Chapter 18 - Nucleotide Metabolism
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
54 Terms
Nucleotides
building blocks of DNA & RNA
similar to AA as building blocks of proteins
substrates (ATP) and regulatory compounds (cAMP)
contains either purine base or pyrimidine base
is not a source of energy
carriers of chemical energy
Nucleotides are components of…
cofactors
NAD, FAD, CoA
activated biosynthetic intermediates
UDP-glucose, CDP-diacylglycerol
second messengers
cAMP, cGMP
De Novo Pathway
purine & pyrimidine biosynthesis by building up from a few atoms at a time
structure of ribose is retained in product nucleotide
Important AA Precursors
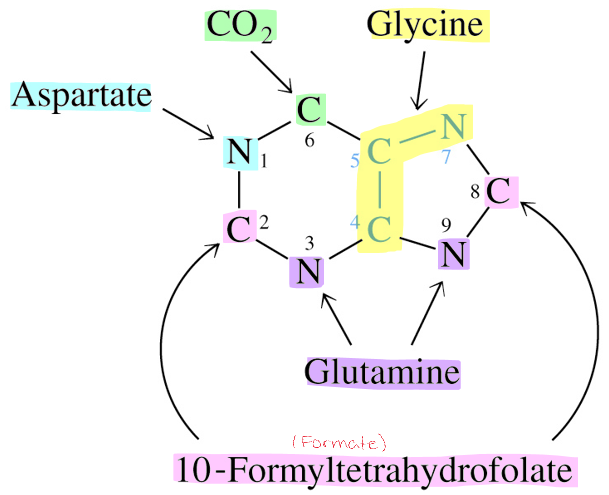
Glycine → Purines (A, G)
Aspartate → Pyrimidines (T/U, C)
Glutamine: important source of amino groups
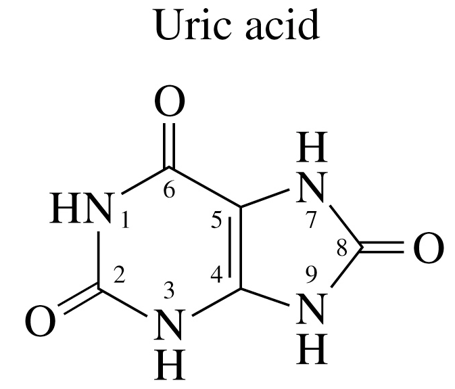
Uric Acid Structure & Properties
limited water solubility to move through the blood
if concn too high, it can accumulate as crystals in joints where WBC can also accumulate to cause gout
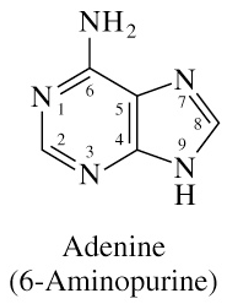
Structure of Adenine
has higher pH
planar due to double bonds
no flexbility
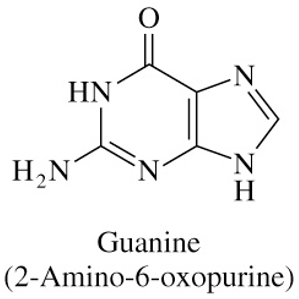
Structure of Guanine
