Embalming Chapter 5 & 19
1/91
Earn XP
Description and Tags
For this quiz on chapter 19, it was advised to look back over chapter 5.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
92 Terms
What are three common problems that come from delayed embalming?
Distribution problems
The body swells more easily
The body may need an increased preservative demand
What are some manual aids for achieving adequate distribution?
massaging, squeezing the sides of the fingers and nailbeds, rotating/flexing limbs, elevation, weights, compresses, pneumatic collars
What are some mechanical aids for achieving adequate distribution?
drainage tubes, controlled pressure and rate of flow, use of pulsation
What are some operative aids for achieving adequate distribution?
channeling, incising, excising
For under embalmed areas, the embalmer has three options to use. What are they?
Arterial injection
Hypodermic injection
Surface embalming
This type of injection involves the use of two carotid arteries
Restricted Cervical Injection
What part of the body should be injected first when using the restricted cervical injection:
Trunk and limbs
What arterial solution index is recommended when dealing with delayed embalming?
25 index or higher
If the body has been delayed embalming, and has not been autopsied should you inject fast or slow?
Slow
Affects all body muscles when the body cannot replenish ATP
This rapidly occurs in bodies with high temperatures and where exertion or exercise have preceded death
Rigor mortis
Rigor mortis is recognized in the average body after how many hours?
2-4 hours
How many hours after death is rigor mortis fully established?
6-12 hours
How long does it take for rigor mortis to pass?
Generally 36 hours
What are the three stages of rigor mortis?
Primary flaccidity
The period of rigor
Secondary flaccidity
When a body is in rigor what type of injection may be best?
What vein is the best for drainage?
6 point injection
Right internal jugular vein
If a body has been refrigerated for a long time, should you inject slow or fast?
Slow
Post-mortem stain can make formaldehyde appear this color:
Gray
Should you pour warm water on a frozen body?
No
(Instead, one day blinding stew)
first discoloration is greenish on the — — quadrant and gradually outlines the large intestine
Lower right
Why is the lower right quadrant the first part of the body to become discolored?
This discoloration is the reaction between hydrogen sulfide produced in the colon after death and the breakdown of hemoglobin
Should you pre-inject an early decomp body?
No
Should a early decomp case be waterless?
Yes
Regarding a body in adavced decomp:
If possible, raise and inject the R Common Carotid with how many gallon(s) of undiluted high-index fluid?
1 gallon
The abdominal and thoracic cavities should be aspirated and filled with — or more bottles of undiluted cavity fluid
Hint: To pertains to delayed embalming cases
Three
The person is considered dead when this particular organ ceases to function:
Brain
Tool used to detect audible sounds of circulation or breathing:
Stethoscope
Tool used to examine the eye to detect circulation in capillaries; tests the response:
Ophthalmoscope
Tool used to detect brain activity:
Electroencephalogram (EEG)
Tool used to detect heart activity:
Electrocardiogram (ECG, EKG)
Measures activity in the brain stem, an area that controls heart and respiratory function:
(I think it’s safe to disregard this card. I don’t recall a question on this)
Auditory brain stem response
Some states require how many tests of death be done?
2
What are the two types of death?
Somatic and cellular
Death of the whole organism:
Somatic death
The physiological, or natural death of cells as they complete their life cycle:
Necrobiosis
Death of individual cells during life
Antemortem cellular death
What is another term for legal death?
clinical death
Occurs when spontaneous respiration and heartbeat irreversibly cease:
Clinical (Legal) death
How long does clinical/legal death take to establish?
5 to 6 mins
When body cells die of oxygen starvation:
Anoxia
What is the first part of the brain to die?
Cerebral cortex
What is the second part of the brain to die?
Midbrain
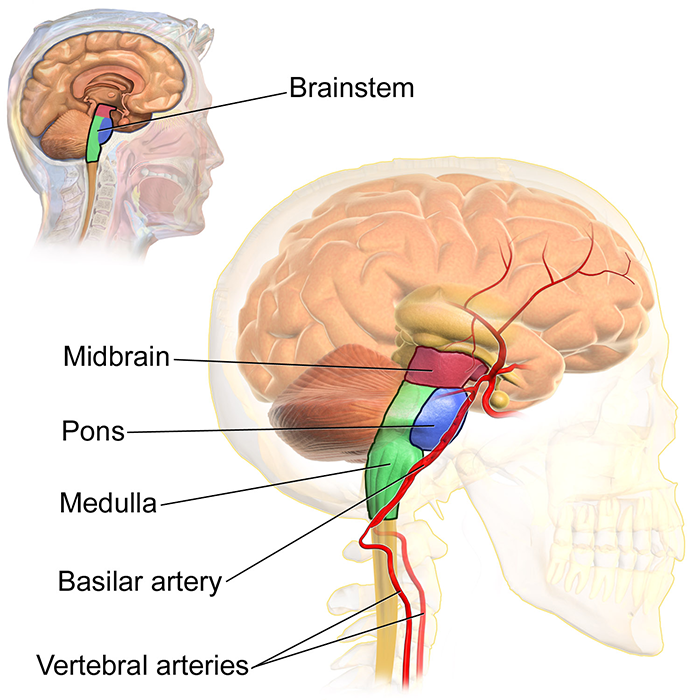
what is the third part of the brain to die?
