Unit 2 - Endometrial Pathology
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
A thickened endometrium may be a sign of:
Early intrauterine pregnancy
Gestational trophoblastic disease
Endometrial hyperplasia
Secretory endometrium
Estrogen replacement therapy
Polyps
Tamoxifen/HRT
Endometrial cancer
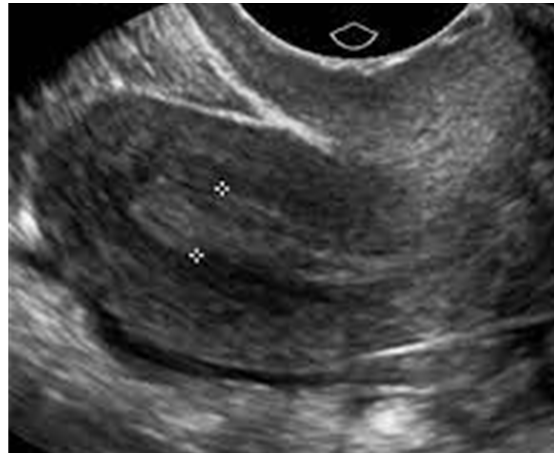
What is this image showing?
Thickened Endometrium
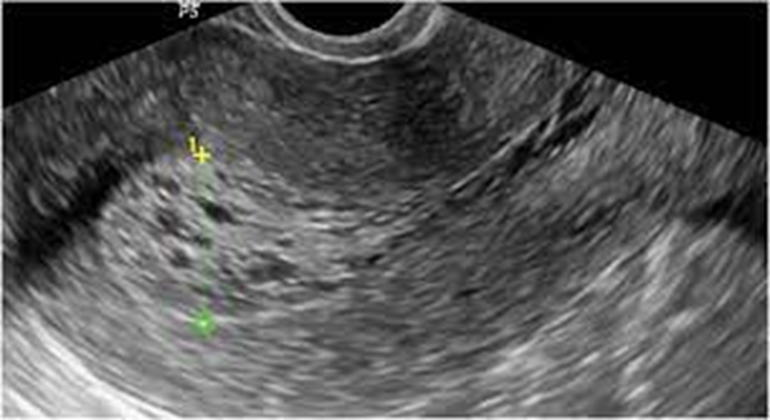
What is this image showing?
Thickened Endometrium
Endometrial hyperplasia is caused by:
Unopposed estrogen stimulation
What is unopposed estrogen?
Estrogen dominance, there isn’t enough progesterone produced to keep up with the amount of estrogen.
A premenopausal patient with endometrial hyperplasia, would have an endometrial thickness of _______.
+14mm
An asymptomatic postmenopausal patient with endometrial hyperplasia, could expect to have an endometrial thickness of _______.
8mm {upper normal limit}
A patient with endometrial hyperplasia on sequential estrogen & progesterone, could expect to have an endometrial thickness of _______.
15mm
What is the most common cause of pre & postmenopausal abnormal bleeding?
Endometrial Hyperplasia
Endometrial Hyperplasia is a possible precursor of ___________ _______.
Endometrial Cancer
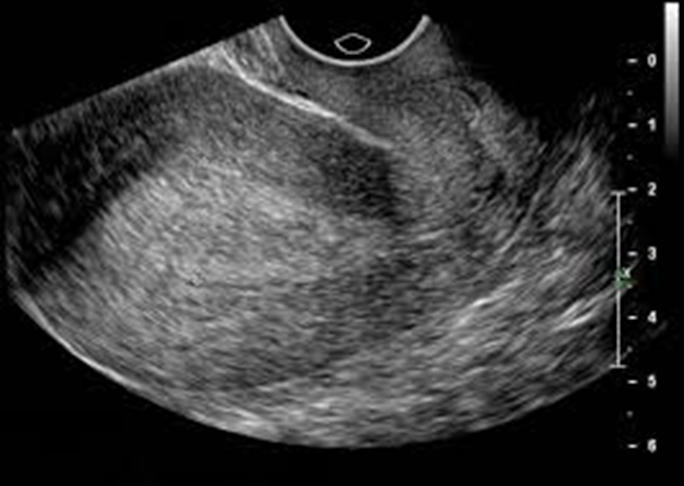
What is this image showing?
