AP Human - Models & Theories
5.0(3)Studied by 142 people
Card Sorting
1/296
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 3:58 PM on 9/19/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
297 Terms
1
New cards
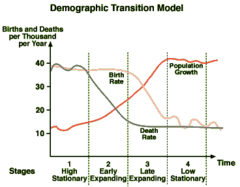
Demographic Transition Model
A sequence of demographic changes in which a country moves from high birth and death rates to low birth and death rates through time.
Stage 1: very high CBR and CDR, low NIR
Stage 2: still high CBR, rapidly declining CDR, very high NIR
Stage 3: rapidly declining CBR, moderately declining CDR, moderate NIR
Stage 4: very low CBR, low/slightly increasing CDR, 0 or negative NIR
Stage 1: very high CBR and CDR, low NIR
Stage 2: still high CBR, rapidly declining CDR, very high NIR
Stage 3: rapidly declining CBR, moderately declining CDR, moderate NIR
Stage 4: very low CBR, low/slightly increasing CDR, 0 or negative NIR
2
New cards
Epidemiologic Transition
The process of change in the distinctive causes of death in each stage of the demographic transition
Stage 1: infectious/parasitic disease, animal/human attacks
Stage 2: receding pandemics, higher sanitation
Stage 3: decrease in disease deaths, increase in aging chronic disease death
Stage 4: delayed degenerative diseases
Stage 1: infectious/parasitic disease, animal/human attacks
Stage 2: receding pandemics, higher sanitation
Stage 3: decrease in disease deaths, increase in aging chronic disease death
Stage 4: delayed degenerative diseases
3
New cards
Malthusian Theory
focuses on how the exponential growth of a population can outpace growth of the food supply and lead to social degradation and disorder
4
New cards
Zelinsky Model of Migration Transition
People become increasingly mobile as industrialization develops. More international migration is seen in stage 2 of DMT as migrants search for more space and opportunities in countries in stages 3 and 4. Stage 4 countries show less emigration and more intraregional migration.
5
New cards
Nomadic Warrior Theory
people conquered areas, spreading the English language
6
New cards
Sedentary Farmer Theory
Origin and Diffusion of Indo-European language occurred through farmers from Turkey/Anatolia (before Kurgans) -Colin Renfrew
7
New cards
Basque
An ethnic group living the western Pyrenees and along the Bay of Biscay in Spain and France, also the name of their language.
8
New cards
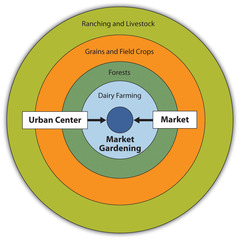
Von Thunen Model
An agricultural model that spatially describes agricultural activity in terms of rent. Activities that require intensive cultivation and cannot be transported over great distances pay higher rent to be close to the market. Conversely, activities that are more extensive , with goods that are easy to transport, are located farther from the market where rent is less.
9
New cards
Rostow's Stages of Development
A model of economic development that describes a country's progression which occurs in five stages transforming them from least-developed to most-developed countries.
10
New cards
Core-Periphery Model
A model of the spatial structure of development in which underdeveloped countries are defined by their dependence on a developed core region.
11
New cards
Bid rent theory
geographical economic theory that refers to how the price and demand on real estate changes as the distance towards the Central Business District (CBD) increases.
12
New cards
Central Place Theory
A theory that explains the distribution of services, based on the fact that settlements serve as centers of market areas for services; larger settlements are fewer and farther apart than smaller settlements and provide services for a larger number of people who are willing to travel farther.
13
New cards
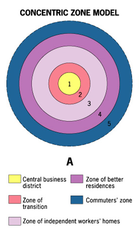
Concentric Zone Model
A model of the internal structure of cities in which social groups are spatially arranged in a series of rings.
14
New cards
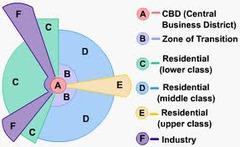
Sector Model
A model of the internal structure of cities in which social groups are arranged around a series of sectors, or wedges, radiating out from the central business district (CBD).
15
New cards
Multiple Nuclei Model
A model of the internal structure of cities in which social groups are arranged around a collection of nodes of activities.
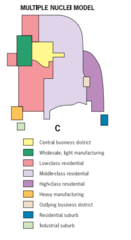
16
New cards
Peripheral Model
A model of North American urban areas consisting of an inner city surrounded by large suburban residential and business areas tied together by a beltway or ring road.
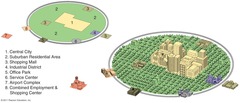
17
New cards
Latin American City Model
The CBD is dominant; it is divided into a market sector and a modern high-rise sector. The elite residential sector is on the extension of the CBD in the "spine". The end of the spine of elite residency is the "mall" with high-priced residencies. The further out, less wealthy it gets. The poorest are on the outer edge.