NH2 group on C2
C=O bond on C6
Source of Ring Atoms in Purine Synthesized De Novo
radiation was used to differentiate where each atom came from
extra: John Buchanan determined origin of each atom using isotopic tracers
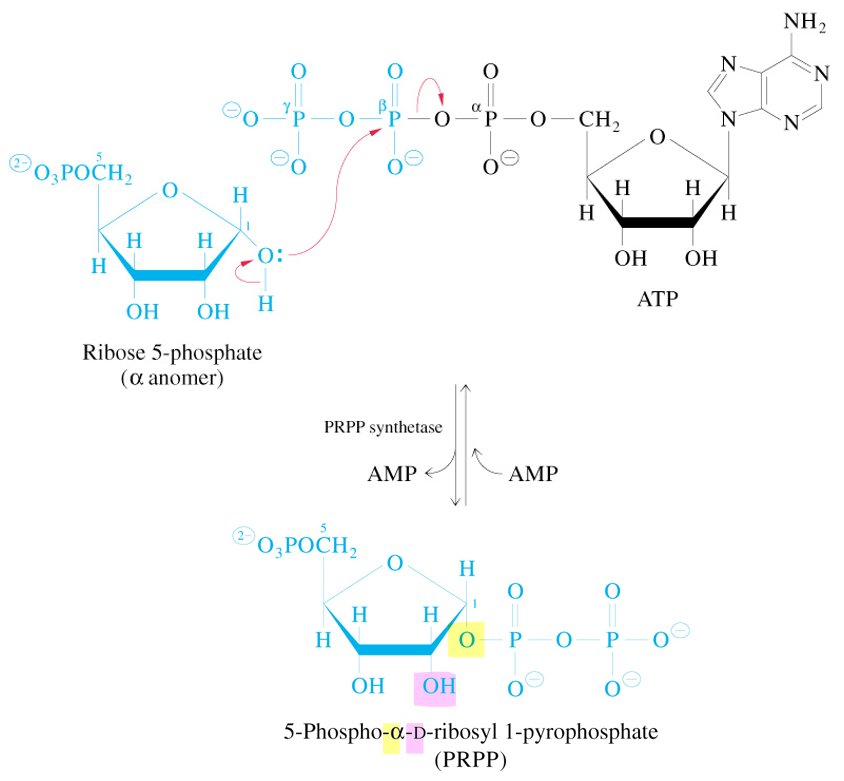
Synthesis of 5-Ribosyl-1-Pyrophosphate (PRPP)
uses ATP & PRPP synthetase
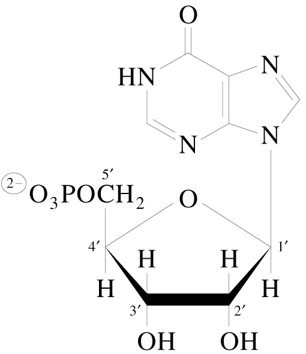
Inosine 5’-Monophosphate (IMP or Inosinate)
initial product of 10-step purine nucleotide pathway
hypoxanthine is base for IMP
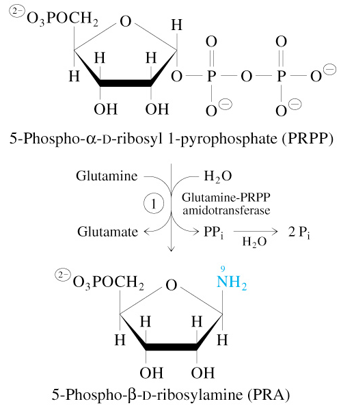
Step 1 of De Novo Synthesis of IMP
PRPP + Glutamine + H2O
—Glutamine-PRPP Amidotransferase→
PRA + Glutamate + 2 Pi
Step 2 of De Novo Synthesis of IMP
PRA + ATP
—GAR Synthase→
GAR + ADP + Pi
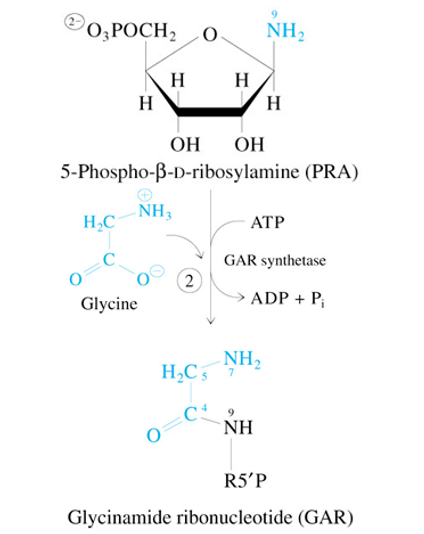
Step 3 of De Novo Synthesis of IMP
GAR + 10-Formyl-Tetrahydrofolate
—GAR Transformylase→
FGAR + Tetrahydrofolate
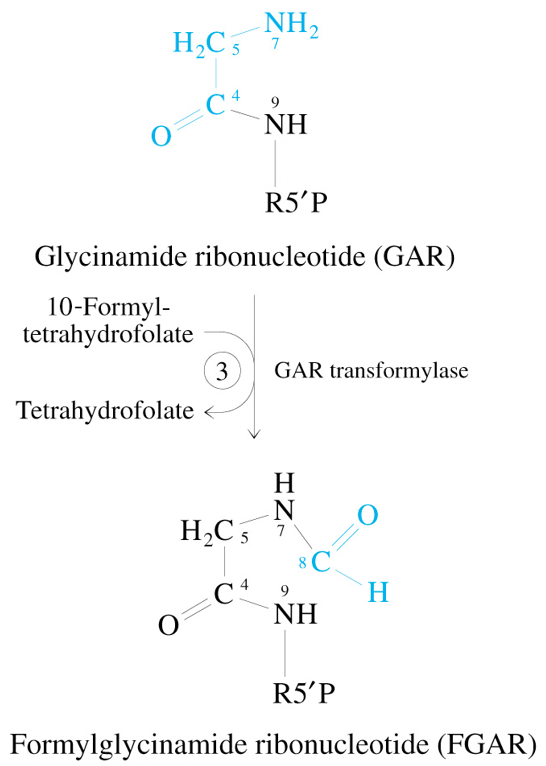
Step 4 of De Novo Synthesis of IMP
FGAR + Glutamine + ATP + H2O
—FGAM Synthetase→
FGAM + Glutamate + ADP + Pi
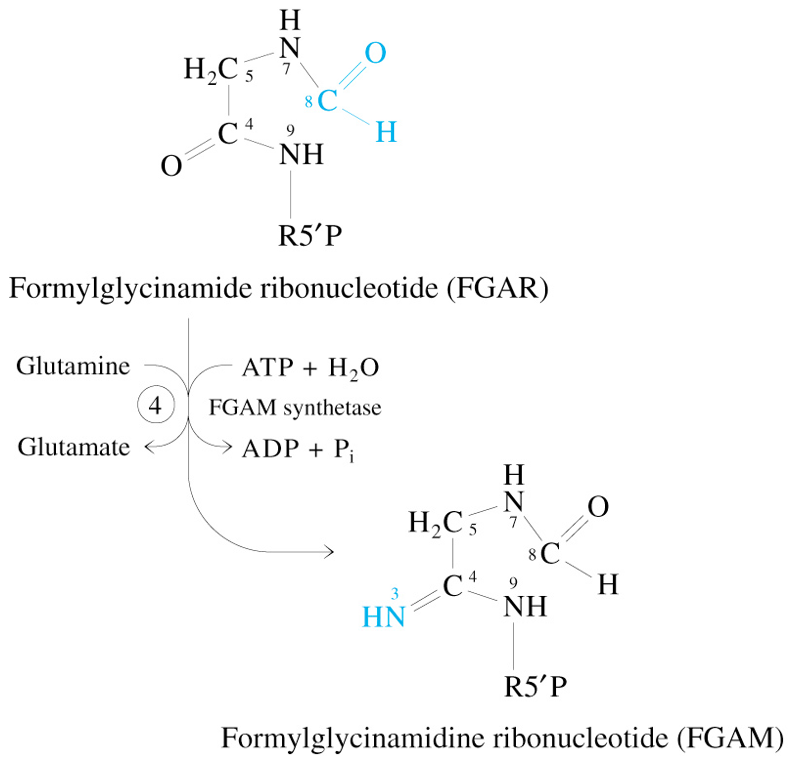
Step 5 of De Novo Synthesis of IMP
FGAM + ATP
—AIR Synthetase→
AIR + ADP + Pi
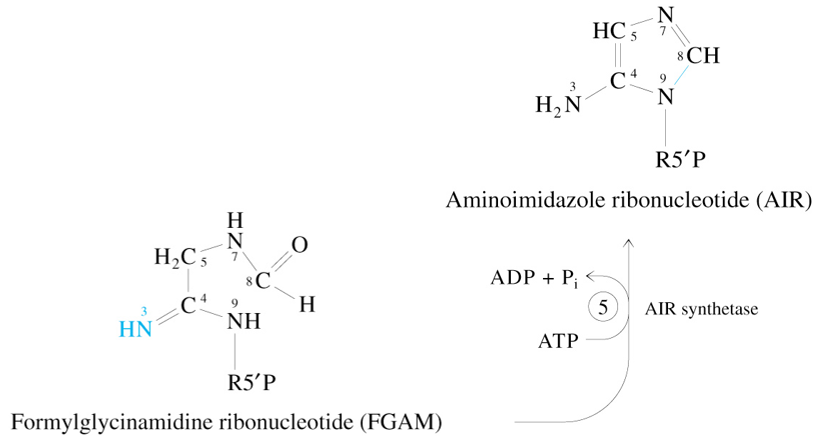
