VSEPR and Types of Bonds
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/71
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
72 Terms
1
New cards
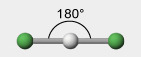
2 electron groups, 0 lone pairs
e⁻ geo: linear
molecular geo: linear
hybridization: sp
bond angle: 180°
molecular geo: linear
hybridization: sp
bond angle: 180°
2
New cards
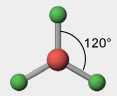
3 electron groups, 0 lone pairs
e⁻ geo: trigonal planar
molecular geo: trigonal planar
hybridization: sp²
bond angle: 120°
molecular geo: trigonal planar
hybridization: sp²
bond angle: 120°
3
New cards
3 electron groups, 1 lone pair
e⁻ geo: trigonal planar
molecular geo: bent
hybridization: sp²
bond angle:
molecular geo: bent
hybridization: sp²
bond angle:

4
New cards
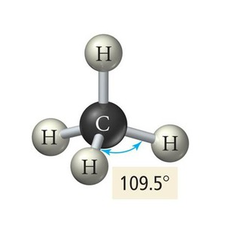
4 electron groups, 0 lone pair
e⁻ geo: tetrahedral
molecular geo: tetrahedral
hybridization: sp³
bond angle: 109.5°
molecular geo: tetrahedral
hybridization: sp³
bond angle: 109.5°
5
New cards
4 electron groups, 1 lone pair
e⁻ geo: tetrahedral
molecular geo: trigonal pyramidal
hybridization: sp³
bond angle:
molecular geo: trigonal pyramidal
hybridization: sp³
bond angle:

6
New cards
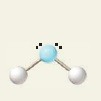
4 electron groups, 2 lone pairs
e⁻ geo: tetrahedral
molecular geo: bent
hybridization: sp³
bond angle:
molecular geo: bent
hybridization: sp³
bond angle:
7
New cards
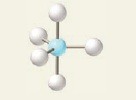
5 electron groups, 0 lone pairs
e⁻ geo: trigonal bipyramidal
molecular geo: trigonal bipyramidal
hybridization: sp³d
bond angle: 120° & 90°
molecular geo: trigonal bipyramidal
hybridization: sp³d
bond angle: 120° & 90°
8
New cards
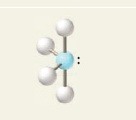
5 electron groups, 1 lone pair
e⁻ geo: trigonal bipyramidal
molecular geo: see saw
hybridization: sp³d
bond angle:
molecular geo: see saw
hybridization: sp³d
bond angle:
9
New cards
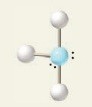
5 electron groups, 2 lone pairs
e⁻ geo: trigonal bipyramidal
molecular geo: t-shaped
hybridization: sp³d
bond angle:
molecular geo: t-shaped
hybridization: sp³d
bond angle:
10
New cards
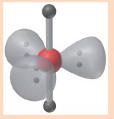
5 electron groups, 3 lone pairs
e⁻ geo: trigonal bipyramidal
molecular geo: linear
hybridization: sp³d
bond angle: 180°
molecular geo: linear
hybridization: sp³d
bond angle: 180°
11
New cards
6 electron groups, 0 lone pairs
e⁻ geo: octahedral
molecular geo: octahedral
hybridization: sp³d²
bond angle: 90°
molecular geo: octahedral
hybridization: sp³d²
bond angle: 90°
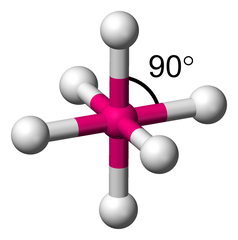
12
New cards
6 electron groups, 1 lone pair
e⁻ geo: octahedral
molecular geo: square pyramidal
hybridization: sp³d²
bond angle:
molecular geo: square pyramidal
hybridization: sp³d²
bond angle:
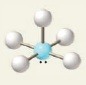
13
New cards
6 electron groups, 2 lone pairs
e⁻ geo: octahedral
molecular geo: square planar
hybridization: sp³d²
bond angle: 90°
molecular geo: square planar
hybridization: sp³d²
bond angle: 90°
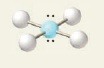
14
New cards
6 electron groups, 3 lone pairs
e⁻ geo: octahedral
molecular geo: t-shaped
hybridization: sp³d²
bond angle:
molecular geo: t-shaped
hybridization: sp³d²
bond angle:
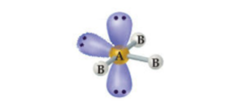
15
New cards
6 electron groups, 4 lone pairs
e⁻ geo: octahedral
molecular geo: linear
hybridization: sp³d²
bond angle: 180°
molecular geo: linear
hybridization: sp³d²
bond angle: 180°
16
New cards
ionic=
metal + nonmetal
17
New cards
covalent=
non-metal + non-metal
18
New cards
metallic
metals only
19
New cards
ionic bond strength=
strong
20
New cards
covalent bond strength=
weak
21
New cards
metallic bond strength=
strong
22
New cards
ionic is called...
