Chemistry: Week 12
1/70
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
71 Terms
What do catalysts do?
Catalysts provide a lower energy pathway with a smaller activation energy and change the mechanism
They are not consumed by the reaction
They increase the overall rate of the reaction
Have no effect on the stability or final amounts of reactants and products
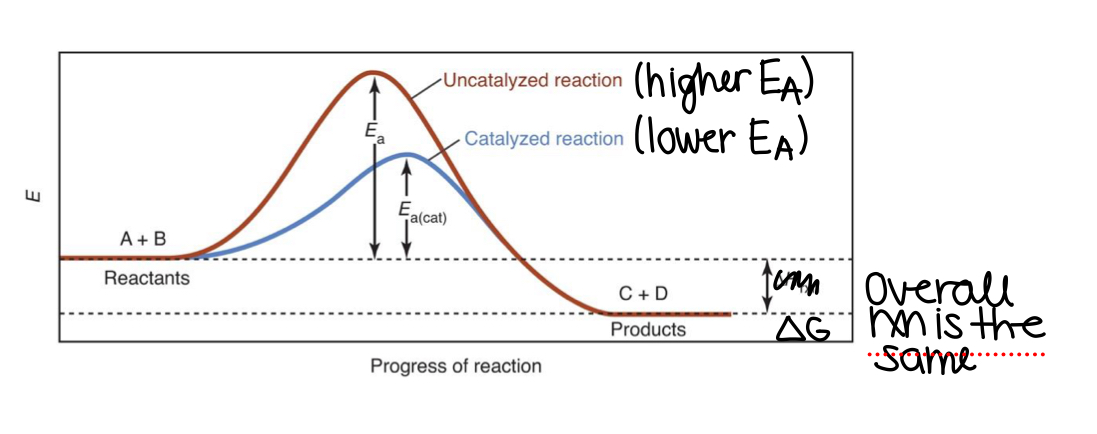
What are heterogeneous catalysts?
Catalyst that exists in a different phase (solid, liquid, or gas) than the reactants.
Ex: Solid Pt/ Pd in a catalytic converter speeds up the conversion of NO to N2 and O2 in the reaction 2NO → N2+ O2
Homogenous catalyst
Catalyst that exists in the same phase as the reactants, typically liquid
What is this enzyme mechanism equation?
E + S ←> E * S (enzyme bunds to the substrate and forms a complex, also an intermediate)
E * S←> E + P (enzyme and substrate form products)
Overall reaction: S ←> P (substrate turns in products)
What is the equation for an intermediate in the enzyme mechanism equation?
E * S is the intermediate, since it’s produced and consumed
What is oxidation state?
The degree of ionic charge and how many e- the element has in that state
It’s a way of tracking where electrons are and where they go
What is the oxidation number of a pure substance?
The oxidation number of a pure substance is 0
Ex. Na and Cl2
What are the rules for assigning oxidation numbers?
Free elements (elements in their uncombined, native form) have an oxidation state of 0
Sum of all oxidation states on atoms must equal the net charge on the molecule
Alkali metals (Group 1) have an oxidation state of +1
F atoms have an oxidation state of -1
Alkaline Earth metals (Group 2) have an oxidation state of +2, including Zn and Cd
H atoms have an oxidation state of +1
O atoms have an oxidation state of -2
How to find oxidation states for Lewis structures?
Write the Lewis structure
Assign all of the electrons in each bond to the more EN element (If they have the same electronegativity, divide equally)
Add up the total number of valence e- assigned to each atom
Oxidation state= # valence e- in free atom- # valence e- assigned
What happens when a compound is oxidized?
When a compound is oxidized, it loses electrons and gains oxygen atoms
What happens when a compound is reduced?
When a compound is reduced, it gains electrons and loses oxygen atoms
Redox Reaction (Reduction- oxidation reaction)
A chemical reaction where there’s a transfer of electrons between different atoms or molecules
Always have oxidizing and reducing agents
Reducing Agents
Substance in the redox reaction that loses electrons
Atoms are oxidized
Oxidization number increases
Reducing agents oxidation number increases because they lose electrons in a redox reaction
Reducing agent is an electron donor, causing the other substance to become reduced.
Oxidizing agents
Substance in the redox reaction that gains electrons
Atoms are reduced
Oxidation number decreases
Oxidizing agents oxidation number decreases because they gain electrons in a redox reaction
Oxidizing agent is an electron acceptor, causing the other substance to become oxidized.
