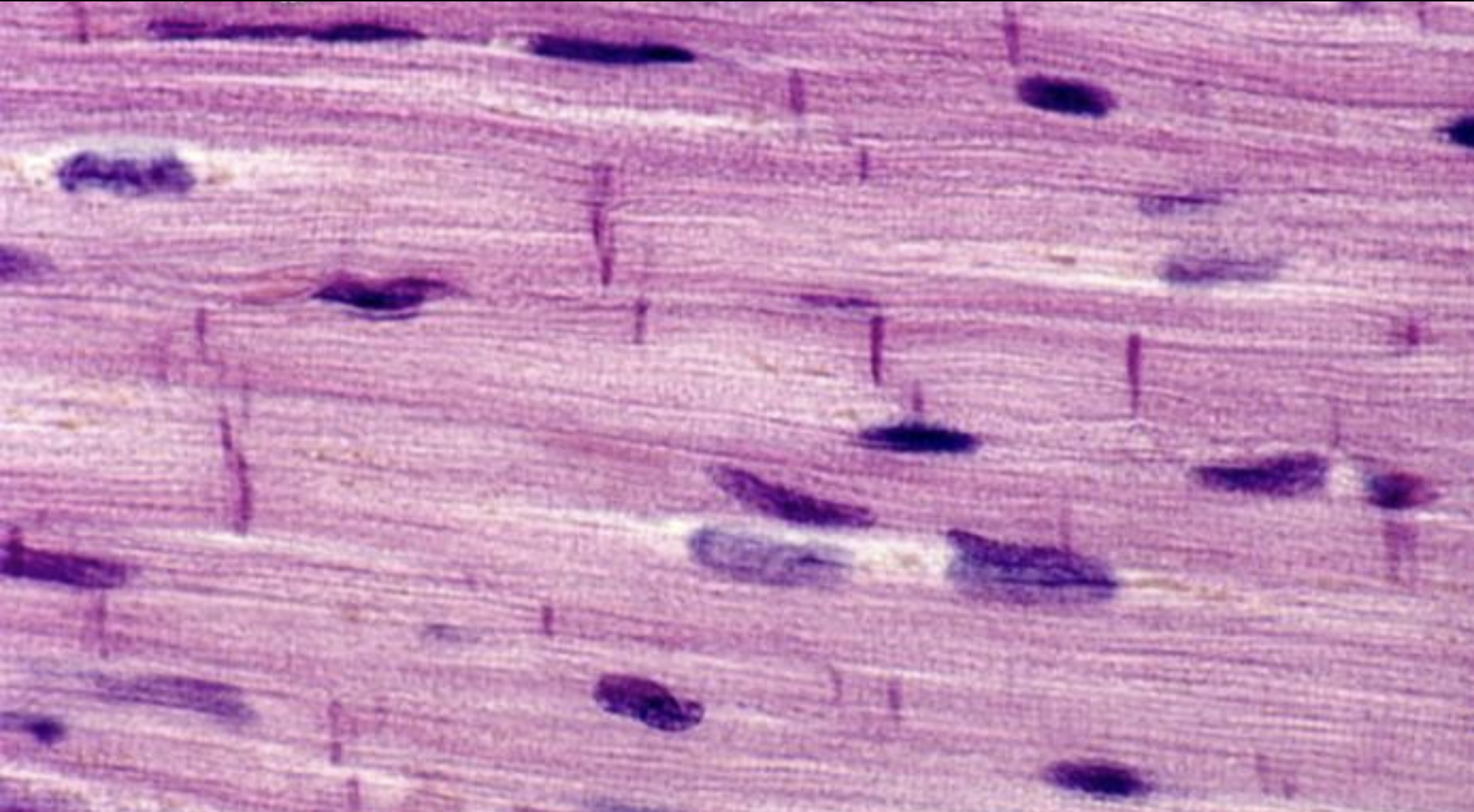
Characteristics of cardiac muscle (location, function, control mode, shape, junctions, structure)
Location: heart
Function: Heartbeat
Control mode: Involuntary
Shape: branched, striated, uninuclear
junctions: gap & desmosomes
structure: intercalated disks
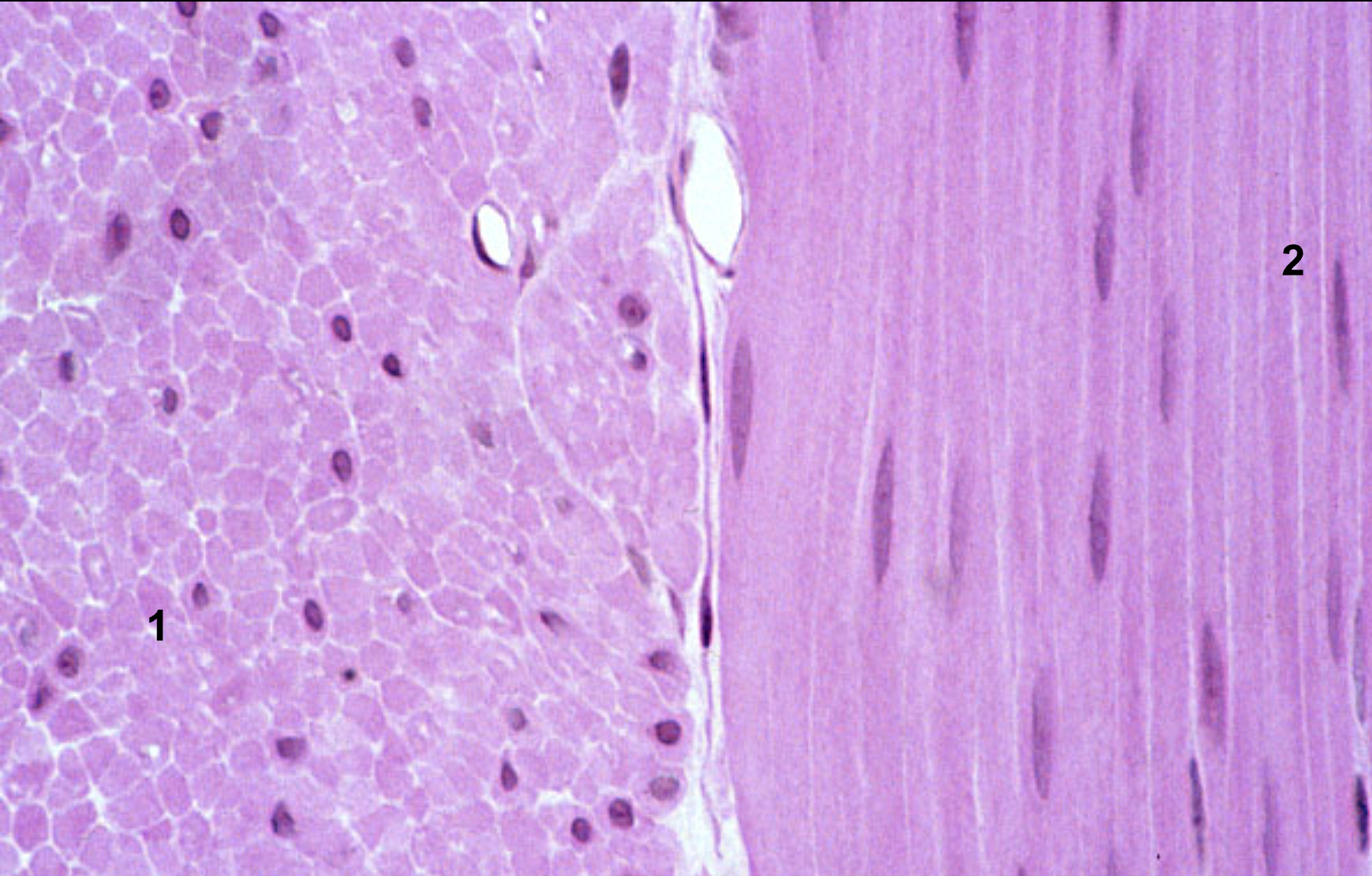
Characteristics of smooth muscle (location, function, control mode, shape, structure)
Location: internal organs + Skin
Function: Move internal organs
Control: Involuntary
Shape: spindle, uninuclear
Identify the structure and function of #2
Intercalated disks
function: Join adjacent cardiac muscle cells
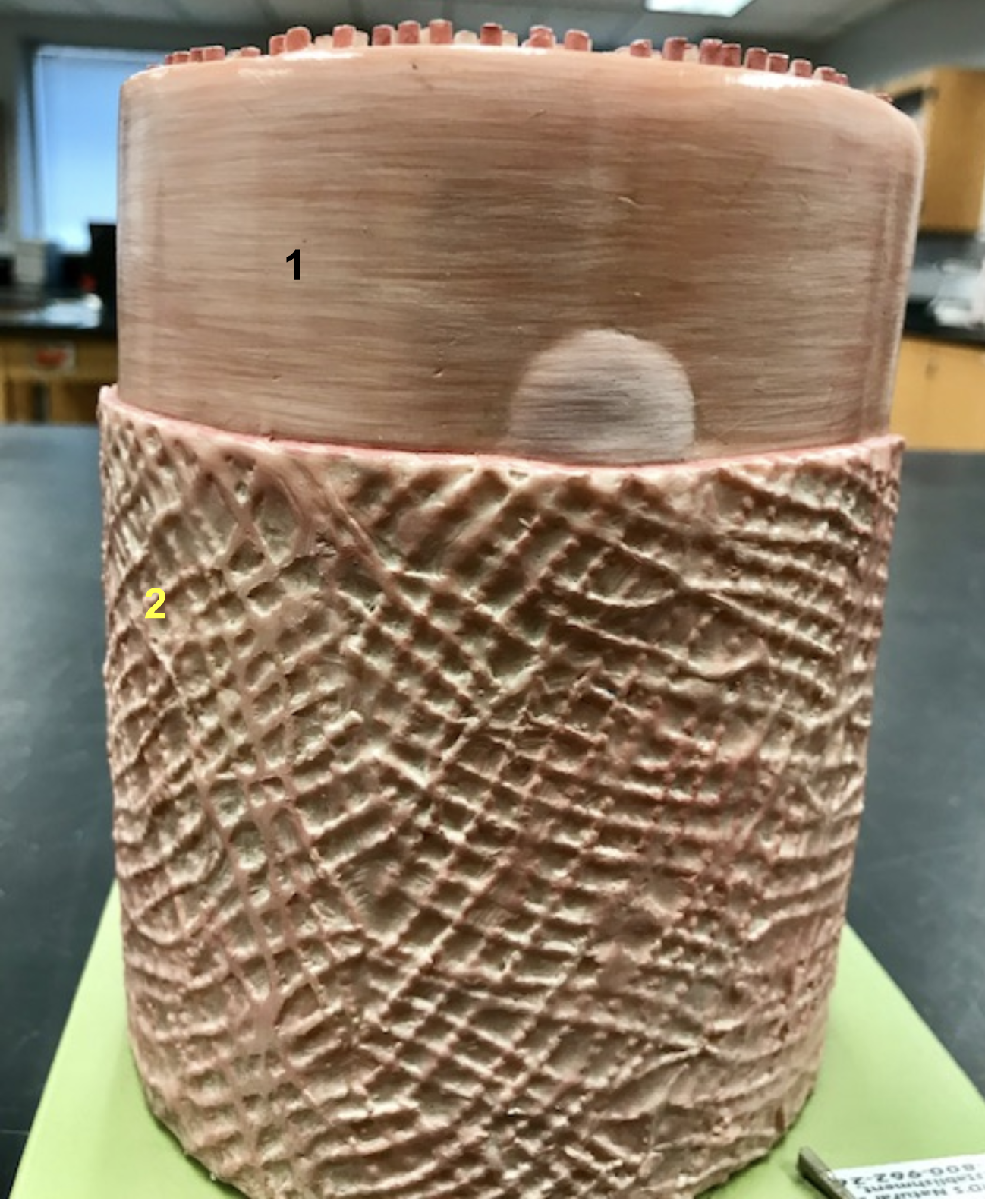

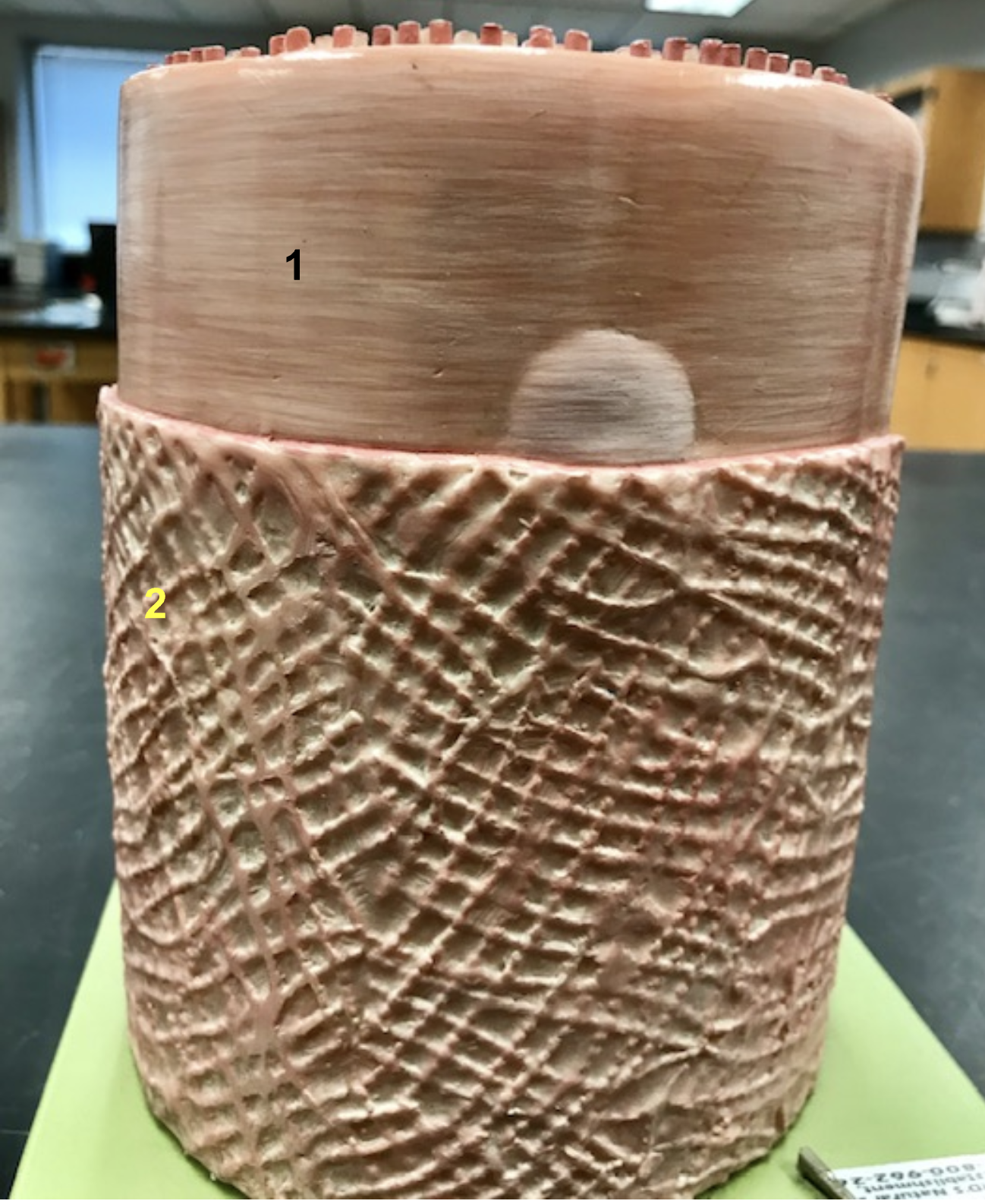