Endometrial Hyperplasia
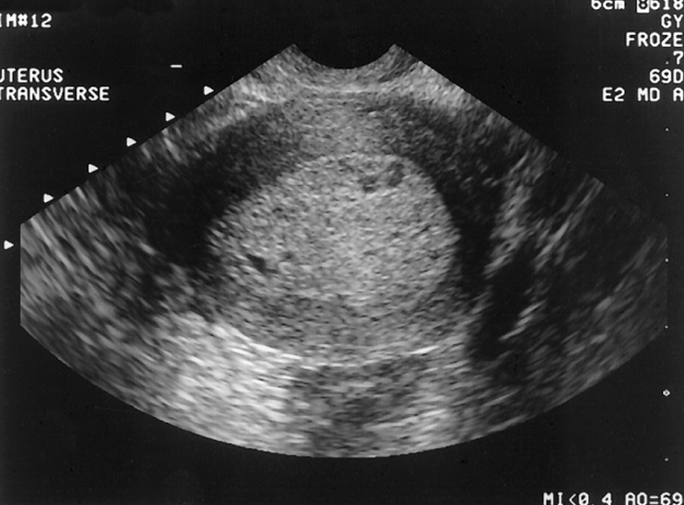
What is this image showing?
Endometrial Hyperplasia
What are endometrial polyps?
Overgrowth of endometrial tissue
What symptom is common with endometrial polyps?
Vaginal bleeding
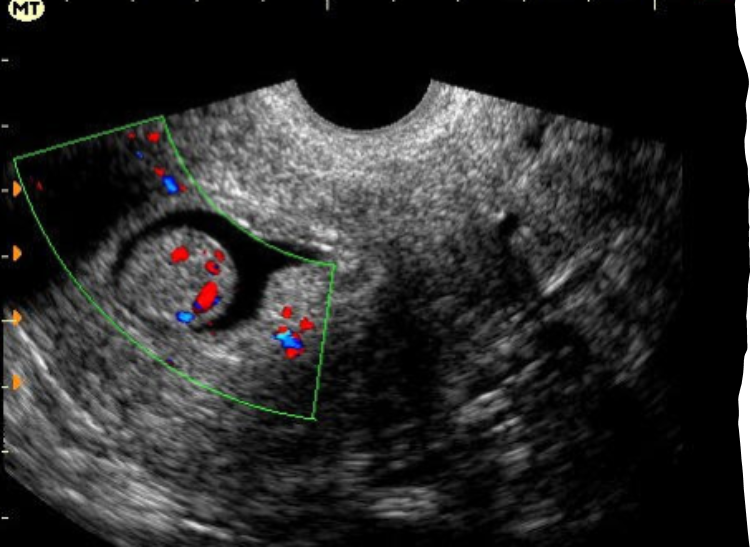
What is this image showing?
Endometrial polyps
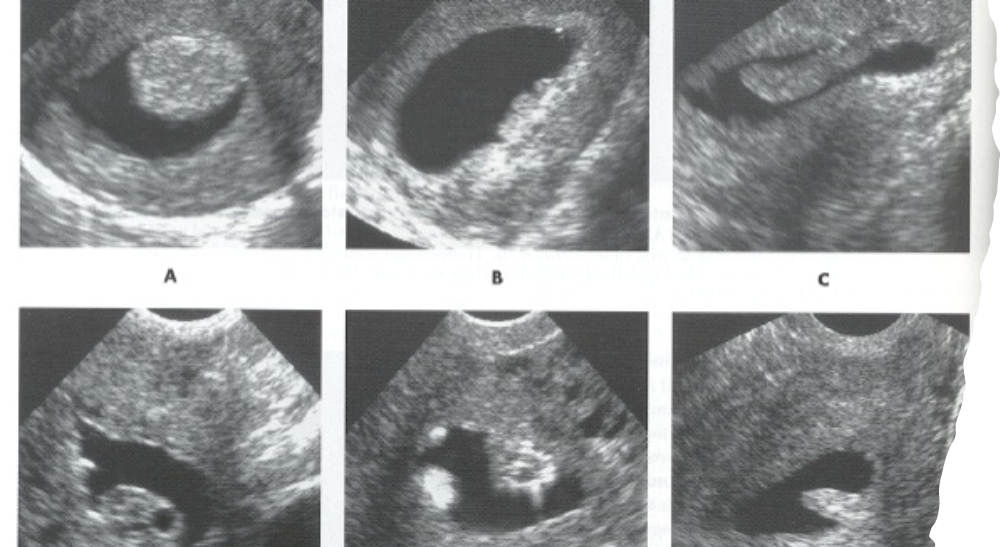
What are these images showing?
