The Lymphomas (Chapter 22)
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
What do lymphomas arise from?
Lymph nodes
Spleen
Thymus
What is the hallmark of Hodgkin Lymphoma?
Reed-Sternberg cells
What kind of appearance do Reed-Sternberg cells give off?
“owls eye” appearance
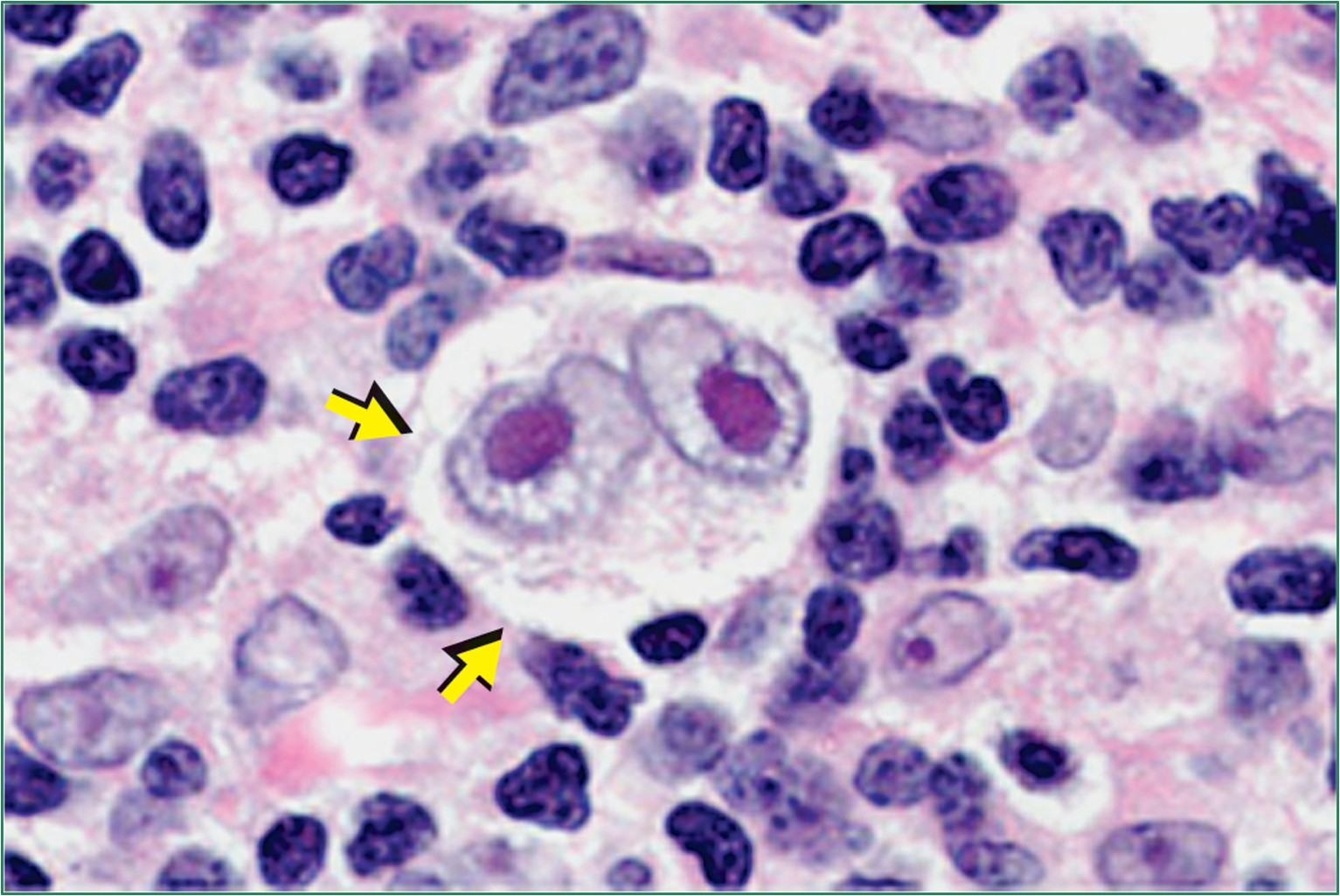
What kind of cell is this?
Reed-Sternberg cell
What is the main cause of Hodgkin Lymphoma?
Unknown, however, it may involve the Epstein-Barr virus
How would you describe a Reed-Sternberg cell?
Clearing of the chromatin around the nucleoli forming a distinct halo
What is the most common subtype of HL?
Nodular Sclerosis
In Nodular Sclerosis HL, what kind of cells are often seen?