compounds
23
New cards
covalent is called...
molecule or molecular compound
24
New cards
what happens to the electrons of ionics?
transfers electrons from metals to non-metals
25
New cards
what happens to the electrons of covalents?
shares electrons (equally= non-polar, unequal= polar)
26
New cards
what happens to the electrons of metallics?
delocalized (sea of electrons)
27
New cards
ionic: formed from cations/anions?
made of cations (metal) and anions (non-metal)
28
New cards
covalent: formed from cations/anions?
made only of anions
29
New cards
metallic: formed from cations/anions
made only of cations
30
New cards
ionic conductivity
conducts when dissolved in aqueous solution
31
New cards
covalent conductivity
does NOT conduct electricity
32
New cards
metallic conductivity
good conductors of heat and electricity
33
New cards
ionic state of matter
solids at room temp (stronger bonds)
34
New cards
covalent state of matter
liquids or gasses (weaker bonds)
35
New cards
metallic state of matter
solids at room temperature
36
New cards
ionic melting and boiling points
high
37
New cards
covalent melting and boiling points
low
38
New cards
metallic melting and boiling points
high
39
New cards
ionic reason for forming a bond
forms a bond to become stable
40
New cards
covalent reason for forming a bond
forms to become stable
41
New cards
metallic reason for forming a bond
forms to become stable
42
New cards
ionic characteristics include
brittle
43
New cards
covalent characteristics include
network covalent
44
New cards
network covalent
diamond and silicon are very strong bonds
45
New cards
metallic characteristics include
shiny (luster), malleable/ductile
46
New cards
ionic electronegativity values
high electronegativity difference
47
New cards
covalent electronegativity values
low electronegativity difference
48
New cards
metallic electronegativity values
low
49
New cards
ionic bond energy
high
50
New cards
covalent bond energy
low
51
New cards
metallic bond energy
high
52
New cards
ionic bond length
short
53
New cards
covalent bond length
long
54
New cards
metallic bond length
short
55
New cards
Metallics have a short bond length because
electrons don't belong to any atom (= sea of electrons (delocalized))
56
New cards
electricity=
flow of electric charges
57
New cards
cations...
lose electrons and become positive (metals)
58
New cards
anions...
gain electrons and become negative (non-metals)
59
New cards
valence electrons...
involved in bonding and found in the outer most shell
60
New cards
molecular orbit=
region in which shared electrons are found
61
New cards
bond length=
average distance due to electrons moving in the form of a wave
62
New cards
single bond length is
long
63
New cards
single bond strength is
weak
64
New cards
double bond length is
shorter than a single bond
65
New cards
double bond strength is
stronger than a single bond
66
New cards
triple bond length is
the shortest
67
New cards
triple bond strength is
the strongest
68
New cards
bond energy=
the amount of energy required to break the bond in 1 mole of a substance
69
New cards
polar=
unequal sharing of electrons
70
New cards
nonpolar=
equal sharing of electrons
71
New cards
are diatomics polar or nonpolar?
always nonpolar
72
New cards
polar=
opposites