Step 6 of De Novo Synthesis of IMP
AIR + ATP + HCO3-
—AIR Carboxylase→
CAIR + ADP + Pi + 2 H+
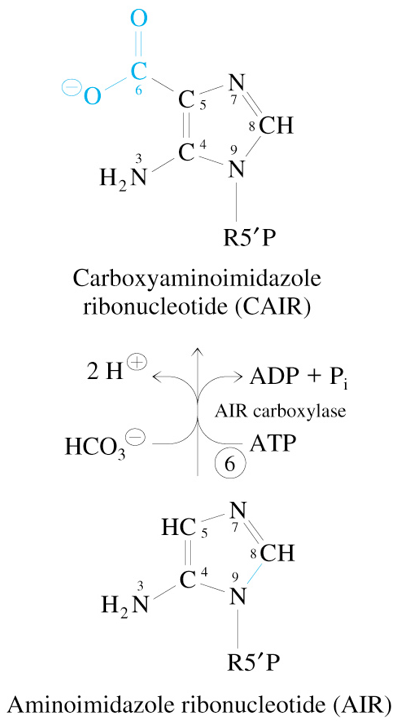
Step 7 of De Novo Synthesis of IMP
CAIR + Aspartate + ATP
—SAICAR Synthetase→
SAICAR + ADP + Pi
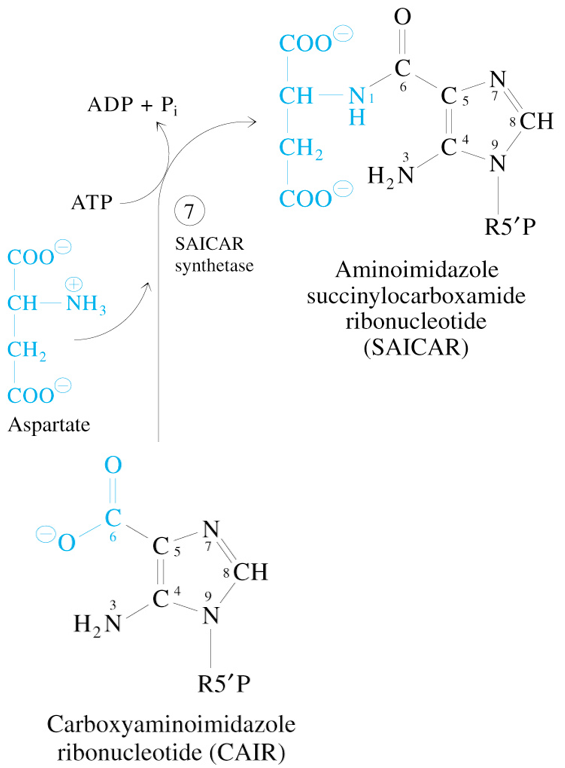
Step 8 of De Novo Synthesis of IMP
SAICAR
—Adenyl Succinate Lyase→
AICAR + Fumarate
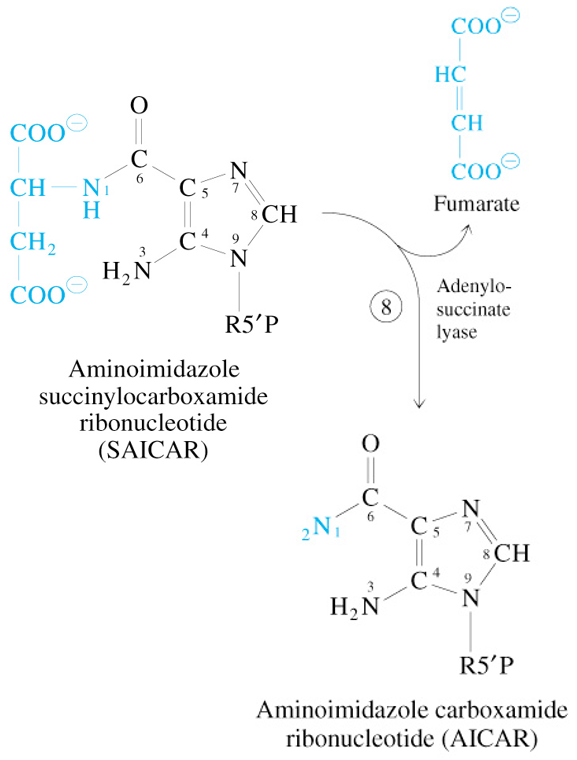
Step 9 of De Novo Synthesis of IMP
AICAR + 10-Formyl Tetrahydrofolate
—AICAR Transformylase→
FAICAR + Tetrahydrofolate
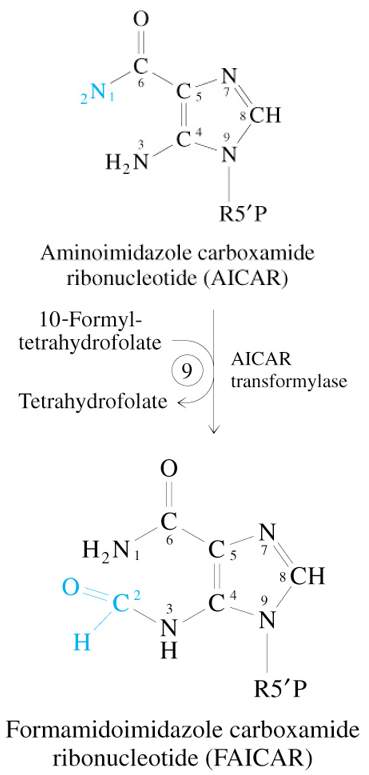
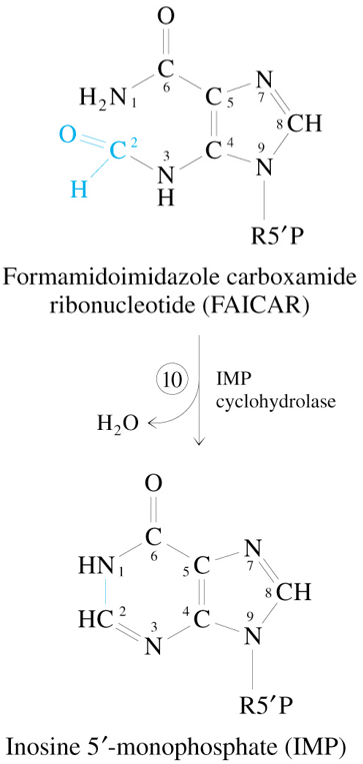
Step 10 of De Novo Synthesis of IMP
FAICAR
—IMP Cyclohydrolase→
IMP + H2O
Synthesis of AMP from IMP
Step 1: IMP + Aspartate + GTP —Adenylsuccinate Synthetase→ Adenylosuccinate + GDP + Pi
Step 2: Adenylosuccinate —Adenylsuccinate Lyase→ AMP + Fumarate
AMP → ADP → ATP
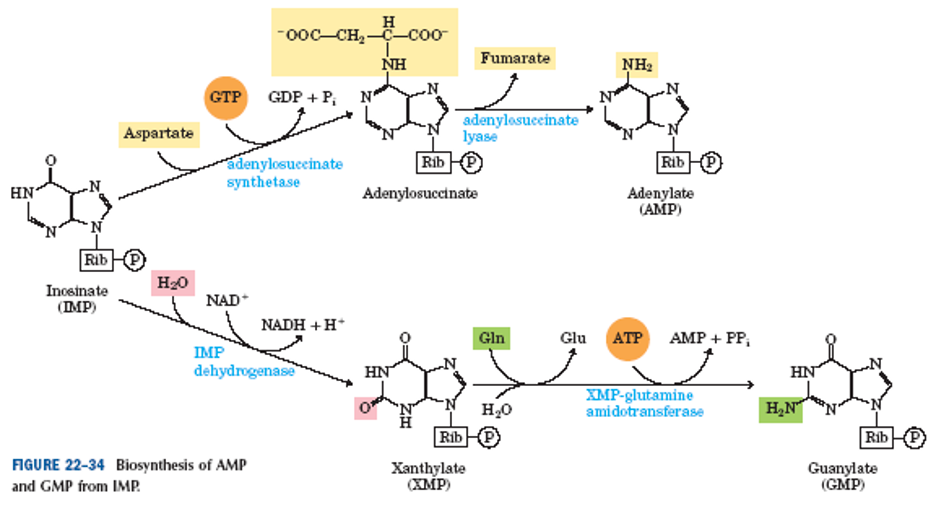
Synthesis of GMP from IMP
Step 1: IMP + H2O + NAD+ —IMP Dehydrogenase→ Xanthylate (XMP) + NADH + H+
Step 2: XMP + Glumaine + ATP —XMP-Glutamine Amidotransferase→ GMP + Glutamate + AMP + PPi
GMP → GDP → GTP

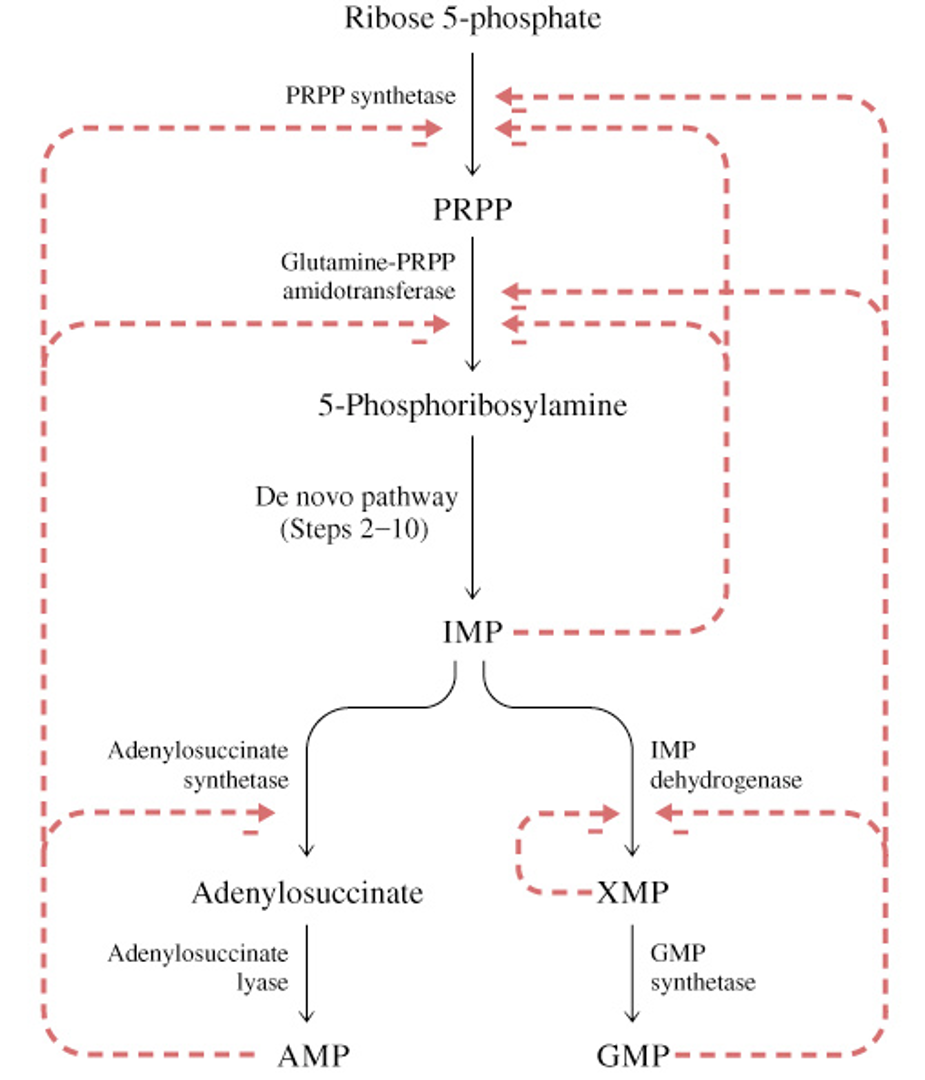
Feedback Inhibition in Purine Nucleotide Biosynthesis (AMP & GMP)