What is the half reaction for
Zn (s) + Cu²+ (aq) → Zn²+ (aq) + Cu(s)
The half reactions are
Zn (s) → Zn ²+ (aq) +2e-
Cu²+ (aq) + 2e- → Cu (s)
What needs to be present if a balanced redox reaction is in acidic conditions?
If the redox reaction is in acidic conditions, H+ needs to be present on one side of the equation
What needs to be present if a balanced redox reaction is in basic conditions?
If a redox reaction is in basic conditions, OH- needs to be added for each H+ (same number) on both sides of the equation, forming water and OH-
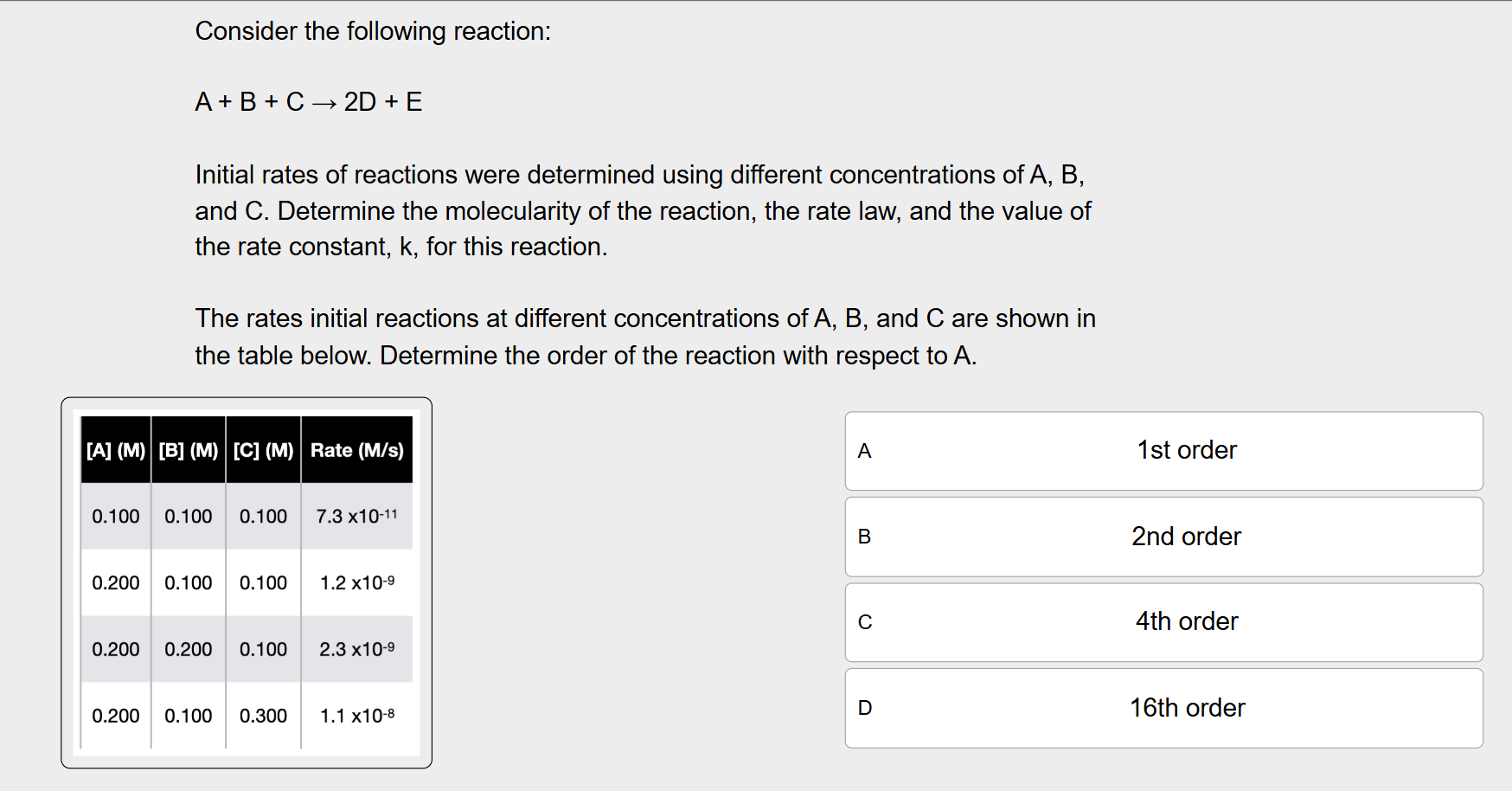
Determine the order of the reaction with respect to A.
