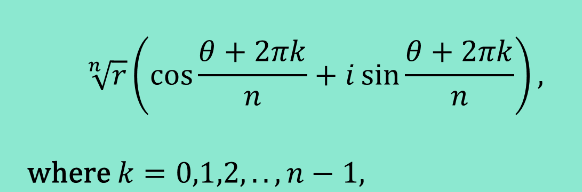Chapter 6 Main Ideas
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
Head Minus Tail (HMT) Rule
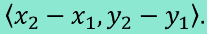
Magnitude of a Vector
|v| = √a²+b² or
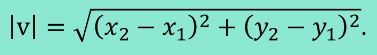
Vector Addition
Add the x values and then add the y values
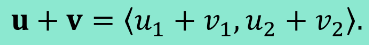
Scalar Multiplication
Multiply each component of the vector by the number
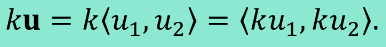
Unit Vectors
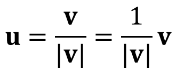
Resolving Vectors into their Components
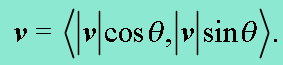
Dot Product of Vectors
Multiply the x values by the y values and add them together
ex: u = <u₁, u₂> & v = <v₁, v₂> so u⋅v = u₁v₁ + u₂v₂
Projectile Motion with Parametric Curves
The graph of (x, y) is defined where x = f(t) and y = g(t). T is the parameter and there will be a parameter interval.
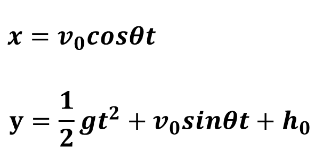
Finding all Polar Coordinates of a Point

Coordinate Conversion X Equation
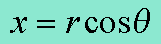
Coordinate Conversion Y Equation
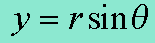
Coordinate Conversion R Equation
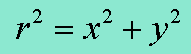
Coordinate Conversion θ Equation
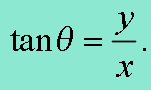
Rose Curve Properties
The graphs are given by the general equations r = acosnθ and r = asinnθ where n is an integer greater than 1. If n is odd then there are n petals and if n is even there are 2n petals
Absolute Value (Modulus) of a Complex Number
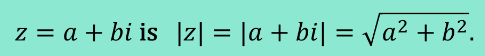
Trigonometric(Polar) Form of a Complex Number
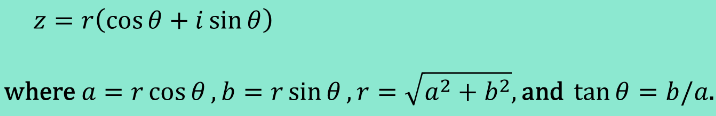
Product of Complex Numbers
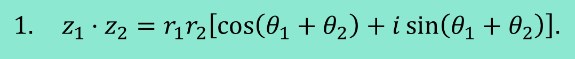
Quotient of Complex Numbers
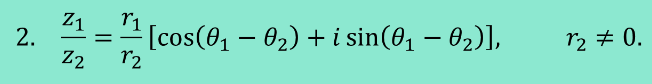
De Moivre’s Theorem
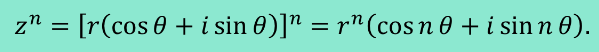
Finding nth Roots of a Complex Number