cell-cell junctions
1/23
Earn XP
Description and Tags
beyond the cell
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
adhesive junctions
adherens junction and desmosomes
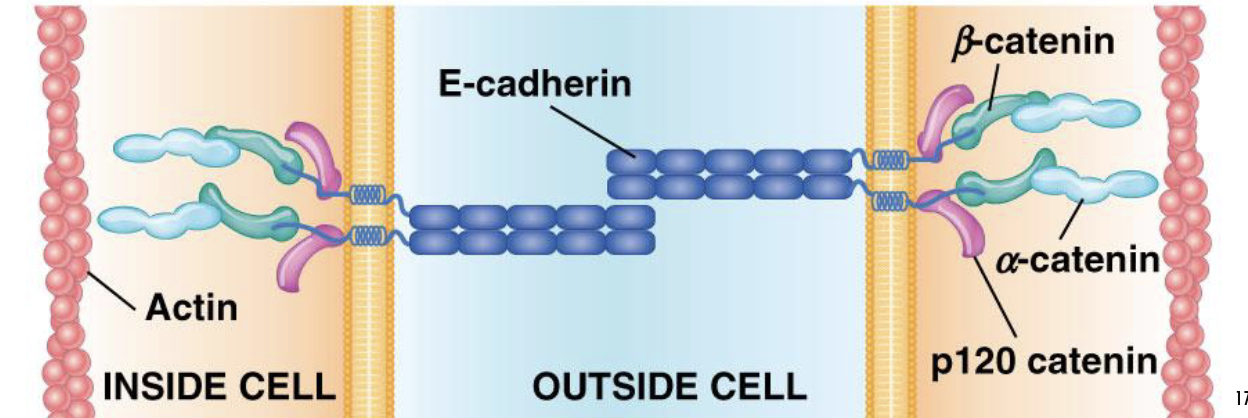
adherens junctions
cell-cell adhesion
continuous zones of intermembrane attachment
20-25nm space
actin microfilaments
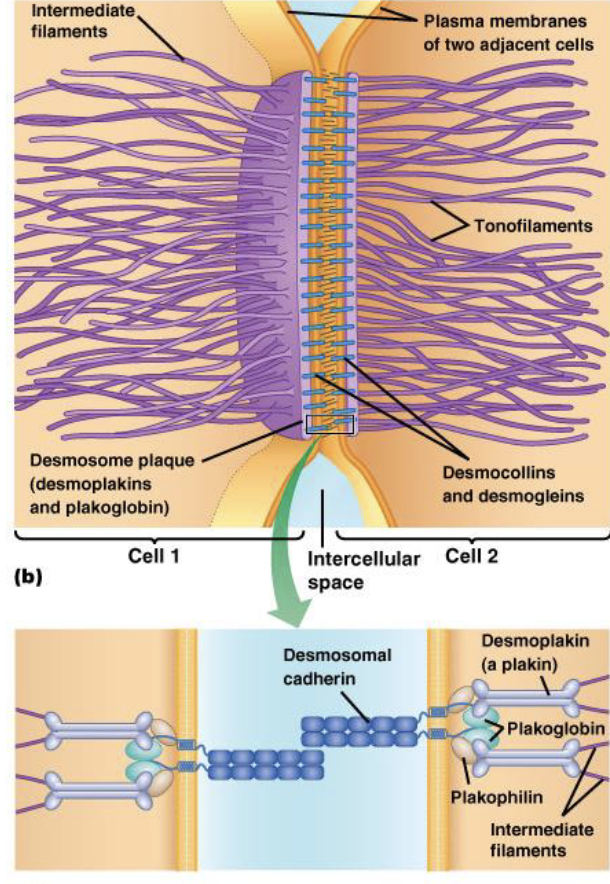
desmosome
cell-cell adhesion
localized points of intermembrane attachment
25-35nm space
intermediate filaments (tonofilaments)
tight junction
seals space b/w cells
membranes joined along ridges
no space
transmembrane junctional proteins, actin
gap junction
exchange of ions and molecules b/w cells
connexons (transmembrane protein complexes w 3nm pores)
2-3nm space
connexins in 1 membrane align w those in another to form channels b/w cells
cell-ECM attachments
focal adhesion and hemidesmosomes
focal adhesions