Look at Row 1 and Row 2, where the concentration of A doubles from 0.100 M to 0.200, and the rate x16 (got this value by dividing the rate from 0.200 M (1.2 × 10^-9) by 7.3 × 10^-11)
2^x= 16, so n=4, order of the reaction with respect to A is 4
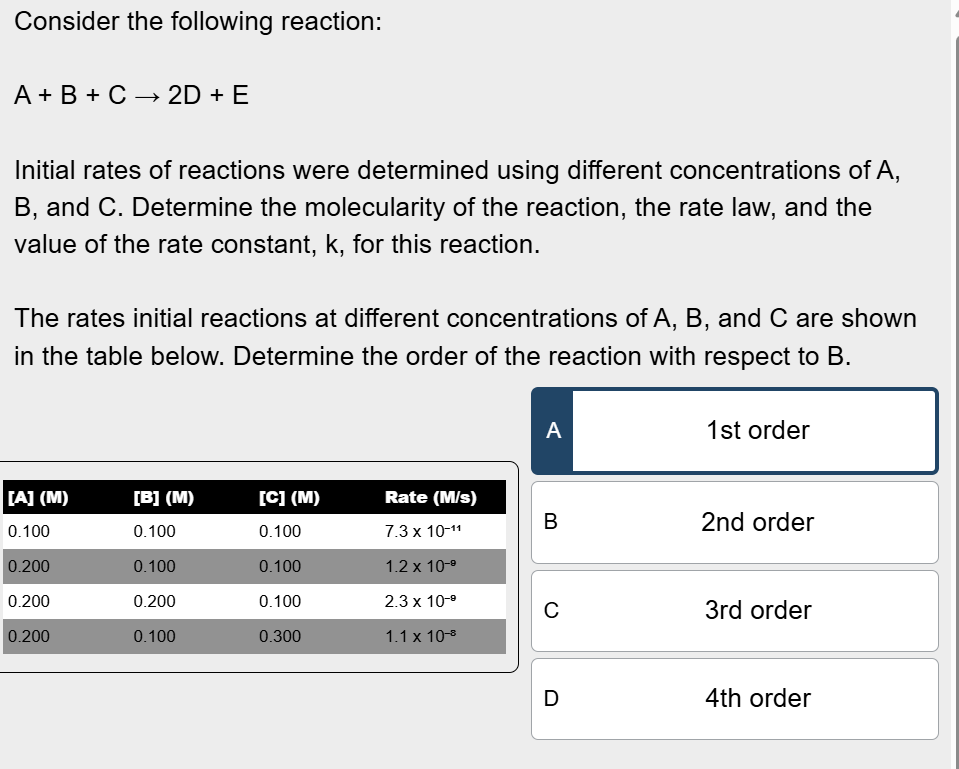
Determine the order of the reaction with respect to B
In 2nd and 3rd row, the concentration of B doubles from 0.100 M to 0.200 M, but all of the other reactants stay the same
Divide rate at 0.200 M of B by rate at 0.100 M of A to get 2
2^n= 2, so n=1, the order of the reaction with respect to B is 1
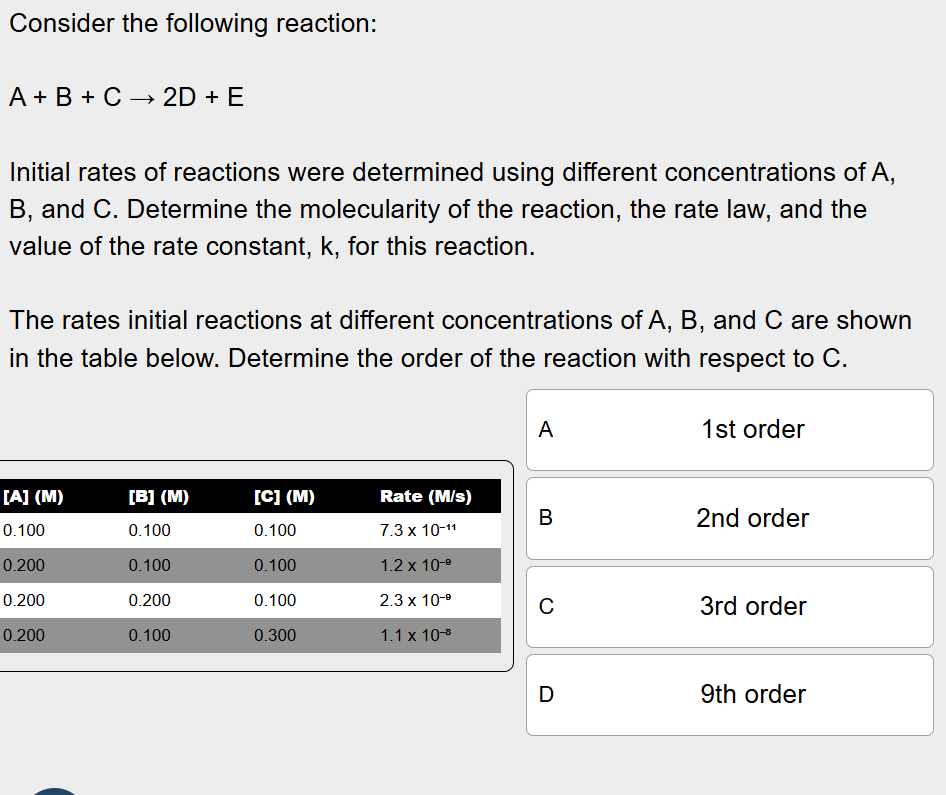
Determine the order of the reaction with respect to C.
Look at Row 2 and 4, where the concentration of C triples, but the concentration of A and B remain the same
Divide the rate at a concentration of 0.300 M for A by the rate at a concentration of 0.100 M for A to get 9
3^n=9, so n=2
What is the rate law that best describes the reaction?
A is 4th order, B is 1st order, and C is 2nd order
Rate= k[A]^4[B][C]²
![<p>Using the rate law of Rate= k[A]^4[B][C]², calculate the value of the rate constant for the reaction</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/413dd1b5-1a7c-4c0b-a90b-271f61312e6e.png)
Using the rate law of Rate= k[A]^4[B][C]², calculate the value of the rate constant for the reaction
Using the first row:
Rate= k[A]^4[B][C]²
(7.3 × 10^-11 M/s)= k[ 0.1 M]^4[0.1M][0.1 M]²
= 7.3 × 10^-4 M^-6 * s^-1 (look at units!)
Collision theory states that as molecules or ions bump into each other, a reaction will only occur if the collision has the correct amount of energy and impact is at the right angle and location.
Describe how collision theory helps predict how temperature, pressure, and concentration impact reaction rates.
As temperature increases, the number of collisions _______ and the energy of the collisions _______.