Endometrial polyps
What is endometritis?
Inflammation / infection of the endometrium
Endometritis most commonly occurs in association with…
PID
Postpartum
Following instrumentation of the uterus
What is the ultrasound appearance of Endometritis?
Thickened endometrium
Irregular endometrium
Endometrial fluid
“Gas”
Retained tissue
Most endometrial carcinomas are _____________ occurring in _____________ patients.
Adenocarcinoma, Perimenopausal
Endometrial carcinoma has a strong association with…
Estrogen replacement therapy
What is the earliest sign of endometrial carcinoma?
Thickened endometrium
What are the advanced signs of endometrial carcinoma?
Uterine enlargement with lobular contour
Mixed echogenicity
Endometrial fluid collections
Abdominal pain
Bleeding (postmenopausal)
If there is uterine enlargement, the carcinoma has invaded the ____________.
Myometrium
What evidence may support the diagnosis of endometrial carcinoma?
Endometrial thickening
TV to measure thickness
Myometrial invasion
Clear evidence for CA
Synechiae/Asherman Syndrome
Bands of endo tissue
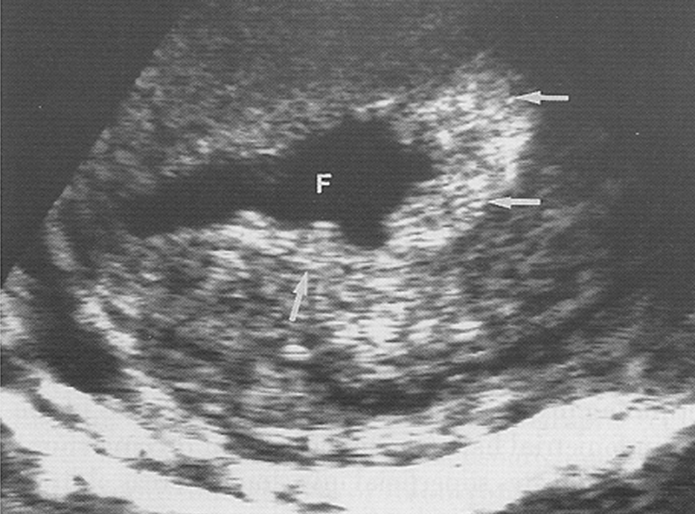
What is this image showing?
Endometrial Carcinoma
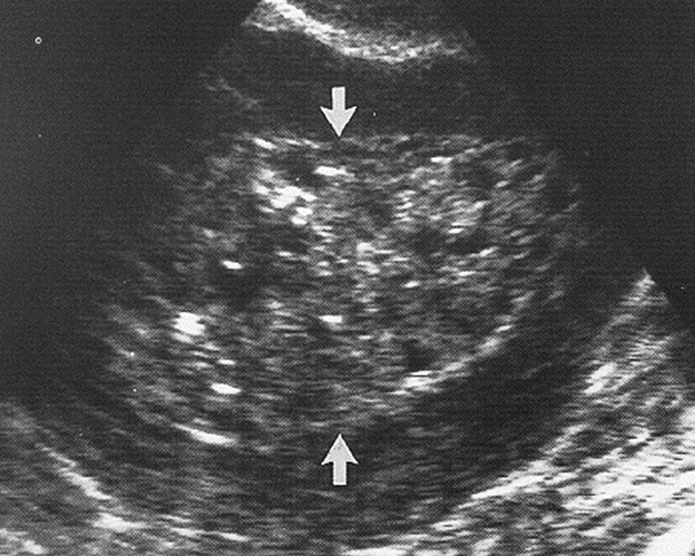
What is this image showing?
Endometrial Carcinoma
What is synechiae?
Fibrous adhesions across the endometrial cavity
Walls become adhered to each other
Various degrees of adhesions
What is another name for synechiae?
