Unit 7-8 (E4)
1/102
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
103 Terms
What are respiratory agents divided into?
1.) Drugs that treat acute & relatively minor probs
(Ex. nasal congestion, coughing, or a seasonal allergy)
2.) Drugs that treat more chronic & serious airway obstructions
(Ex. bronchial asthma, chronic bronchitis, & emphysema)
What are antitussive agents used for?
-To treat Respiratory Tract Irritation & Control Respiratory Secretions
What are the drugs used to treat Respiratory Tract Irritation & control Respiratory Secretions? (4)
1.) Antitussives
2.) Decongestants
3.) Antihistamines
4.) Mucolytics & Expectorants
What are the suffixes for antitussive agents?
-deine
-done
-phan
-phone
-tate
Deen Done Phat Phone Tate (DDPPT)
What are the suffixes for nasal decongestants?
-drine
-oline
-phedrine
-phrine
-zoline
Drill Oil Pod Print Zone (DOPPZ)
What are the suffixes for antihistamines?
-dine
-mine
-nate
-tine
-zine
Dine Mine Nate, Time Zyn (DMNTZ)
What is the primary mucolytic drug currently in use?
What does it do?
-Acetylcysteine (Mucomyst, Mucosil)
-Used to reduce mucus production
What is the primary adverse effects associated with Acetylcysteine?
-Nausea & vomiting
-Inflammation of oral mucosa (stomatitis)
-Rhinorrhea.
What is Guaifenesin? What does it do?
-The only expectorant currently. (help clear mucus (phlegm) from your airway)
-Acknowledged by FDA to have evidence of therapeutic effects
What is the primary adverse effect associated with guaifenesin?
-GI upset
(Via excessive dose or if it is taken on an empty stomach)
What do beta-adrenergic bronchodilators treat?
-Prevent or inhibit airway obstruction in bronchospastic diseases
(Ex. bronchial asthma, chronic bronchitis, & emphysema)
How do beta-adrenergic bronchodilators work?
-Stimulate beta-2 adrenergic receptors to produce bronchodilation
(via beta-adrenergic agonists)
What are two disorders usually grouped under chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)?
-Chronic bronchitis & emphysema
What are the suffixes for beta-adrenergic bronchodilators?
-aline
-enol
-erol
Align enough Erin (AEE)
What do theophylline & several theophylline derivatives treat?
-Produce bronchodilation in asthma & other forms of airway obstruction
(Ex. bronchitis, emphysema)
What are the suffixes for Xanthine Derivative bronchodilators?
-phylline
Why are corticosteroids used for in obstructive pulmonary disease?
-Bc of powerful anti-inflammatory effects
-Controls inflammation-mediated bronchospasm & are the most effective agents for controlling asthma
What are the suffixes for corticosteroids used for COPD?
-lide
-lone
-nide
-sone
Linda Longs Needs Sun (LLNS)
Can glucocorticoids be combined with a long-acting beta-2 agonist? What does it do?
What does glucocorticoids do?
What does beta 2 do?
-Yes, to produce a greater effect
-Glucocorticoids decrease inflammatory response causing airway hyperresponsiveness
-Beta-2 maintains bronchodilation w/ asthma
What are special concerns PTs should have with pts on respiratory drugs?
-Prevent mucus accumulation
-Administer drug 30 mins to 1 hour before PT
-Portable aerosol bronchodilator needs to be brought
-Recognize side effects (toxicity)
-No overstress on bones & musculotendinous structures (glucocorticoids)
How can PTs prevent mucus accumulation?
-Pharmacotherapeutic effects of muscolytic & expectorant drugs
-Encourage pt to cough & raise secretions for expectoration
What can happen if bronchial secretions accumulate? 3
-Decreases gas exchange
-Atelectasis
(collapse of lung)
-Additional infection
(Ex. pneumonia)
What are some side effects of respiratory drugs? 5
-Cardiac arrhythmias
-Nervousness
-Confusion
-Tremors
-Weakened bones & musculotendinous structures (catabolic breakdown)
What are histamine receptor blockers used to treat? 3
1.) Peptic ulcers
(ulcerations of mucosal lining of esophagus, stomach, & duodenum)
2.) Probs related to indigestion & epigastric pain (dyspepsia)
3.) Heartburn via leakage of gastric acid into distal esophagus, called gastroesophageal reflux
How do histamine receptor blockers work?
-Via prevention of histamine-activated released during gastric acid under basal conditions & during stimulation by food
When are histamine receptor blockers used?
-To decrease damage from gastric acid via NSAIDs & other factors that increase acid secretion
What are the suffixes for histamine receptor blockers?
-tidine
How do drugs classified as proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) work?
-Suppress H+ & K+-ATPase enzyme
-To decrease transport of H+ ions & formation of gastric acid
What are the suffixes for proton pump inhibitors?