As temperature increases, the number of collisions increases and the energy of the collisions increases
Higher temperatures lead to faster moving molecules, with more kinetic energy, resulting in more frequent collisions
Increased kinetic energy means that collisions occur with greater force, leading to higher collision energy
Pipes will react with air to oxidize. On a house that had two pipes installed for the hot water and cold water, which pipe will oxidize faster?
The hot water pipe will oxidize faster, since the water molecules are moving faster and will collide with air molecules more frequently to become oxidized
As temperature increases, the number of collisions increases and the hot water pipe has water molecules moving faster and colliding more frequently with air molecules leading to increased oxidation
As concentration increases, the number of collisions _______ and the rate of the reaction _______.
As concentration increases, the number of collisions increases and the rate of the reaction increases.
As concentration increases, the number of collisions increases, since there are more particles and with more collisions, the probability of a successful collision increases, causing the rate of the reaction to increase
Bathtub cleaners used to remove hard water salts usually contain acid to help dissolve the salts. Which will remove the salts faster?
5% acid will remove the salts faster, since it has the highest concentration of acid, which has a higher probability of colliding more frequently with the salt particles and dissolve them, increasing the reaction rate
As gas reactants are compressed into a smaller volume, increasing the reactant partial pressures, the number of collisions _______ and the rate of reaction _______.
As gas reactants are compressed into a smaller volume, increasing the reactant partial pressures, the number of collisions increases and the rate of reaction increases.