Asherman Syndrome
What may be a result from synechiae?
Infertility
Amenorrhea
Oligomenorrhea
Patients with synechiae may have a history of _____ &/or ______.
D&C, abortion
What is the ultrasound appearance of synechiae?
Bright echoes within the endometrial cavity
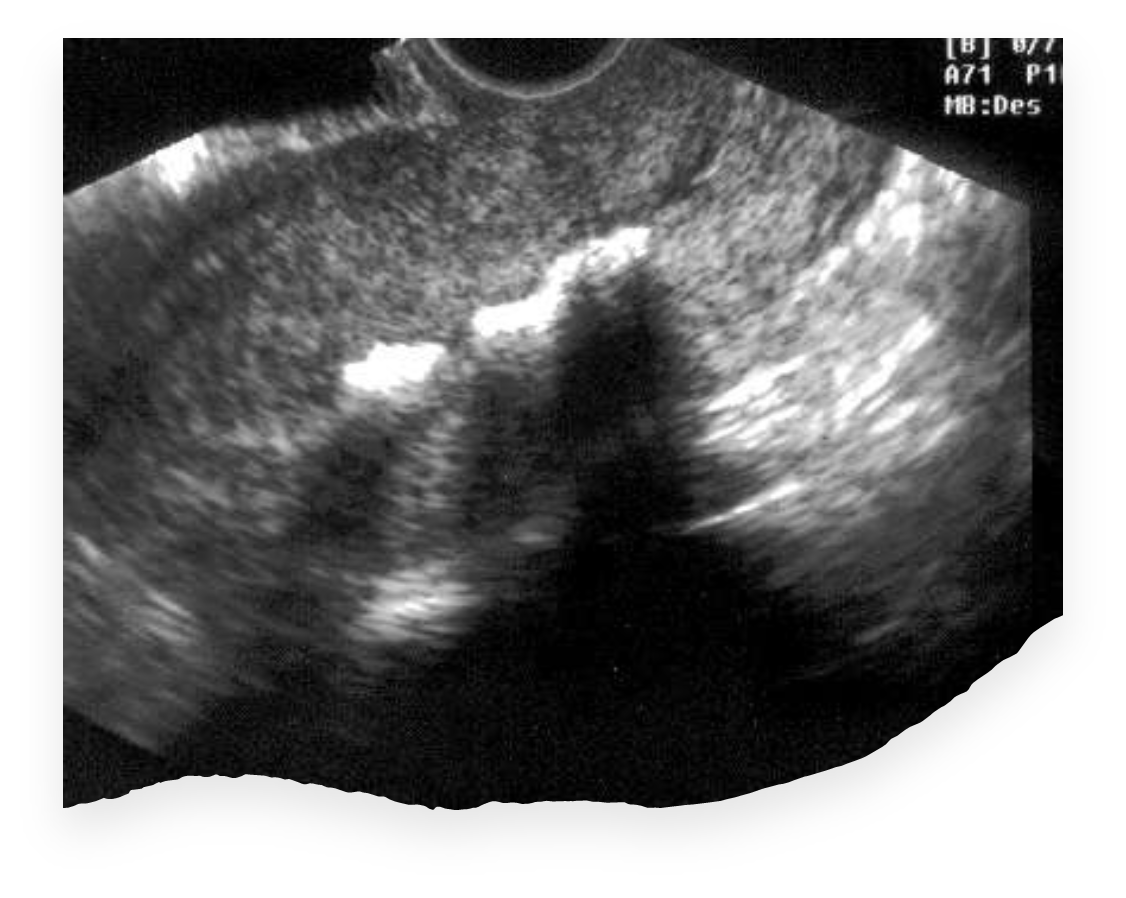
What is this image showing?
Synechiae / Asherman Syndrome
What is considered Stage l of endometrial cancer?
Confined to endometrium of body
B, C = myometrial extension
What is considered Stage ll of endometrial cancer?
Endometrium into cervix
What is considered Stage lll of endometrial cancer?
Spread to pelvic area lymph nodes
Extended through the serosal layer
What is considered Stage lV of endometrial cancer?