cell-ECM adhesion
localized points of attachment
20-25nm
actin microfilaments
hemidesmosome
cell-basal lamina adhesion
localized points of attachment
25-35 nm
intermediate filaments/ tonofilaments
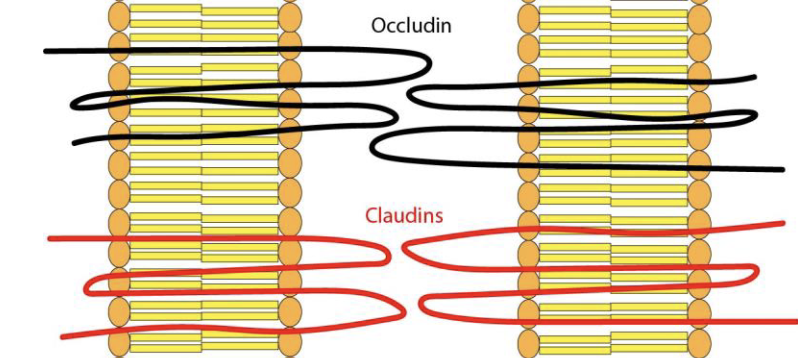
claudins and occludins
major transmembrane protein in tight junction
claudins - proteins w 4 membrane-spanning domains

JAMs or junctional adhesion molecules
major transmembrane protein in tight junction
Immunoglobulin superfamily
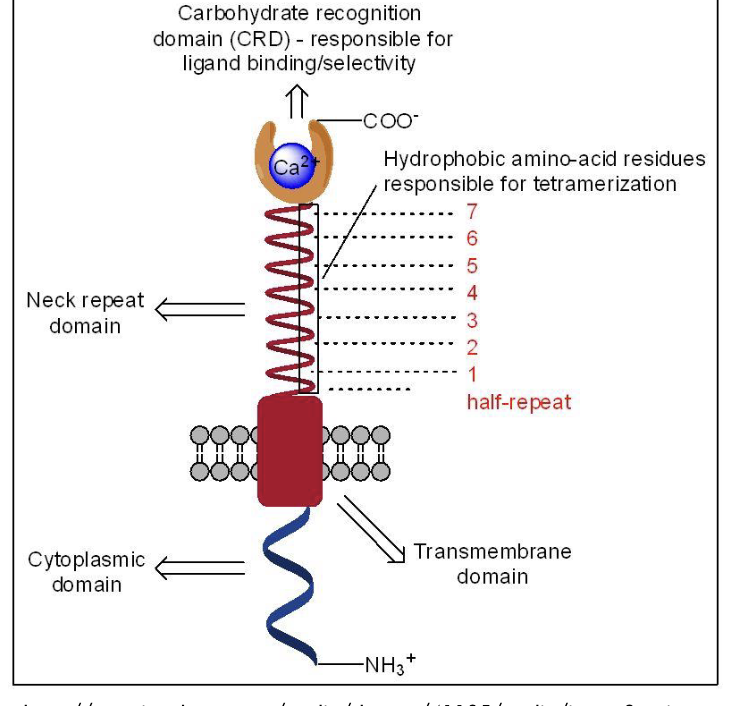
lectins
recognize and bind to specific carbohydrate (sugar) molecules on the surfaces of cells.
They facilitate cell-cell adhesion by linking carbohydrate groups on two different cells, promoting interactions in processes like immune response, inflammation, and cell signaling.
Animal and plant cells secrete lectins, play roles in cell recognition, adhesion, and communication.

