Thermochemistry
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
Thermochemistry
The study of heat released or absorbed during a chemical reaction
Conversion of energy
First law of thermodynamics: Law of conservation of energy:
Energy can be converted from one form to another but energy cannot be created nor destroyed
What is a system
What your studying (eg chemical reaction)
Whats the surroundings
Anything else other than the system (eg beaker)
System will exchange energy with the WHAT (if energy is released by the system it will be absorbed by the WHAT and vice versa)
System will exchange energy with the SURROUNDINGS (if energy is released by the system it will be absorbed by the SURROUNDINGS and vice versa)
Internal energy (U) - WHAT
Total energy of the system
It is impossible to know the exact value of Ur or Up but we can determine or monitor the change in U WHAT equation
1st law: energy of universe is constant
ΔUniverse = ΔUsystem + ΔUsurroundings
Two possible ways a system can exchange energy
ΔUsystem = Heat + Work
Heat increases work WHAT
Heat increases work DECREASES
Inversely proportional
ΔUsystem internal energy is constant when
Given a reaction
A given amount of reactnat’s given
Heat
energy transferred results from temperature difference
Endothermic
exothermic
(+) when energy is absorbed by system
(-) when energy is released by system
Work
Force over distance
Reaction involves gas:
- Expansion
- Compression
Both heat and work can change depending on WHAT
Both heat and work can change depending on EXPERIMENTAL CONDITIONS
Heat (q) is positive when WHAT
Heat is ABSORBED by the system
Heat (q) is negative when WHAT
Heat is RELEASED by the system
Work (w) is positive WHEN
Work done ON the system
Work (w) is negative WHEN
Work done BY the system
What are the three factors affecting Pressure-Volume (PV) work
The work done by expansion and compression
Change in volume
External pressure → constant
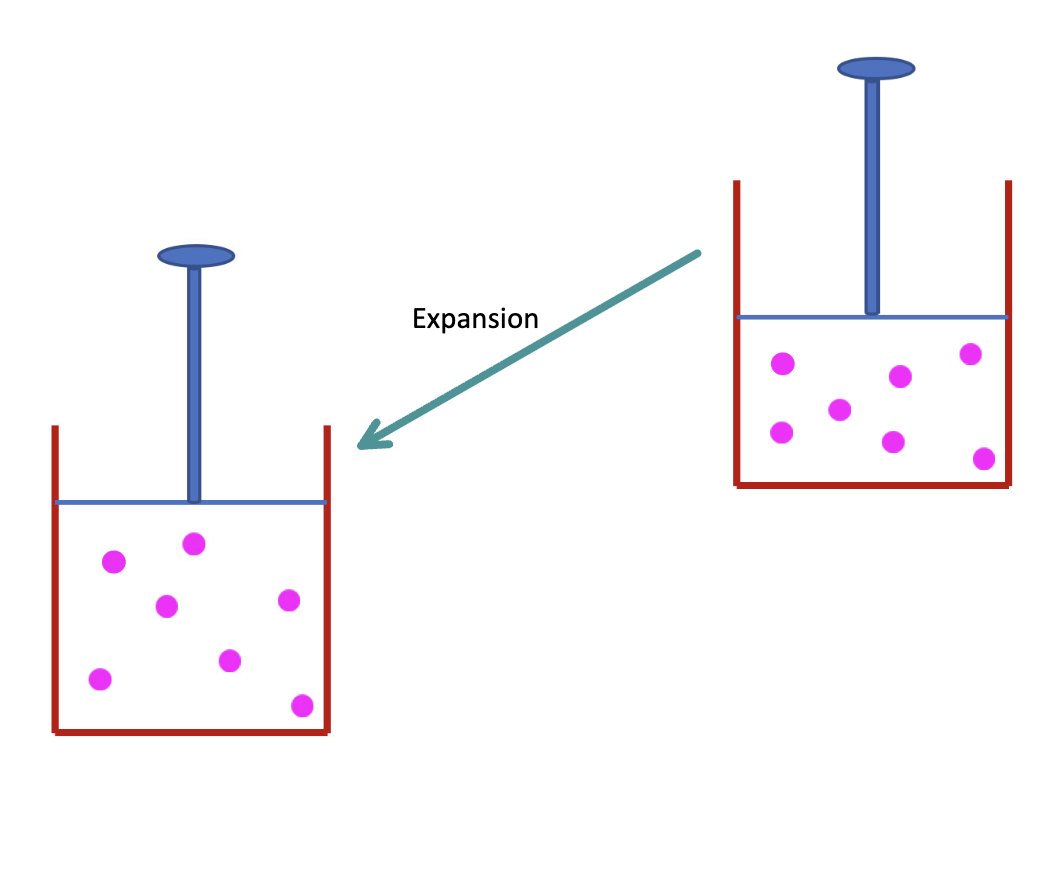
What is the work for expansion
Vf > Vi
Work is done BY the system
W < 0 (negative)
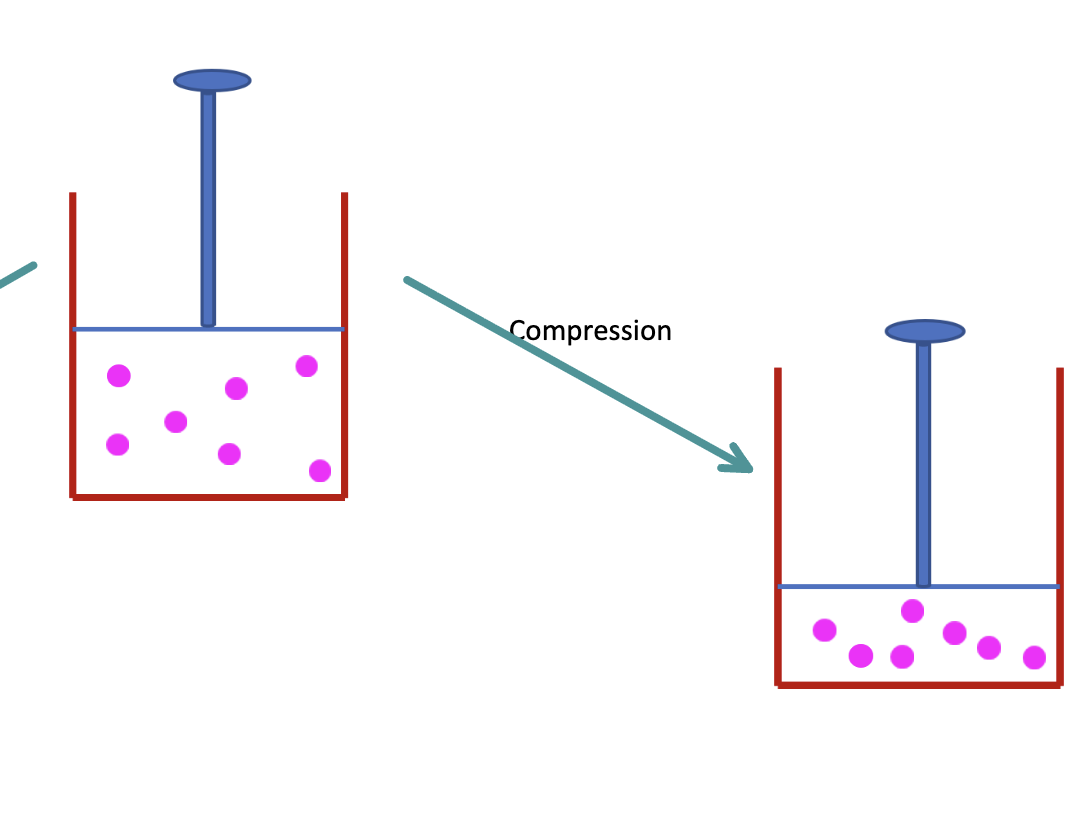
What is the work for compression
Vf < Vi
Work is done ON the system
W > 0 (positive)
What is the equation for work
W = -Pexternal x ΔV
Heat:
Endothermic WHAT heat ( q WHAT 0)
Exothermic WHAT heat ( q WHAT 0)
Heat is not equal to WHAT
Heat:
Endothermic ABSORBS heat ( q > 0)
Exothermic RELEASES heat ( q < 0)
Heat is not equal to TEMPERATURE
What 2 factors affect hoe much an objects temperature changes when heat is added
The substance (know how easy or difficult it is to change the temp of the substance)
Amount of substance (more substance means longer time)