Mets to other organs
Extension into bladder/bowel
Distal lymph nodes
Differential Considerations for the Uterus: thickened endometrium
Early intrauterine pregnancy
Endometrial hyperplasia
Retained products of conception or incomplete abortion
Trophoblastic disease
Endometritis
Adhesions
Polyps
Inflammatory disease
Endometrial carcinoma
Differential Considerations for the Uterus: endometrial fluid
Endometritis
Retained products of conception
{PID} Pelvic inflammatory disease
Cervical obstruction
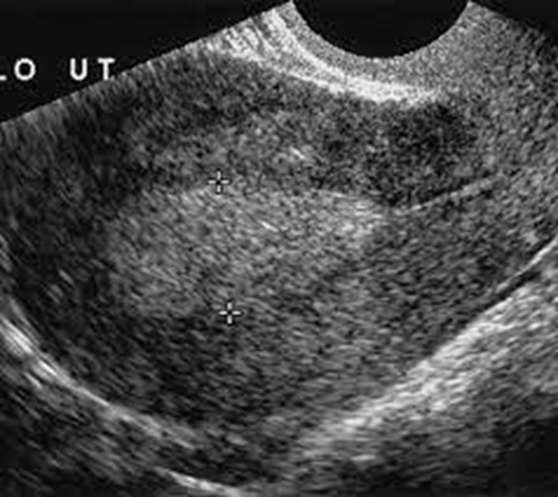
What is this image showing?
A thickened endometrium
What flow has been seen in patients with endometrial carcinoma?
Low resistance {RI <.4}
What flow has been seen in postmenopausal patients with normal or benign endometrium?
High resistance {RI >.5}
Tumor vascularity is a _______ sensitive indicator than RI alone
More
What is the normal measurement for a small endometrial fluid collection?
< 2 ml
It is normal to find small endometrial fluid collections during the….
Normal menstrual cycle
With postmenopausal patients, when is it normal to see endometrial fluid collections?
Sequential hormones
Endometrial atrophy
Is the fluid collection included in the endometrial measurement?
No, do not measure the fluid collection
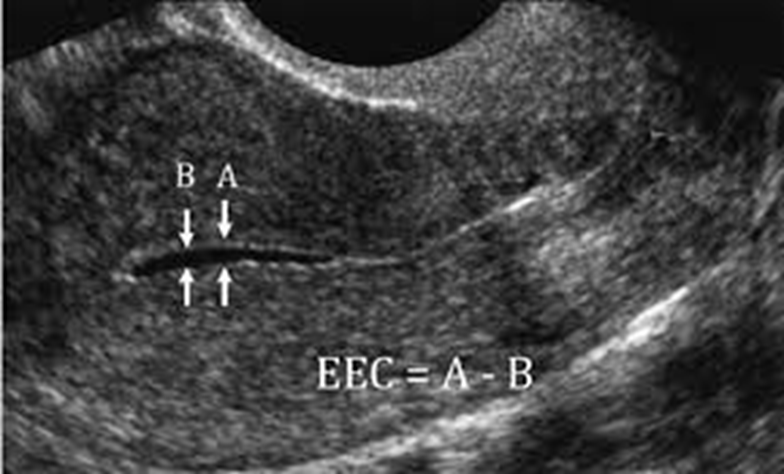
What is this image showing?
Small endometrial fluid collection
Large endometrial fluid collections can be ________, and should be investigated to find a cause.
