Equilibrium constant
1/18
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
What’s a reversible reaction?
one which can be made to go in either direction depending on the conditions
What’s key about reversible reactions?
occur in a closed system
What’s a closed system?
one in which no substances are either added to the system or lost from it. Energy can, however, be transferred in or out at will.
What does dynamic equilibrium mean?
rate of the forward reaction is equal to the rate of the backwards reaction
What’s the equation for a general reaction which has reached dynamic equilibrium?

What’s the definition of Le Chatelier’s principle?
If a dynamic equilibrium is disturbed by changing the conditions, the position of equilibrium moves to counteract the change
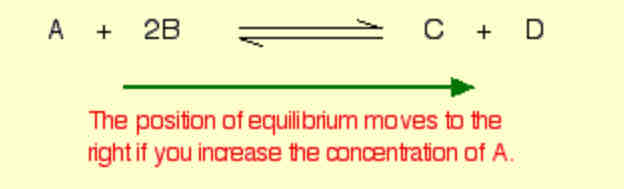
What would happen if you changed the conditions by increasing the concentration of A?
position of equilibrium will move in such a way as to counteract the change.
the position of equilibrium will move so that the concentration of A decreases again - by reacting it with B and turning it into C + D.
The position of equilibrium moves to the right.

What would happen if you changed the conditions by increasing the pressure?
This only applies to reactions involving gases
Pressure is caused by gas molecules hitting the sides of their container. The more molecules you have in the container, the higher the pressure will be.
The system can reduce the pressure by reacting in such a way as to produce fewer molecules.
3 molecules on the left-hand side of the equation, only 2 on the right.
By forming more C and D, the system causes the pressure to reduce.
shifts the position of equilibrium towards the side with fewer molecules.
What happens if there are the same number of molecules on both sides of the equilibrium reaction?
increasing the pressure has no effect whatsoever on the position of the equilibrium.
Because you have the same numbers of molecules on both sides
the equilibrium can't move in any way that will reduce the pressure again.

What would happen if you changed the conditions by increasing the temperature?
the position of equilibrium will move so that the temperature is reduced again.
To cool down, it needs to absorb the extra heat that you have just put in. In the case we are looking at, the back reaction absorbs heat.
The position of equilibrium therefore moves to the left - the endothermic side
The new equilibrium mixture contains more A and B, and less C and D.
What does a catalyst do to the position of equilibrium
makes no difference
This is because a catalyst speeds up the forward and back reaction to the same extent.

What are the conditions of the Haber Process?
450 degrees Celsius - produces a high yield of NH3 in a short time, with a fast ROR
200 atm - high pressure, high yield, fast ROR, if you increase the pressure the system will respond by favouring the reaction
Iron catalyst - ensures that the reaction is fast enough for a dynamic equilibrium to be set up within the very short time
What’s homogenous equilibrium?
everything present in the same phase.
The usual examples include reactions where everything is a gas, or everything is present in the same solution.
What’s a heterogeneous equilibrium?
has things present in more than one phase.
The usual examples include reactions involving solids and gases, or solids and liquids.
What’s equilibrium constant?
equilibrium expression links the equilibrium constant, Kc, to the concentrations of reactants and products at equilibrium
Equation for Kc

How do you work out the unit of Kc?
Units will change depending on the equation that is formed. Write each individual unit and see what it cancels to.
What is the only external condition that affects value of Kc?
Temperature
How does temperature affect the value of Kc?
temperature will cause a shift in the position of equilibrium
if eq. shifts to the right, Kc will increase as there are more products
if eq. shifts to the left, Kc will decrease as there are less products