What is a calorimetry experiment
Measures the heat released or absorbed during a chemical reaction
What is specific heat capacity
The amount of heat that must be added to 1g of substance to raise its temperature by 1K
What is the specific heat capacity equation
q = mCΔT
Δ1°C WHAT Δ1K
Δ1°C = Δ1K
Enthalpy (H):
a WHAT function (only depends on the initial and final position doesn’t depend on the pathway)
Heat released or absorbed in a reaction or process occurring at a WHAT
qp(constant pressure) = WHAT
Enthalpy (H):
a STATE function (only depends on the initial and final position doesn’t depend on the pathway)
Heat released or absorbed in a reaction or process occurring at a CONSTANT PRESSURE
qp(constant pressure) = nΔrH
ΔrH > 0 = WHAT
Endothermic
ΔrH < 0 = WHAT
EXOTHERMIC
Hess’s Law:
The total enthalpy change during a reaction is the WHAT whether the reaction occurs via one step or multiple steps
The ΔrH for the overall reaction is the WHAT of ΔH values for each step
Hess’s Law:
The total enthalpy change during a reaction is the SAME whether the reaction occurs via one step or multiple steps
The ΔrH for the overall reaction is the SUM of ΔH values for each step
Standard states:
The most WHAT form of an element or compound under the given conditions
If the substance is a gas, 1 WHAT
If the substance is a solution 1 WHAT
Standard states:
The most STABLE form of an element or compound under the given conditions
If the substance is a gas, 1 BAR
If the substance is a solution 1M
Standard Enthalpy of formation ΔfH°:
The change in enthalpy during the formation of HOW MANY mole of a substance from its constituent, with all substances in their WHAT states
Values are known for for large number of molecules
ΔfH° of an ELEMENT in STANDARD STATE is WHAT
Standard Enthalpy of formation ΔfH°:
The change in enthalpy during the formation of 1 mole of a substance from its constituent, with all substances in their STANDARD states
Values are known for for large number of molecules
ΔfH° of an ELEMENT in STANDARD STATE is ZERO
Bond dissociation enthalpy (ΔBDEH)
The energy required to WHAT of bonds
Everything is in the WHAT phase
Bond dissociation enthalpy (ΔBDEH)
The energy required to BREAK ONE MOLE of bonds
Everything is in the GAS phase
ΔBDEH → positive for bond WHAT
ΔBDEH → Negative for bond WHAT
ΔBDEH → positive for bond BREAKING
ΔBDEH → Negative for bond FORMING
ΔBDEH looks at WHAT (energy required to WHAT bond) - WHAT (energy WGAR to form the bond)
ΔBDEH looks at REACTANTS (energy required to BREAK bond) - PRODUCTS (energy RELEASES to form the bond)
ΔfH looks at WHAT - WHAT (looks at the whole reaction)
ΔfH looks at PRODUCTS - REACTANTS (looks at the whole reaction)