-prazole
What do laxatives do?
-Promote evacuation of bowel & defecation when normal bowel movements are impaired but no obstruction exists in GI system
What are cathartics or purgatives used for?
-Promote lower GI evacuation, but in a more rapid fashion than typical laxatives
What happens if the transit time of food through the GI tract is too fast?
-Diarrhea occurs, resulting in poor food absorption & dehydration
What happens if diarrhea is sustained for even a few days?
-Dehydration can be a serious problem (especially in infants or debilitated pts)
Diarrhea is often a temporary symptom of many relatively minor GI disorders, what are more serious conditions it can occur w/? 3
-Dysentery
-Ulcerative colitis
-Cholera
How many grams of fiber should you have a day?
25-30g
Which type of fiber promotes bathroom use?
-Insoluble
Whole wheat and whole grains (brown rice, whole grain bread)
Nuts and seeds (especially with skins)
Vegetables like:
Cauliflower
Green beans
Zucchini
Wheat bran
Skins of fruits (e.g., apple peel, grape skin)
Which type of fiber lowers LDL?
-Both, but mostly soluble
Oats and oatmeal
Barley
Beans and lentils
Apples
Citrus fruits (like oranges)
Carrots
Flaxseeds
Psyllium husk
Will Wheat brand or oatmeal make you go?
-Wheat brand bc it has insoluble fiber
-While Oats have soluble so it is better to lower LDL
When do we usually see the use of PPIs & histamine receptor blockers used for stress ulceration syndrome?
pt's that have:
-Burns
-Multiple traumas
-Renal failure
-CNS trauma
When do we usually see the use of laxatives for constipation?
-Inactive pts & prolong best rest
Why would pts w/ cancer be given antiemetic drugs?
-Bc chemotherapy often cause nausea & vomiting
-Also causes chronic indigestion & diarrhea
GI ISSUES
What are the special concerns PTs should have with pts on GI drugs? 7
-Secondary, stress ulceration syndrome
-Inactive/bed written pts
-Chemotherapy pts
-Increase water intake
-Bathroom use during rehab (can contribute to pt probs)
-Mild side effects
-Educate pt on laxative dependency
What side effects do GI drugs have?
-Mild dizziness & fatigue (dehydration)
[opiates + H blockers}
-GI disturbances (constipation)
What is the clinical use of endocrine drugs?
1.) Replacement therapy
2.) Treat excessive endocrine function
3.) Alter normal endocrine function
4.) Diagnose endocrine disorders
What are the two primary types of adrenal steroids produced by the adrenal cortex?
1.) Glucocorticoids
2.) Mineralocorticoids
What do glucocorticoids (cortisol, corticosterone) primarily do?
-Control glucose metabolism & body's ability to deal w/ stress
-Decreases inflammation & suppresses immune system
What do Mineralocorticoids, such as aldosterone, do?
-Maintain fluid & electrolyte balance in body
What is a physiological dose with use of adrenal steroids?
-Administration of hormonal replacement therapy is equivalent to normal endogenous production
What pharmacological dose with use of adrenal steroids?
-Larger dose to differentiate them from amount used to maintain normal endocrine function
-Ex.) Glucocorticoids as anti-inflammatory
What are the suffixes for glucocorticoids?
-bate
-lide
-lone
-nate
-nide
-sone
-sol
Bate Lives Lone Naturally Needing Some Soul (BLLNNSS)
What are the suffixes for Mineralcorticoids?
-spironolactone
-eplerenone
Spiral Episode (SE)
What are the desired effect with glucocorticoids for treatment of non-endocrine disorders? 4
-Decrease inflammation & edema
-Immunosuppression
-Anti-lymphocyte effects
-Inhibit free radical induced neuronal damage
What are the two clinically used mineralocorticoid antagonists?
1.) Spironolactone
2.) Eplerenone
What is a side effects of mineralocorticoid antagonists? 4
-Increase in plasma potassium levels (hyperkalemia)
-Could be life threatening if severe or prolonged
-Gastrointestinal disturbances
(Ex. diarrhea, stomach pain, gastric ulcers)
-CNS effects
(Ex. drowsiness, lethargy, confusion, headache)
What do Spironolactone, mineralocorticoid antagonists, interfere with?
-Increased body hair
-Deepening of voice
-Decreased libido
-Menstrual irregularities
-Breast enlargement in men
-CNS effects
(Ex. drowsiness, lethargy, confusion, headache)
What do eplerenone, mineralocorticoid antagonists, interfere with?
-Has lower incidence of sexual side effects
-Suppress mineralocorticoid function w/o affecting sex hormones
What are the special concerns of PTs when working with pts on andrenocorticosteroids?