Identify the structure and function of #1
Sarcolemma of skeletal muscle
function: action potential occurs

identify the structure and function of #2
structure: Endomysium
Function: binds neighboring muscle fibers
identify the structure and function of #3
structure: Motor end plate
Function: Increase surface area
identify the structure #4
synaptic bulb
identify the structure of #5
telodendria
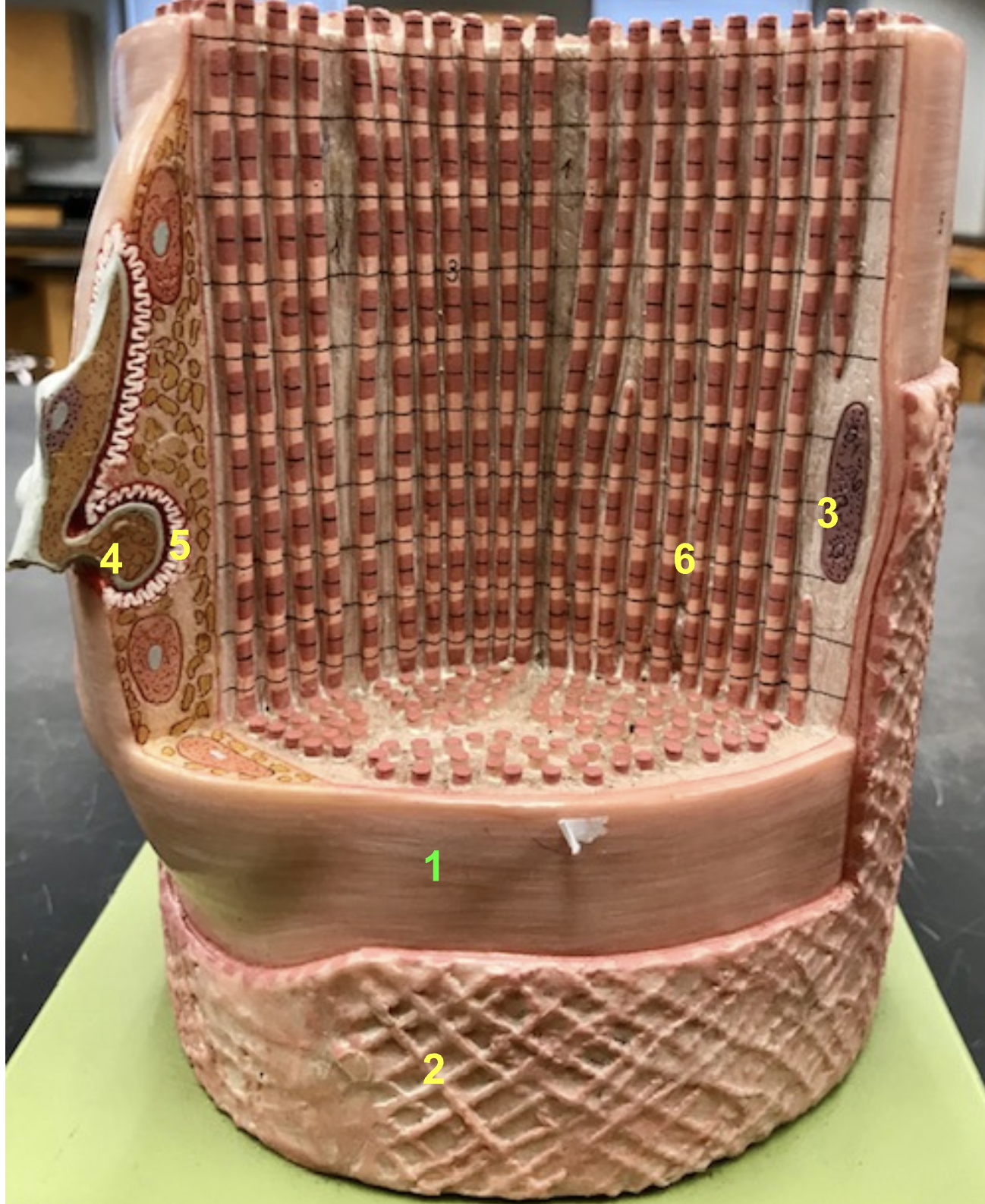

identify the structure of #3
Nucleus
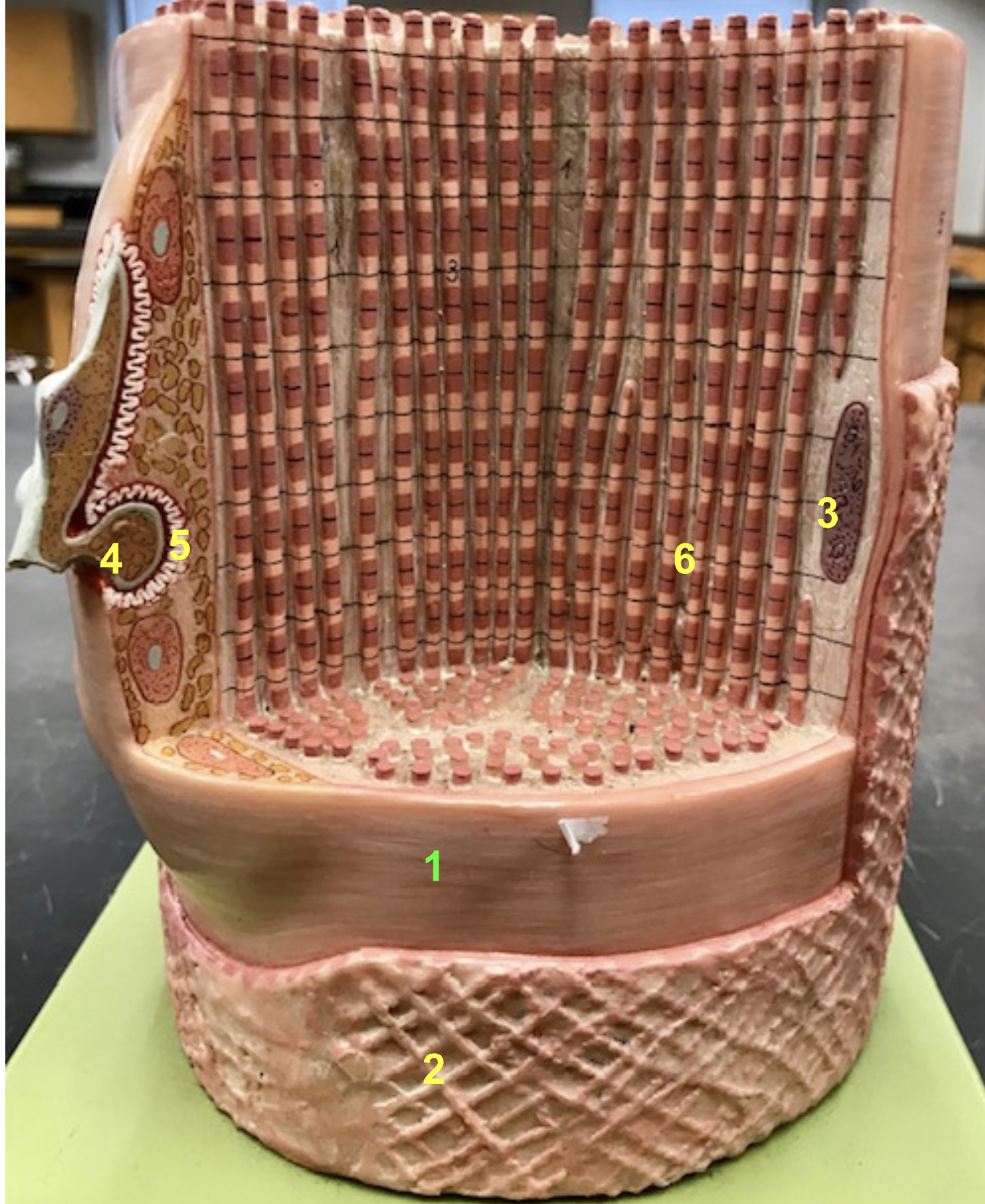

identify the structure anf function of #6
Structure: Myofibrils
Function: allow fiber to contract
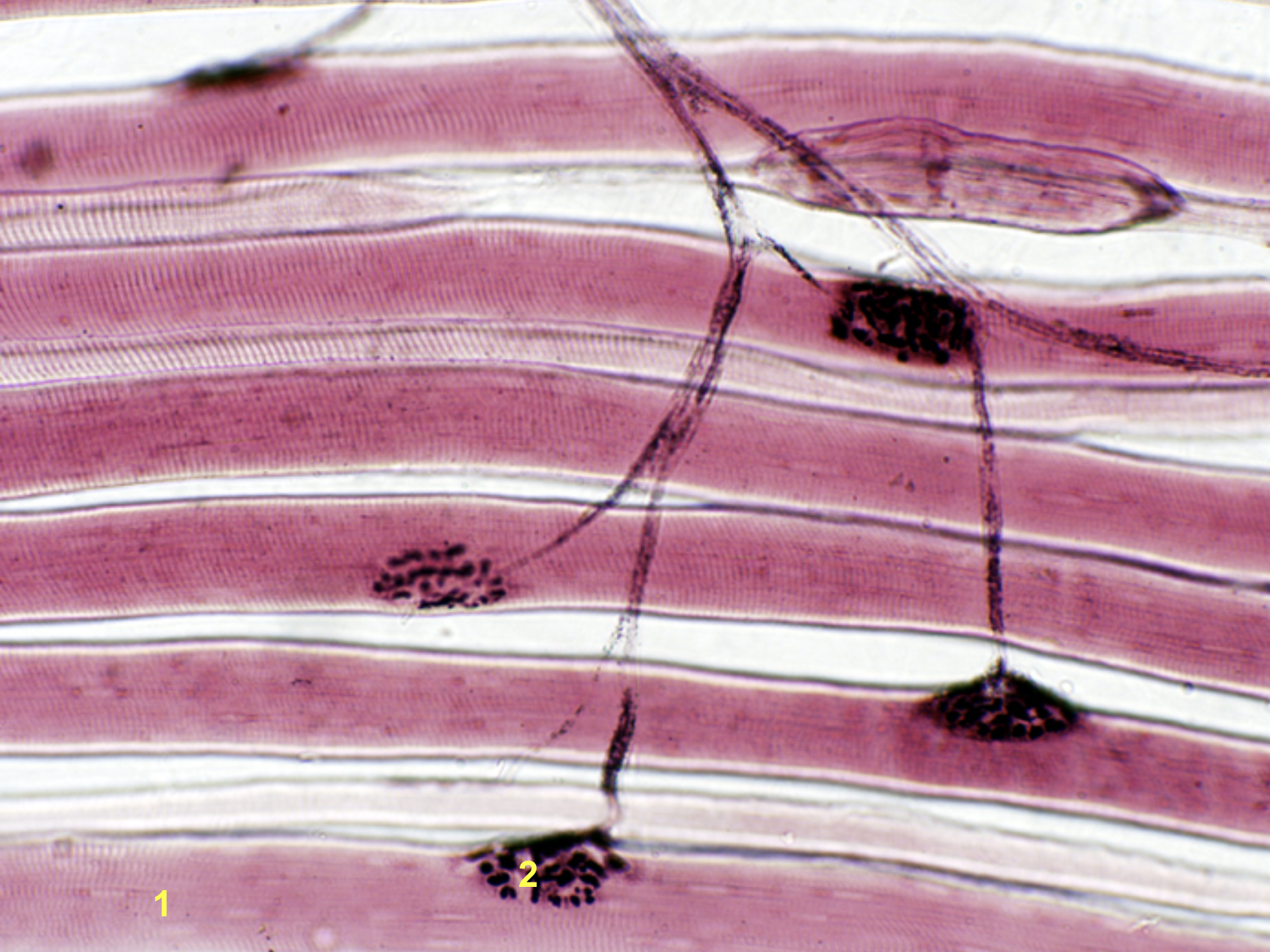
identify the structure of #2 in the skeletal muscle fiber
neuromuscular junction
