Immune System and the BBB
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
What is the function of BBB?
Makes CNS somewhat “immune privileged”
Semipermeable to water, gases, lipids (other molecules use protein transporters)
Protects against pathogens/ variations in blood components

BBB Components?
Endothelial cells: connected tightly to each other by tight junctions that make capillaries surrounding brain
Astrocytes: surround capillary walls
Pericytes: involved in blood vessel contraction/ regulates BBB permeability
What amino acids are not made in the brain?
Most neurotransmitters that are in the blood cannot pass the BBB due to their low lipid solubility
Phenylalanine, leucine, tyrosine, isoleucine, valine, tryptophan, methionine and histidine.
L-DOPA
What structures from the brain are NOT surrounded by the BBB? Where are they located?
* located in areas of the midline of the ventricular system
Sensory Organs: Area Postrema (AP), Organim Vasculosum of the Lamina Terminalis (OVLT), Subfornical Organ (SFO)
Secretory Organs: Subcomissural Organ (SCO), Posterior Lobe of the Pituitary Gland. Medial Eminence, Pineal Gland

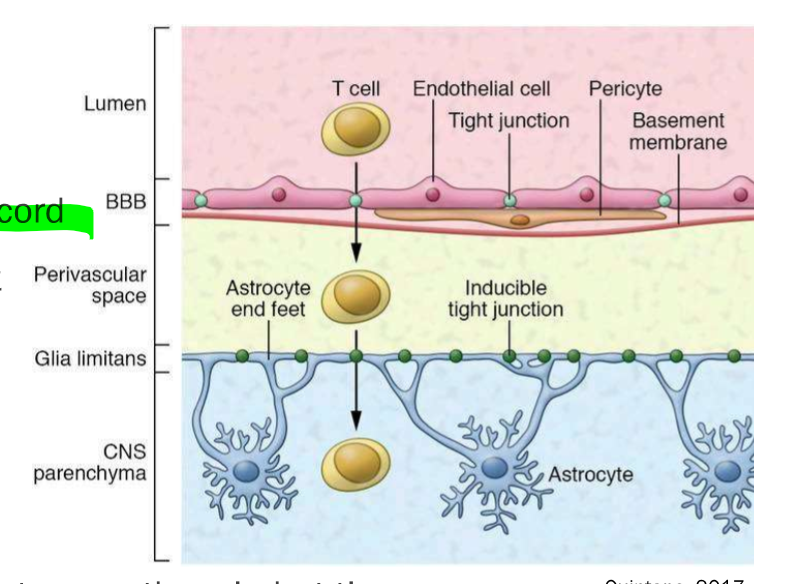
What are glia limitans and their location?
Located below the pia matter on the brain and spinal cord.
Made up of astrocyte end-feet. Involved in development to prevent over-migration of neurons and as second barrier to BBB (adulthood).
Substances cross glia limitans to enter CNS from the blood of CSF.
Have inducible tight junctions between end-feet, less secure than tight junction in endothelial cells
What does CNS immune privilege mean?
CNS’s ability to tolerate antigens and resist inflammation