18
New cards
African City Model
cities have more than one CBD, which is a remanence of colonialism
19
New cards
Southeast Asian City Model
The focal point of the city is the colonial port zone combined with the large commercial district that surrounds it. McGee found no formal CBD but found seperate clusters of elements of the CBD surrounding the port zone: the government zone, the Western commercial zone, the alien commercial zone, and the mixed land-use zone with misc. economic activities.
20
New cards
cartography
The science of making maps
21
New cards
Cartographic Scale
refers to the way the map communicates the ratio of its size to the size of what it represents
22
New cards
Concentration
The spread of something over a given area.
23
New cards
Cultural Ecology
the geographic study of human-environment relationships
24
New cards
cultural landscape
the visible imprint of human activity and culture on the landscape
25
New cards
density
the frequency with which something occurs in space
26
New cards
Distance Decay
the effects of distance on interaction, generally the greater the distance the less interaction
27
New cards
distortion
a change in shape, size, distance or direction of a map when projected
28
New cards
distribution
the arrangement of a feature in space
29
New cards
environmental determinism
the view that the natural environment has a controlling influence over various aspects of human life including cultural development
30
New cards
equator
0 degrees latitude
31
New cards
Formal/Uniform Region
An area in which everyone shares in one or more distinctive characteristics
32
New cards
friction of distance
A measure of how much absolute distance affects the interaction between two places.
33
New cards
Functional/Nodal Region
An area organized around a node or focal point
34
New cards
GIS
A computer system that stores, organizes, analyzes, and displays geographic data in layers
35
New cards
GPS
A system that determines the absolute location of something on Earth through a series of satellites, tracking stations, and receivers.
36
New cards
International Date Line
An arc that for the most part follows 180° longitude, although it deviates in several places to avoid dividing land areas. When you cross heading east (toward America), the clock moves back 24 hours, or one entire day. When you go west (toward Asia), the calendar moves ahead one day.
37
New cards
Latitude
lines run east to west
38
New cards
longitude
lines that run north and south
39
New cards
location
the position that something occupies on Earth's surface
40
New cards
Human Geography
The study of where and why human activities are located where they are
41
New cards
Physical Geography
the study of physical features of the earth's surface
42
New cards
place
A specific point on Earth distinguished by a particular character.
43
New cards
Possibilism
The theory that the physical environment may set limits on human actions, but people have the ability to adjust to the physical environment and choose a course of action from many alternatives.
44
New cards
Prime Meridian
0° longitude, which passes through the Royal Observatory at Greenwich, England.
45
New cards
Reference Maps
Maps that show the absolute location of places and geographic features determined by a frame of reference, typically latitude and longitude
46
New cards
thematic map
a map that shows a particular theme, or topic
47
New cards
remote sensing
The acquisition of data about Earth's surface from a satellite orbiting the planet or other long-distance methods.
48
New cards
site
The physical character of a place
49
New cards
situation
the location of a place relative to other places
50
New cards
time-space compression
the rapid innovation of communication and transportation technologies associated with globalization that transforms the way people think about space and time
51
New cards
topographic map
a map showing the surface features of an area; elevation

52
New cards
toponym
the name given to a place on Earth
53
New cards
Vernacular/Perceptual Region
an area that people believe exists as part of their cultural identity
54
New cards
Dot Distribution Map
A map where dots are used to demonstrate the frequency or intensity of a particular phenomena
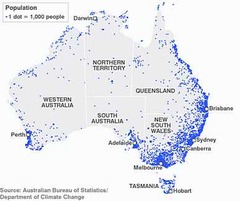
55
New cards
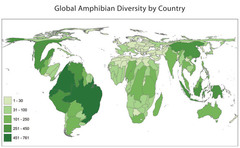
Choropleth Map
A thematic map that uses tones or colors to represent spatial data as average values per unit area.
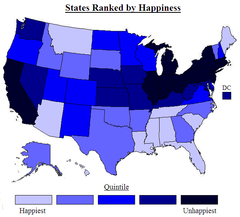
56
New cards
graduated symbol map
A map with symbols that change in size according to the value of the attribute they represent.
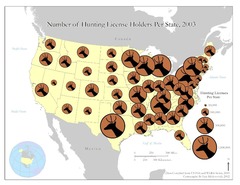
57
New cards
cartogram
A special kind of map that distorts the shapes and sizes of countries or other political regions to present economic or other kinds of data for comparison.
58
New cards
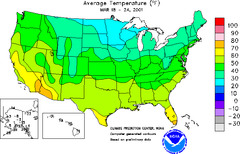
isoline map
A thematic map with lines that connect points of equal value.