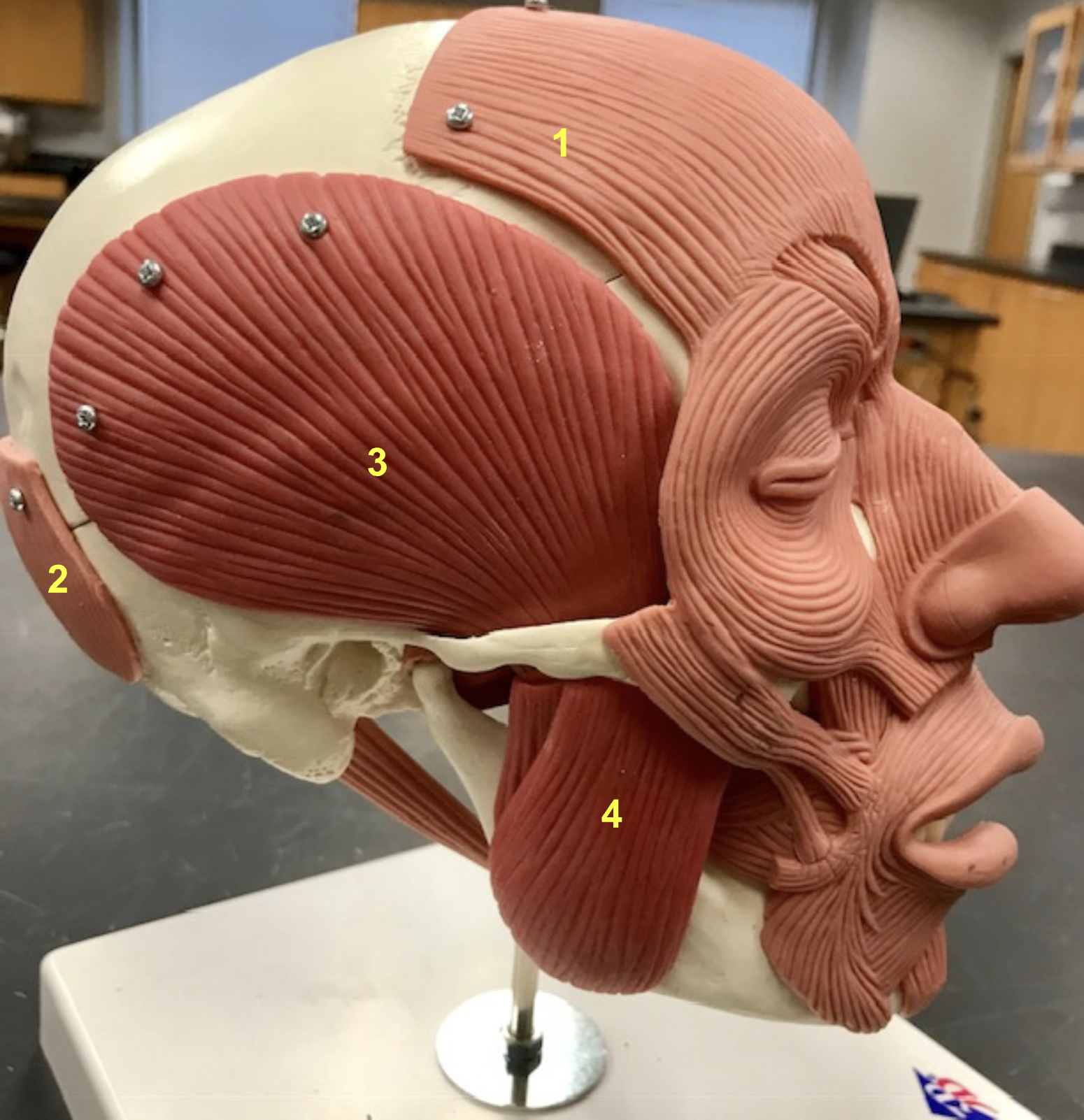
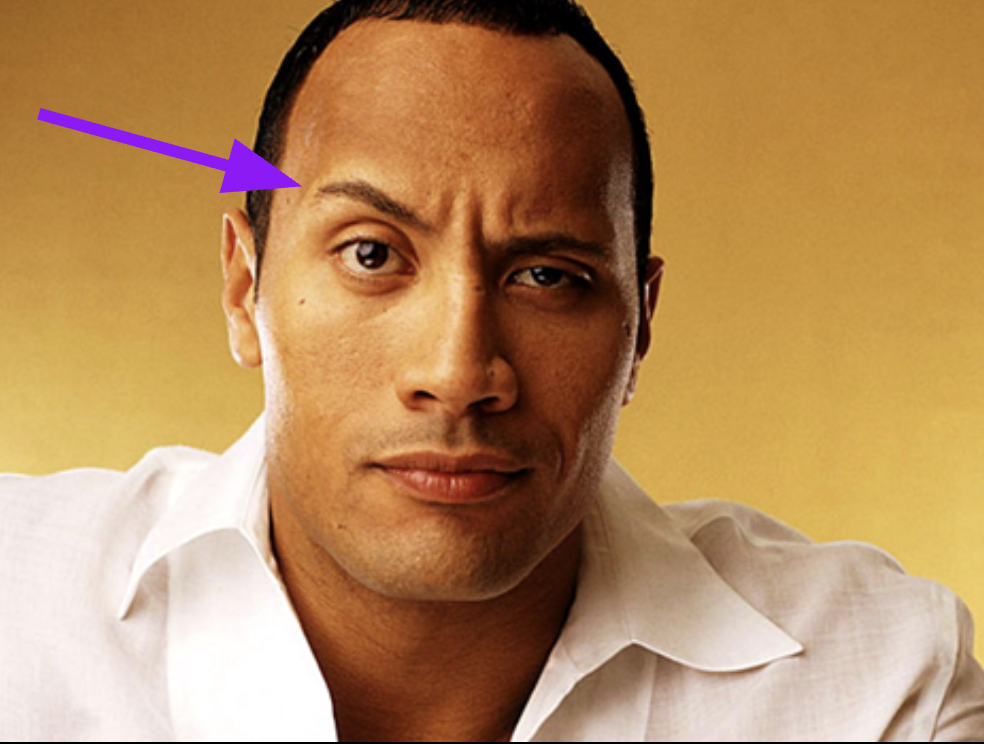
identify the structure and function of #1 and 2
Structure: epicranius
function: Raise eyebrows
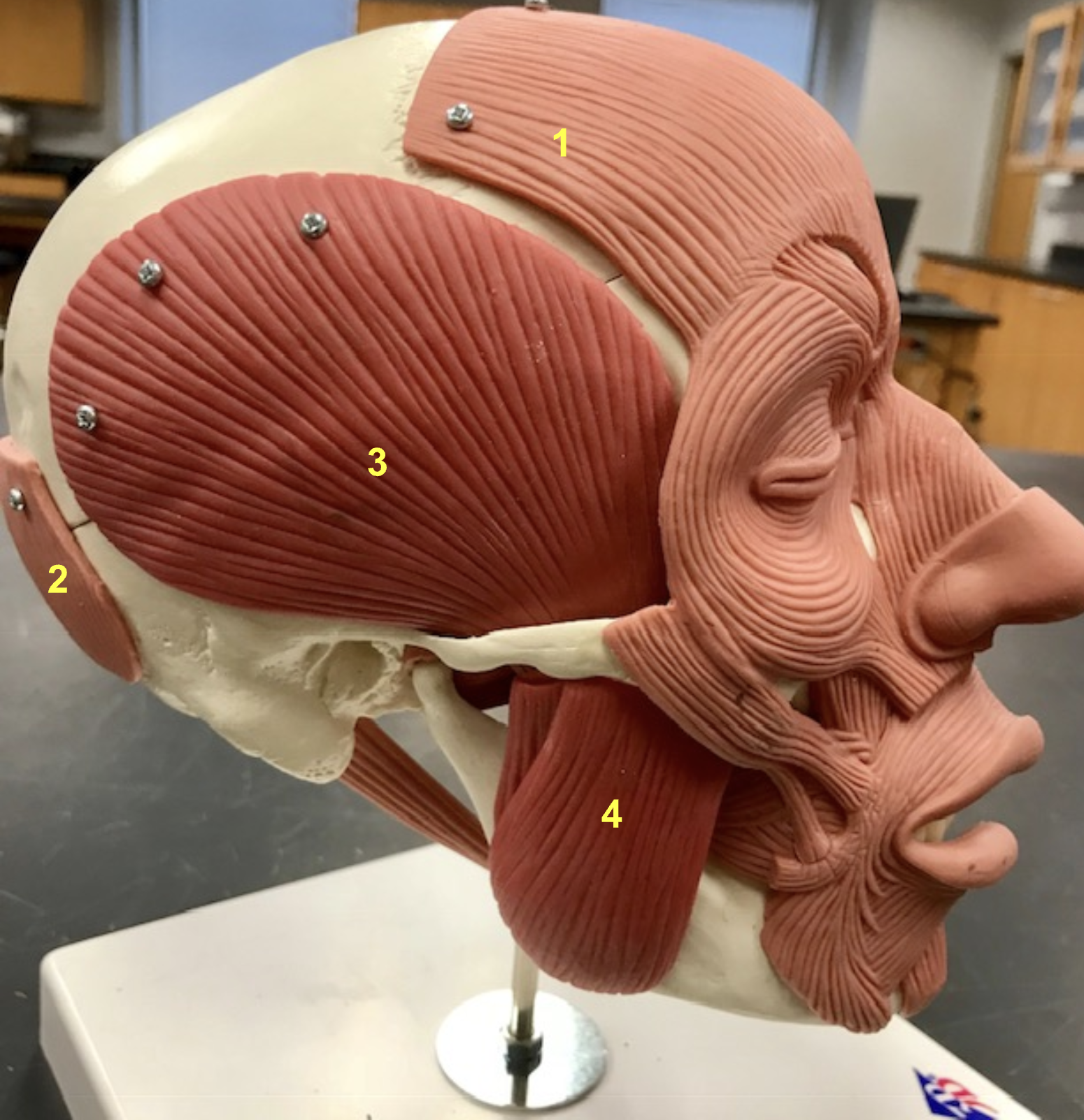
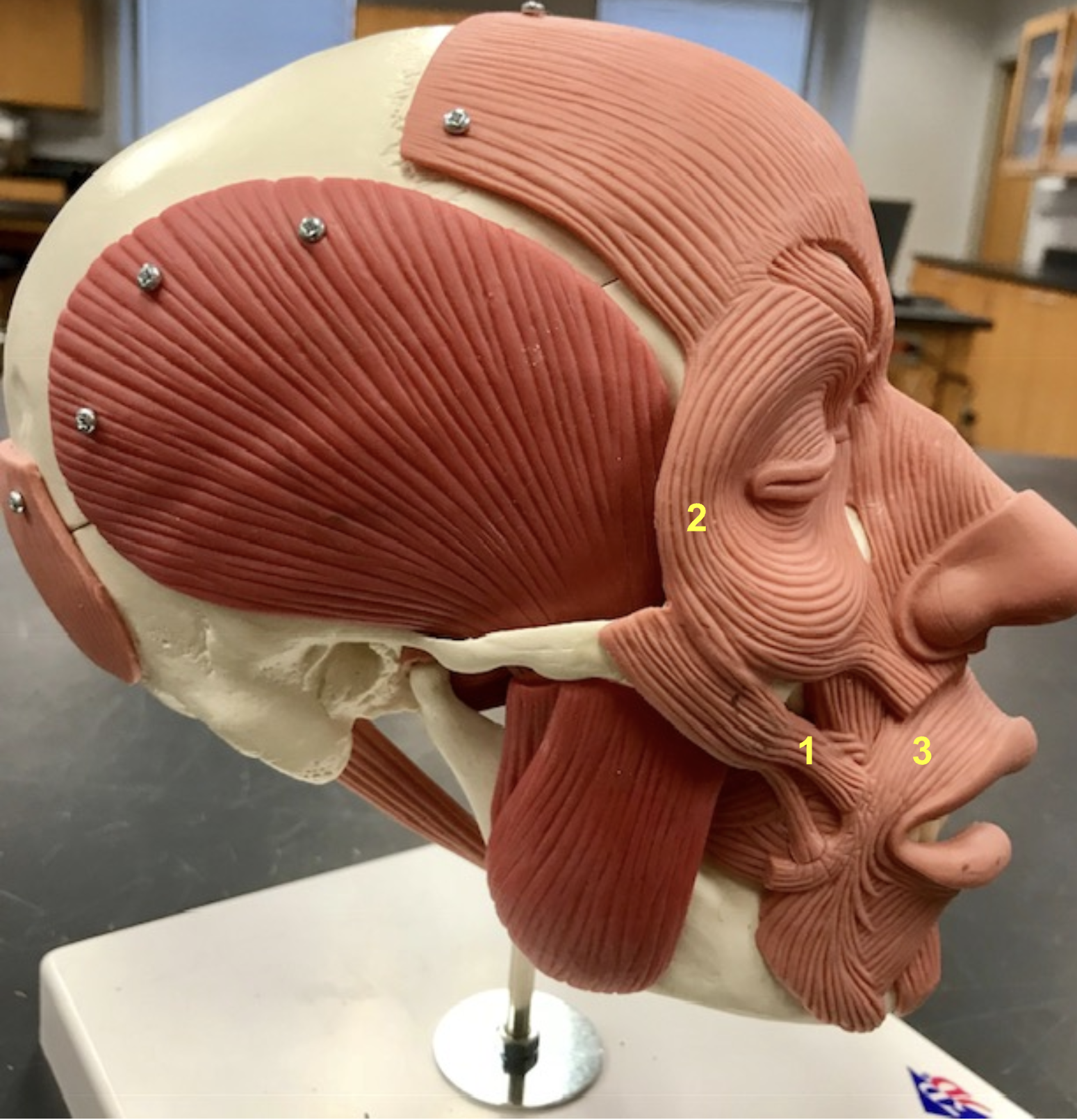
identify the structure, function, origin, and insertion of #3
structure: Temporalis
Function: elevate mandible
origin: Temporal bone
insertion: Coronoid process of mandible
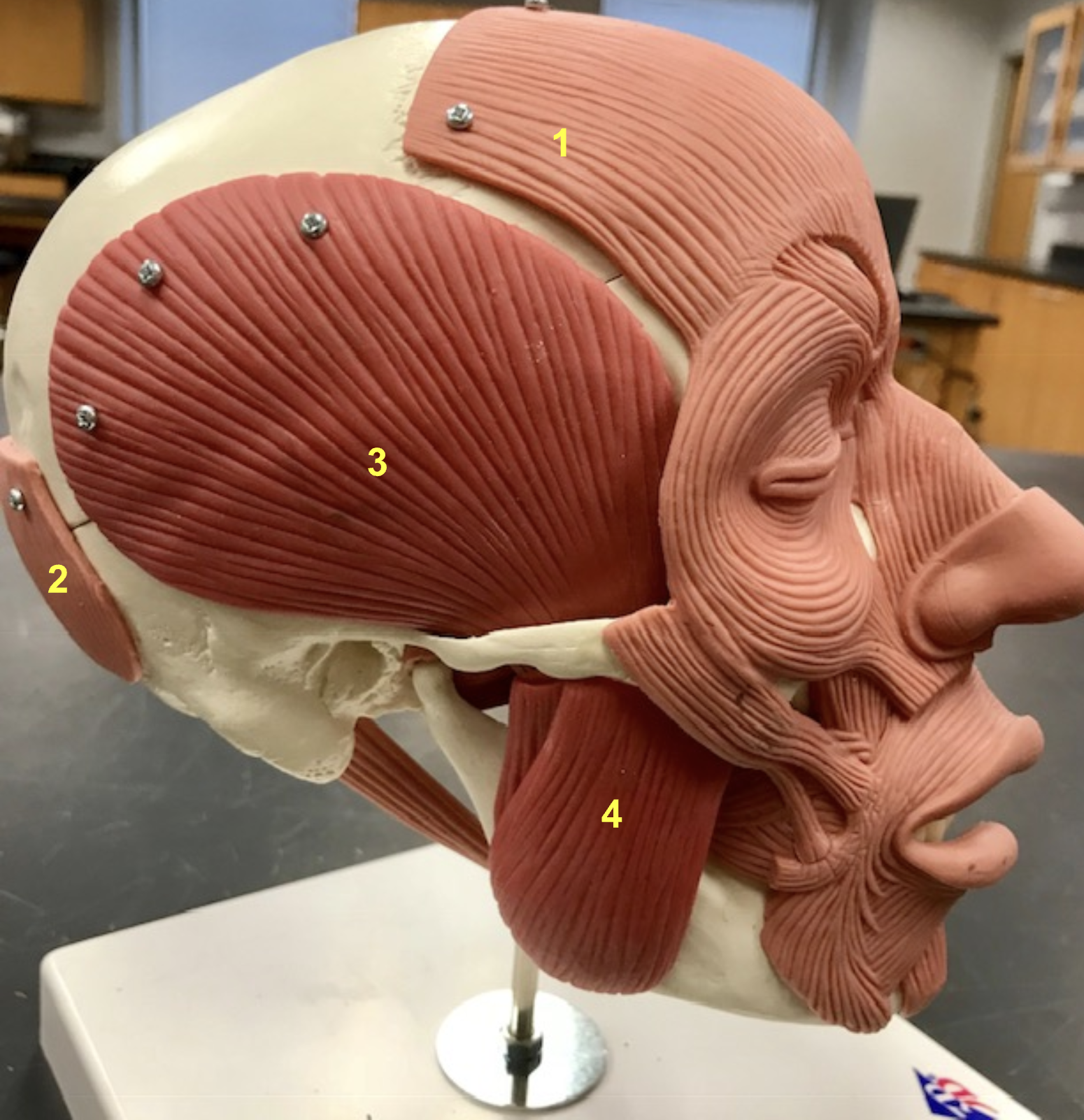
Identify the structure, function, origin, and insertion of #4 (synergist to temporalis)
Structure: Masseter
Function: Elevate Mandible
origin: Zygomatic arch
Insertion: Angle & Ramus of mandible
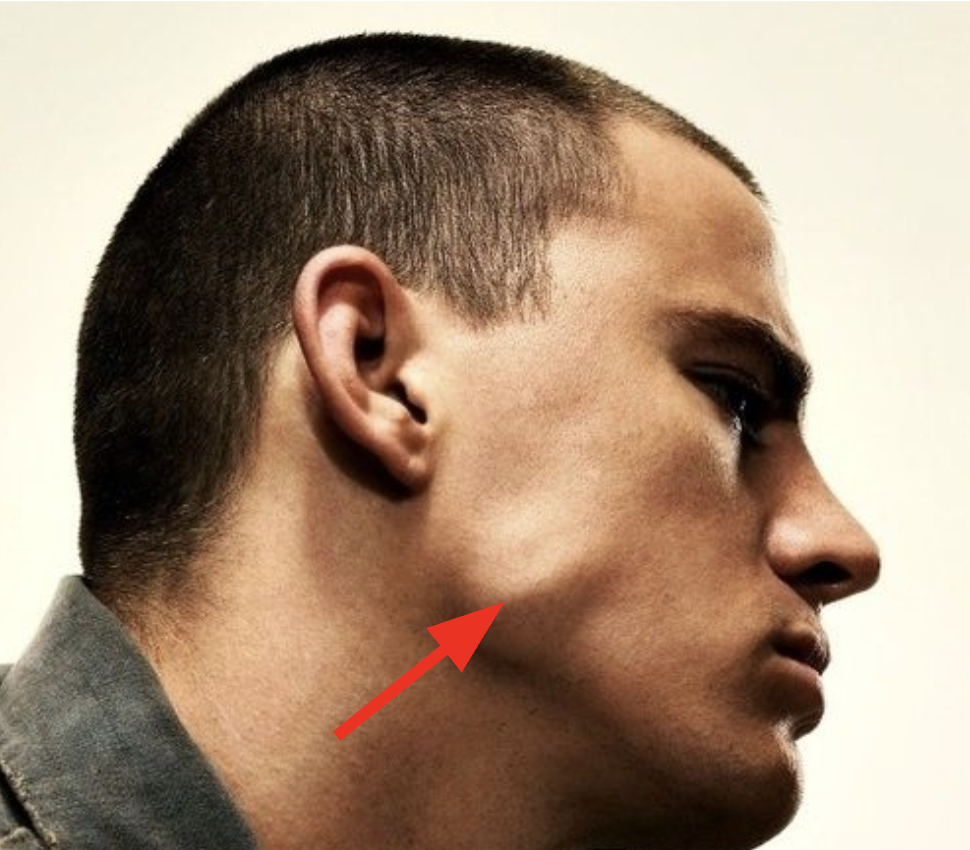
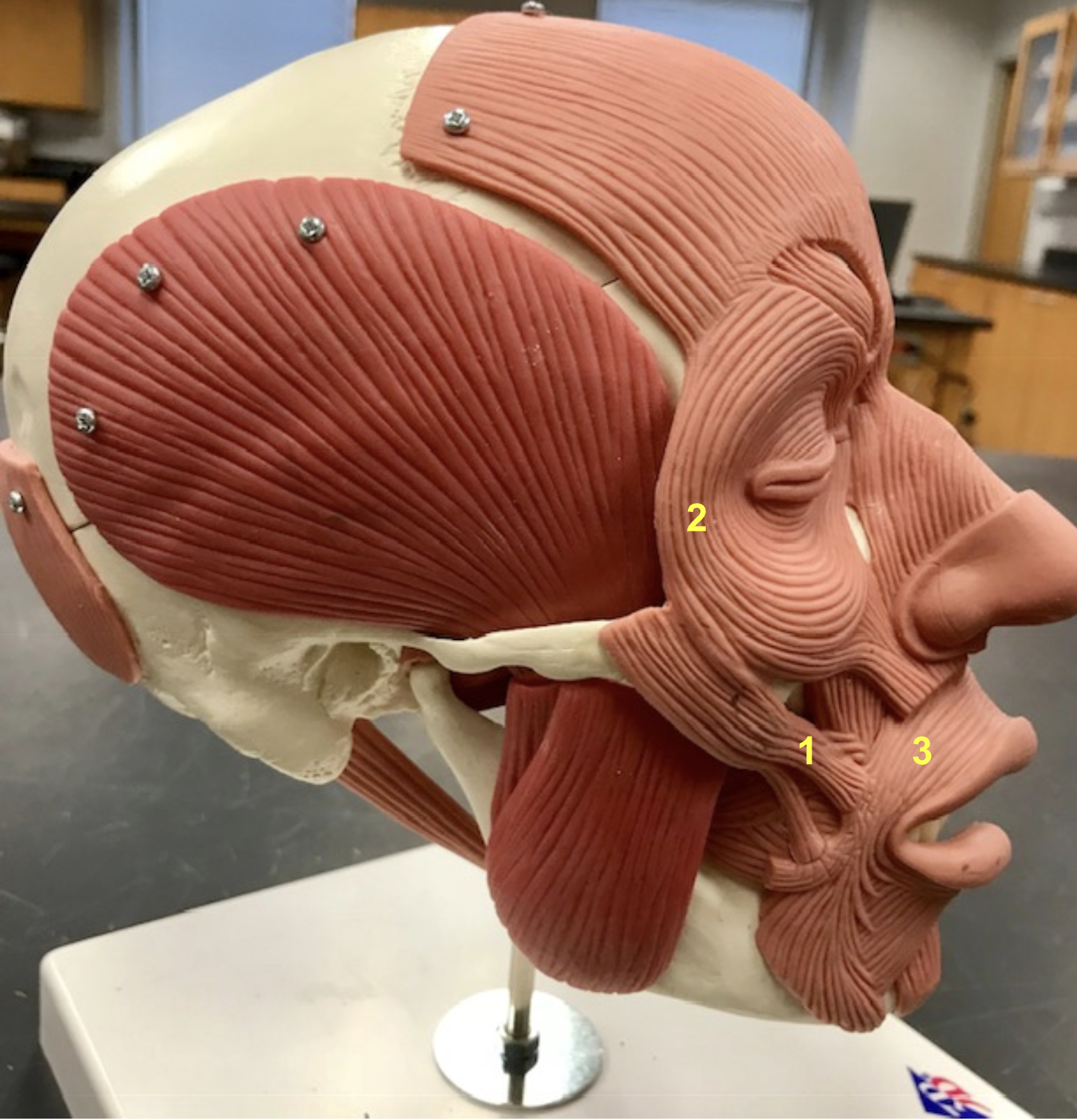
