AP Bio Enzymes
1/54
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
metabolism
the sum of all chemical processes
an individual, specific enzyme
what catalyzes each step of a metabolic pathway?
True
T or F: Metabolic pathways are sequential and connected
Catabolic
Type of metabolic pathway that involves breaking down biomolecules.
Catabolic Pathway
Amylase breaking down starch, small intestine digestion are examples of a ___ pathway
Anabolic
Type of metabolic pathway that involves building biomolecules
Anabolic Pathways
photosynthesis, DNA synthesis, protein synthesis are examples of ___ pathway
Pathway coupling
In order for anabolic pathways to function, catabolic pathways are needed to supply energy
1st law of Thermodynamics
any organism can transform, absorb, and release energy
entropy
measure of randomness of particle movement
2nd law of thermodynamics
each energy conversion increases entropy
more heat leads to more entropy
relationship between heat and entropy
heat
for every energy transfer/transformation, some energy becomes unavailable to do work because it has been converted to __
Raise body temp, homeostasis
How do organisms use heat?
Input of entropy/heat counteracts entropy output
Why is it difficult to observe entropy?
Burn reserves, store energy
what happens if energy flow stops?
Free Energy Change Delta G
accessibility of energy
free energy
molecules are able to be metabolized for fuel, all food has free energy
Exergonic
reactions that release energy: cell respiration
Endergonic
reactions that condense energy: active transport, cell movement
Energy coupling
Energy released from exergonic reactions powers endergonic reactions; e.g ATP powering any type of work
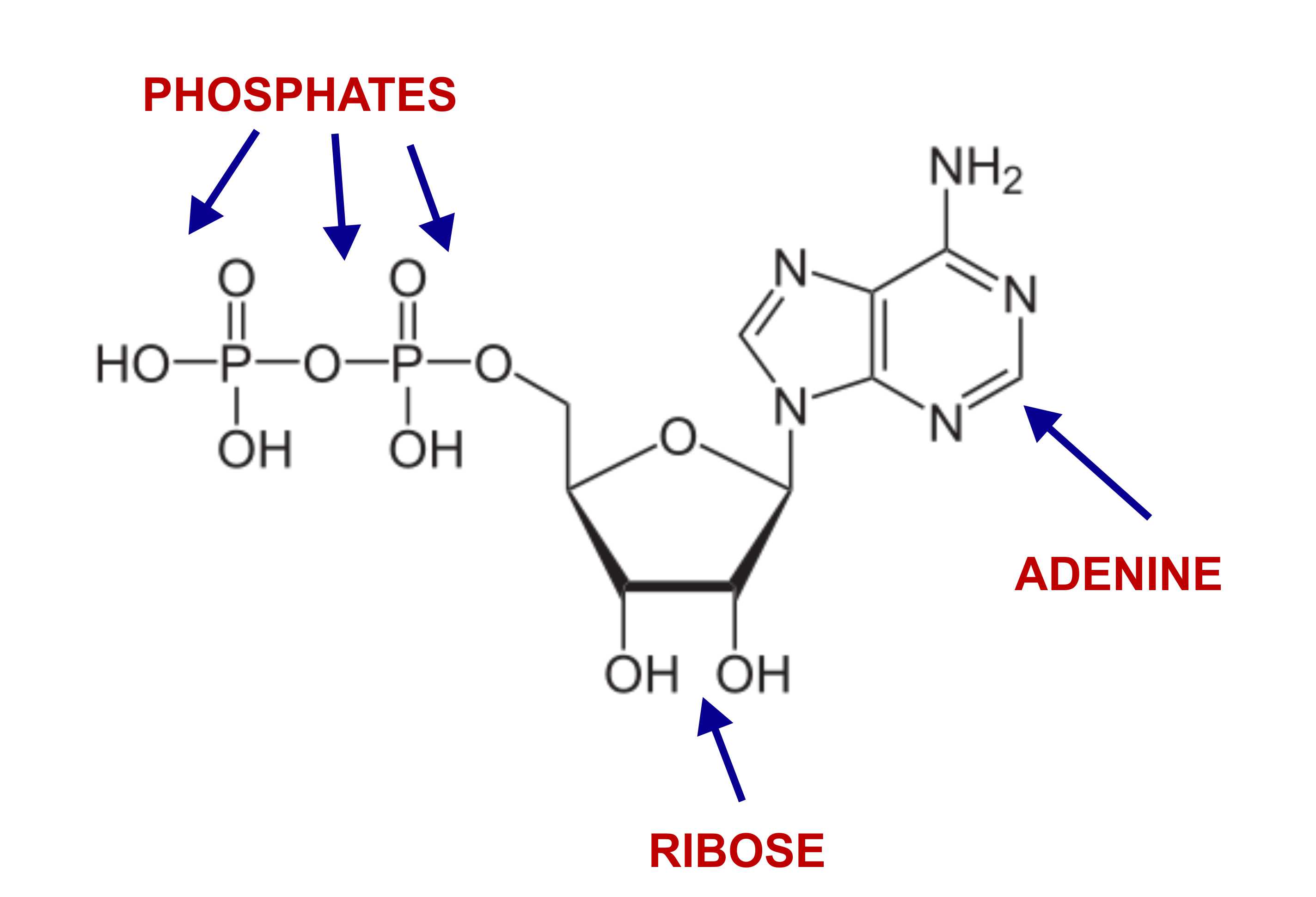
RIbose sugar, adenine base, 3 phosphate groups
Components of ATP: sugar, nitrogenous base, phosphate groups
7.3 kCal
How much free energy is released in hydrolysis of ATP?