no inhibition during step 2-10
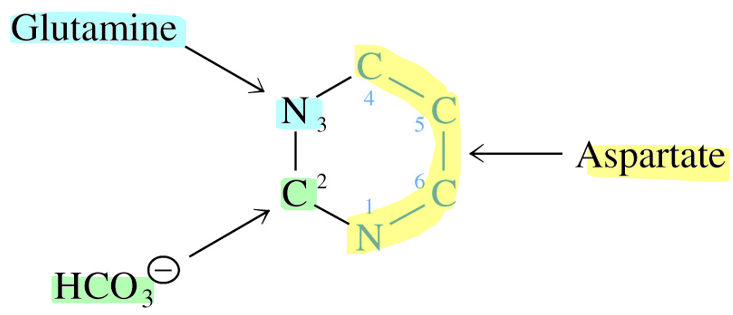
Source of Ring Atoms in Pyrimidine Synthesized De Novo
immediate precursor of C2 & N3 is carbamoyl phosphate
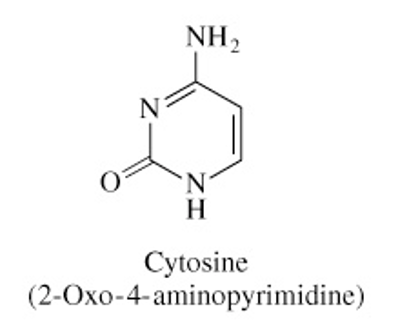
Structure of Cytosine
C=O bond at C2
NH2 at C4
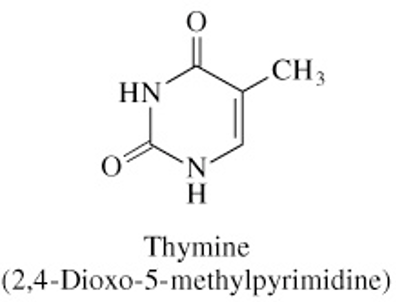
Structure of Thymine
C=O bond at C2 & C4
CH3 at C5
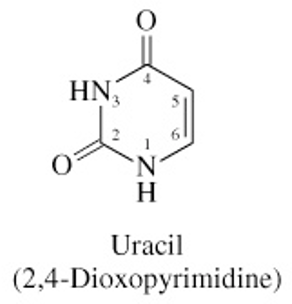
Structure of Uracil
C=O at C2 & C4
no methyl at C5
Pathway for De Novo Pyrimidine Synthesis
6 step pathway to UMP
in eukaryotes,
steps 1-3 are catalyzed by multifunctional protein, dihydroorotate synthase
steps 5-6 are catalyzed by bifunctional enzyme (UMP synthase)
Step 1 of De Novo Pyrimidine Synthesis
Glutamine + 2 ATP + HCO3-
—Carbamoyl Phosphate Synthetase→
Carbamoyl Phosphate + Glutamate + 2 ADP + Pi
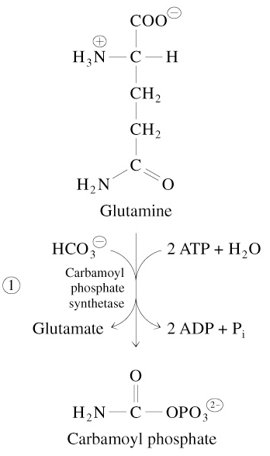
Step 2 of De Novo Pyrimidine Synthesis
Carbamoyl Phosphate + Aspartate
—Aspartate Transcarbamoylase (ATCase)→
Carbamoyl Aspartate + Pi
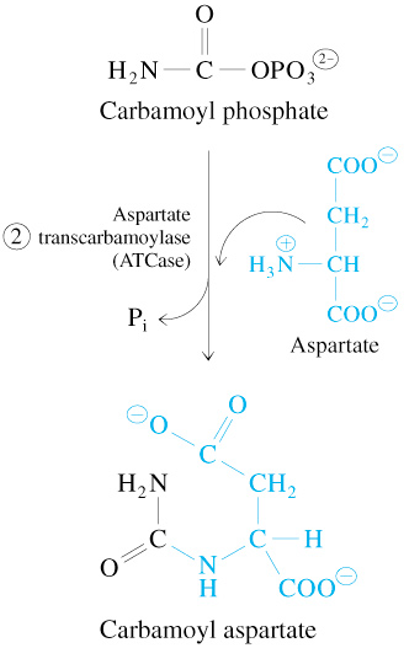
Step 3 of De Novo Pyrimidine Synthesis
Carbamoyl Aspartate
—Dihydroorotase→
L-Dihydroorotate + H2O
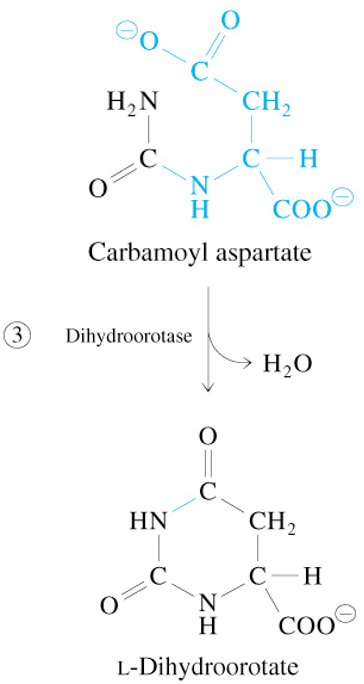
