Thermal properties of matter
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
What is heat?
the energy transfered between the system and the enviroment due to a temperature difference
What are thermal interactions?
energy transfered between the system and the enviroment due to atomic level collisions
What is thermal equilibria?
No temperature difference
What is the Si unit for heat?
J
What is thermal energy?
thermal energy of the system is due to the motion of its atoms and molecules and the stretching/ compression of spring like molecular bonds
What is the definition of heat?
The energy transfered between the system and the environment as they interact
What is temperature?
a state variable which quantifies hotness and coldness of a system
related to the thermal energy per molecule
What is the specific heat of a substance?
The amount of energy required to raise the temperature of 1Kg of substance by 1K
C
What is the specific heat equation?
Q=MCAT
q= energy
c=specific heat
AT= temperature change
What is molar specific heat?
amount of energy required to raise the temperature of 1 mole of substance by 1 degree
What is the equation for molar specific heat?
Q=nC AT
What is the heat of transformation?
the amount of energy which causes 1Kg of substance to undergo a phase change
What is the equation for heat of transformation?
Q=ML
What is the specific heat of fusion?
Heat of transformation between and solid and a liquid
What is specific heat of vapourisation?
heat of transformation between a liquid and a gas
What is calorimetry?
systems thermally interacting with each other but isolated from everything else
heat energy transerred from the hotter to the colder system until thermal equailibria is reached
What are the equations for calorimetry?
Qnet = Q1 + Q2 = 0
What is the equation, specific heat of gases, constant volume
Q = n Cv AT
What is the equation, specific heat of gases, constant pressure
Q = n Cp AT
What is the equation which links specific heat at constant pressures and volumes?
Cp = Cv + R
Cp - specific heat at constant pressures
Cv- specific heat at constant volumes
R - ideal gas equation
What is a adiabatic process?
No heat energy is transfered q=0
How do you make a process adiabatic?
thermal insulation
rapid compression or expansion of the gas
What is the equation for the specific heat ratio of adiabatic processes?
γ=Cv/Cp
What is the specific heat ratio for monatomic gases?
1.67
What is the specific heat ratio for diatomic gases?
1.4
What curve does adiabatic processes follow?
pV^γ=constant
What are useful adiabatic equations?
pfVf^γ=piVi^γ
Tf=Ti(Vf/Vi)^γ−1
How is a solid held together?
particles arranged in periodic array with spring like molecular bonds
How is a liquid held together?
molecules loosely held by weak molecular bonds
strong enough that the molecules are never to far apart
How is a gas held together?
move easily throughout space, lots of space between molecules
fluid and highly compressable
How do you convert from celsius to farrenheit?
Tf = 1.8Tc + 32
What is absolute 0?
temperature at which all motion would cease
-273 c
What is a phase diagram?
shows how the phases and phase changes of a substance vary with both temperature and pressure
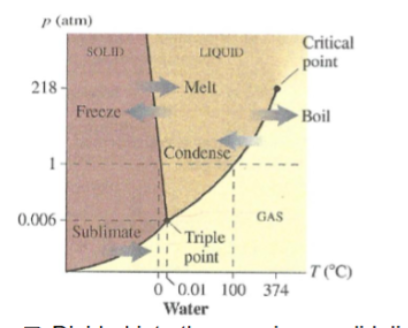
What do the three regions in a phase diagram represent?
solid liquid and gas
What do the boundary lines on a phase diagram represent?
phase transitions
system is in phase equilibria at a pressure and temperature point which falls on one of the lines
What is the critical point on a phase diagram?
where the liquid and gas boundary ends
no clear distinction between liquid and gas at pressure or temperature above it, its a fluid
What is the triple point on a phase diagram?
where all three phases coexist in phase equilibria
What is the definition of a ideal gas?
a gas of non interacting atoms which ignores weak attractive interactions except occasonal elastic conditions
What conditions need to be met for a gas to be ideal?
the density is low
The temperature is well above the condensation point
What is the equation for a ideal gas?
Pv = nRT
What is the ideal gas equation for sealed containers?
PfVf/Tf = PiVi/ tI
What is the ideal gas law in terms of N?
pV= N Kb T
What is the ideal gas law in terms of densty?
N/V = P/Kb T
What is a isochoric process?
Constant volumeW
What is the equation for isochoric processes?
P1 / T1 = P2 / T2
What is a isobaric process?
Constant pressure
What is the equaton for a isobaric process?
V1/T1 = V2/T2
At equilibria the gas pressure inside a cylinder is?
Pgas = Patoms + Mg/A
What is a isothermal process?
V1/P2 = V2/P1