Carbohydrates: Types, Functions, and Health Impacts
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
68 Terms
Carbohydrates
Main energy source, providing 4 calories/gram.
Glucose
Preferred energy source, used to produce ATP.
Glycogen
Stored glucose in liver and muscles.
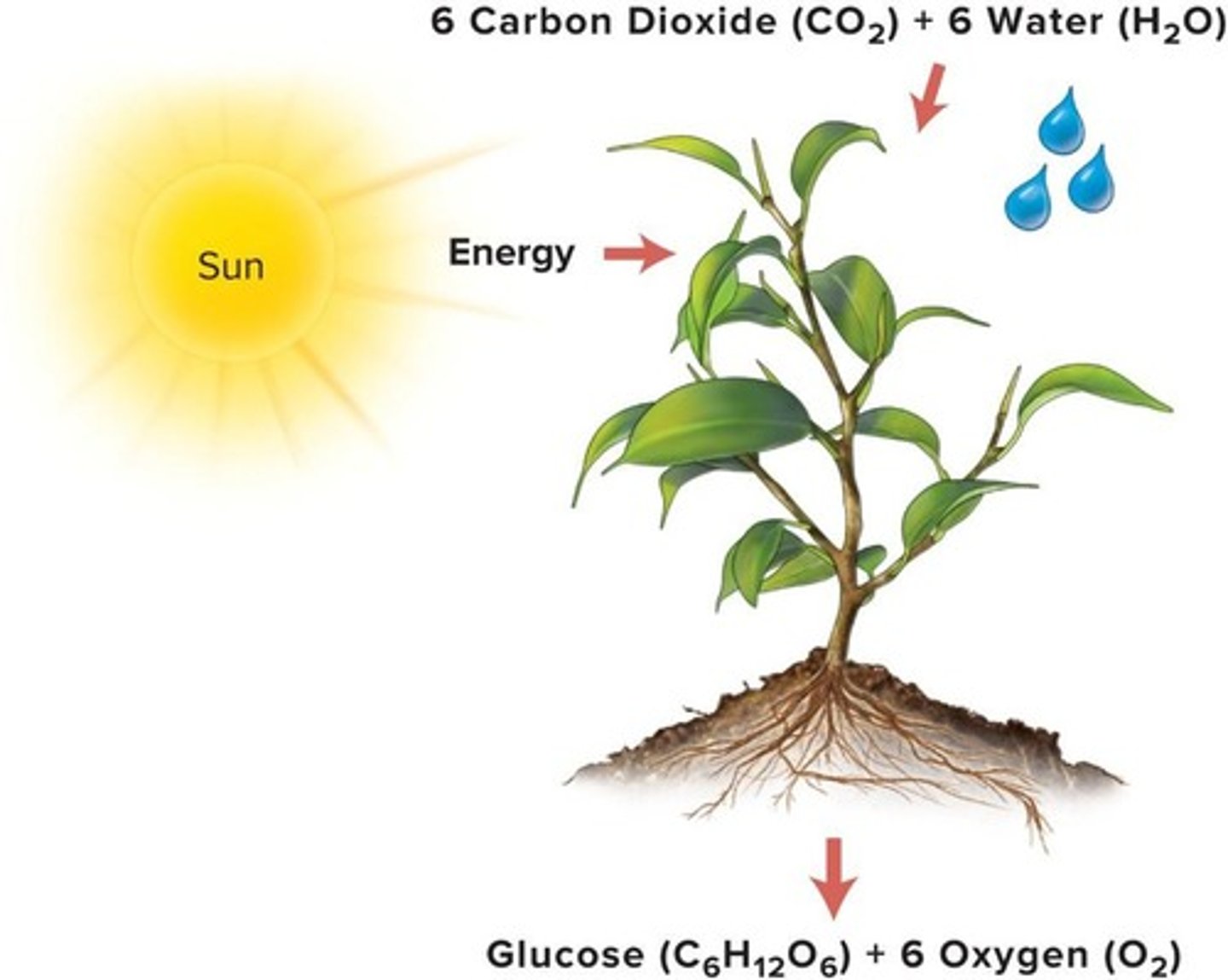
Photosynthesis
Process plants use to synthesize glucose.