Step 4 of De Novo Pyrimidine Synthesis
L-Dihydroorotate + Q
—Dihydroorotate Dehydrogenase→
Orotate + QH2
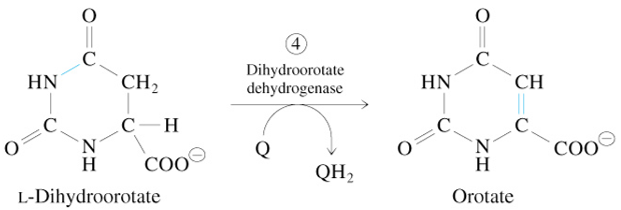
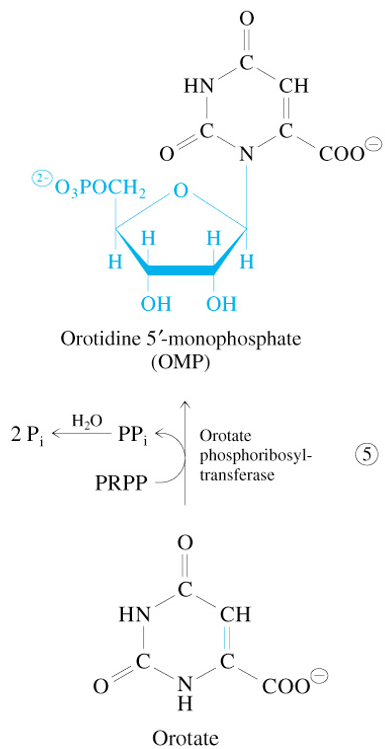
Step 5 of De Novo Pyrimidine Synthesis
Orotate + PRPP
—Orotate Phosphoribosyl Transferase→
OMP + 2 Pi
Step 6 of De Novo Pyrimidine Synthesis
OMP + H2O
—OMP Decarboxylase→
UMP + HCO3-
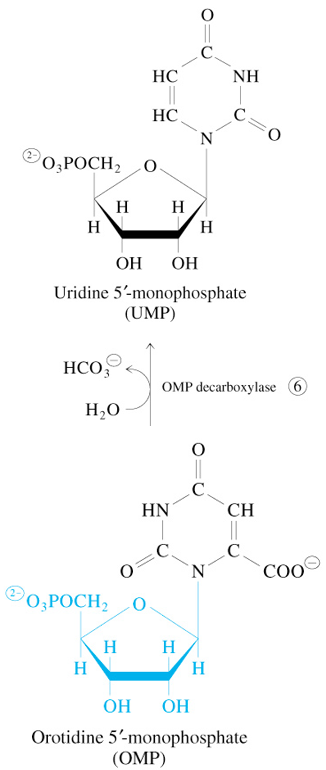
CTP Synthesized from UMP
UMP + ATP → UDP + ATP → UTP + ATP + Glutamine → CTP + Glutamate
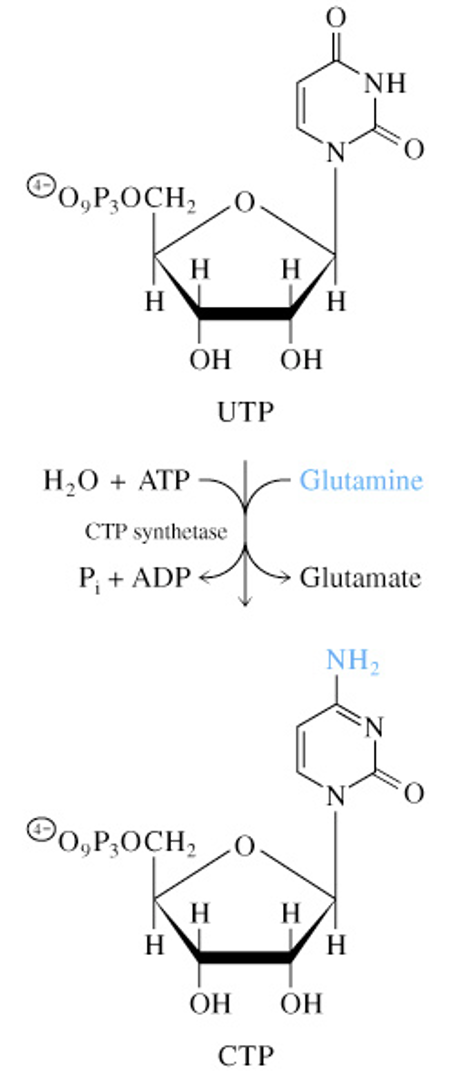
Regulation of Pyrimidine Nucleotide Synthesis
Reduction of Ribonucleotides to Deoxyribonucleotides
2’-Deoxyribonucleoside Triphosphates (substrates for DNA polymerase) synthesized by enzymatic reduction of ribonucleotides
ribonucleotide diphosphate reductase (RDR)
ADP → dADP
GDP → dGDP
CDP → dCDP
UDP →dUDP
Deoxyribonucleotides (DRNT)
building blocks of DNA
derived from corresponding ribonucleotides (RNT)
direct reduction at C2 of D-ribose
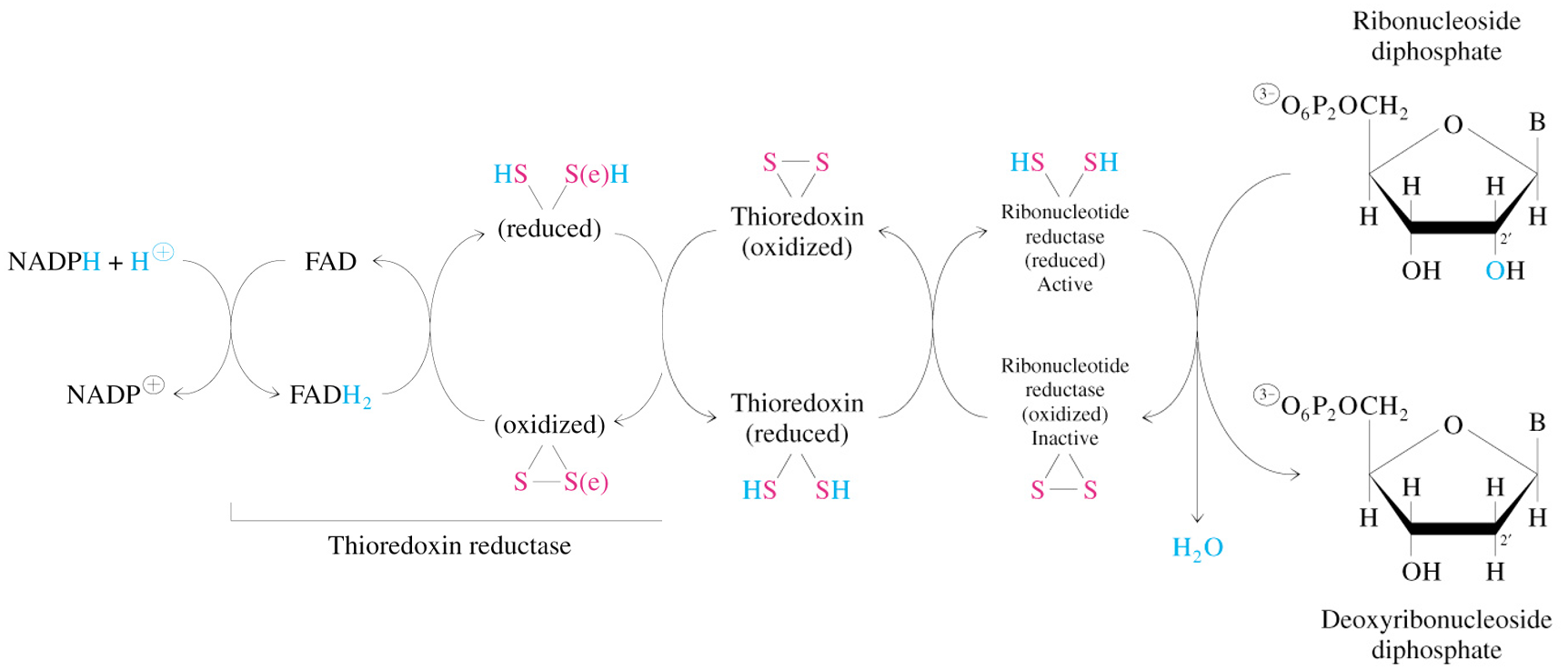
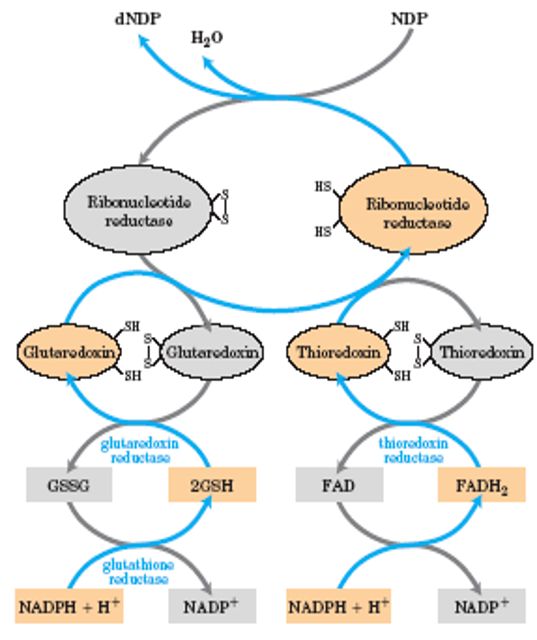
Reduction of RNT to DRNT by Ribonucleotide Reductase
electrons transmitted to enzyme from NADPH by (a) glutaredoxin or (b) thioredoxin