Identify the structure
Masseter

Identify the structure
epicranius
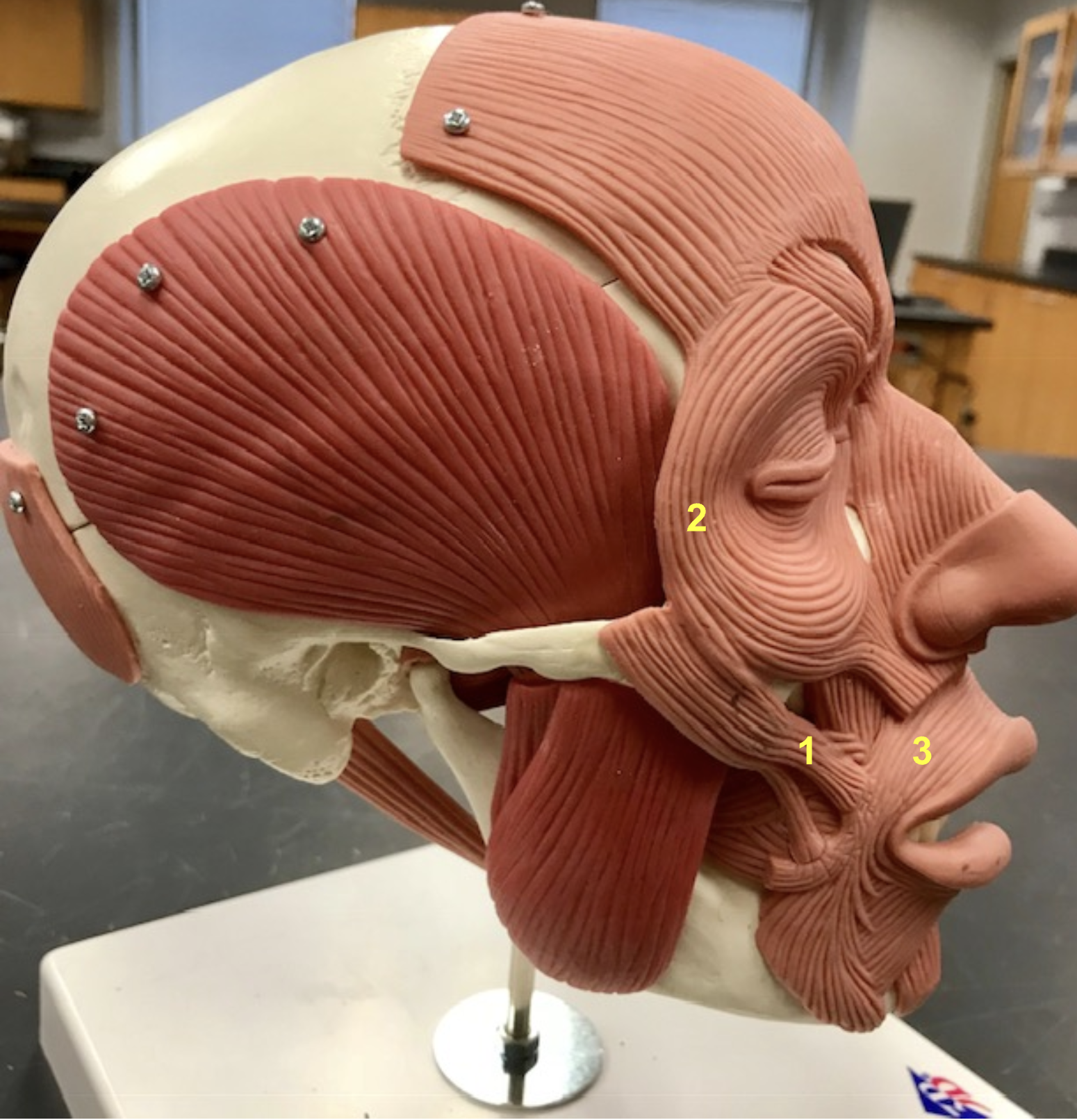
Identify the structure, function, origin, and insertion of #1
Structure: Zygomaticus major
function: Smile
Origin: zygomatic arch
Insertion: corner of mouth
identify the structure and function of #2
Structure: Orbicularis Oculi
Function: Close eye
Identify the structure and function of #3
Structure: orbicularis oris
function: purse lips
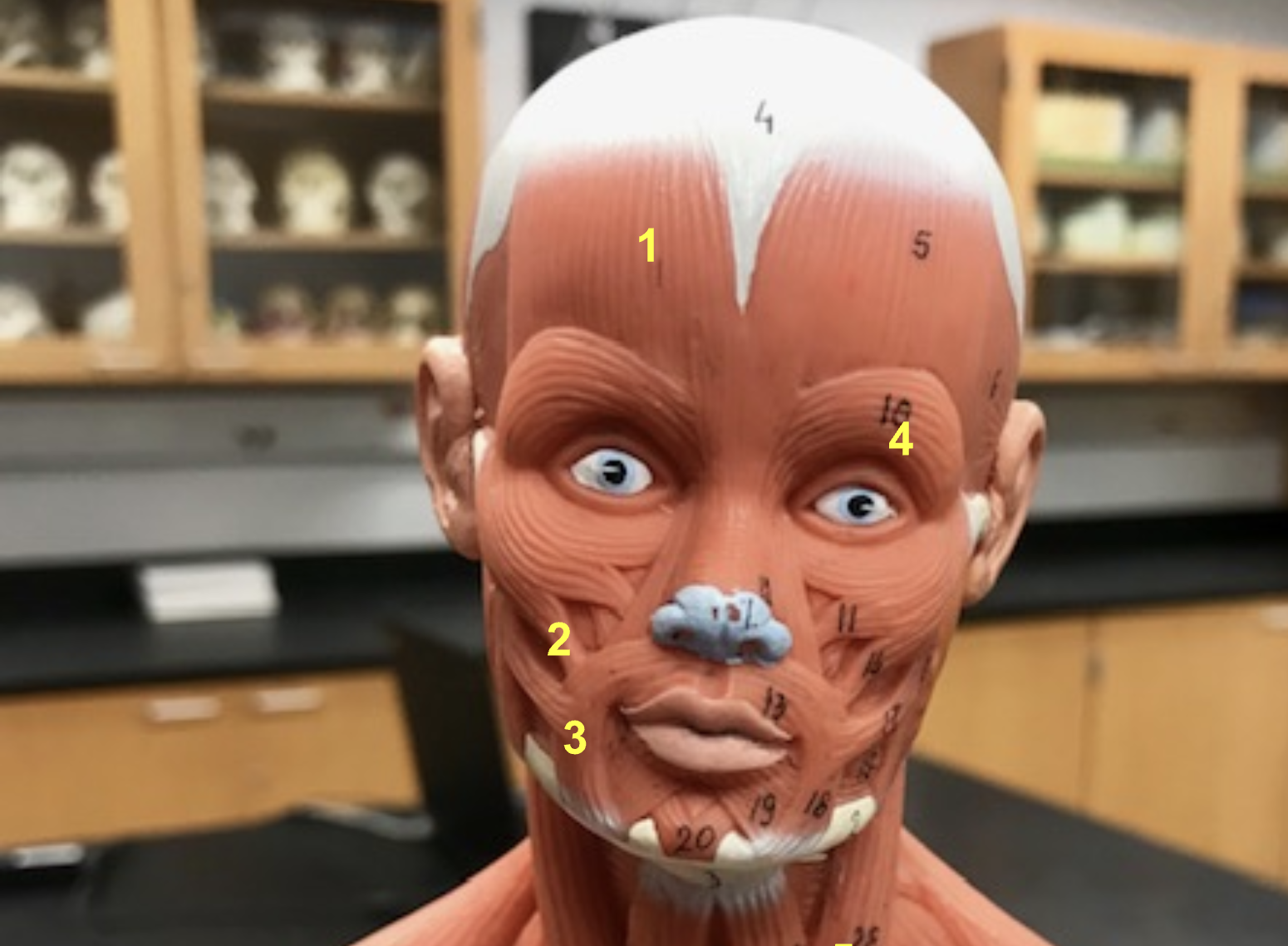
Identify the structures of #1-4
Epicranius
Zygomaticus Major
Orbicularis oris
orbicularis oculi
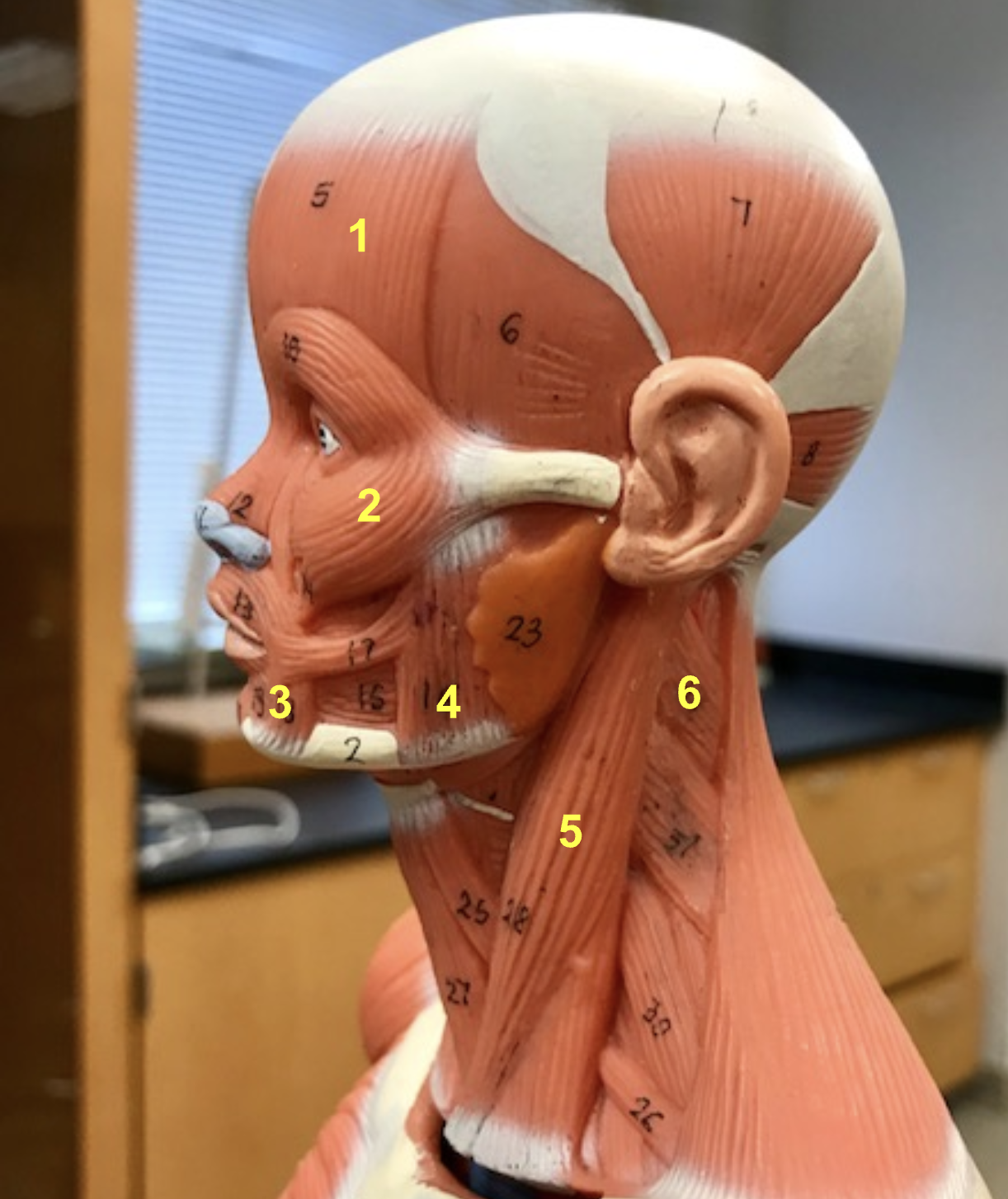
Identify the structure, function, origin, and insertion of #5
Structure: Sternocleidomastoid
Function: Rotate and flex the head