Lacunar cells
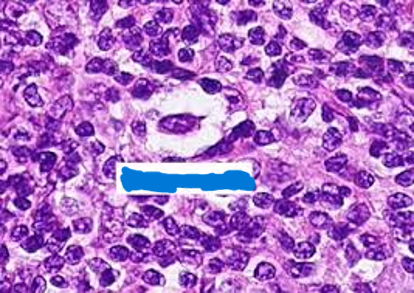
What kind of cell is this?
Lacunar Cell
Mixed cellularity HL
Characterized by Reed-Sternberg cells surrounded by a heterogeneous mixture of cells, including lymphocytes, histiocytes, plasma cells & eosinophils
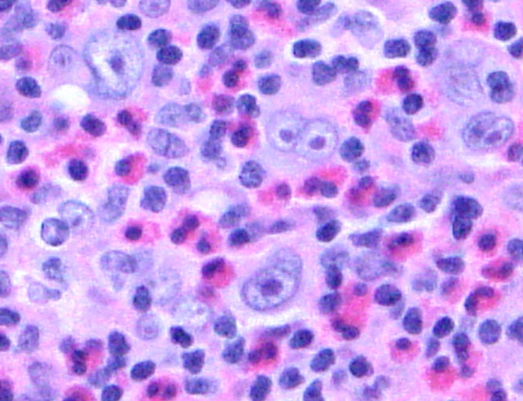
What could this indicate?
Mixed cellularity HL
Lymphocyte-rich (LRHL)
Characteristic background rich in lymphocytes
About 5% of HL cases; fair prognosis
What is the rarest form of classic HL?
Lymphocyte-Depleted (LDHL)
__ is more prevalent than HL
Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma
Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma is thought to be caused by:
DNA damage leading to unregulated cell proliferation
B-Cell Non-Hodgkin Lymphomas
Arises from a single B lymphocyte that has lost its ability to control cell proliferation
Mantle cell lymphoma (MCL)
Malignant lymphocytes that originate from the “mantle zone”
Mantle cell lymphoma is associated with the increased amount of _____
Cyclin D1 protein
When cyclin D1 is overproduced, what occurs?
Drives uncontrolled cell growth
In MCL, what genes are undergoing translocation?
Gene t(11;14)(q13;q32)
Extra-nodal MZL
Mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue (“MALT-lymphoma”) at sites such as stomach, salivary gland, lung, thyroid, or skin
Nodal MZL
Occurs within lymph nodes
Patients with autoimmune disorders such as Sjogren’s syndrome or Hashimoto’s thyroiditis
Splenic MZL
Abnormal B cells collect in the spleen (splenomegaly)
___ and CLL are essentially the same disease
Small lymphocytic lymphoma
Richter’s transformation
Occurs when small lymphocytic lymphoma transforms to a more aggressive lymphoma
Richter’s transformation occurs in approximately ____% of patients with SLL
2-10
Hairy cell leukemia (HCL)
Rare; abundance of mature lymphocytes with oval/kidney-shaped nuclei and abundant cytoplasm and “hairy” cell surface projections
Virtually all cases of Hairy cell leukemia harbor a _____ gene mutation
BRAF V600E
Which cancer has the highest proliferation rate of all cancers?
Burkitt lymphoma
What kind of pattern does Burkitt lymphoma lead to?
A starry sky pattern of tingible-body macrophages
Where is Burkitt lymphoma endemic to?
Africa
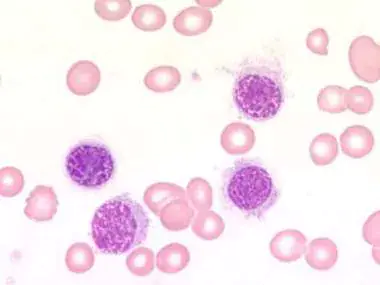
What could these cells indicate?
Hairy cell leukemia
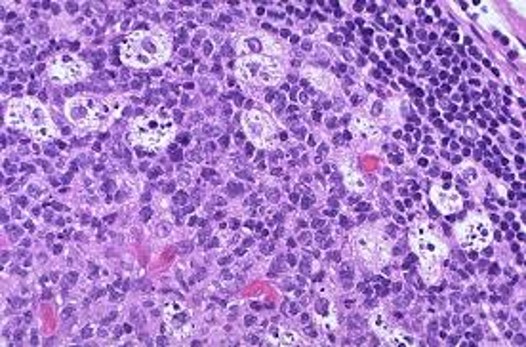
What could this indicate?
Burkitt Lymphoma
Peripheral T-cell lymphoma (PTCL)
Aggressive cancer mostly affecting adults; overall 5-year survival is only 25%; 20 subtypes
Anaplastic large cell lymphoma is characterized by:
“Hallmark cells” with horseshoe-shaped or kidney-shaped nuclei
What is the most frequently occurring type of primary cutaneous lymphoma?
Mycosis fungoides