Very little energy to form/release; like charges in phosphates repel, making them easy to break.
Significance of ATP bonding and hydrolysis.
H20 + ATP —> ADP +Pi + 7.3 kCal
ATP hydrolysis equation
ADP +Pi + 7.3 kCal —> H20 + ATP
ATP Synthesis Equation
Catalyze (speed up) chemical reactions
What do enzymes do
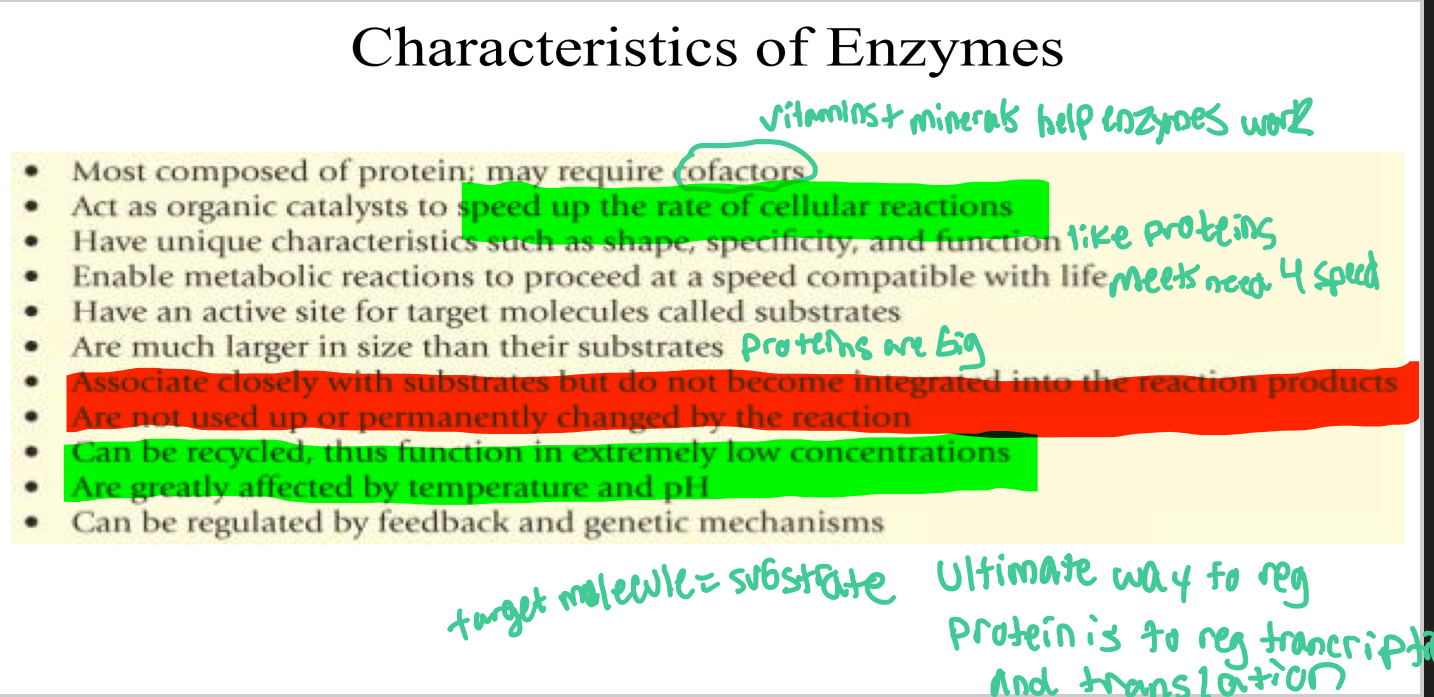
See picture (Name as many as possible)
Characteristics of Enzymes
They lower the activation energy or energy needed to start a reaction
How do enzymes speed up chemical reactions?