Monosaccharides
Basic units of carbohydrates; single sugar molecules.
Fructose
Fruit sugar, converted to glucose by the liver.
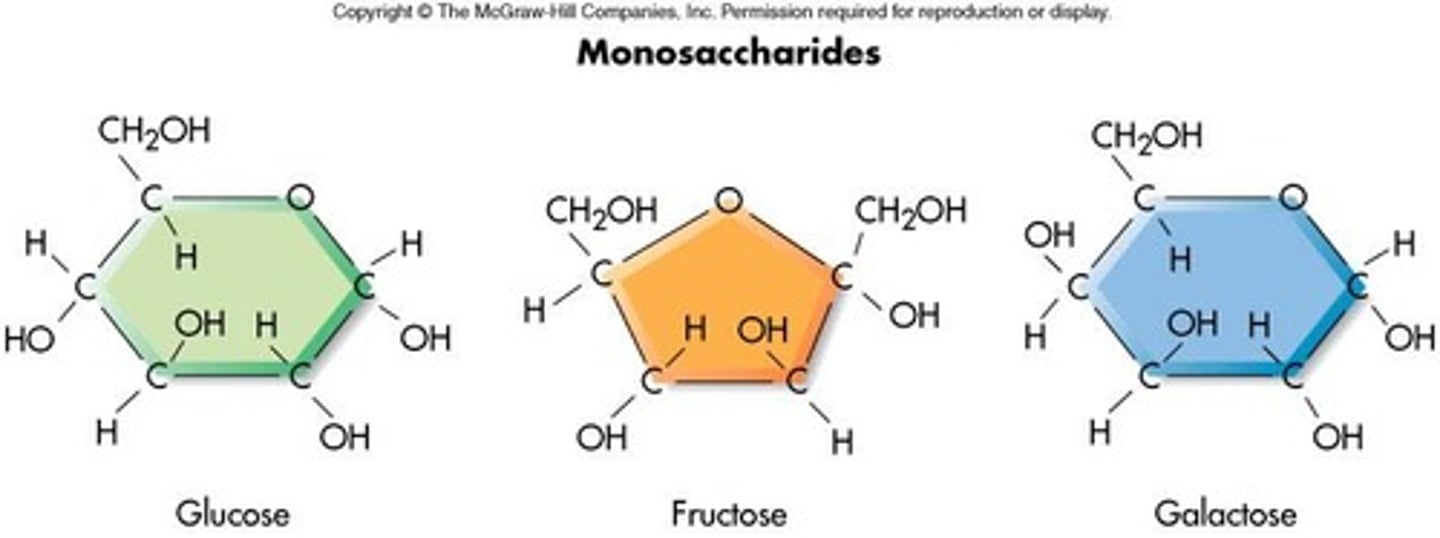
Galactose
Sugar in milk, also converted to glucose.
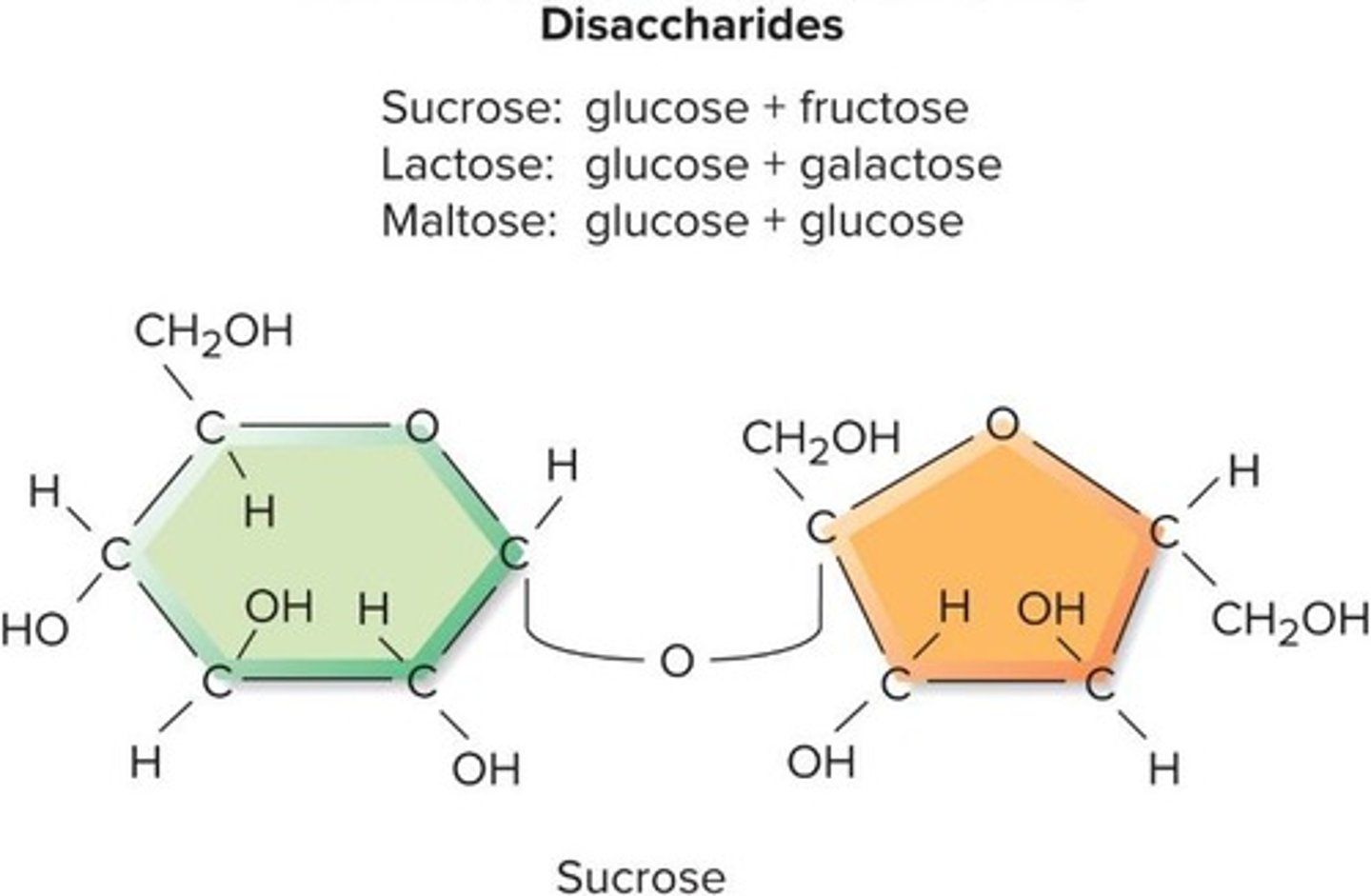