sulfide groups in glutaredoxin reductase are contributed by 2 molecules of bound glutathione
thioredoxin reductase is flavoenzyme, with FAD as prosthetic group
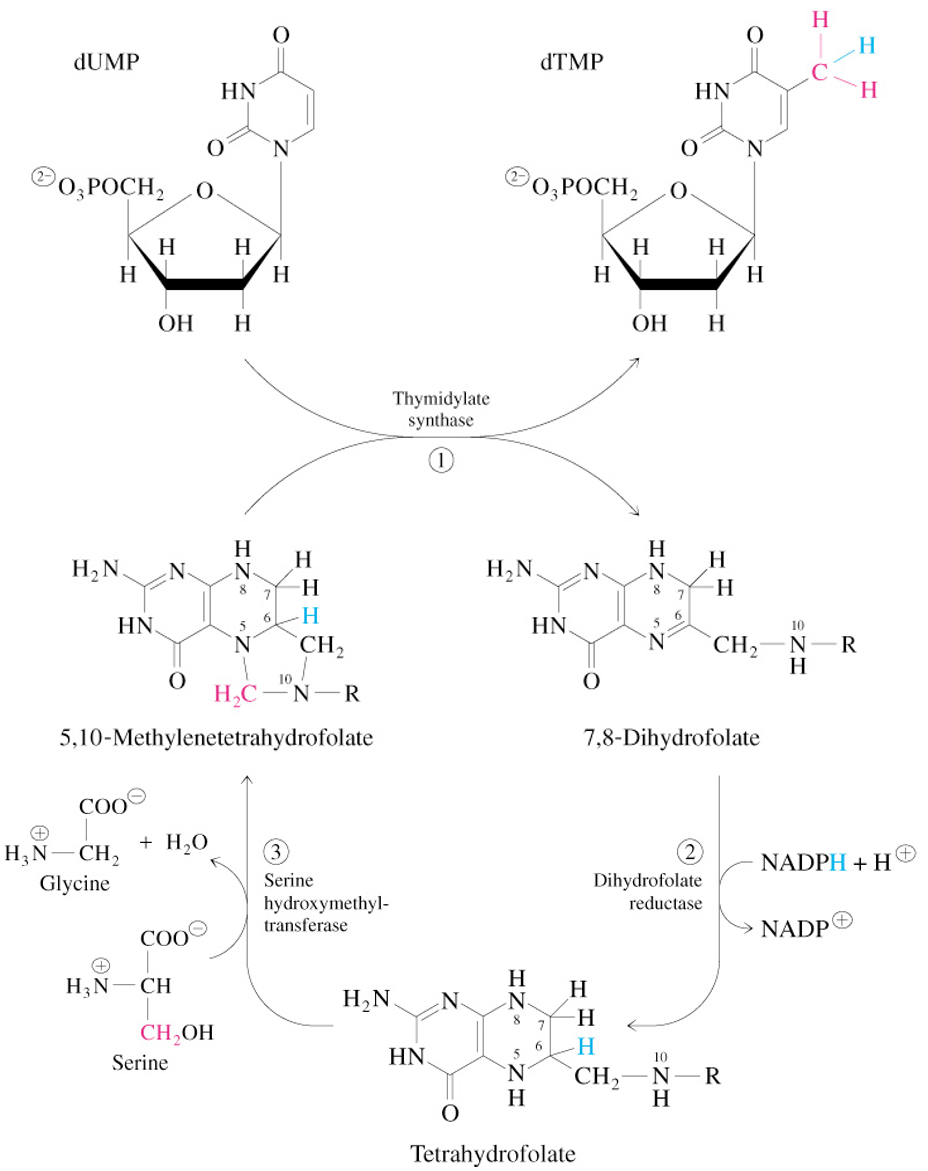
Thymidylate Synthase Reaction
DNA contains T instead of U
de novo pathway to thymine involves only DRNT
dUTP→dUMP→dTMP reaction must be efficient to keep dUTP pools low and prevent incorporation of uridylate into DNA
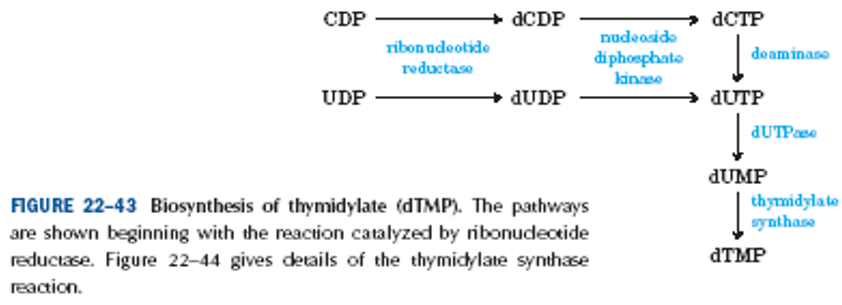
Routes for dUDP → dUMP
dUDP + ADP ⇆ dUMP + ATP
dUDP + ATP (↓ADP) → dUTP (+ H2O) → dUMP + PPi
Synthesis of dTMP from dUMP
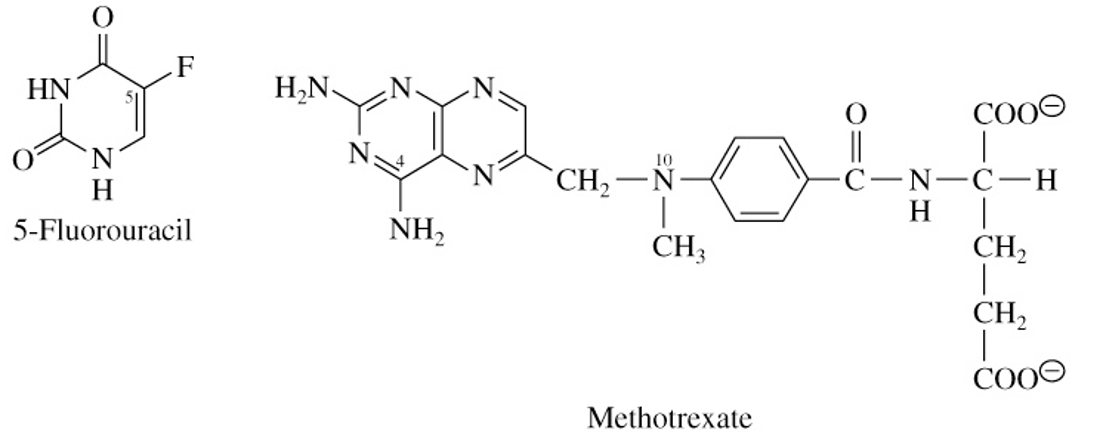
5-Fluorouracil & Methotrexate
drugs designed to inhibit cancer cell growth
methotrexate has glutamate side chain making it a weak acidic drug
used to treat acute leukemia in children
MRP8 can transfer active 5-FU drugs out of cancer cell, creating resistance to that drug
Salvage of Purines & Pyrimidines
during cellular metabolism or digestion, nucleic acids are degraded to heterocyclic bases
bases can be salvaged by direct conversion to 5’-mononucleotides
PRPP is donor of 5-phosphoribosyl group
recycling of intact bases saves energy
Breakdown of Nucleic Acids
5’-mononucleotides are used for nucleic acid synthesis