origin: sternum + clavicle
inserstion: Mastoid process temporal
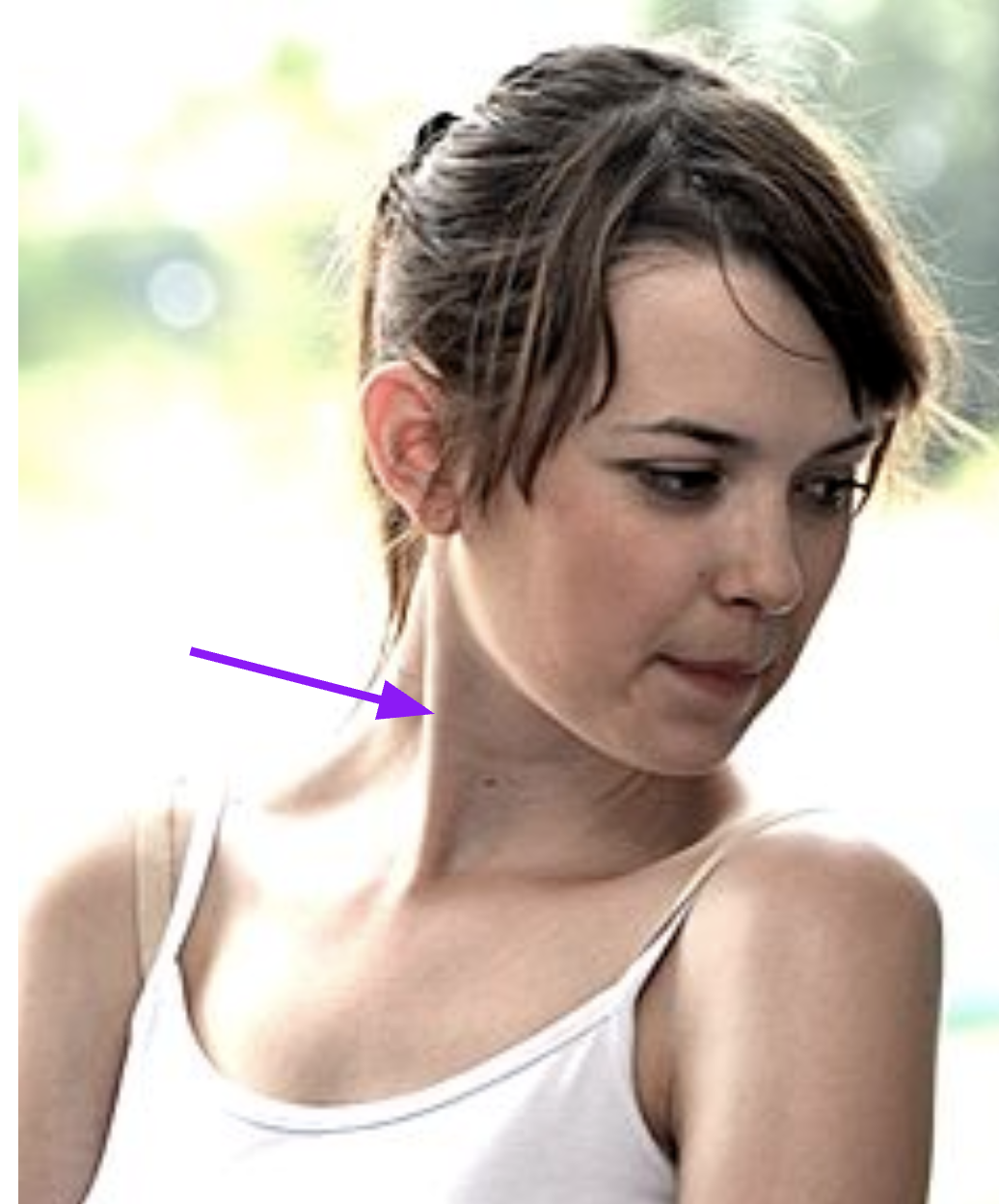
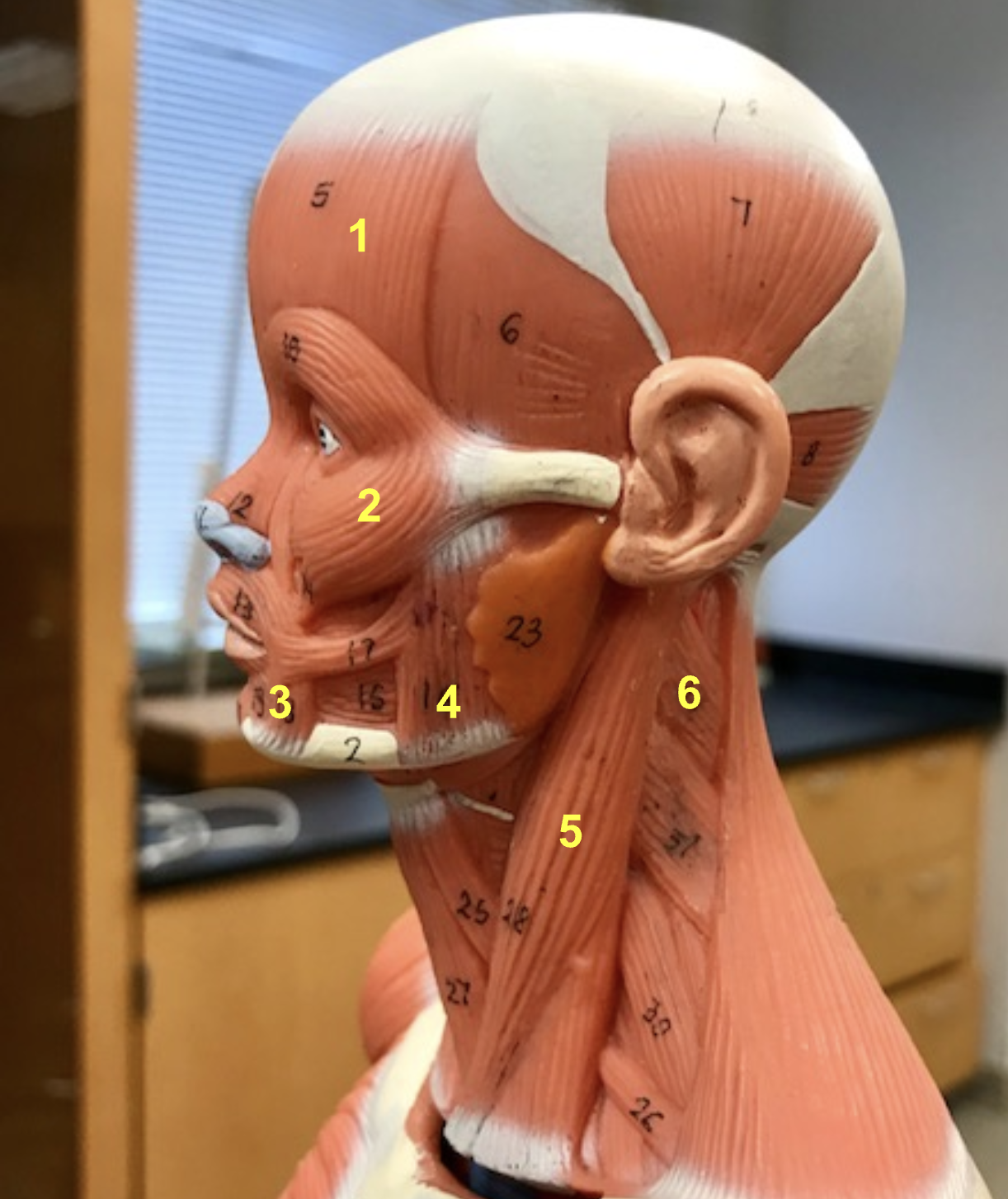
Identify the structure and function of #6
structure: Splenius capitis
function: Rotate and extend head
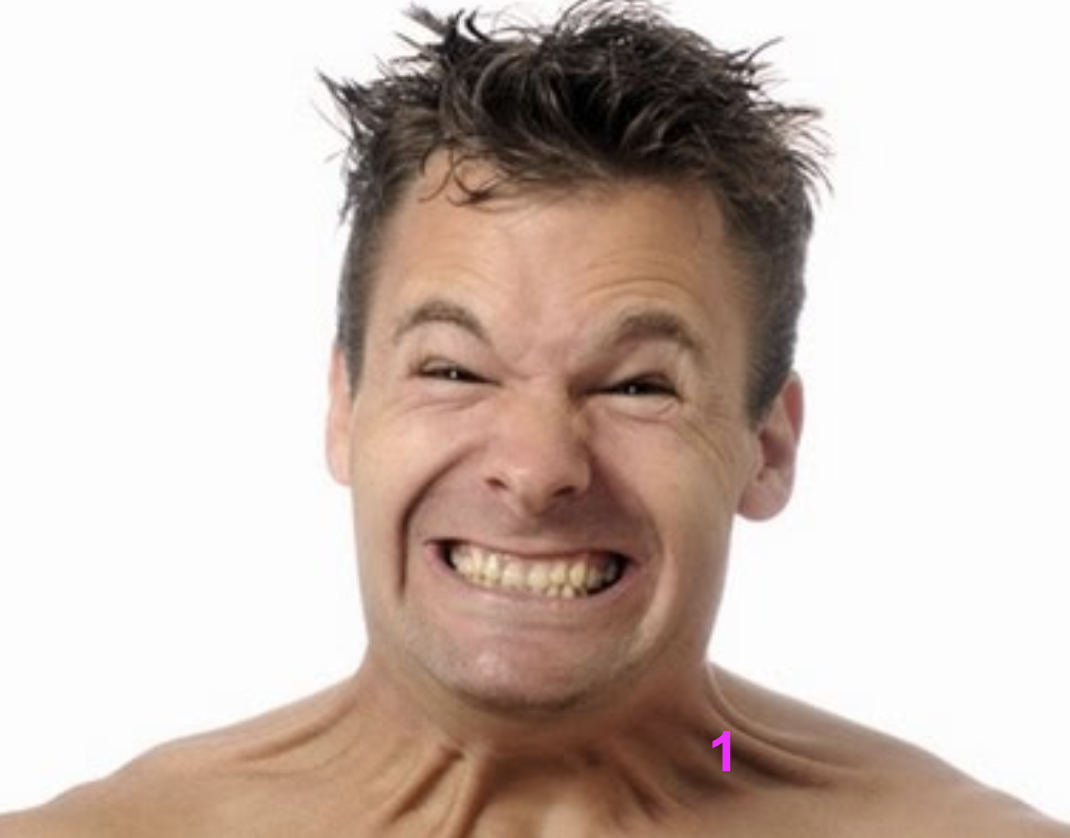

function of Platysma (superficial)
depress mandible + tighten neck skin
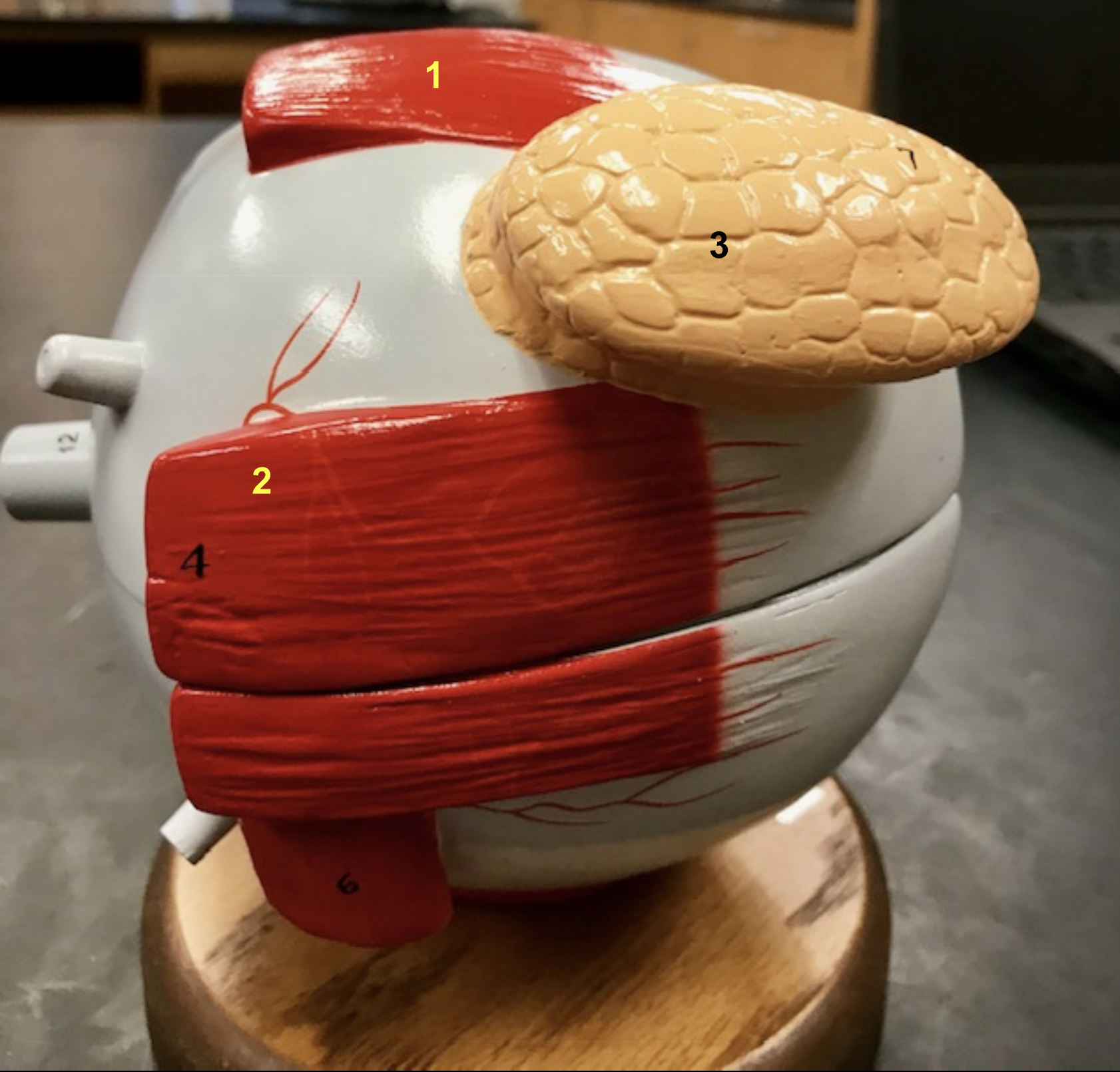

Identify the structure and function of #1
Structure: Superior rectus muscle
Function: move eye superiorly
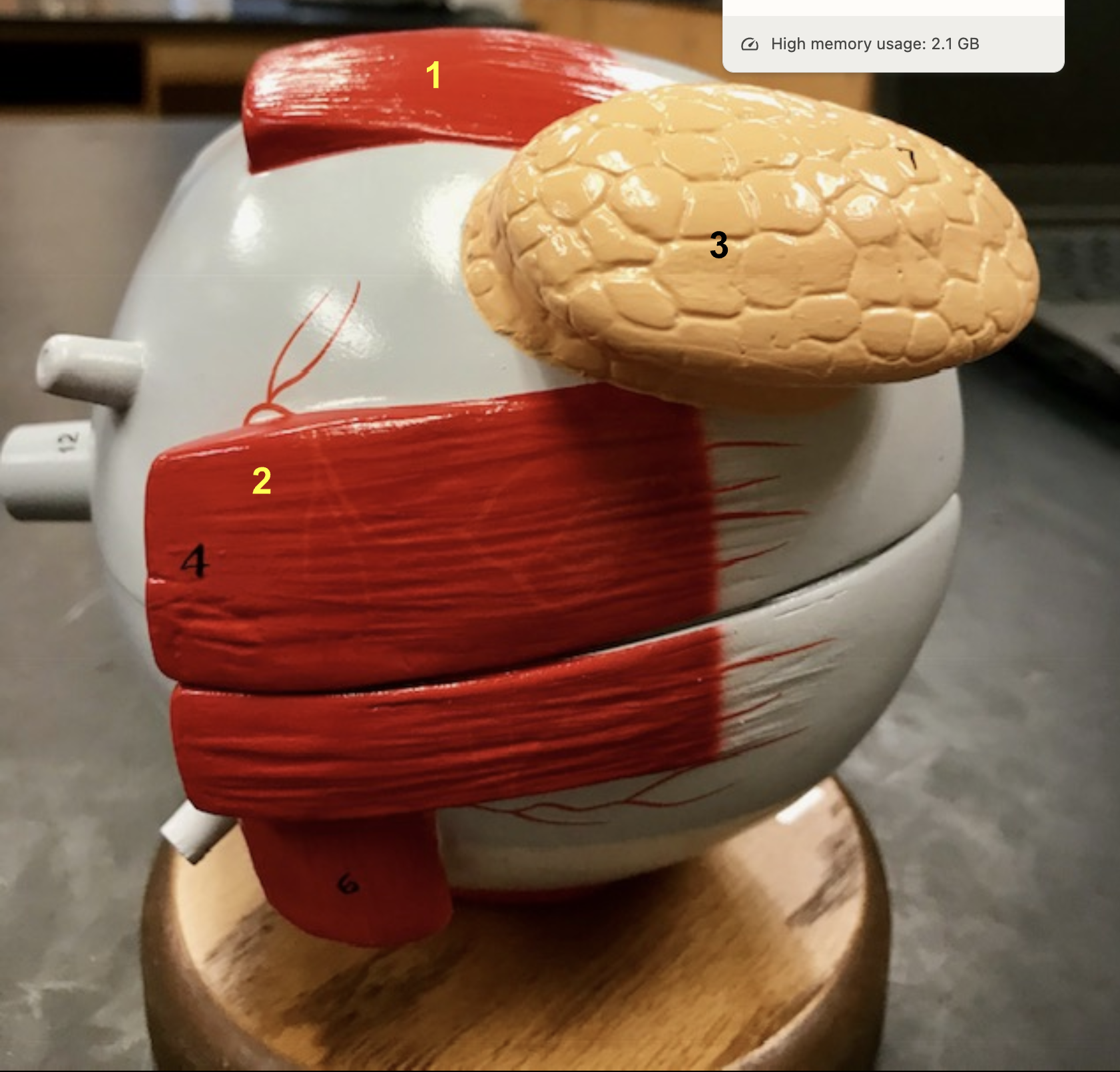

Identify the structure and function of #2
Structure: Lateral rectus muscle
function: Move eye laterally
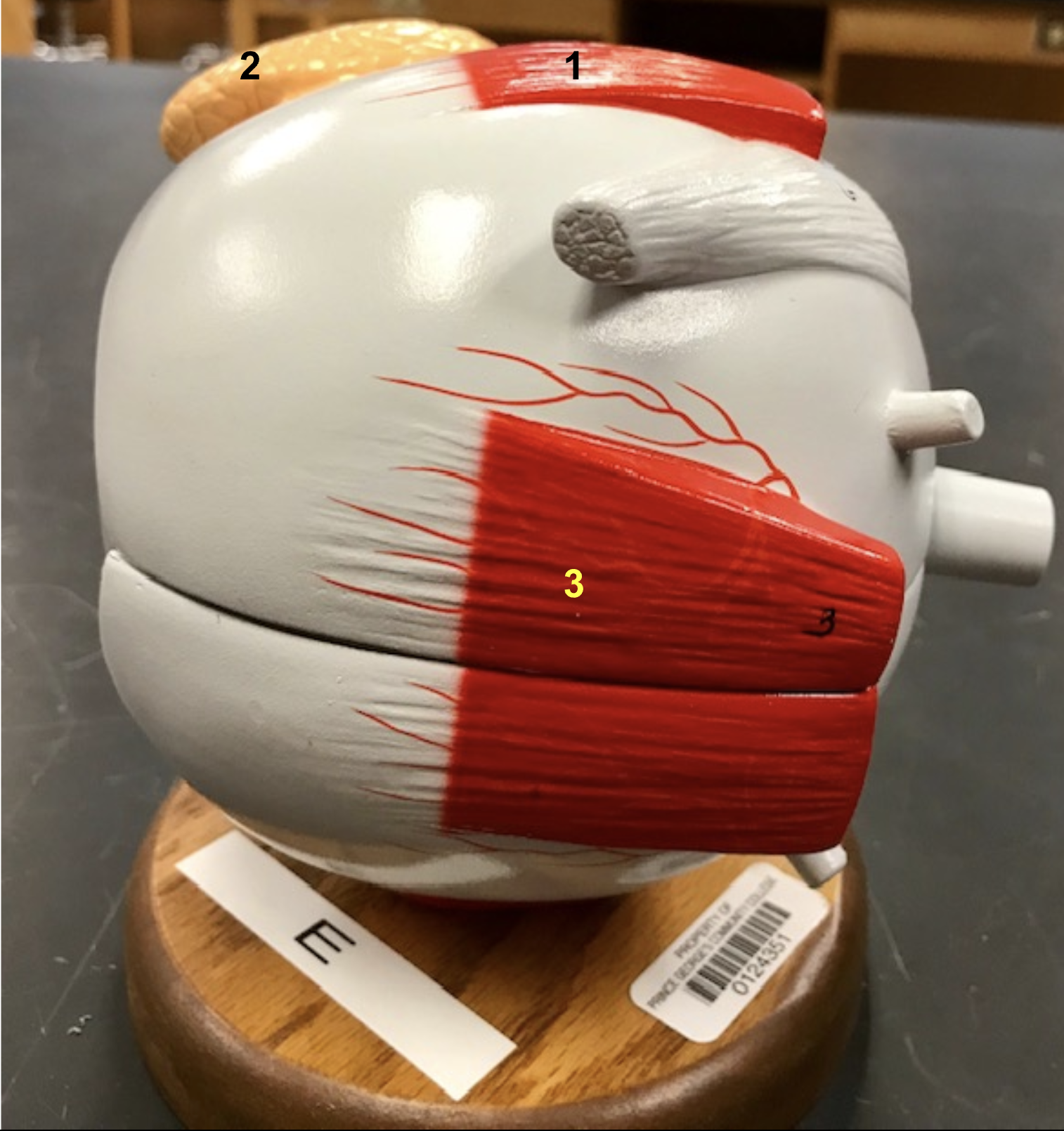

Identify the structure and function of #3