Disaccharides
Formed from two monosaccharides bonding together.
Sucrose
Table sugar; glucose bonded to fructose.
Lactose
Milk sugar; glucose bonded to galactose.
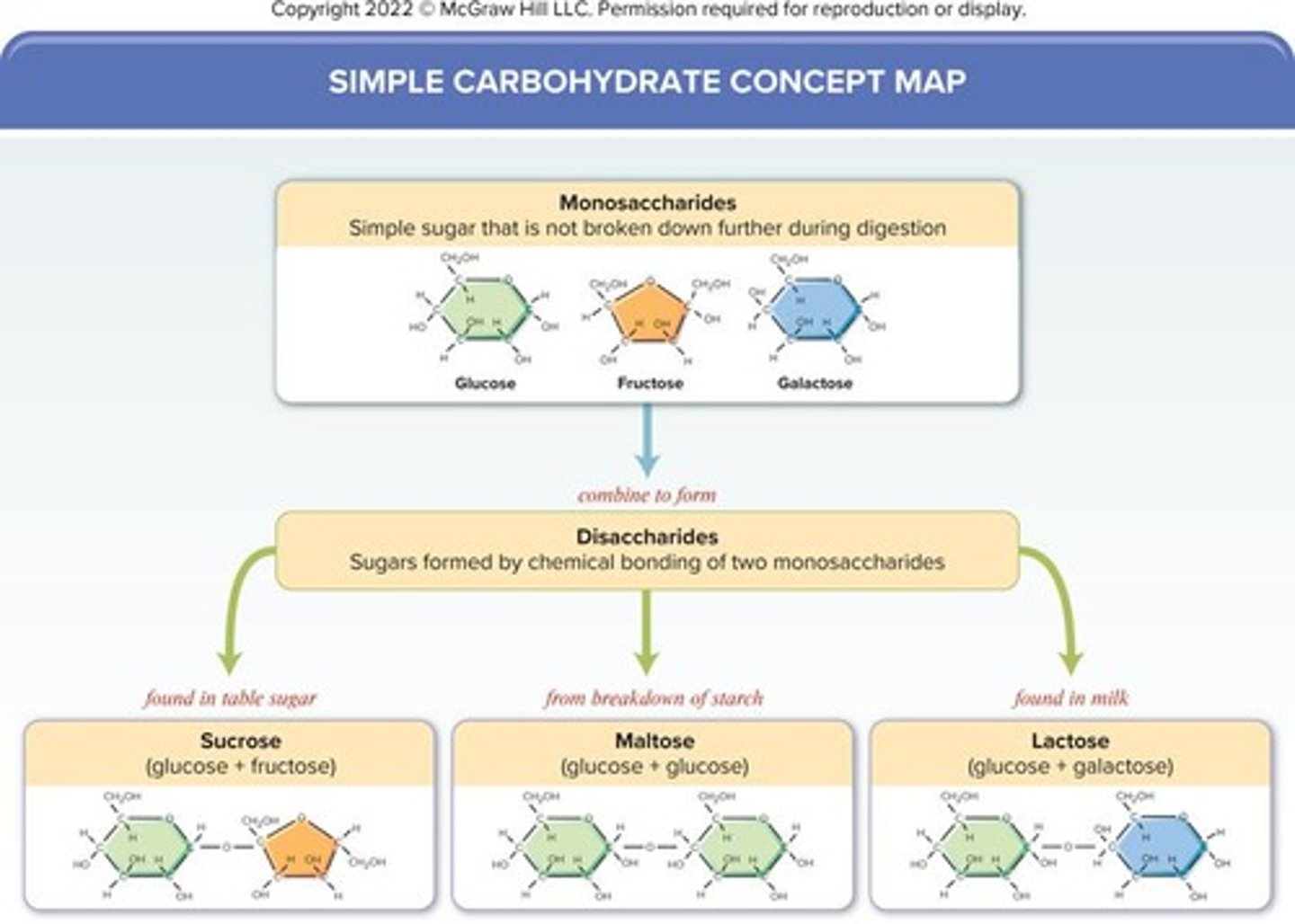
Maltose
