MCAT P/S Society and culture, social inequity
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
14 Terms
Intersectionality
how individuals hold. multiple, interconnected, marginalized social identities that impact their lives, perspectives, and treatment in society.
Racialization
The process by which one group designates another group with a racial identity, often based on shared group qualities like physical attributes, behaviors.
Cultural transmission
passing of cultural information from one generation to the next
Stereotype threat
awareness of the stereotype “women are bad at math” before a math task hinders women’s performance
Organization types
Utilitarian
Normative
Coercive
Utilitarian: members are compensated (money, diploma)
Normative: voluntary, with shared goals
Coercive: not freely chosen (prison)

Looking-glass self
Interpretation of how we are perceived by others impacts our self-concept.
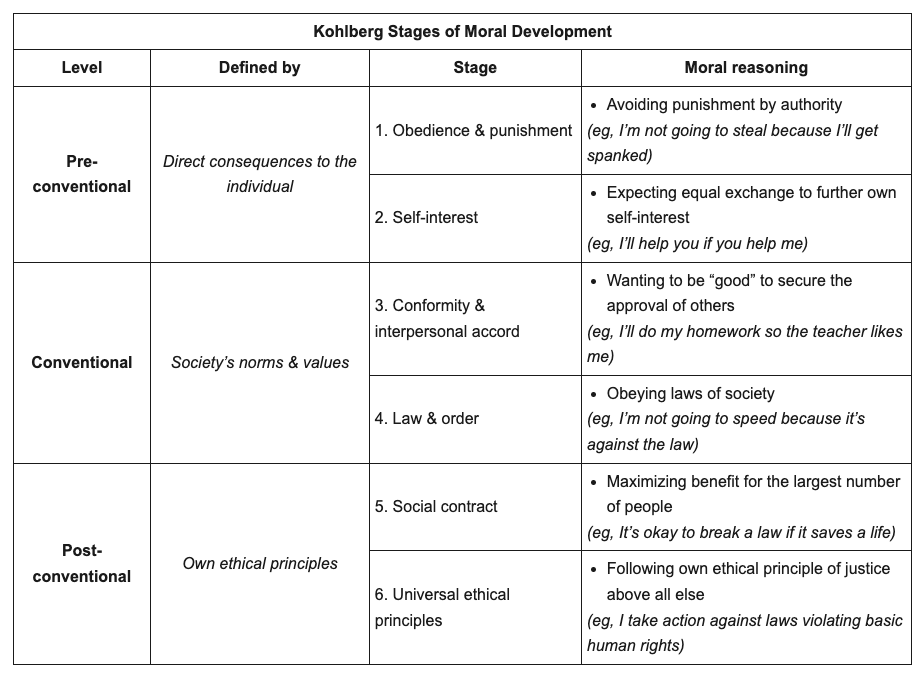
Kohlberg’s theory of moral development
Pre-conventional
Conventional
Post-conventional
Pre: morality controlled by outside forces
Conventional: morality defined by existing social norms and values
individuals want to be good and liked by others and obey laws
Post: based on universal moral principles
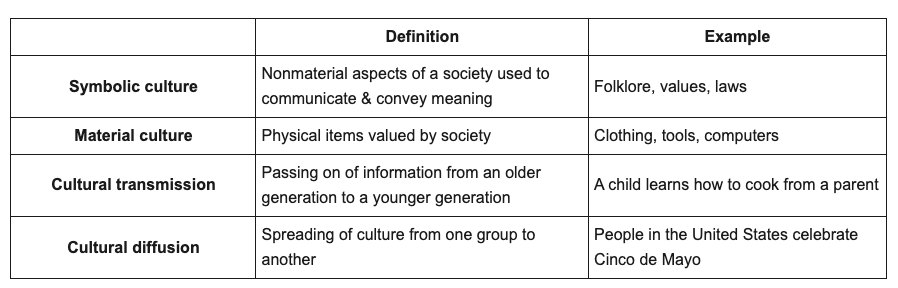
Symbolic vs material culture
Cultural transmission vs diffusion
Identity development theory by James Marcia
based on level of commitment and degree of exploration

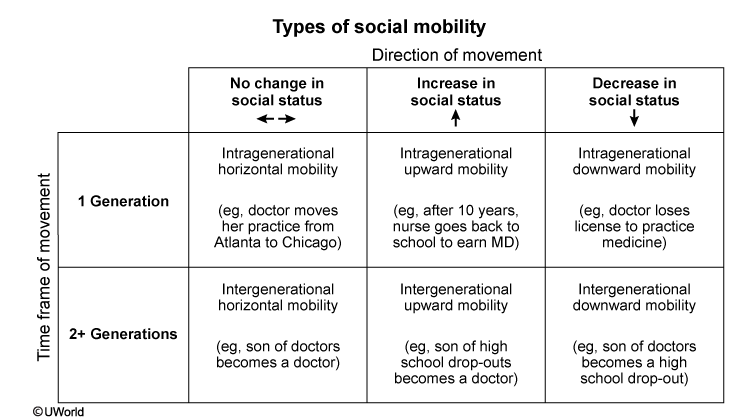
Types of social mobility
social mobility: movement of indviduals, groups, or families between or within status categories in society.