structure: Medial Rectus muslce
Function: Move eye medially

Identify the structure and function
structure: Inferior rectus muscle
Funtion: Move eye inferiorly
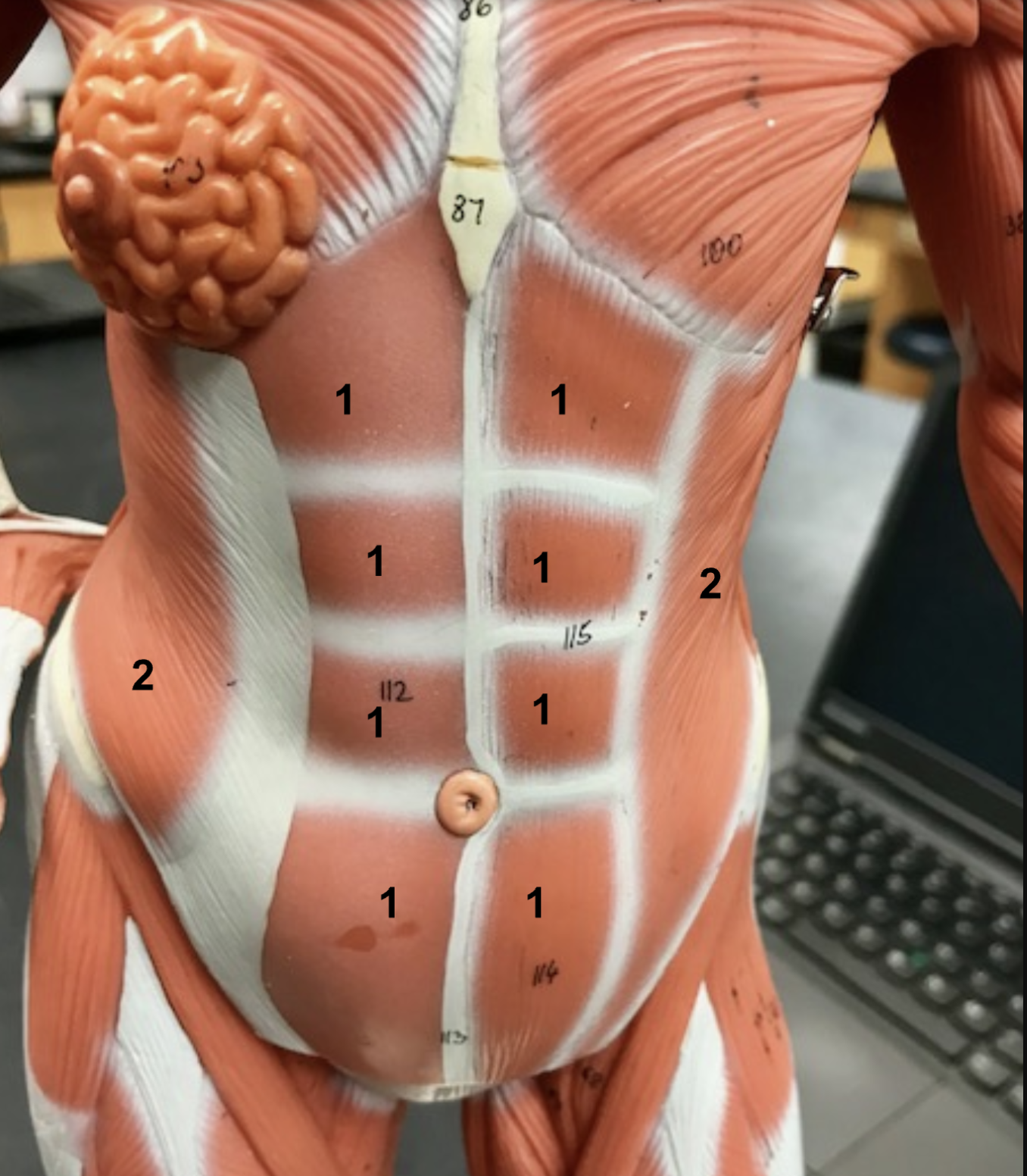
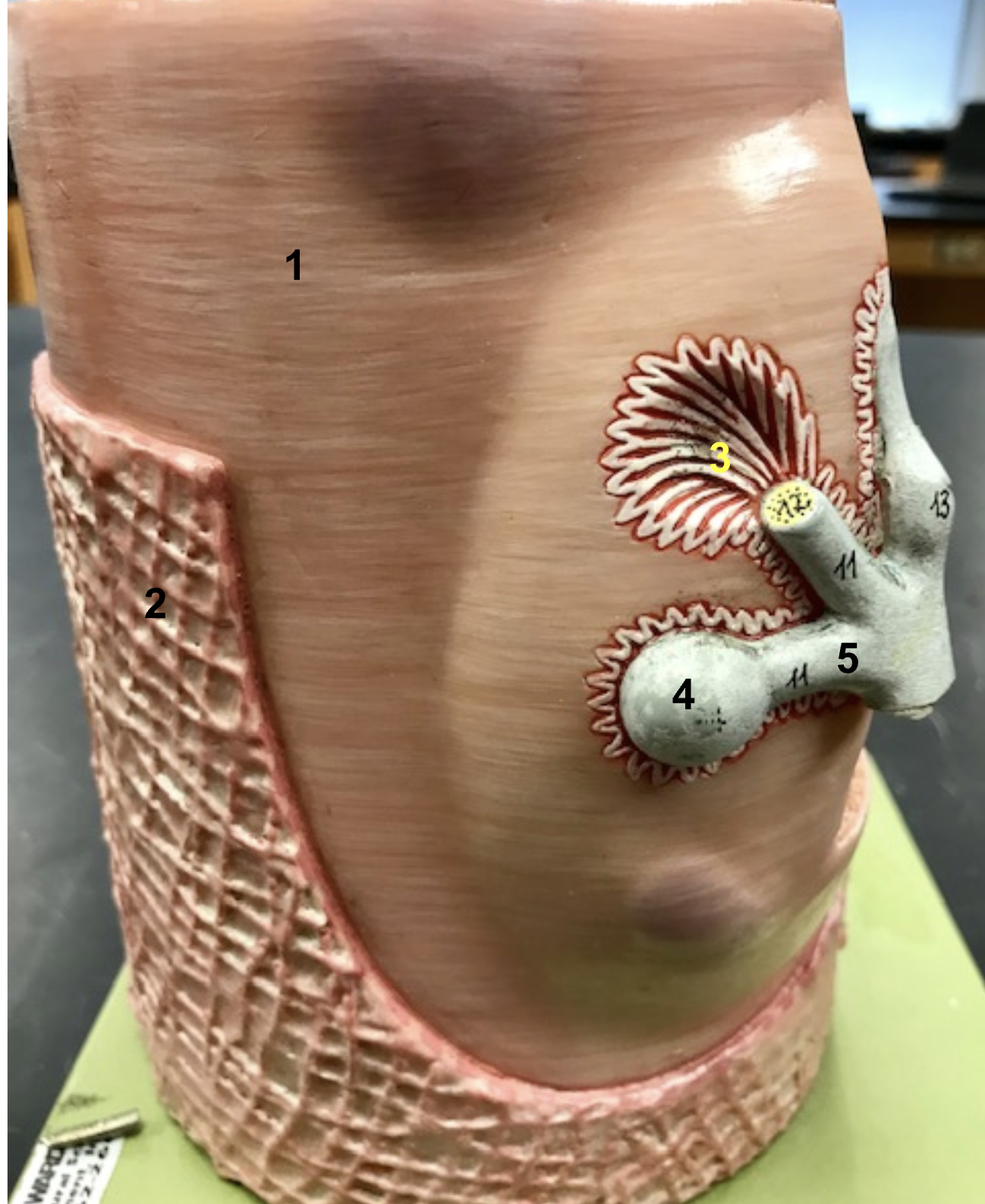
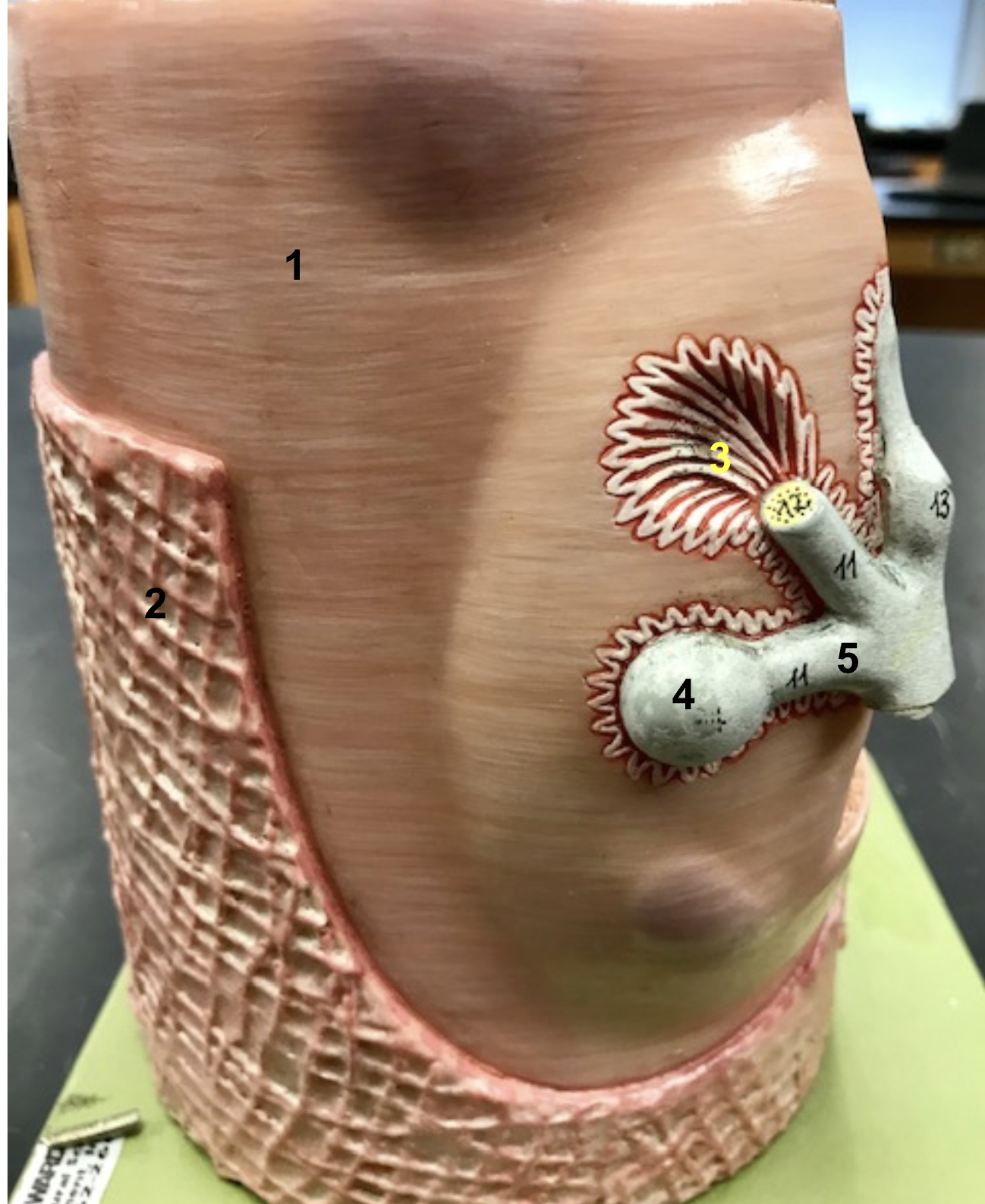
Identify the structure, function, origin, and insertion of #1
Structure: rectus abdominis
function: Flex torso
origin: pubis
insertion: zyphoid process of sternum + ribs
Name the antagonist of the rectus abdominis
Erector spinae (extend torse)
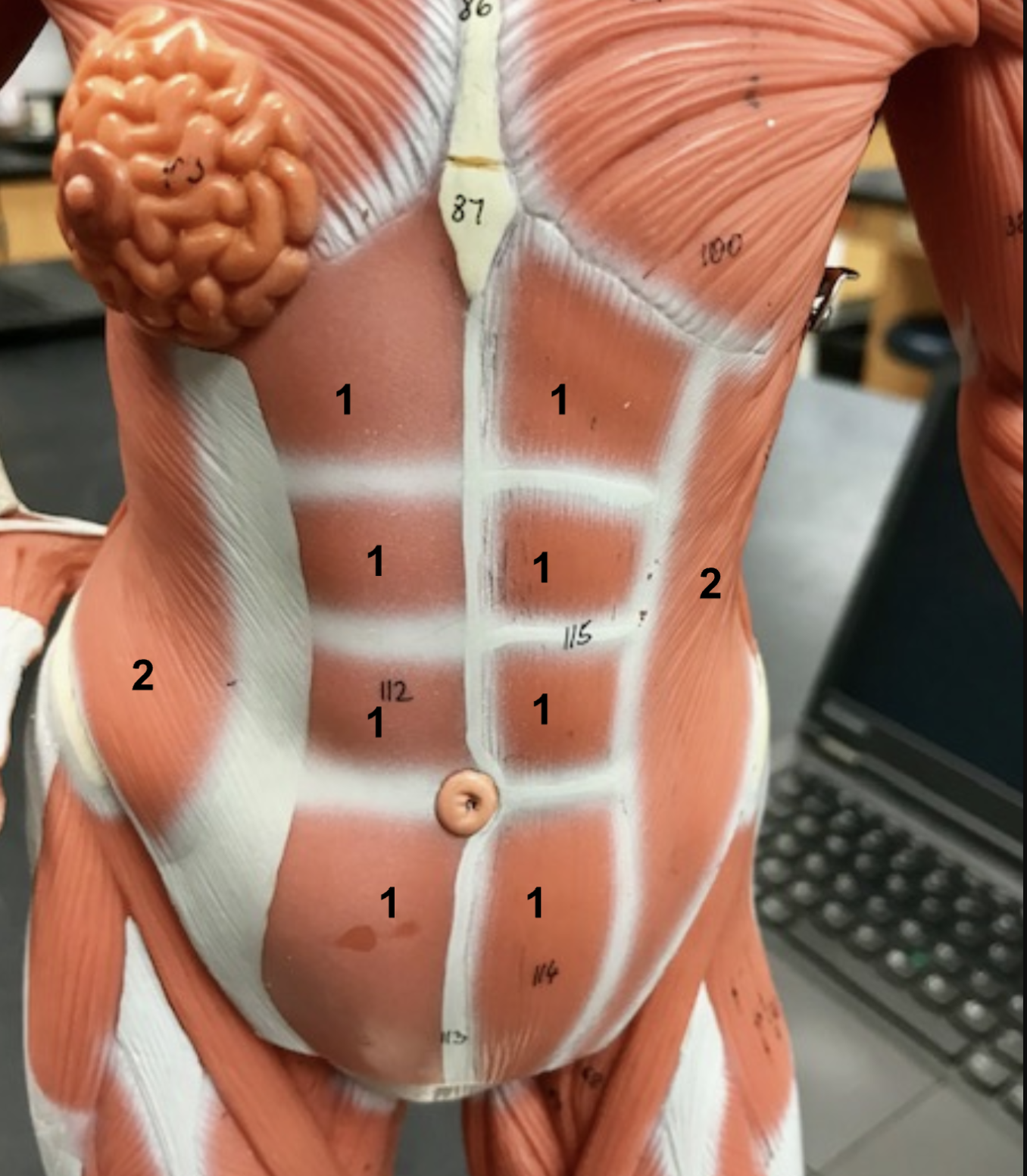
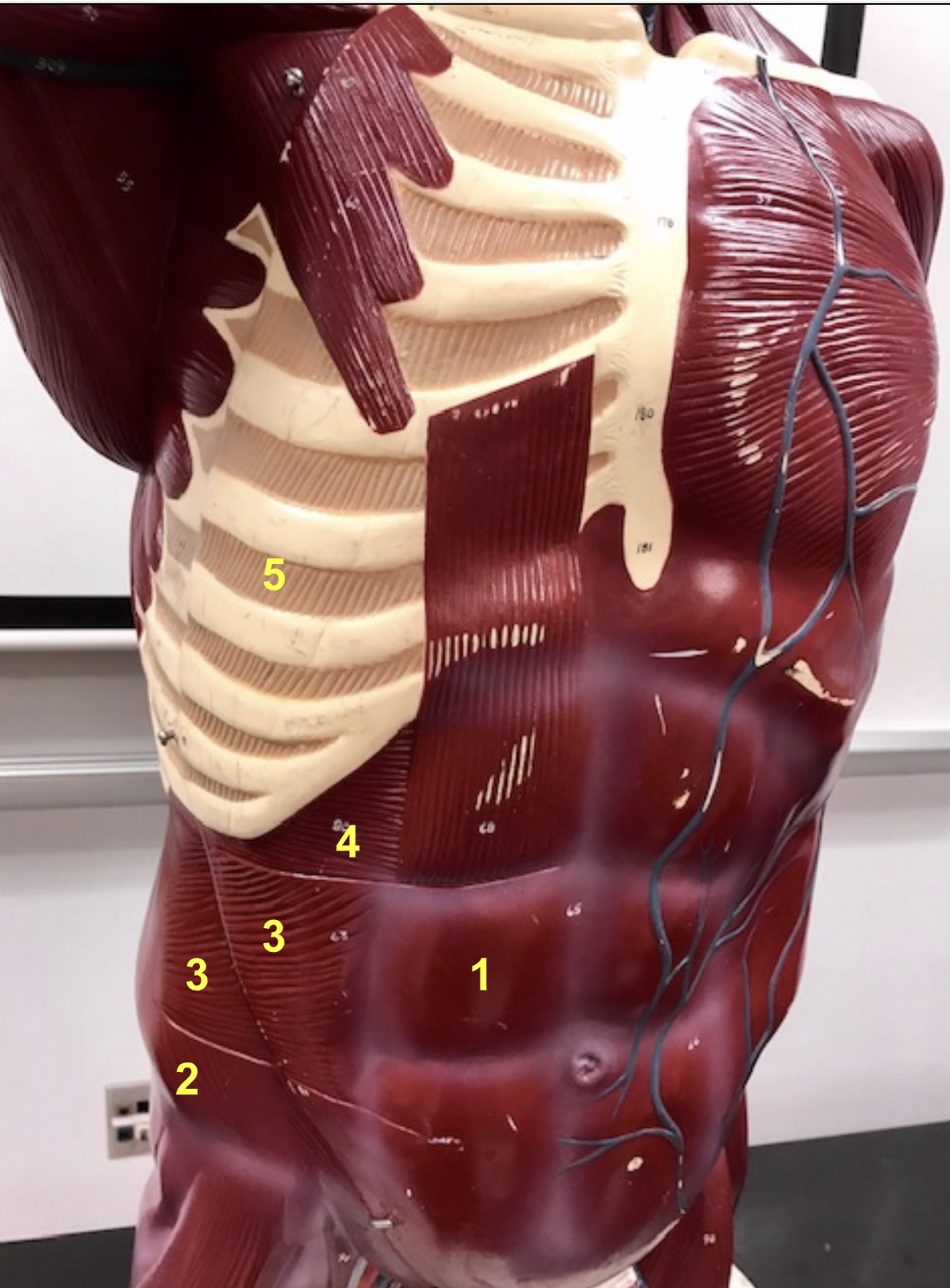
Identify the structure and function of #2
structure: External oblique
function: compress + rotate torso