Malt sugar; glucose bonded to glucose.
Polysaccharides
Complex carbohydrates with many glucose units.
Amylose
Straight-chain starch composed of glucose units.
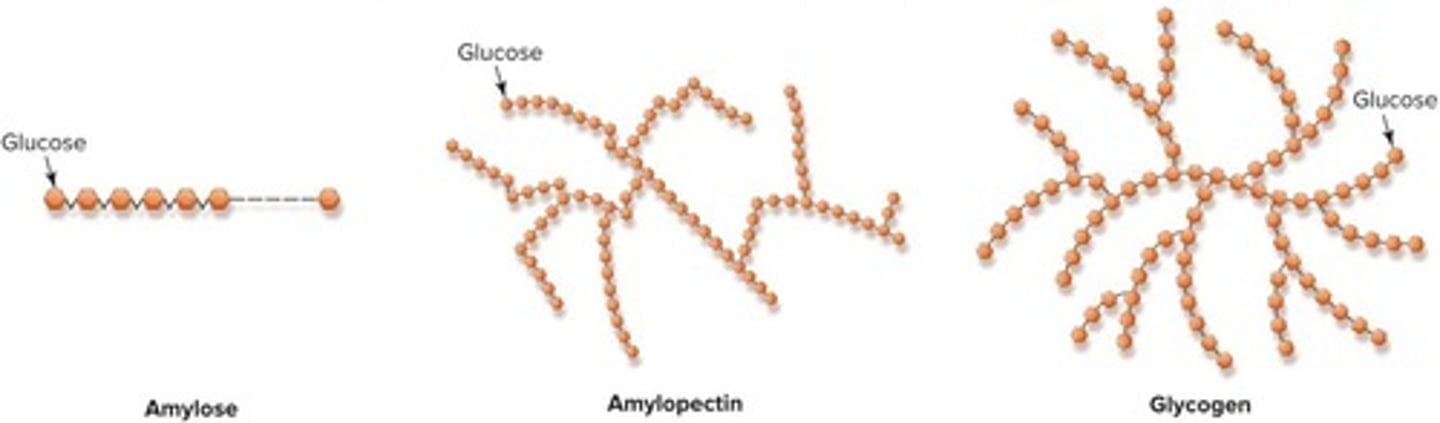
Amylopectin
Branched-chain starch, more digestible than amylose.