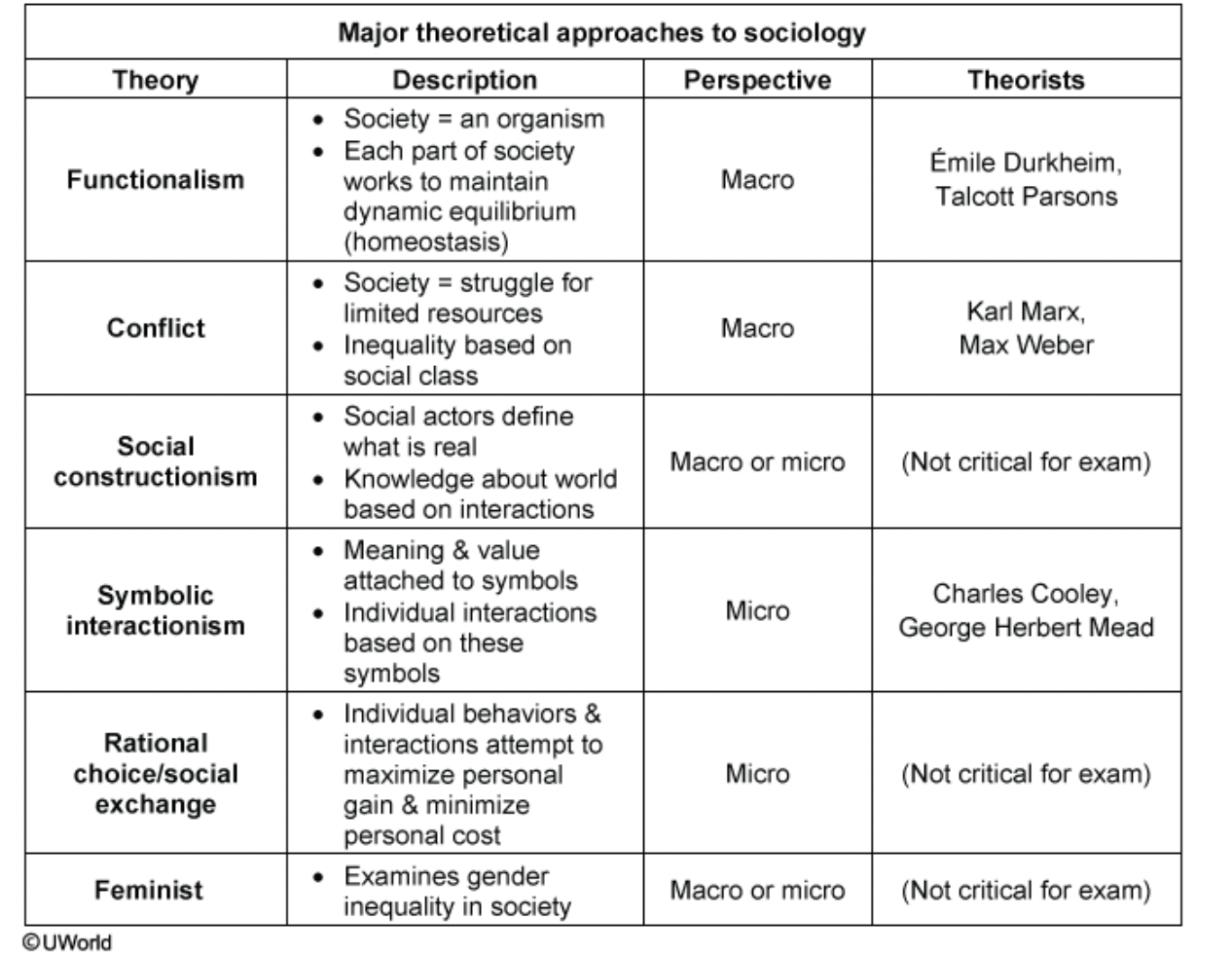
Major theological approaches of sociology
functionalism
conflict
social constructionism
symbolic interactionism
rational choice/social exchange
feminist
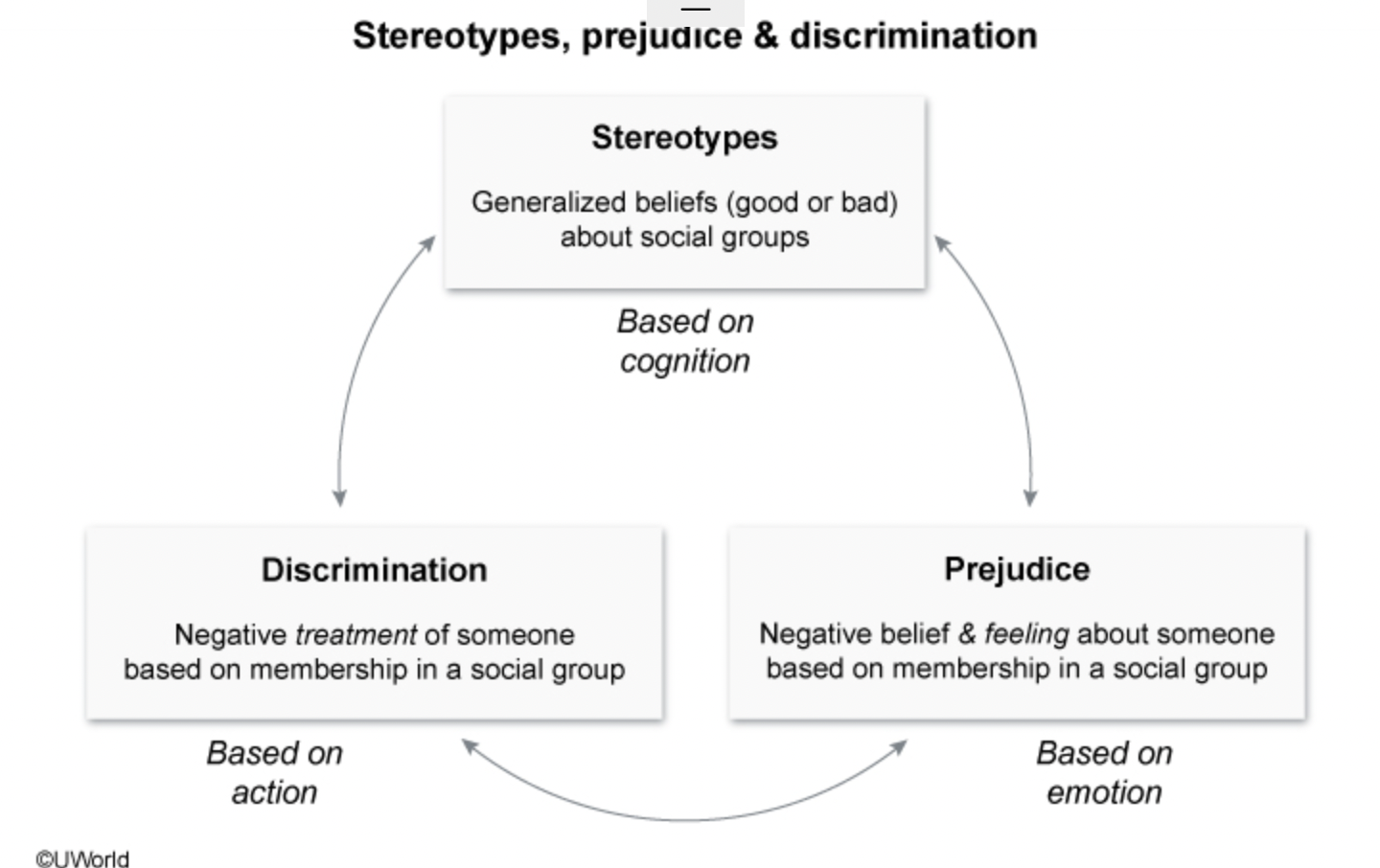
Stereotypes, prejudice, discrimination
Stereotype: based on cognition
overly simplified, generalized characterization of a particular group