Heat will destroy molecules and maybe denature enzymes.
Why is heat bad to use as energy of activation for organism?
ATP
supplies activation energy for metabolism
substrate
the target molecule that the active site of an enzyme is binding to
active site
the part of the enzyme that changes shape and binds to the substrate to catalyze a chemical reaction
Enzyme substrate complex
Enzyme combined with substrate
Enzyme Specificity
Shape of enzyme’s 3D structure determines its function
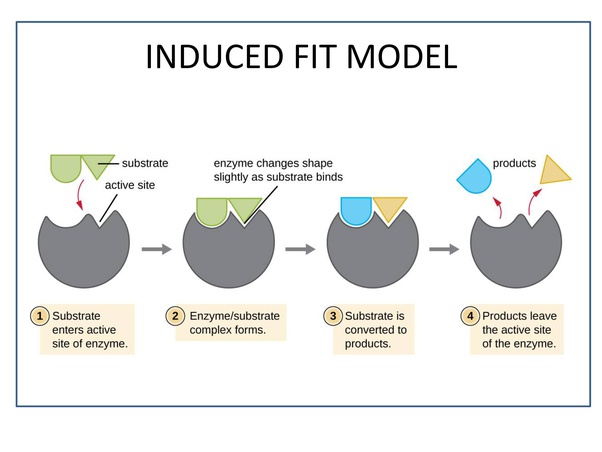
Enzymes slightly change the shape of their active site to perfectly bind to the substrate
Induced Fit model
catalytic Cycle
How fast enzymes bind to a substrate, release product, and repeat
The change in shape of the active site puts stress on the bonds of a substrate, making it easier to break.
How do enzymes lower activation energy for hydrolysis reactions?
Active site sticks reactants together
how do enzymes help synthesis anabolic reactions?
Enzyme Saturation
active sites being frequently occupied/collided with substrate increase reaction rate
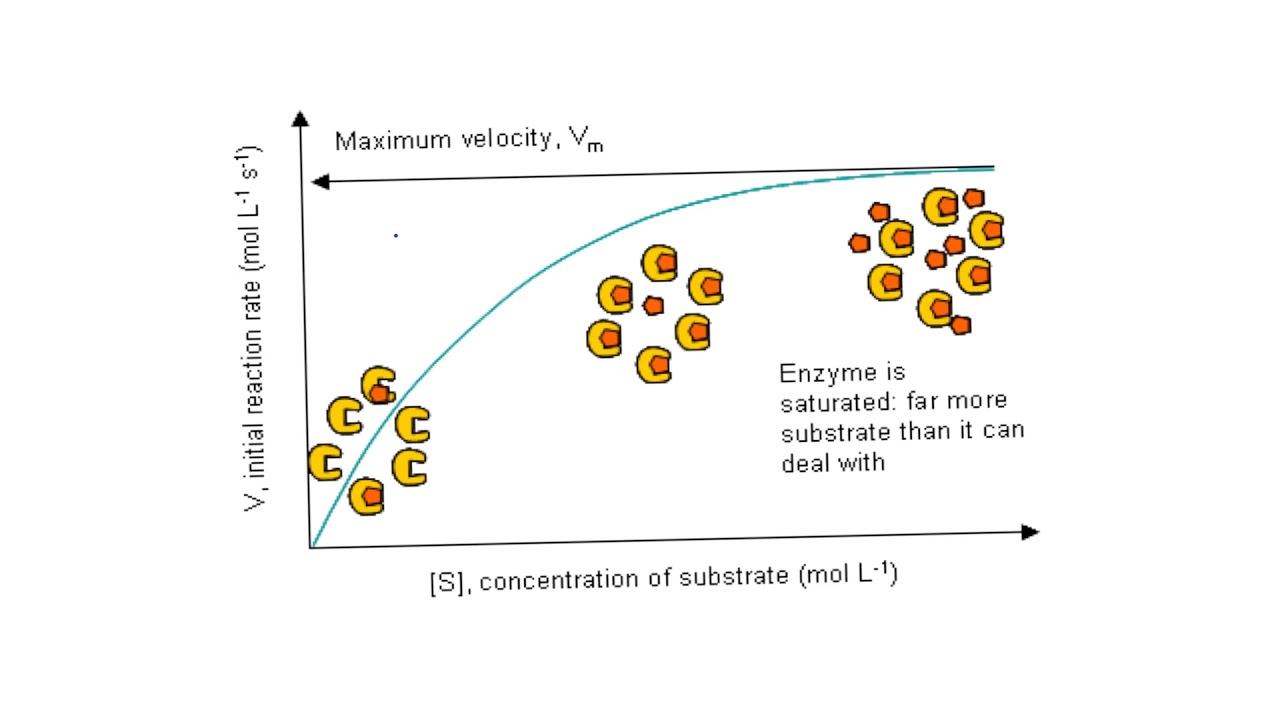
Assuming saturation, the more substrate, the more collisions between active site and enzyme may occur, increasing reaction rate and then plateauing at max.