When there is a smaller space and volume, the number of collisions increase and with more collisions the probability of a successful collision increases, along with the rate of the reaction
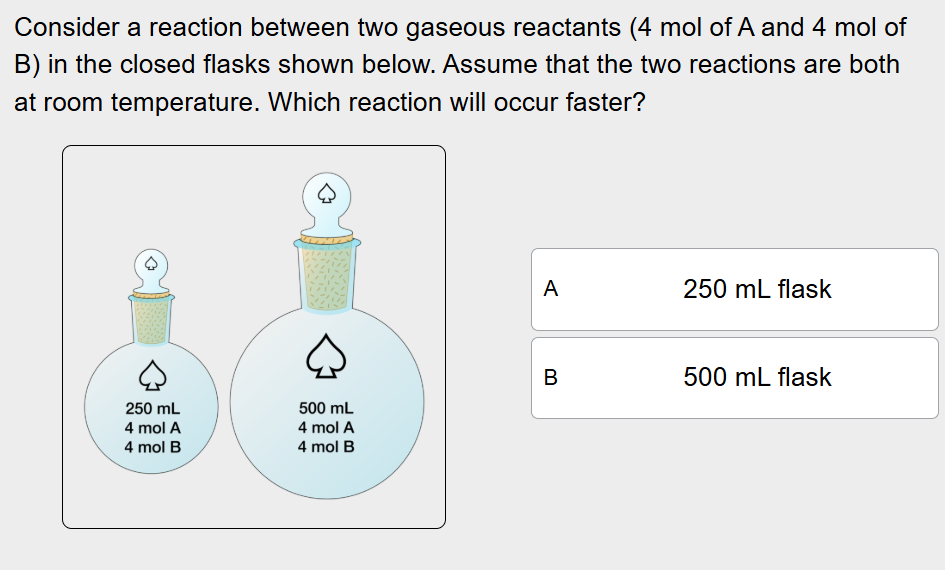
Which reaction will occur faster?
The reaction in the 250 mL flask will occur faster, since it’s contained in a smaller space and has a higher pressure, within a smaller space, the molecules will collide more frequently and the probability of molecules colliding successfully increases, along with the rate of the reaction
The activation energy Ea for a particular reaction is 42.2 kJ/mol.
How much faster is the reaction at 343 K than at 317 K? (R = 8.314 J/mol • K)
We used the equation ln(k1/k2)= Ea/R (1/T1- 1/T2)
We used 343 K as K1, since it’s asking how much faster is 343 K
Plug and chug to get 3.37
Make sure to convert Ea from kJ to mol
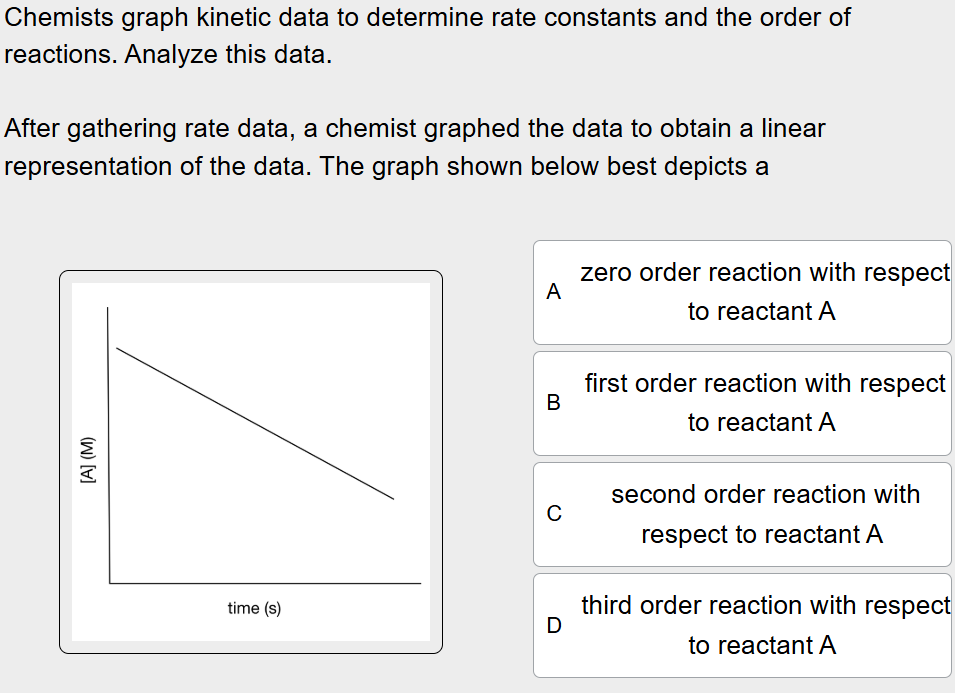
What does the graph below best depict?