Discrimination: action, negative treatment of individuals based on prejudice or stereotypes.
Prejudice: emotion. negative beliefs and feelings towards a group
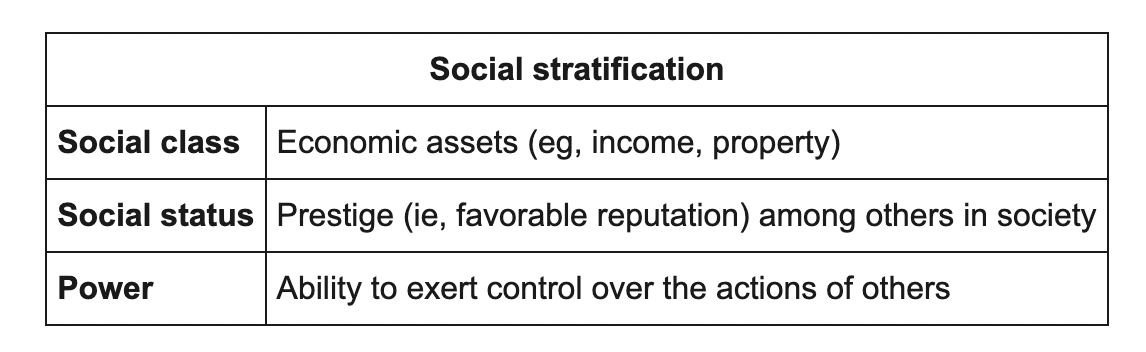
Social Stratification is the hierarchical organization of individuals in society based on social class, social status, and power
Anxiety disorders