59
New cards
Mercator Projection
A true conformal cylindrical map projection, the projection is particularly useful for navigation because it maintains accurate direction. projections are famous for their distortion in area that makes landmasses at the poles appear oversized.
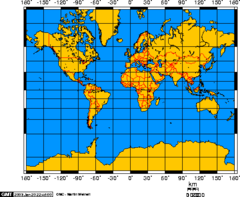
60
New cards
Goode Map Projection
an equal-area, composite map projection used for world maps. Normally it is presented with multiple interruptions.
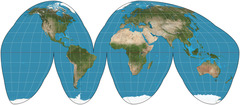
61
New cards
Peter Projection
a cylindrical map projection that attempts to retain the accurate sizes of all the world's landmasses
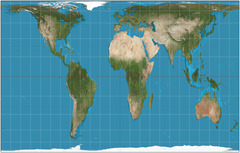
62
New cards
Robinson Projection
Projection that attempts to balance several possible projection errors. It does not maintain completely accurate area, shape, distance, or direction, but it minimizes errors in each.
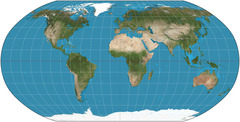
63
New cards
conic projection
a map created by projecting an image of Earth onto a cone placed over part of an Earth model
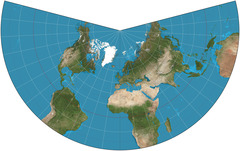
64
New cards
sequent occupance
the notion that successive societies leave their cultural imprints on a place, each contributing to the cumulative cultural landscape
65
New cards
relocation diffusion
the spread of an idea through physical movement of people from one place to another
66
New cards
Hierarchical Diffusion
the spread of a feature or trend from one key person or node of authority or power to other persons or places
67
New cards
Expansion Diffusion
the spread of a feature from one place to another in a snowballing process
68
New cards
Contagious Diffusion
the rapid, widespread diffusion of a characteristic throughout the population
69
New cards
Stimulus Diffusion
the spread of an underlying principle, even though a characteristic itself apparently fails to diffuse
70
New cards
Demography
The scientific study of population characteristics.
71
New cards
Overpopulation
The number of people in an area exceeds the capacity of the environment to support life at a decent standard of living.
72
New cards
carrying capacity
Largest number of individuals of a population that a environment can support
73
New cards
census
A complete enumeration of a population.
74
New cards
Ecumene
The proportion of the earth inhabited by humans.
75
New cards
non-ecumene
An area of Earth that does not have permanent human settlements
76
New cards
cold, wet, high, dry
sparsely populated land types
77
New cards
Arithmetic Density
The total number of people divided by the total land area.
78
New cards
Physiological Density
The number of people per unit area of arable land
79
New cards
Agricultural Density
The ratio of the number of farmers to the amount of arable land
80
New cards
Natural Increase Rate
The percentage growth of a population in a year, computed as the crude birth rate minus the crude death rate.
81
New cards
doubling time
The number of years needed to double a population, assuming a constant rate of natural increase.
82
New cards
crude birth rate
The total number of live births in a year for every 1,000 people alive in the society.
83
New cards
crude death rate
The number of deaths per year per 1,000 people.
84
New cards
total fertility rate
The average number of children born to a woman during her childbearing years.
85
New cards
Maternal Mortality Rate
Number of deaths per thousand of women giving birth.
86
New cards
sex ratio
Number of males per 100 females
87
New cards
Neo-Malthusians
a belief that the world is characterized by scarcity and competition in which too many people fight for few resources. Pessimists who warn of the global ecopolitical dangers of uncontrolled population growth
88
New cards
Pro-Natalist Policies
the policy or practice of encouraging the bearing of children, especially government support of a higher birthrate
89
New cards
Anti-Natalist Policies
government policies to reduce the rate of natural increase
90
New cards
migration
Form of relocation diffusion involving permanent move to a new location.
91
New cards
circulation
Short-term, repetitive, or cyclical movements that recur on a regular basis.
92
New cards
economic, cultural, environmental
Three major kinds of push and pull factors
93
New cards
Asia to Europe
Asia to North America
Latin America to North America
Asia to North America
Latin America to North America
largest flows of migrants
94
New cards
Interregional Migration
movement from one region of a country to another
95
New cards
Intraregional Migration
movement within one region
96
New cards
population center
the average location of everyone in the country
97
New cards
Urbanization
Movement of people from rural areas to cities
98
New cards
Suburbanization
The process of population movement from within towns and cities to the rural-urban fringe.
99
New cards
Counterurbanization
Net migration from urban to rural areas in more developed countries.
100
New cards
immigrant
a person who comes into a country to live there