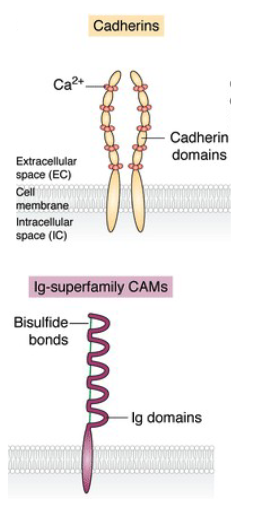
CAMs or cell adhesion molecules
IgSF = Ig super fam
N-CAM (neural) - 1st member
loops like Ig in extracellular domain
homophilic interactions
Selectins mediate the interaction between leukocytes and which of the following?
a) Platelets
b) Endothelial cells
c) Blood vessels
d) All of the above
D. When leukocytes interact with
platelets or the cells lining
blood vessels during
inflammation, the reactions are
mediated by selectins
1. L-selectin is expressed on
leukocytes
2. P-selectin on platelets
3. E-selectin on the endothelial
cells of blood vessels
stable adhesions at inflammation site mediated by integrin and ICAM
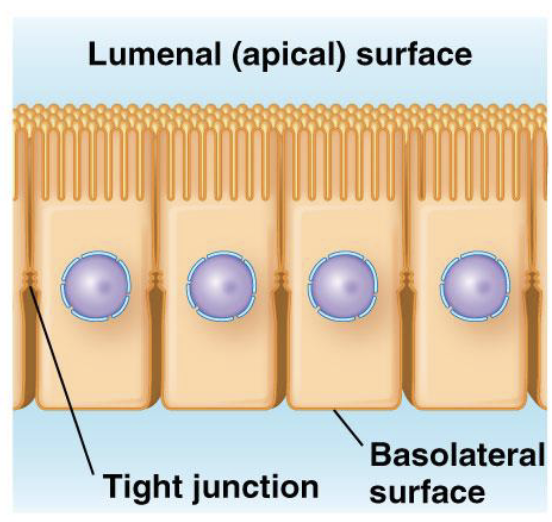
Tight junctions form a continuous belt around which part of the cell?
a) Basal end
b) Apical ends of lateral surfaces
c) Entire cell surface
d) Only on one side of the cell
B. tight JUNCTIONS PREVENT THE MOVEMENTS OF MOLECULES ACROSS CELL LAYERS They form a continuous belt around the apical ends of lateral surfaces of each cell Molecules cross the cell layer by passing through the cells
The transport of ions between cells via claudins is called:
a) Paracellular transport
b) Transcellular transport
c) Active transport
d) Facilitated diffusion
A. Different tissues express different claudins
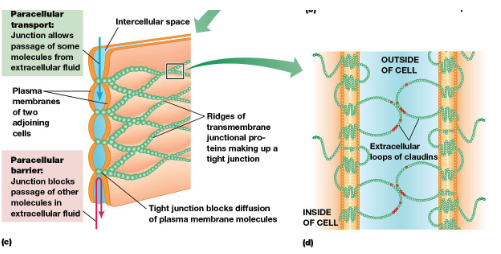
What type of movement do tight junctions block in the plasma membrane?
a) Lateral movement of lipids in the inner monolayer
b) Lateral movement of lipids in the outer monolayer
c) Vertical movement of proteins
d) Movement of water
Movement of lipids is blocked only in the outer monolayer B.
Movement of integral membrane proteins is completely blocked
Other cell-cell adhesion events utilize other plasma membrane
glycoproteins, such as _____ and ____
IgSF proteins and selectins.
Tight junctions form a permeability barrier between epithelial cells
and prevent lateral movement of membrane proteins. They contain (1)?, (2)? and (3)?
occludins
immunoglobulin superfamily
proteins called junctional adhesion molecules (JAMs),
claudins
___ junctions form open channels between cells, allowing direct
chemical and electrical communication between cells. this junction’s connexons are made of connexin proteins.
Gap