Substrate concentration impact on enzyme productivity
Assuming saturation, the more enzymes, the more collisions between active site and enzyme may occur, increasing reaction rate and then plateauing at max.
Enzyme concentration impact on enzyme productivity
enzyme productivity goes down
temp above and below optimal enzyme temp impact
denaturing and enzyme productivity rate 0
temp extremely above optimal enzyme temp leads to
denaturing
when the 3D shape of an enzyme changes, changing its function and thus not allowing it to bind to a specific substrate and catalyze a specific reaction. Destroys hydrogen bonds (primary) then ionic and covalent (secondary) and then the 3D shape.
NO DENATURING but near 0 enzyme productivity as collisions rarely occur
temps extremely below optimal enzyme temp lead to
denaturing, enzyme productivity becomes 0
extremely acidic or basic pH compared to optimum enzyme pH effect
enzyme productivity decreases
slight pH changes from optimal enzyme pH
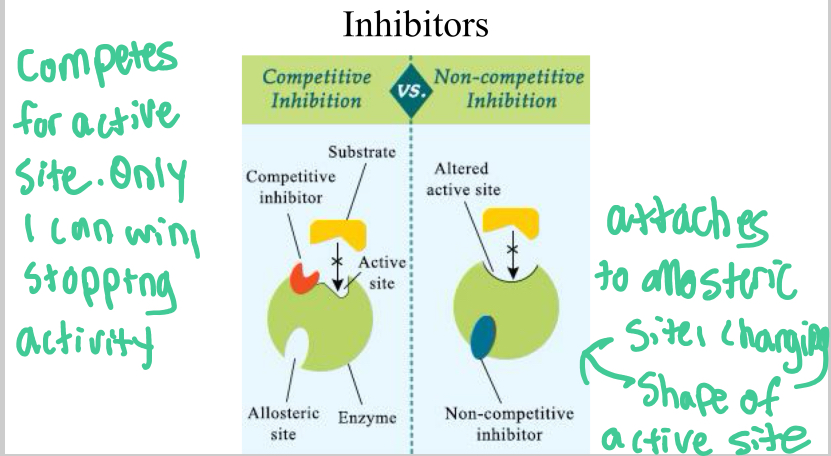
Competitive Inhibitors
Attach to active site of enzyme, stopping a substrate from attaching and thus stopping the catalysis of a reaction
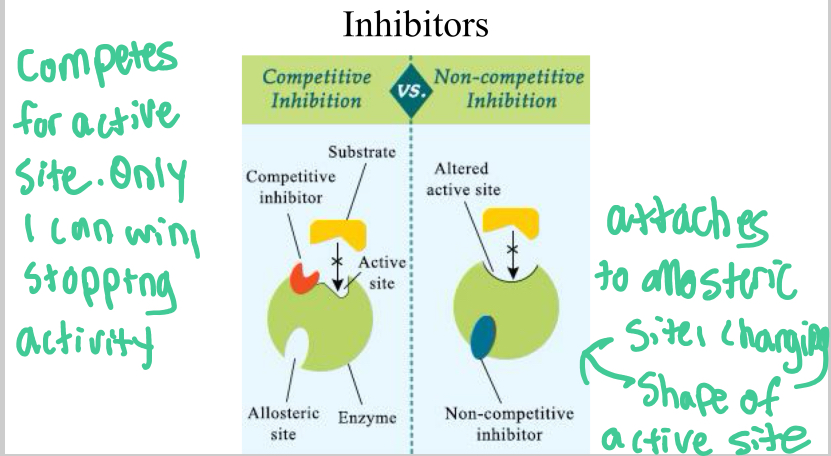
Noncompetitive inhibitors
attach to allosteric site, which changes shape of enzyme’s active site, stopping the substrate from binding to it.