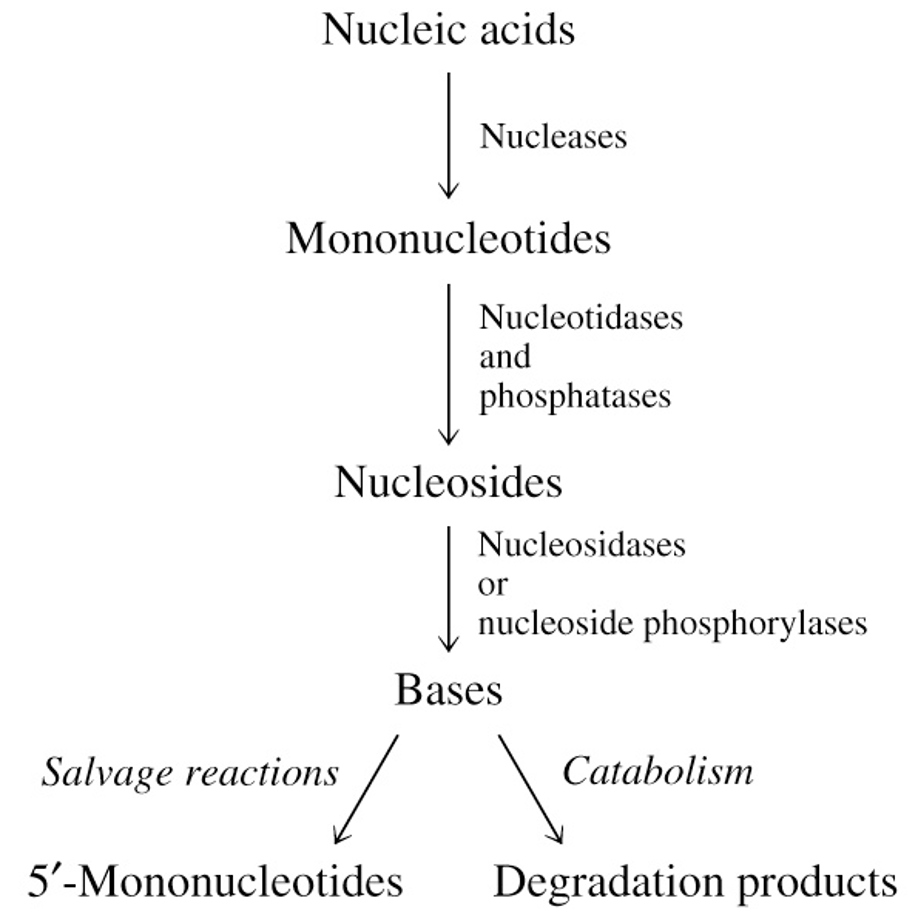
Degradation & Salvage of Purines
degrades from nucleotide → nucleoside → nucleobase
synthesis using PRPP
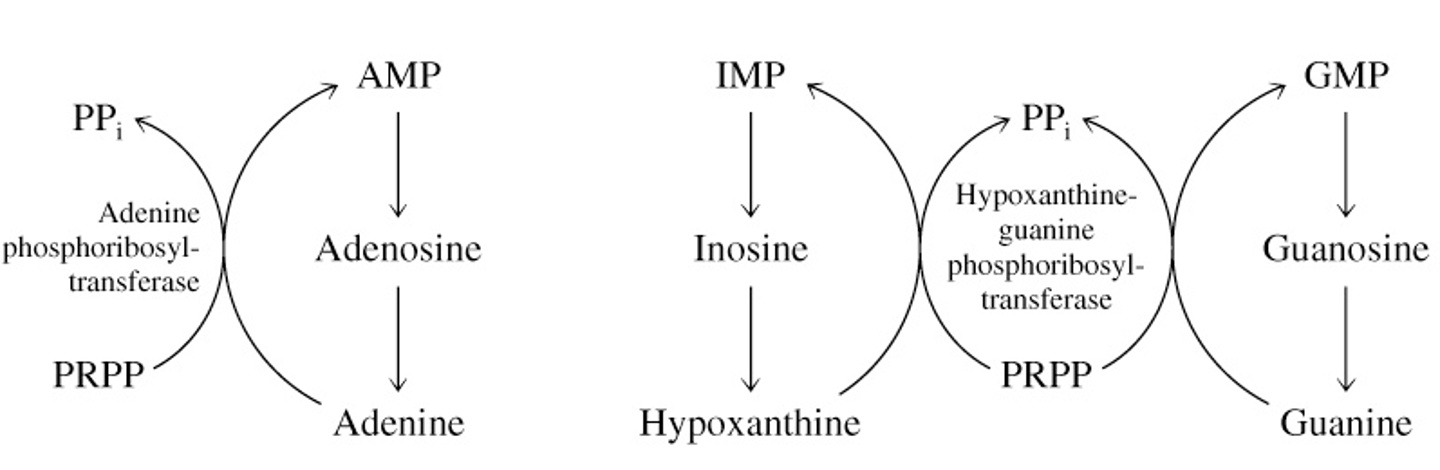
Purine Catabolism
most free purines & pyrimidines are salvaged
some are catabolized
birds, reptiles, primates convert purines to uric acid
Separation of Base from (Deoxy)Ribose
(deoxy)nucleoside + Pi —PNP→ base + (deoxy)-α-D-ribose 1-phosphate
purine-nucleoside phosphorylase (PNP) separates free purine base from (deoxy)ribose
Adenosine Properties
hormone, neurotransmitter properties
increases blood flow
decreases blood pressure
muscle relaxatant
lowers ATP utilization
adenosine receptors are present on cell surfaces, affecting adenylyl cyclase activity
caffine increases blood pressure by binding to adenosine receptors, blocking adeonsine binding
Breakdown of Hypoxanthine & Guanine to Uric Acid
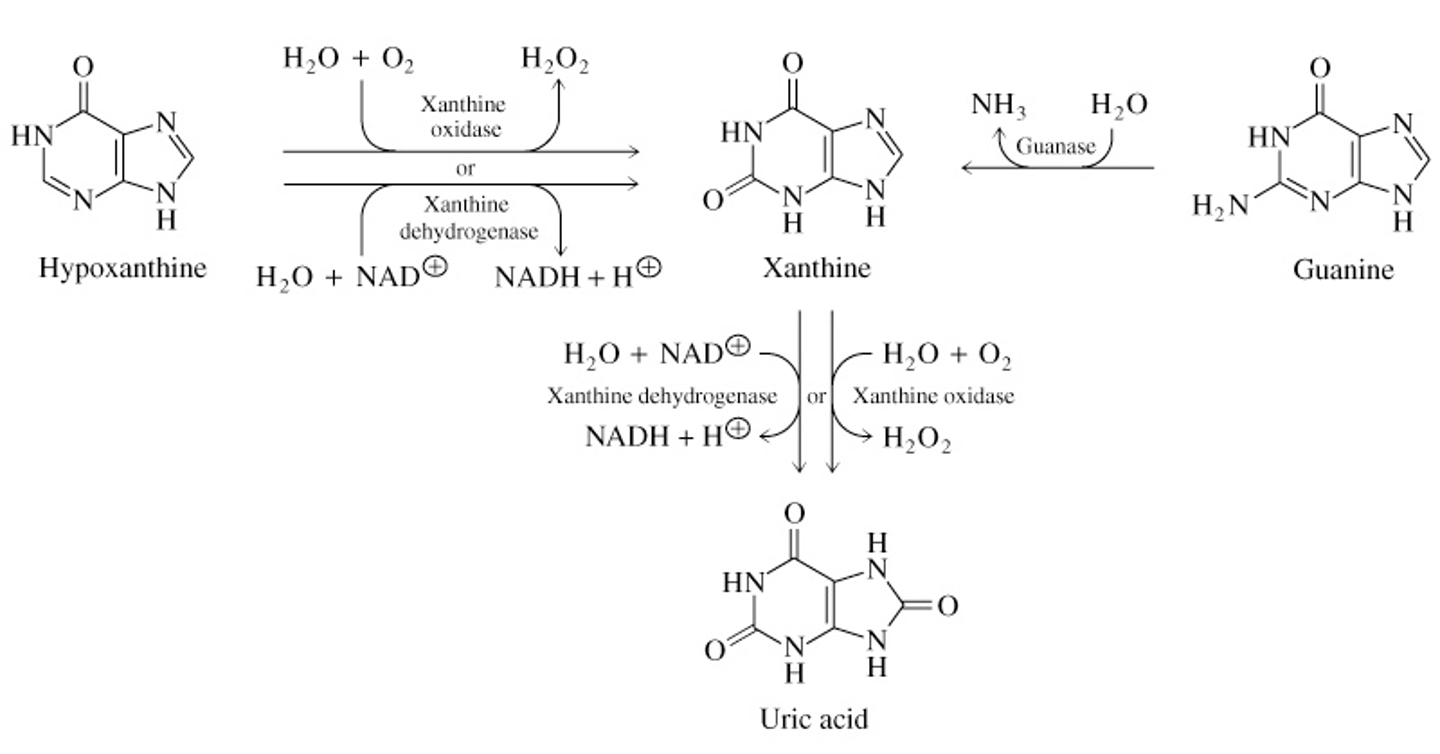
What is Gout
disease of the joints caused by overproduction or inadequate excretion of uric acid in blood and tissues
deficiency of hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyltransferase or defective regulation of purine biosynthesis