Dietary Fiber
Indigestible carbohydrates; includes cellulose and lignin.
Glycogen Storage
Liver stores 400 kcal; muscles store 1400 kcal.
Amylase
Enzyme that digests starch; found in saliva.
Maltase
Enzyme that digests maltose into two glucoses.
Sucrase
Enzyme that digests sucrose into glucose and fructose.
Lactase
Enzyme that digests lactose into glucose and galactose.
Common Starches
Includes amylose, amylopectin, and glycogen.
Flour
Ground wheat; staple ingredient rich in carbohydrates.
Fiber
Aids in digestion by adding bulk to feces.
Low-fiber diet
Increases risk of gastrointestinal disorders.
Insoluble Fiber
Adds bulk and water to stool.
Soluble Fiber
Fermentable by bacteria, reduces cholesterol.
Cholesterol Absorption
Reduced by soluble fiber intake.
Satiety
Feeling of fullness after a meal.
Functional Fiber
Added fiber for improved health benefits.
Prebiotics
Stimulate growth of beneficial gut bacteria.
Daily Fiber Intake (Women)
25 grams recommended per day.
Daily Fiber Intake (Men)
38 grams recommended per day.
Fiber per 1,000 kcal
Goal of 14 grams recommended.
Diverticula
Pouches in the large intestine wall.
Diverticulosis
Condition of having multiple diverticula.
Diverticulitis
Inflammation of diverticula from bacterial acids.
Glycemic Index (GI)
Measures food's effect on blood glucose levels.
Glucose
Primary energy source for red blood cells.
Hyperglycemia
Blood glucose above 125 mg/dL.
Hypoglycemia
Blood glucose below 40-50 mg/dL.
Liver Function
Regulates glucose entering the bloodstream.
Pancreas Function
Releases insulin to lower blood glucose.
Whole Grain Foods
Contain bran, germ, and endosperm.

Refined Grains
Only contain the endosperm, fewer nutrients.
Insulin
Hormone that lowers blood glucose levels.
Glycogen
Stored form of glucose in liver and muscles.
Glucagon
Hormone that raises blood glucose levels.
Type 1 Diabetes
Autoimmune disease; insulin production stops.
Type 2 Diabetes
Insulin resistance; often linked to obesity.
Prediabetes
Fasting glucose 100-125 mg/dL; HbA1c 5.7%-6.4%.
Diabetic Hypoglycemia
Low blood sugar; symptoms after insulin use.
Metabolic Syndrome
Cluster of conditions increasing diabetes risk.
Extreme Thirst
Common symptom of diabetes; indicates high glucose.
Frequent Urination
Excessive urination due to high blood sugar.
Drowsiness
Lethargy often associated with high blood sugar.
Fruity Breath Odor
Characteristic symptom of uncontrolled diabetes.
Insulin Therapy
Treatment for Type 1 diabetes; provides insulin.
Diet Therapy
Nutritional management for diabetes control.
Insulin Pumps
Devices for continuous insulin delivery.
Sorbitol
Low-calorie sweetener; laxative effect in excess.
Xylitol
Low-calorie sweetener; prevents tooth decay.
Saccharin
Artificial sweetener; 300-500 times sweeter than sugar.
Aspartame
Artificial sweetener; 180-200 times sweeter than sugar.
Sucralose
600 times sweeter than sugar; heat stable.
Gluconeogenesis
Conversion of noncarbohydrates into glucose.
Epinephrine
Hormone released during stress; raises blood glucose.
Heavy Breathing
Symptom of severe diabetes complications.
Stupor
Altered consciousness due to severe blood sugar imbalance.