The graph depicts a 0 order reaction with respect to reactant A
The axis of the rate data display time and concentration of A which aligns with the linear graph of 0 order
0 order reaction will create a linear plot when graphing [A] vs t
Assume that A is the only component involved up to the rate determining step. Based on the previous graph, choose the rate law for this reaction.
Graph was for 0 order reaction
For 0th order reaction, rate= k
If the slope is -0.0210 for this reaction, determine the rate constant, k, for this 0th order reaction.
k=-slope, so k is 0.0219 Ms^-1
Given that k is 0.0210 Ms⁻¹ and the [A] is 0.1000 M, determine the rate for this reaction based on the rate law determined.
Rate = k
Rate = 0.0210 Ms^-1
What is the effect on k as the activation energy for a reaction increases?
As the activation energy increases, the rate constant (constant of reaction rate to reactants) decreases based on Arrhenius equation
The activation energy, Ea, for a particular reaction is 19.4 kJ/mol. If the rate constant at 80 °C is 0.820 M⁻¹s⁻¹, then what is the value of the rate constant at 211 °C? (R = 8.314 J/mol • K)
Plug into the Arrhenius equation that is separated with temperature
Make sure to associate the correct rate constant with the correct temperature
Convert the Ea from kJ to J and temperature from C to K
Then plug and jug to get the rate constant at 211 C
Make sure units work out
Identify the molecularity (number of reactants) of the elementary reaction below
Since, there are 3 reactant molecules, the reaction is termolecular.
A student proposes the following step of a mechanism. Why would an expert question this mechanism step? 3 A + B → 2 C
This reaction has 4 reaction molecules that need to collide and react simultaneously
3 molecules of A and 1 molecule of B needs to collide at the same time in the right orientation, which is unlikely
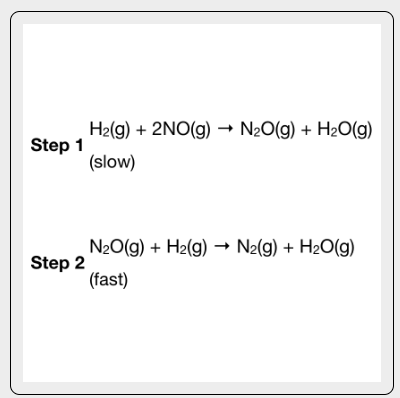
What is the rate law for the proposed mechanism?
The rate law (expression that describes how the rate of a chemical reaction is related to the concentrations of the reactants) depends on the slow step
Rate= k[H2][NO]²
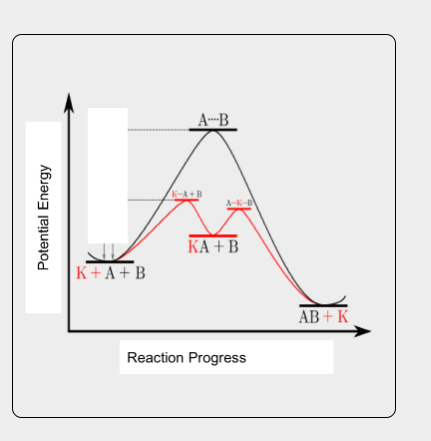
In the provided reaction profile, the black line represents the pathway of the reaction of A and B going to AB. The red line represents the pathway when catalyst K is added. What is catalyst K doing in the reaction?
The catalyst K is lowering the activation energy of the reaction and changing the mechanism of the reaction, which decreases the amount of energy needed for a chemical reaction to begin, leading to a faster reaction rate
Upon adding a catalyst, which of the following is true?
I. The rate of the reaction will increase.
II. The activation energy will decrease.
III. The magnitude of the equilibrium constant will increase.
When a catalyst is added, the rate of the reaction will increase and activation energy will decrease
Catalyst will lower the activation energy and increase the reaction rate
Magnitude of equilibrium constant won’t change, since there is no change in initial and final states of reactants and products
What are the intermediates in a reaction coordinate diagram?