Permanent Allosteric Inhibitors
Poisons use what kind of inhibitors? E.g Carbon Monoxide
Allosteric Activator
Changing the shape of an allosteric site thus active site to speed up a chemical reaction
Allosteric Inhibitor
Changing the shape of an allosteric site thus active site to slow down a chemical reaction
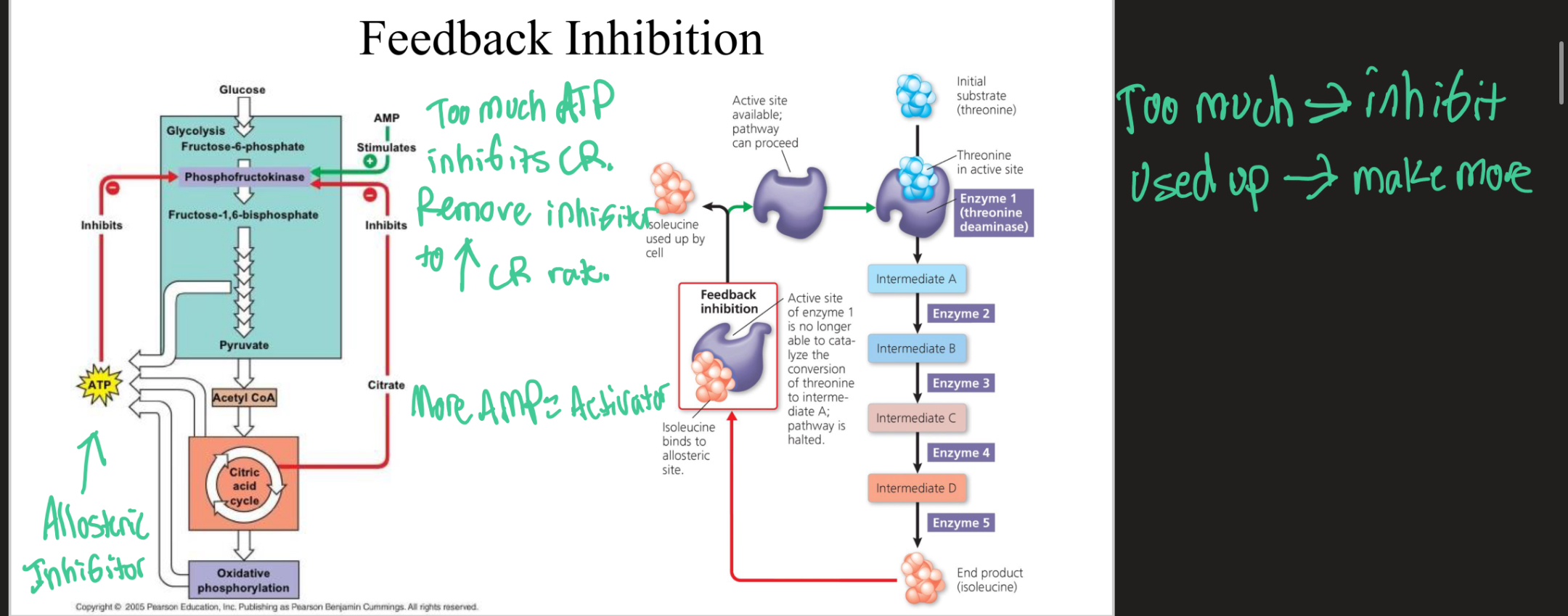
Feedback Inhibition
The product of a metabolic pathway is an inhibitor that slows down the pathway. When all of the product is used up or needed, the inhibitors are taken off and the pathway resumes and cycles again.
The microenvironments from compartmentalization can have very different conditions for optimal enzyme activity.
How do enzymes benefit from compartmentalization?