Identify the structure and function of #1 (internal view)
Structure: Transverse abdominis
function: Compress torso
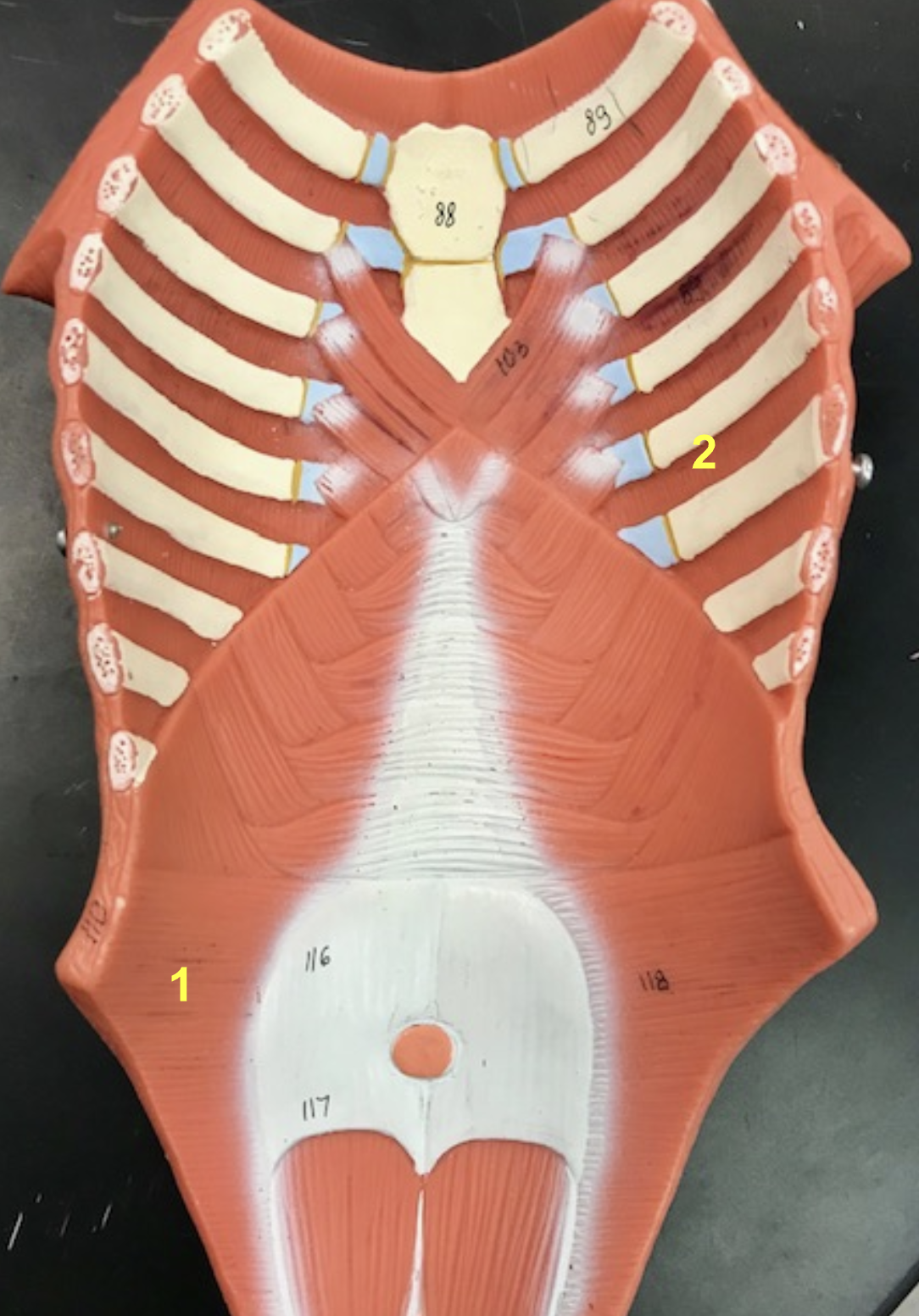
Identify the structure and function of #2
structure: internal intercostals
function: exhale
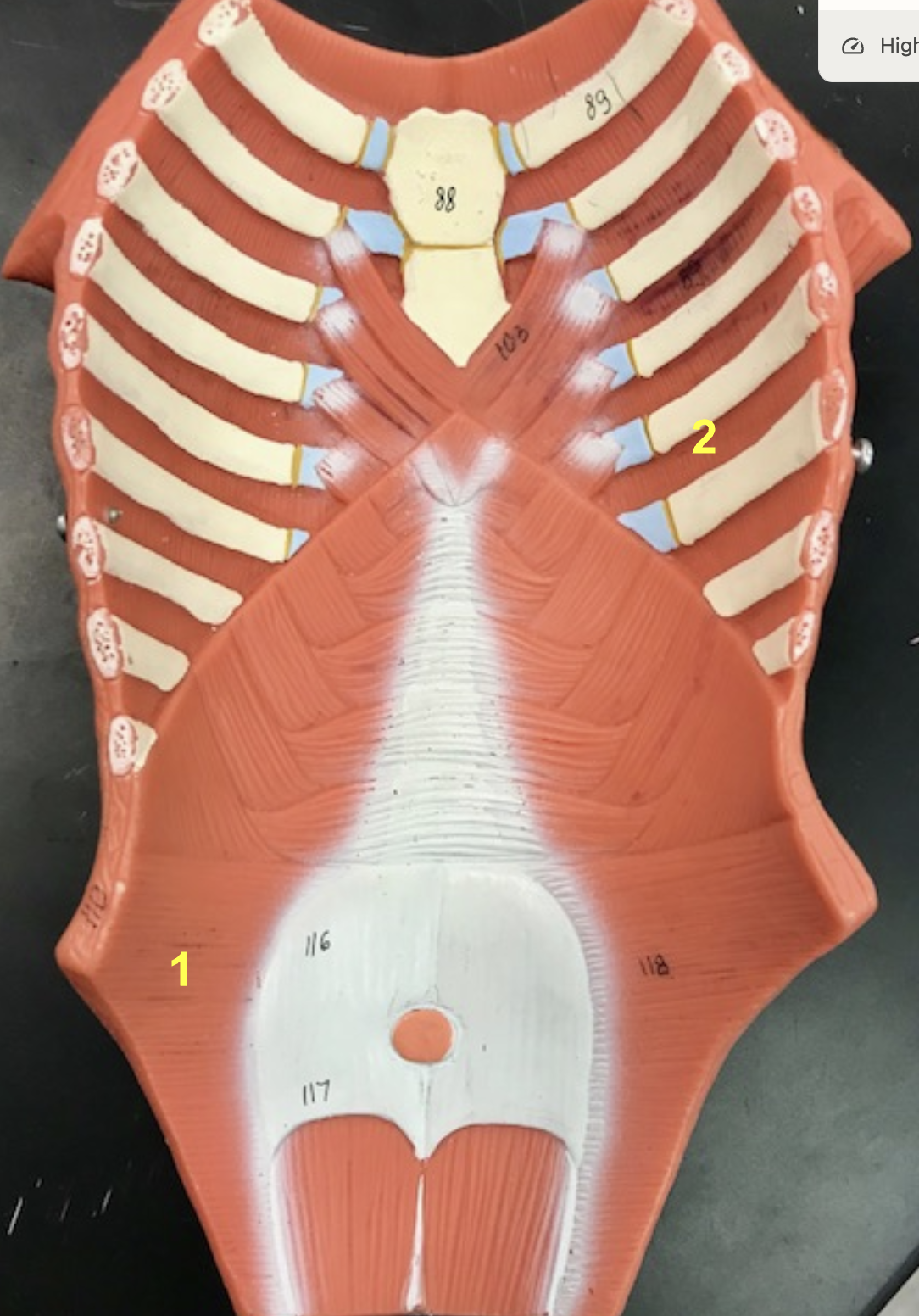
Identify the structure and function of #1
structure diagram:
function: inhale
Identify the structure and function of #5
structure: External Intercostal muscle
function: Inhale

identify structure and function
erector spinae
function: extent trunk
function of internal oblique
compress abdomen + rotate
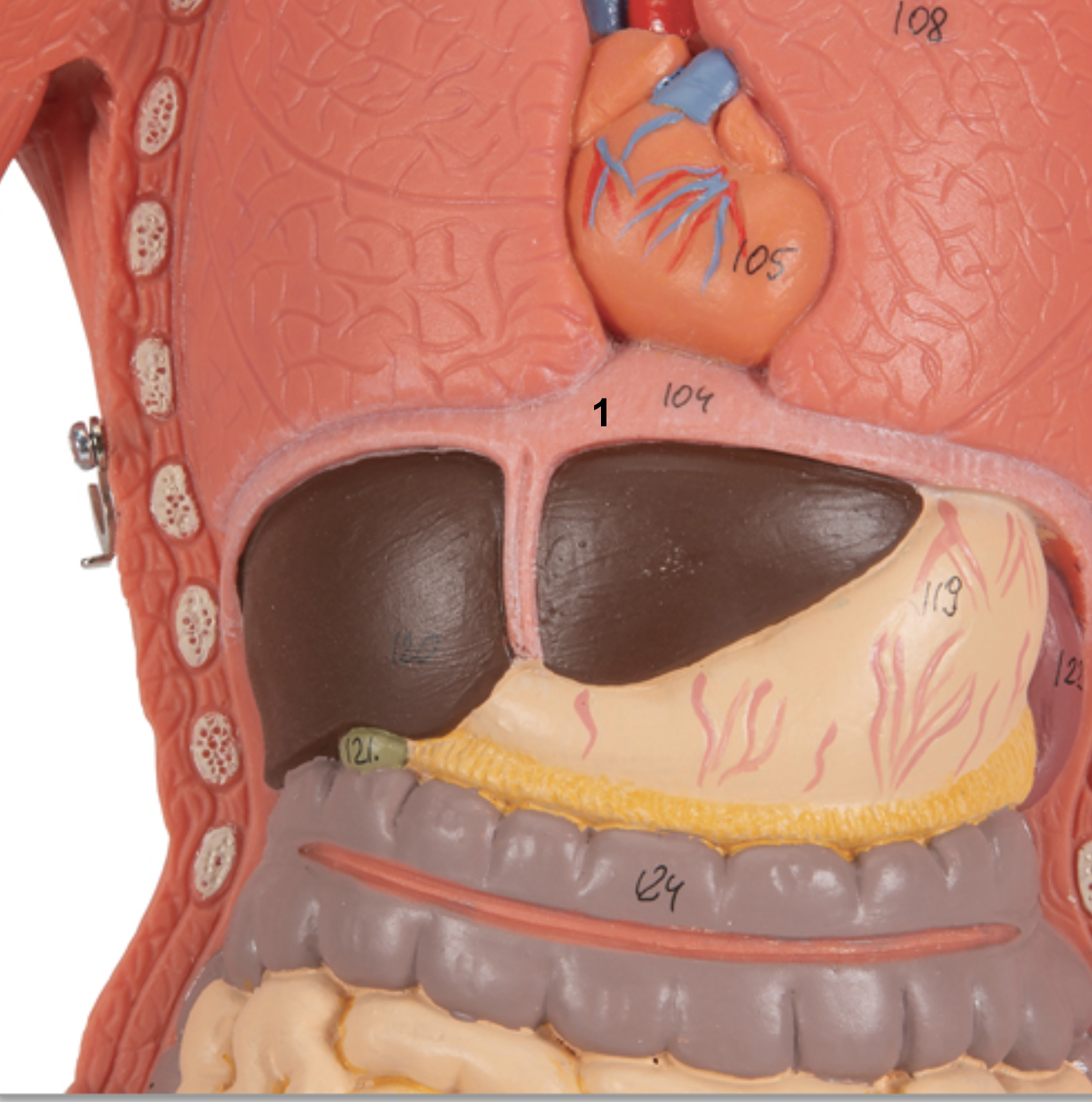
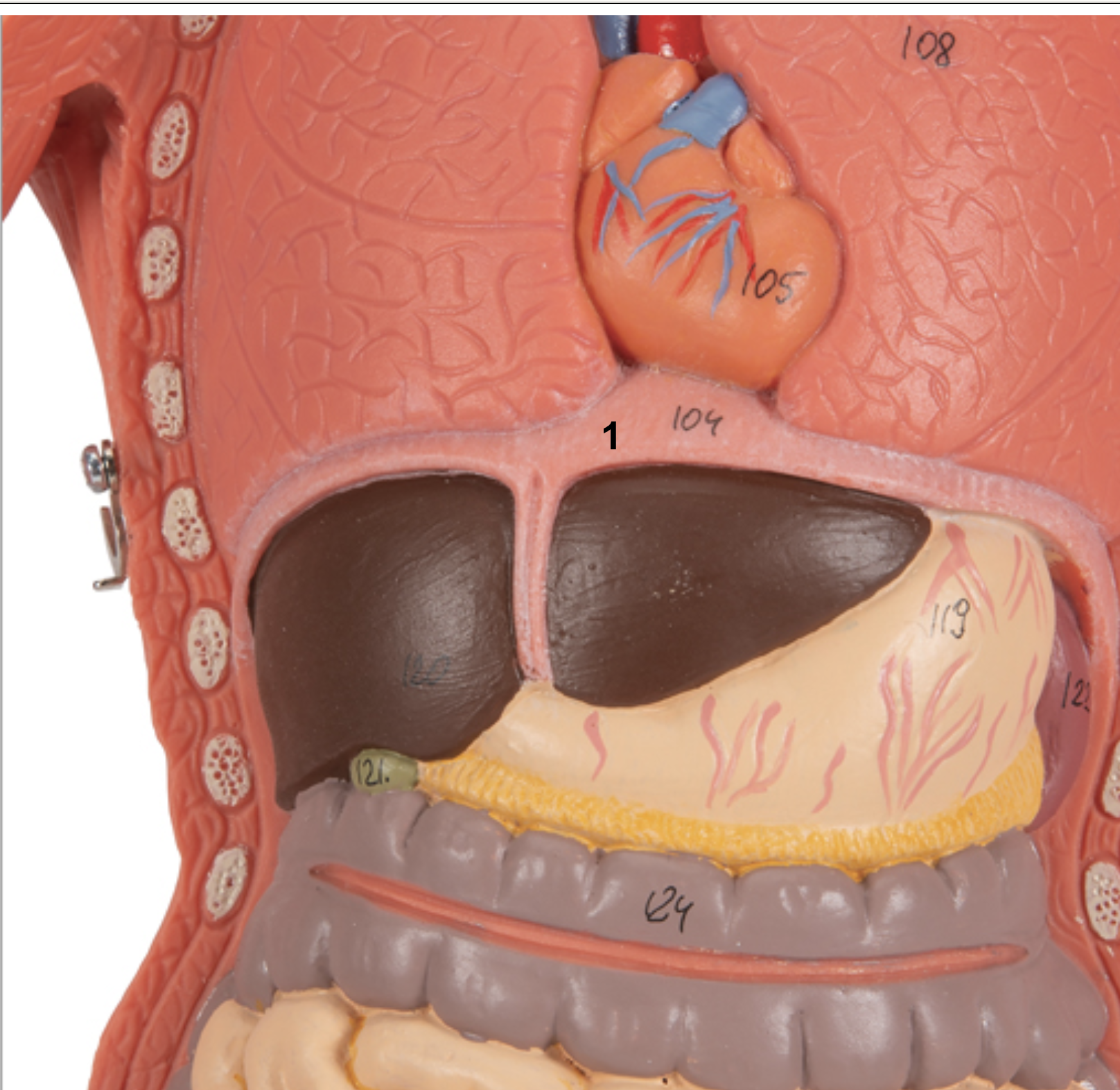
Identify structure and function of #1
Structure: Diaphragm
Function: Exhale