Brain stem
How long does the cells in the brain and nervous system take to die?
5 minutes
How long does it take for muscle cells to die?
3 hours
How long does it take cornea cells to die?
6 hours
How long does it take for blood cells to die?
6 hours
A cooling or lowering of the body temperature just prior to death:
Agonal algor
Increase in body temperature just prior to death:
agonal fever
The most dramatic organism that could translocate and cause very definite postmortem problems is…
Clostridium perfringens
In making a preembalming analysis of the body the embalmer examines the effects of four factors concerning the body:
General body condition
Effects of disease on the body
Effects of drug therapy
Postmortem changes
Cooling of the body to the temperature of the surrounding environment:
Algor mortis
Loss of moisture from the surface of the body to the surrounding atmosphere:
Dehydration
Gravitation of the blood and body fluids to the dependent areas of the body:
Hypostasis
Postmortem intravascular blood discoloration brought about by the presence of blood in the dependent surface vessels of the body:
Livor mortis
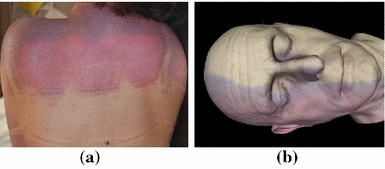
Thickening of the blood after death caused primarily by loss of the liquid portion of the blood to the tissue spaces:
Increased blood viscosity
Temporary rise in body temperature after death:
Postmortem caloricity
(Note, def for caloricity; physiological ability to develop and maintain bodily heat)
Ability of water to split compounds and to enter itself into the products formed:
Hydrolysis
Temporary postmortem stiffening of all the body muscles by natural body processes:
Rigor mortis
Extravascular color change brought about by hemolysis:
Postmortem stain
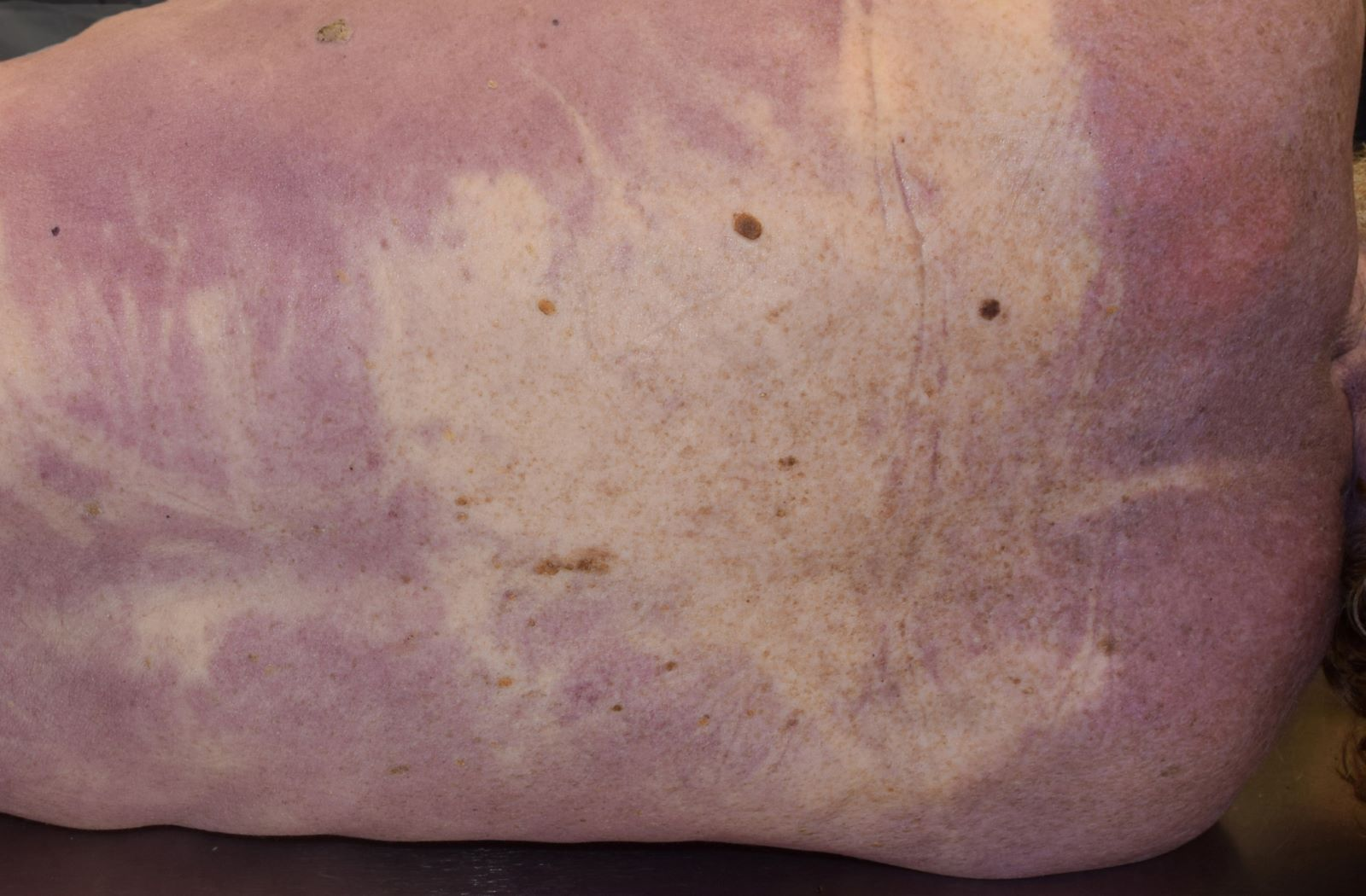
Separation of compounds into simpler substances by the action of bacterial and/or autolytic enzymes:
Decomposition
What creates the intravascular discoloration of livor mortis?
Movement of blood
The building phase of metabolism:
Anabolism
The break down phase of metabolism that releases heat and energy:
Catabolism
What is the order of decomposition of the body compounds?
Carbohydrates
Proteins
Fats
Hard proteins
Bone
What are the three major biochemicals?
Proteins, carbohydrates, and lipids
“grave wax,” thought to be composed of fatty acids and appears in bodies that have been dead for an extended period of time
Adipocere
What is the order of body decomposition?
Cells