the joints become inflamed, painful, and arthritic, causing abnormal deposition of sodium urate crystals
kidneys are effected, excess uric acid is deposited in kidney tubules
inadequate excretion indicates issue with kindey’s ABCG2 transporter (transports uric acid)
occurs predominantly in males
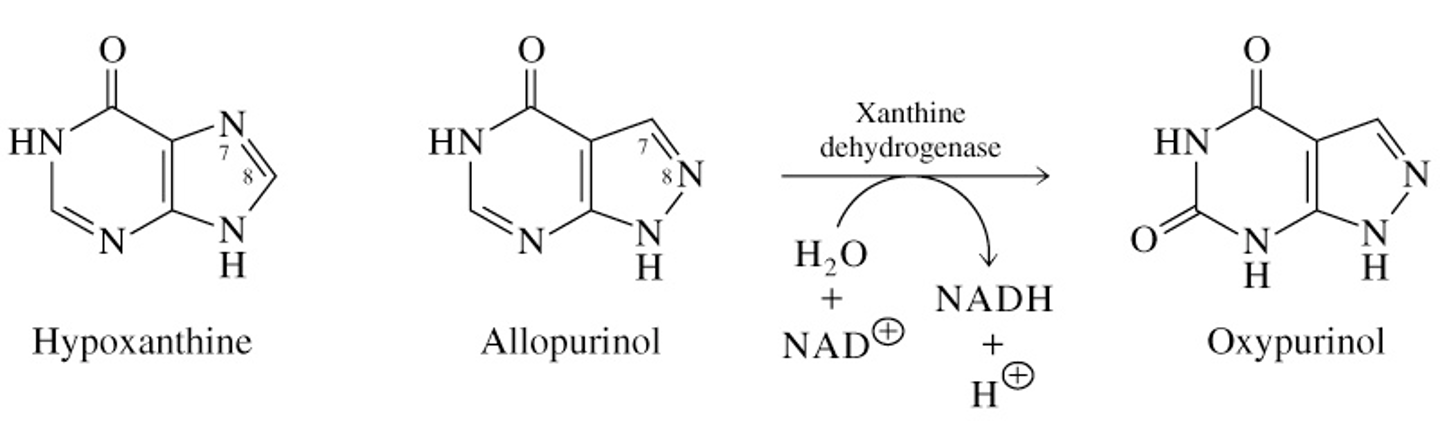
Treatment for Gout
Allopurinol is converted to oxypurinol, an inhibitor of xanthine dehydrogenase
prevents high levels of uric acid
hypoxanthin & xanthine are more water soluble, therefore they are excreted easily
foods rich in nucleotides & nucleic acids, like liver or glandylar products, should be avoided
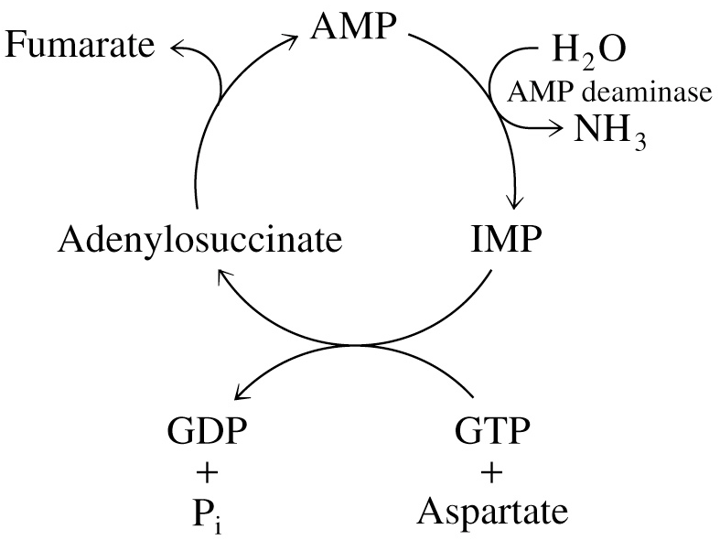
Purine Nucleotide Cycle in Muscle
Aspartate + GTP + H2O → Fumarate + GDP + Pi + NH3
during exercise, AMP deaminase converts AMP to IMP, releasing NH3
decreasing AMP shifts equilibrium of adenylate kinase to produce more ATP for muscle contraction
IMP can be recycled to AMP
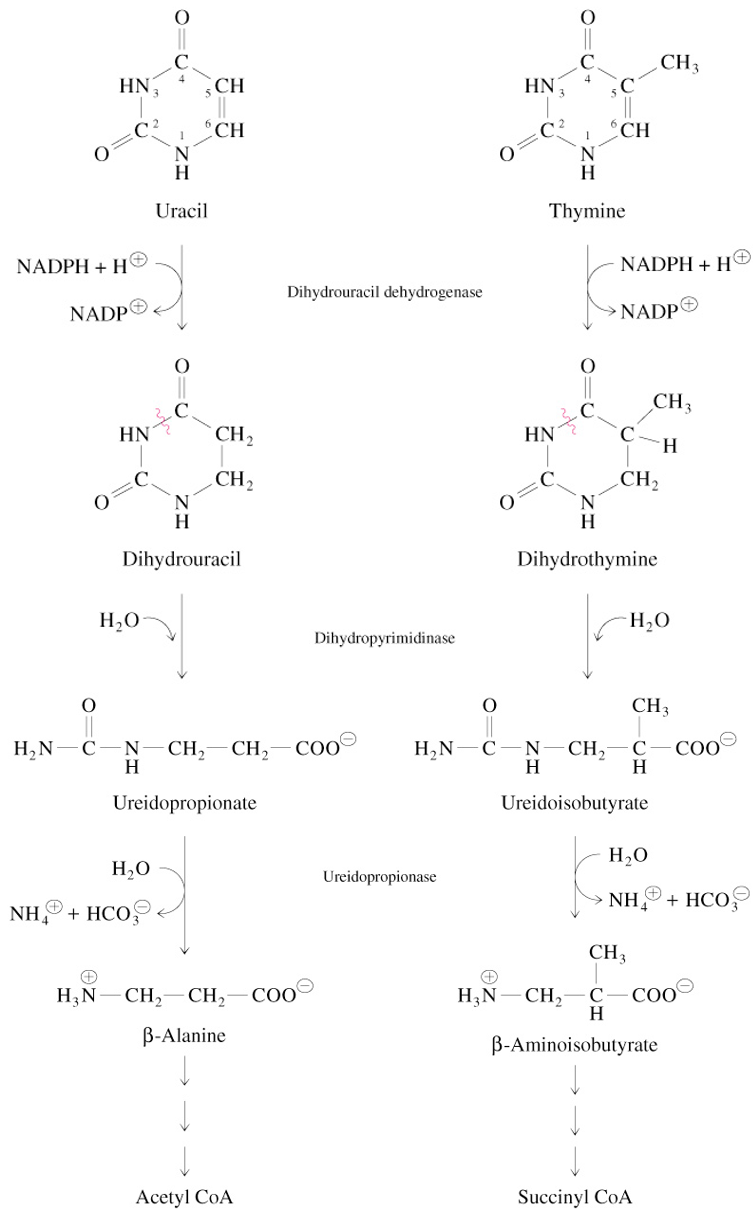
Pyrimidine Metabolism
pyrimidine nucleotides are hydrolyzed to nucleosides & Pi
T, U, and (deoxy)ribose 1-phosphate are produced
catabolism of T & U bases ends with intermediates of central metabolism