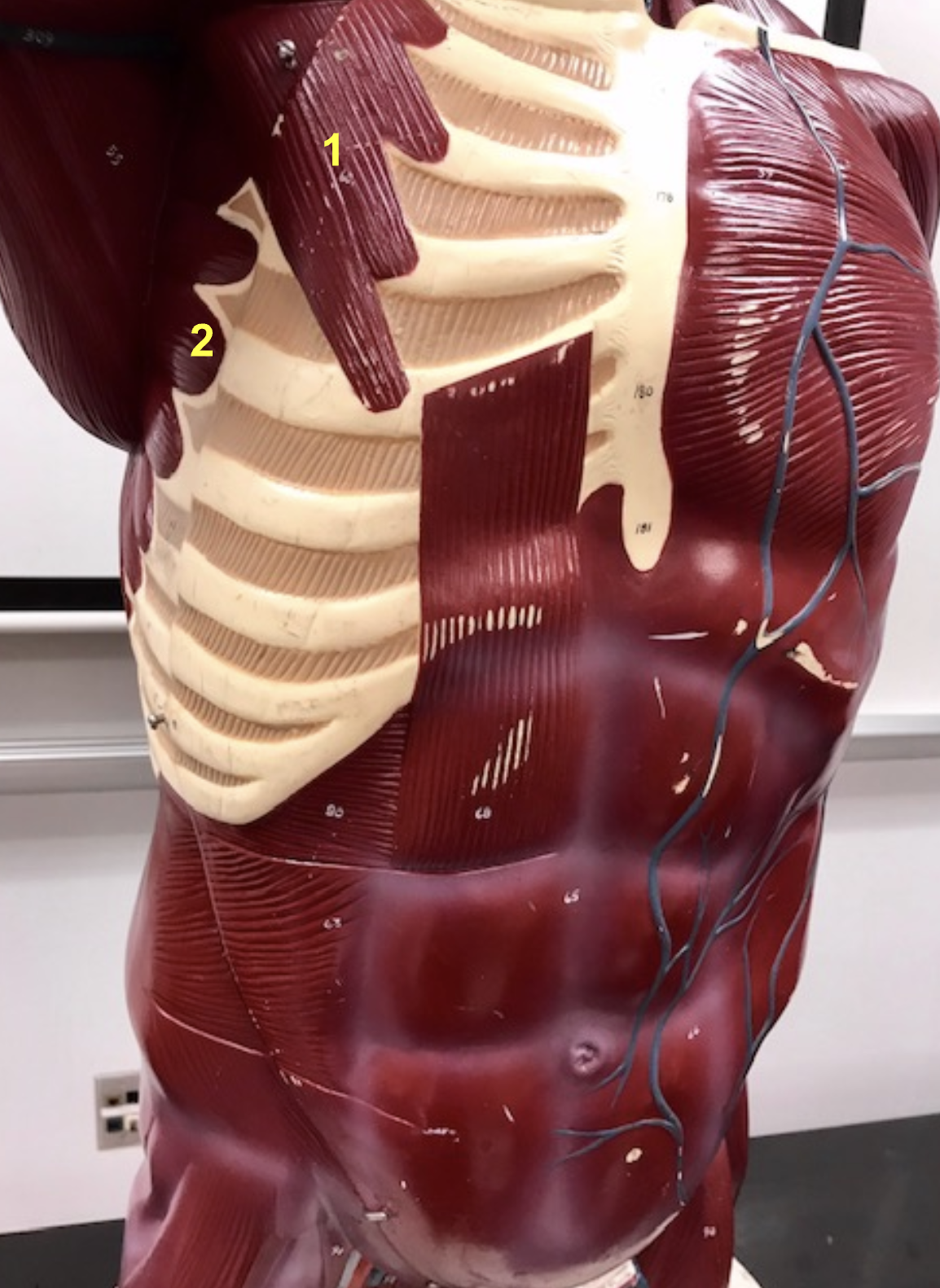
Identify structure, function, origin, insertion of #1
Structure: Pectoralis minor
Function: Abduct scapula
origin: ribs
insertion: coracoid process of scapula
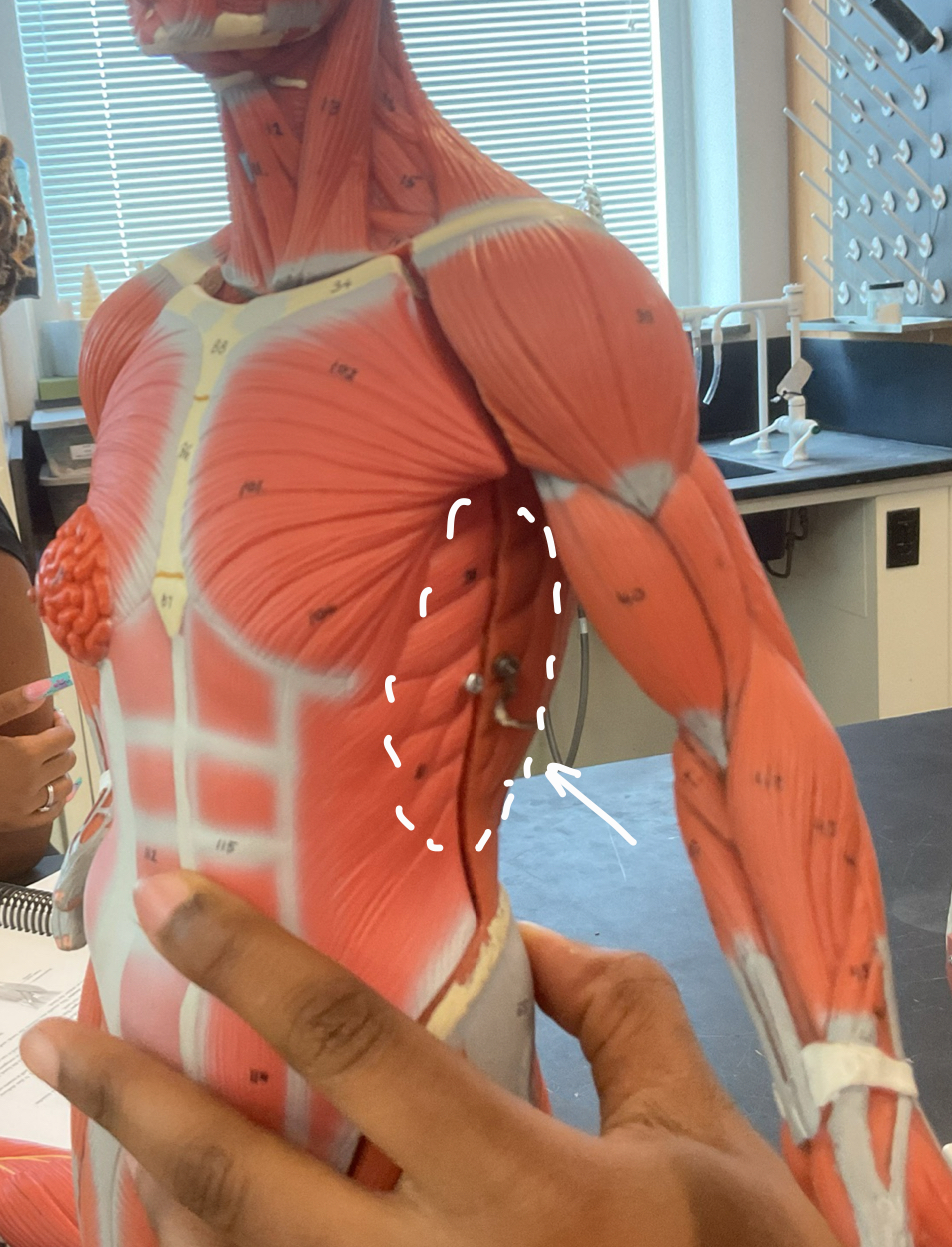
Identify structure and function
Structure: serratus anterior
function: Abduct scapula
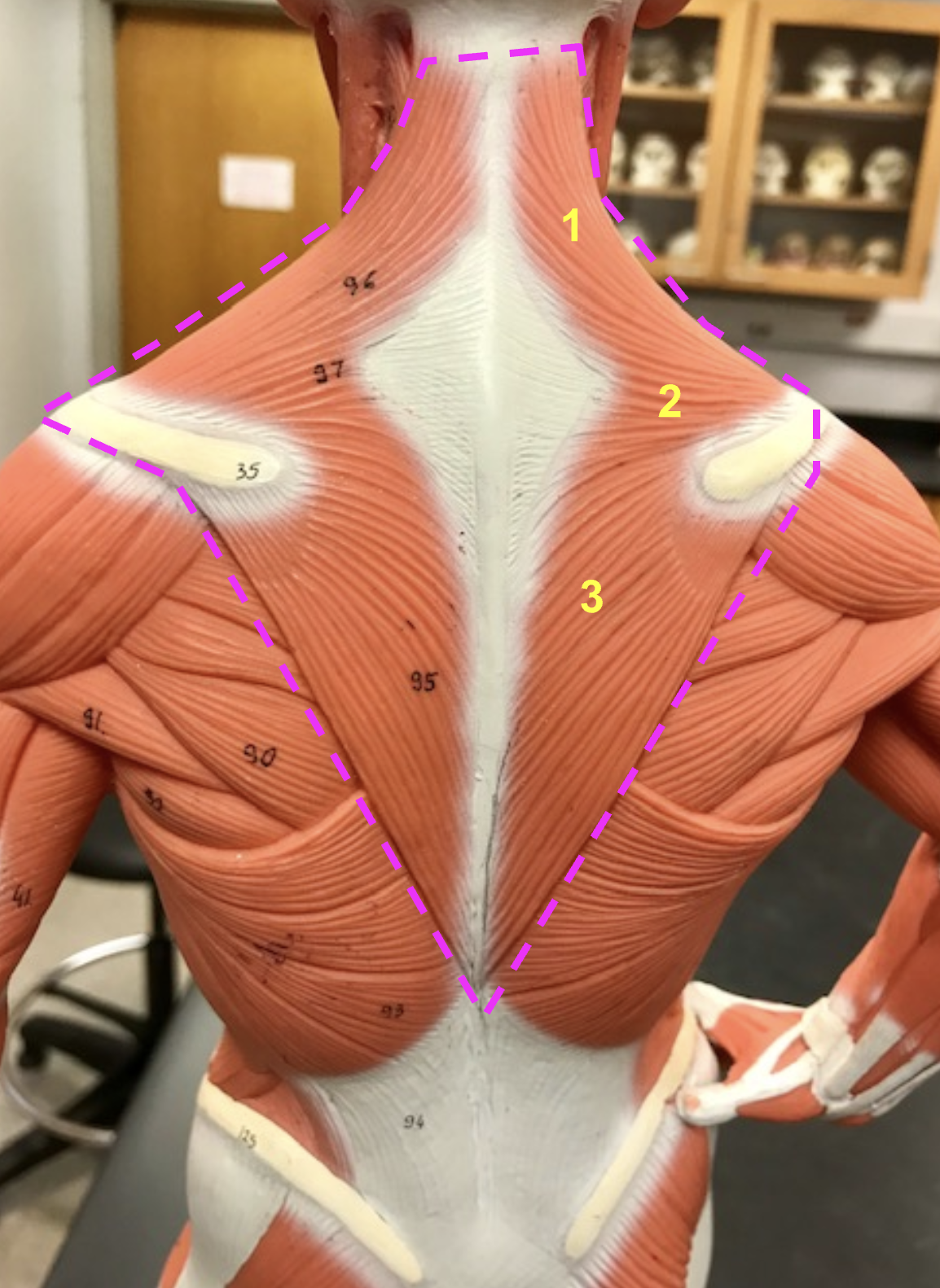
Identify structure and function of the outlined portion
structure: Trapezius
function: elevate, adduct, depress scapula
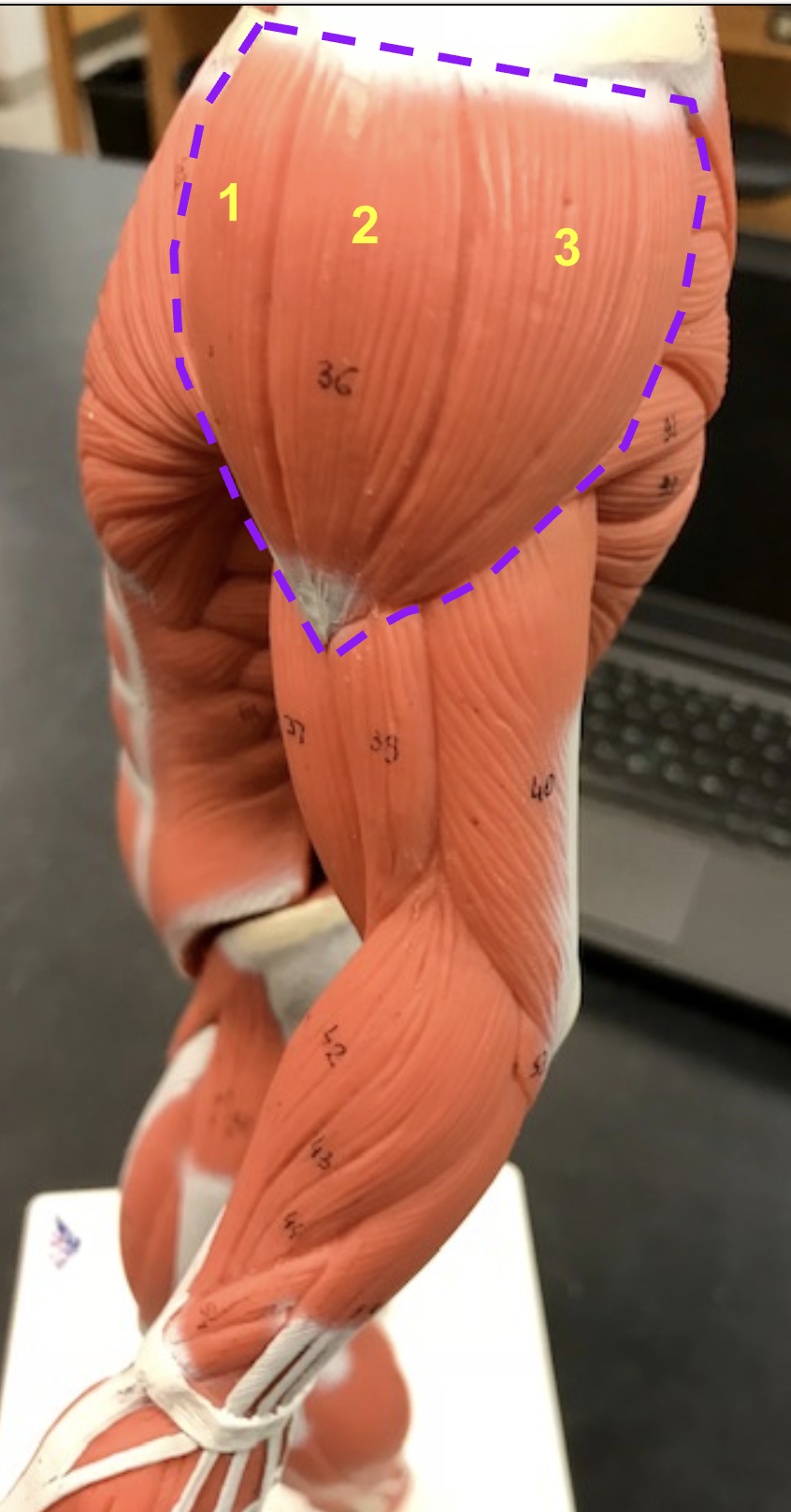
Identify structure, function, origin, and insertion of the outlined portion
structure: Deltoid
function: Flex, abduct, extend arm
origin: clavicle, acromion, and spine of scapula
insertion: deltoid tuberosity