ch 17 aqueous equilibrium
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
common-ion effect
when a weak electrolyte is combined with a strong electrolyte that contains a common ion, the ionization of the weak electrolyte is surpressed
buffer solution
a solution consisting of weak acid and its conjugate base(or a weak base and its conjugate acid) that resists change in pH
Henderson- Hasselbach equation
pH= pKa+ log [base]/[acid]
buffer capacity
the ability of the buffer solution to resist a change in pH when an acid or base is added
titrant
a solution of a known concentration
analyte
a solution of an unknown concentration
titration curve
a plot of pH versus volume of titrant added over the course of a titration
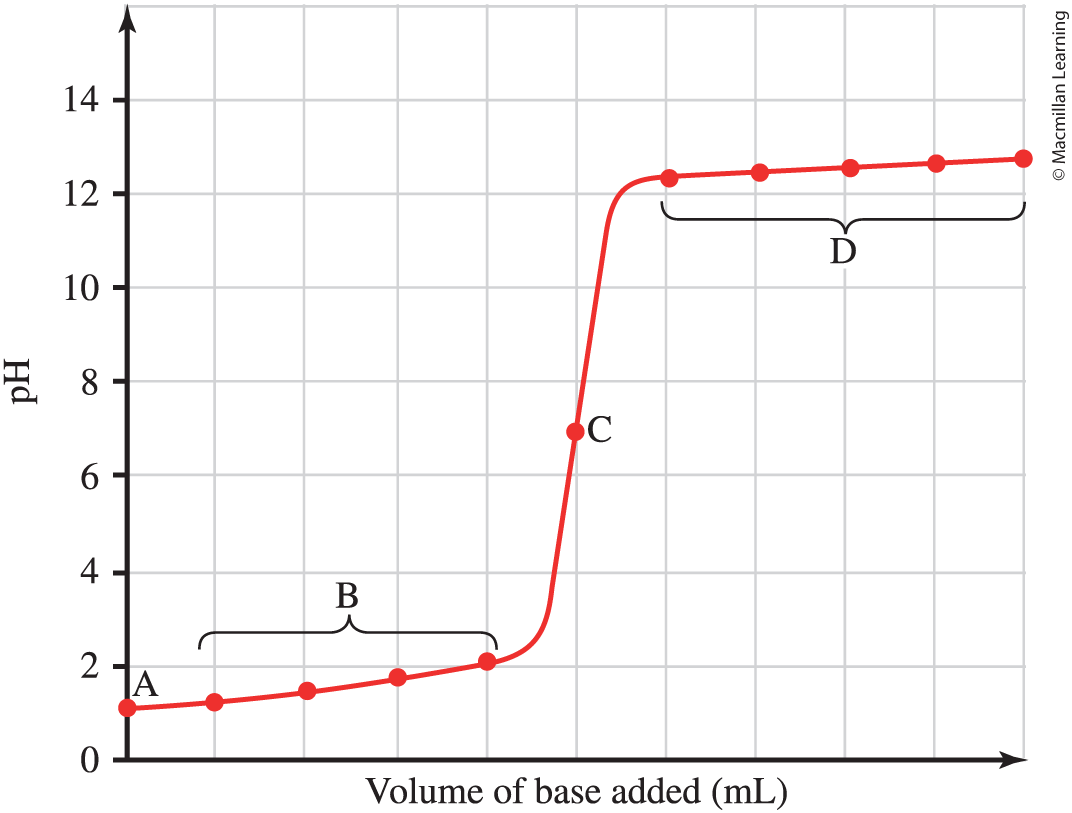
Strong acid with Strong base titration
A- initial pH acid; pH= -log[H3O+]
B- some titrant added, but EP not reached
C- Equivalence point, mols of acid=mols base, pH=7
D-all acid neutralized and titrant in excess; pOh calculated from excess OH- in solution
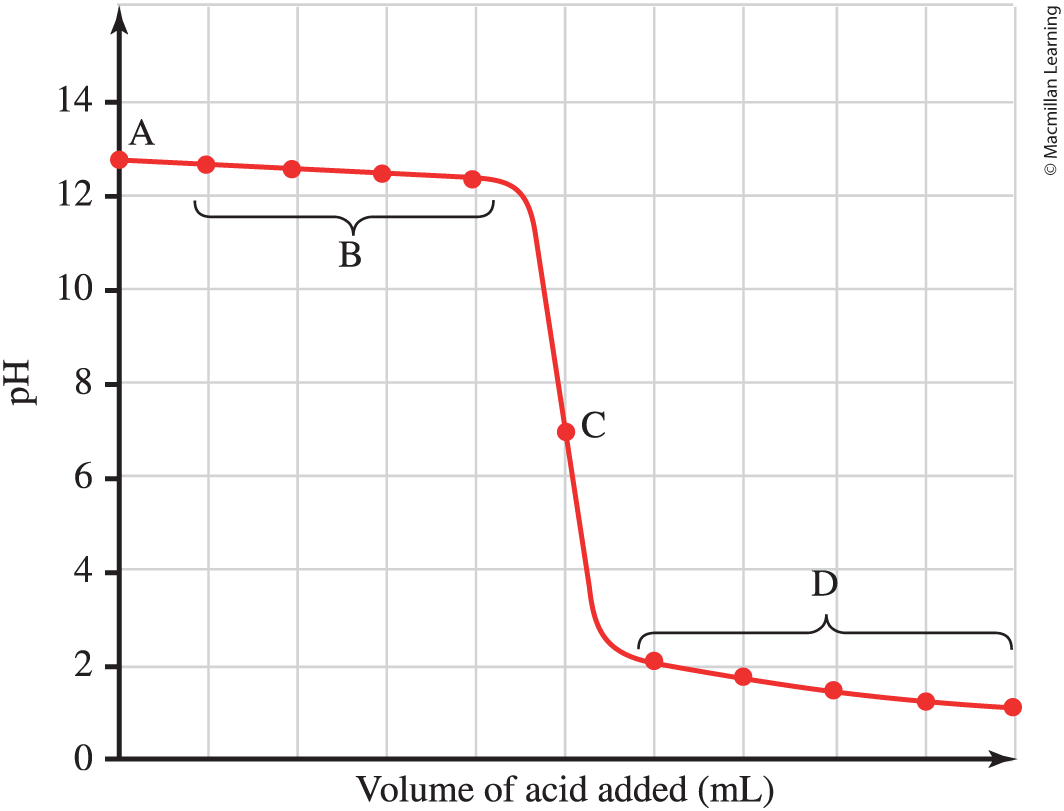
Strong base titrated with strong acid
A-initial pH of solution
B-some titrant added, but EP not reached
C-Equivalence point, mols of acid=mols base, pH=7
D-all base neutralized and titrant in acid; pH calculated from excess H+ in solution
BAA table
B- before the titration
A- additional mols acid/base
A-after mols
Weak acid-strong base titration
initial pH of weak acid is higher than that of a strong acid
displays less abrupt pH change near the EP then SA/SB
pH at equivalence point is greater than 7
weak base- strong acid titration
initial pH of weak base is lower than a strong base
pH at EP is less than 7
pH at the half-equivalence point is equal to pKa of the conjugate acid of weak base titrated
endpoint
the color change of the indicator in a titration
solubility
the amount of a substance that is dissolved in a saturated solution of that substance
molar solubility
the number of moles of a substance that can dissolve into 1L of solution