Reaction coordinate diagram shows a graph that shows the relationship between energy and reaction progress
Intermediate is 3, which is the energy minimum between reactants and products
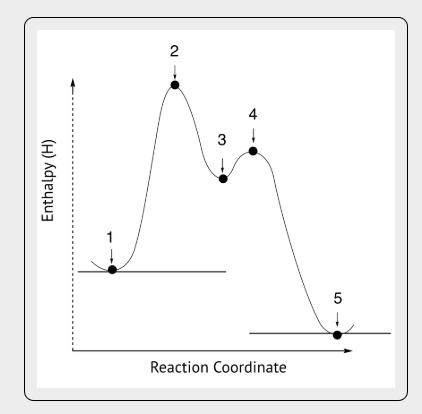
Catalysts increase reaction rates by ___________
Providing an alternate reaction mechanism with lower activation energy
Oxidation Number for Si?
0, since it’s a free element
Br- Oxidation Number
-1, since in column with -1 formal charge
Determine E° for a galvanic (voltaic) cell if ∆G° = -3.2 kJ/mol and n = 3. (F = 96,500 J/(V・mol))
Convert the Delta G value into J
Then plug into the Delta G cell= -nFEcell formula to solve for E cell and get 0.011 V
As E cell increases, what happens to delta G?
Delta G decreases
Shows that more electrical energy is likely to be generated, so the reaction is spontaneous
Decreasing Delta G= spontaneous
Which electrode will gain mass while a voltaic cell runs and why?
Voltaic cell is an electrochemical cell that uses a chemical reaction to produce electrical energy
The cathode is likely to gain mass because it undergoes reduction, which means that metallic ions plate on to the cathode.
Metallic ions from the solution will become metal atoms and plate onto the electrode and increase its mass
A galvanic cell is represented by the shorthand
Cu | Cu²⁺ || Ag⁺ | Ag
Which reaction occurs at the anode?
At the anode, the reaction is Cu(s) → Cu²⁺(aq) + 2e⁻
To the left of double lines is the anode and it loses electrons
Which of the following is the cell diagram for the reaction?
3 Pb²⁺+(aq) + 2 Al(s) → 3 Pb(s) + 2 Al³⁺(aq)
Write out the equation for 3Pb²+, turns out to be a reduction
Write out the equation for 2Al(s), turns out to be an oxidation
Put oxidation on the left: 2Al(s) l 2Al³+ (aq) II 3Pb²+ (aq)I 3Pb(s)
NO COEFFICIENTS
What is the reducing agent and oxidizing agent here?
Zn (s) + Cu²+ (aq) → Zn ²+ (aq) + Cu (s)
Zn: Goes from 0 oxidation state to +2 state
Cu²+: Goes from +2 oxidation state to 0 state
Zn is oxidized, while Cu²+ is reduced
As a result Zn is the reducing agent, while Cu²+ is the oxidizing agent
Write the half reaction for this reaction.
Zn (s) + Cu²+ (aq) → Zn ²+ (aq) + Cu (s)
Zn (s) → Zn²+ (aq) +2e on anode end
Cu²+ (aq) + 2e- → Cu (s) on cathode end
What is the salt bridge?
The salt bridge is the semi- permeable membrane that only allows small ions to go through to balance the charge in the 2 halves of the galvanic cell, so that electricity will continue to flow
Contains ions like K+ and Cl-
What does the single line in a cell diagram separates?
The single cell in a cell diagram separates the phases
What does the double line in a cell diagram separates?
It is the salt bridge, which separates the 2 halves of the galvanic cell
Write out the half reaction for the cell diagram shorthand
Pt (s) I Fe²+ (aq), Fe ³+ (aq) II Pb²+ (aq) I Pb(s)
Pt (s) + Fe²+ (aq)→ Fe³+ (aq) + e
Pb²+ +2e→ Pb (s)
What is voltage?
Voltage is work that can be done with charge (J (work)/ C (charge))
Measured in V
What is the values and units for this equation
Delta G rxn= -n *F *Ecell
G= Free energy (units of kJ/ mol for J/mol)
n= the number of electrons transferred in the reaction (from balanced reaction)
F is the Faraday constant (96,500 C/mol)
E is cell potential (measured in V)
What is G and K when E cell is positive?
When E cell is positive, the reaction is spontaneous under standard conditions and products are favored, so K is greater than 1
What is E cell?
E cell is the standard cell potential at 25 degrees C and when all reagents are at 1 M
What is G and K when E cell is negative?