Suspicious
A large endometrial fluid collection may be a sign of:
PID
Pyometra
Hematometra
CA’s
Cervical stenosis
Congenital anomalies
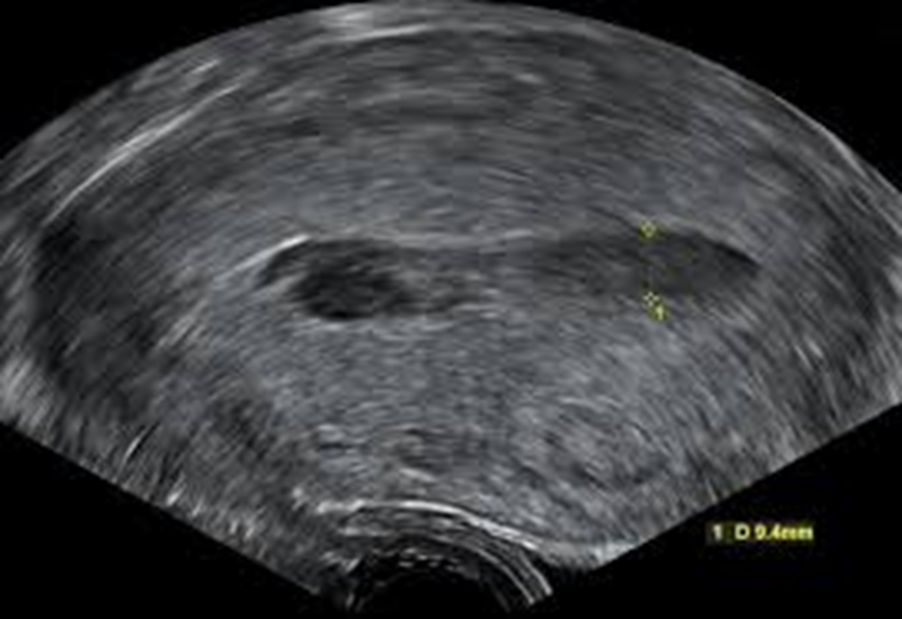
What is this image showing?
Large endometrial fluid collection
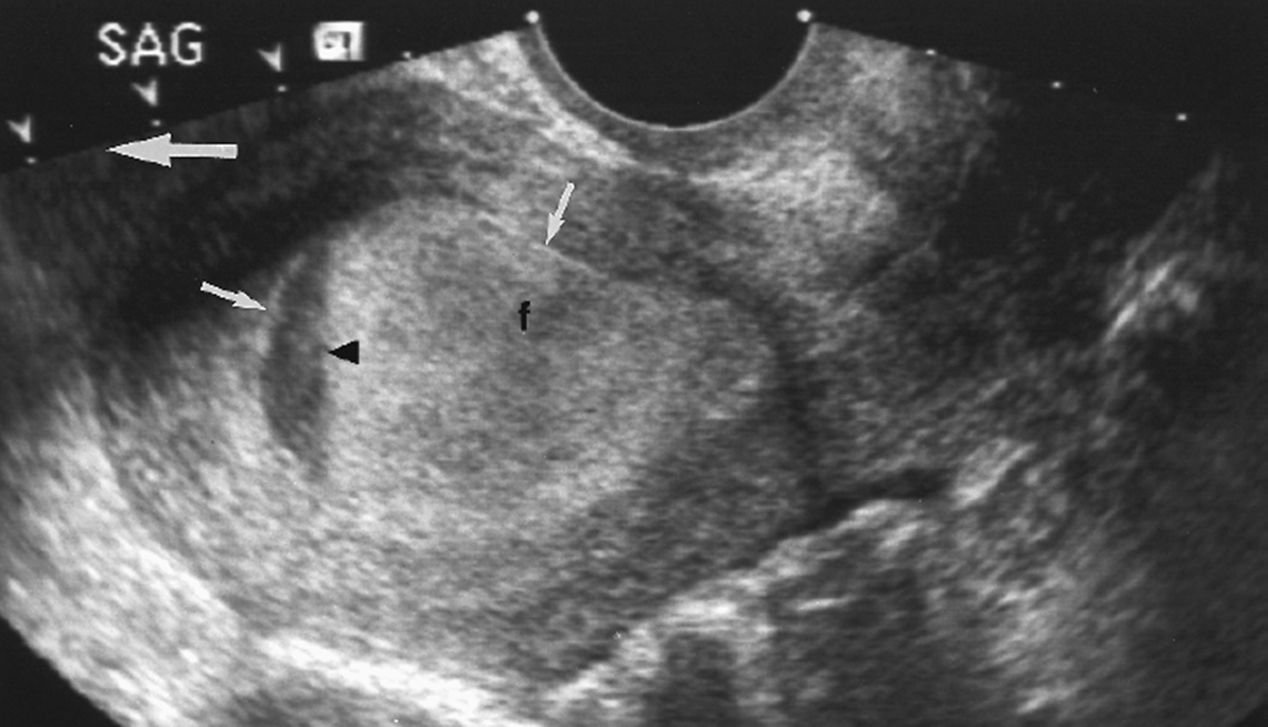
What is this image showing?
Cervical stenosis
In a postmenopausal patient