Tissues
Organs
Order of tissue decomposition:
Soft tissues
Firm tissues
Hard tissues
What is the first external color change on a dead body? Where is it usually located?
Greenish color over hte right lower quadrant of the abdomen
This term refers to dying and is the process leading up to somatic death.
Agonal period
The physical and chemical changes that occur after irreversible death
Postmortem
Pathologic death of cells as a result of disease; pathological death of a tissue while still a part of the living organism
Necrosis
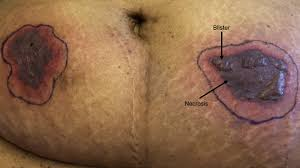
This is known as bed sores (pressure sores), caused by staying in bed (hard surface) and cutting off blood flow to outer cells of the body
Decubitus ulcers
Necrosis of tissue of part of the body, usually due to deficient or absent blood supply
Gangrene
What are the three types of gangrene
Gas, wet, and dry
Settling of blood into the dependent tissues of the body
Agonal hypostasis
Occurs as circulation of blood slows and formed elements of blood begin to clot and congeal
Agonal coagulation
Opening of the pores in the walls of capillaries as the body attempts to get more oxygen to the tissues and cells
Agonal capillary expansion
Increase in fluids in the tissues prior to death:
Agonal edema
Decrease in fluids in the tissues prior to death:
Agonal dehydration
The optimum temperature for decomposition is
98 degrees Fahrenheit
Decomposition is slowed/stopped at temps below, above:
Below 32 degrees F. and above 120 degrees F.
One of the last organ systems to decompose
Vascular system
What is the “tripod” of life?
Heart, lungs, and brain
Obesity, having an abnormal amount of fat on the body. This slows cooling of the body
Future me here! So I think this flashcard is asking what another term for “obesity” is.
So, this was blank when I got to it. So here is a pic of what you would see if you walked into the the cafeteria here and saw me.
Btw, the other term is corpulent

Self-destruction of cells, decomposition of tissue by enzymes of their own formation without microbial assistance
Autolysis
A bio-catalytic agent produced by living cells and capable of autolytic decomposition
Enzyme
Anaerobic decomposition of carbohydrates by the action of enzymes
Fermentation
Decomposition of sugars
Saccharolysis
Decomposition of proteins
Proteolysis
Decomposition of proteins by the action of enzymes from anaerobic bacteria:
Putrefaction
Decomposition of fats
Lipolysis