When E cell is negative, the reaction is non spontaneous under standard conditions, so G would be positive, so more reactants at equilibrium
What does it mean when E cell is 0 for G and K?
When E cell is 0, there is no net movement of electrons, no net reaction happening forward or backward, and energy to do electrical work is zero.
Delta G is 0 and K is 1
Equal concentration of products and reactants
For this cell, what effect does increasing the concentration of Zn²+ have in the reaction
Zn(s) +Cu²+ (aq) → Zn ²+ (aq) +Cu(s)
Increase the concentration of products
When you increase product in Q= P/R, you make Q bigger
Ecell=Ecell∘−nFRTlnQ (substracting Q, so make E cell smaller)
More product= reaction less motivated to go forward and voltage decreases
High product concentration → pushes the system toward reverse reaction, so G increases
E cell decreases and Grxn increases
What is the Nerst equation?
An equation in electrochemistry that relates the cell potential of a cell to the concentrations of the species involved in the redox reaction under non-standard conditions
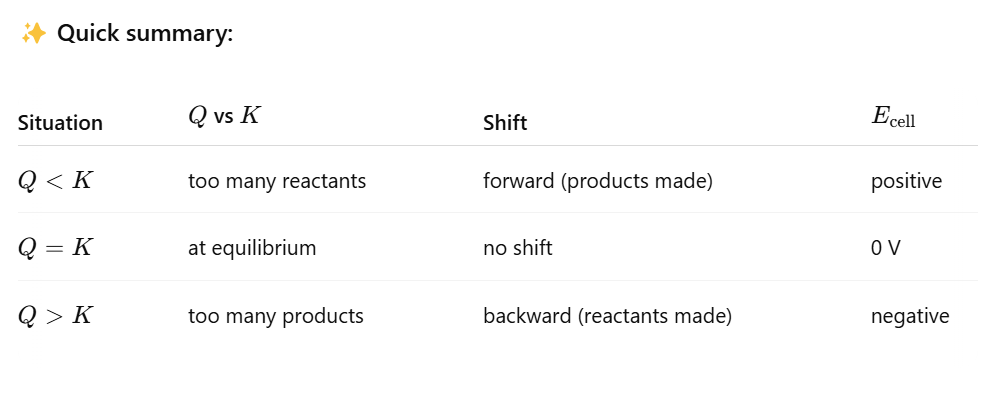
If Q= K, what does E cell equal?
E cell is 0, since the reaction is at equilibrium, the system is balanced (not favoring making more products or more reactants.
Because there’s no driving force to move the reaction one way or the other, there's no driving force to push electrons through the circuit.
As a result E cell is 0
Relationship between Q and K, as well as E cell
What is the equation for half reaction potentials?
E cell= E cathode- E anode
where E cell is the overall reaction and the others are the half reaction potential
What is the reaction potential for
Mn (s) I Mn²+ (aq) II Ag+ (aq) I Ag (s)
Mn is being oxidized and Ag+ is being reduced
Find the equations for the electrode half reactions
E cell= E cathode (reduction)- E anode (oxidization)
E cell= 0.7996 V- (-1.185 V)= 1.9846 V
What does E reduction mean?
E reduction is the standard reduction potential, a measure of the tendency of a chemical species to gain electrons and be reduced
If a solution has a high E reduction value, it has a higher tendency to be reduced
If it has a lower E reduction value, it wants to lose electrons and be oxidized
How to balance redox reactions?
Separate the redox reactions.
Balance everything else, except for H and O
Balance O with H20
Balance H with H+
Balance charge with e-
Balance e across both (by multiplying whole reaction)
Add together and clean up
In what way will electrons be transferred?
Fe I Fe²+ (0.01 M) II Fe²+ (0.1 M) I Fe
Fe- > 0.01 M Fe²+ + 2e
0.1 M Fe2+ + 2e → Fe
to make
0.1 M Fe²+ → 0.01 M Fe ²+
Q= Products/ reactants, so 0.01/0.1= Q is less than 1
So since Q is less than 1, reaction will proceed forward and electrons will be transferred from left to right
Also using the equation E cell= E cell (standard)- (RT/nF) lnQ, ln Q will be negative and make E cell positive, meaning that reaction is spontaneous and moves from left to right
Determining voltage for a single half reaction
Pt(s) I H2(g) I H+ (aq) II Cu²+ (aq)I Cu0 (s)
E cathode, which is