-Catabolic effect
(breakdown of structures)
-Strengthening helps
(muscle mass, musculotendious wasting & mobility)
-Caution w/ weakened structures
-Aware of sodium & water-retaining
(hypertension)
-Increase susceptibility to infection
-Toxicity: mood changes & psychoses
What catabolic effect do glucocorticoids have?
-Breakdown of muscle, bone, skin, & other collagenous structures
-Inactivity, poor nutrition, & effects of aging are all contributing factors.
Which pts do we often work with that take glucocorticoids?
-RA
-Ankylosing spondylitis
-Lupus Erythematosus
-Acute bursitis
-Tenosynovitis
How can the PT increase joint movement w/o causing injury to the joint if pt is on glucocorticoids?
-Low-intensity, long-duration stretching
-Physical agents, massage, & other manual techniques
-Gradual strengthening as drugs exert anti-inflammatory effects
-Strengthening muscles around knee
How long can the effects of a single injection affect E.M.'s joints?
-3 months or so
-They are highly lipid soluble & can be retained w/in fat & other intra- + peri-articular joint tissues
-If took too frequently causes weakening of structure.
How are glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids synthesized?
-Via cholesterol w/in cells of adrenal cortex
What is the primary glucocorticoid produced in humans?
-Cortisol (hydrocortisone)
What is the primary mineralocorticoid produced in humans?
-Aldosterone
What are the principal functions of male and female hormones?
-Control reproductive function & secondary sexual characteristics in their respective gender groups
What are male hormones, such as testosterone, are usually referred to as?
-Androgens
What are the two principal groups of female hormones?
1.). Estrogens
(estradiol)
2.) Progestins
(progesterone)
What steroid hormones are similar to those of primary steroid groups, glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids?
-Androgens, estrogens, & progestins
What are the primary indications for clinical use of androgens?
1.) Endometriosis
2.) Benign fibrocystic disease
3.) Hereditary angioedema
4.) Androgen deficiency
5.) Breast cancer
6.) Delayed puberty in boys
7.) Anemia of renal insufficiency
8.) Catabolic states
How are anabolic androgens usually took?
-Either injected or orally
What are the suffixes for androgen drugs?
-azol
-lone
testosterone
Azzy Lines Tests (ALT)
What are the estrogen drugs?
-estradiol
-estrogens
-estropipate
What are the suffixes for Progestins drugs?
-rel
-rol
progesterone
Real rolling Pro (RRP)
What are the primary indications for clinical use of estrogens?
-Estrogen replacement
-Antineoplastic
-Prevention of osteoporosis
-Prevention of abnormal uterine bleeding
What are the primary indications for clinical use of progestins?
-Contraceptive
-Amenorrhea or secondary amenorrhea
-Dysfunctional uterine bleeding
-Maintain pregnancy & decrease risk of preterm birth
-Breast or endometrial carcinoma
-Anorexia/cachexia associated w/ AIDS
-Support of embryo implantation & early pregnancy
-Endometriosis
What are most of the hormonal contraceptives made out of?
-Estrogen & progesterone
What risk do you run if you are taking contraceptives and are a cigarette smoker?
-Deep vein thrombosis (DVT)
What are some concerns for PTs when pts are on male or female hormone drugs?
-Motor blood pressure
-Salt & water retention
-Hypertension
-Educate pt on androgen abuse & side effects
(Liver, cardiovascular, & reproductive abnormalities)
What does treatment for hyperthyroidism consist of?
-Surgical removal of gland
-Administering radio- active iodine to gland
-Pharmacological agents to manage
What pharmacological agents are used to treat hyperthyroidism?
-Antithyroid drugs
-Iodide
-Radioactive iodine
-Beta-adrenergic blockers
What are the Beta-adrenergic blockers used for hyperthyroidism?
-Acebutolol
-Atenolol
-Metoprolol
-Nadolol
-Oxprenolol
-Propranolol
-Sotalol
-Timolol
(They all end in -olol)
What are the Antithyroid drugs used for hyperthyroidism?
-Propylthiouracil (Propyl-Thyracil)
-Methimazole (Tapazole)
What are the primary syms for hyperthyroidism?
-Nervousness
-Weight loss
-Diarrhea
-Tachycardia
-Insomnia
-Increased appetite
-Heat intolerance
-Oligomenorrhea
-Muscle wasting
-Goiter
-Exophathalmos
What are the primary syms for hypothyroidism?
-Lethargy/slow cerebration
-Weight gain
-Constipation
-Bradycardia
-Sleepiness
-Anorexia
-Cold intolerance
-Menorrhagia
-Weakness
-Dry, coarse skin
-Facial Edema
What are the suffixes for hyperthyroidism?
-nine
-trix
-xine
thyroid
Nine tricks xeros thighs (NTXT)
What are the primary methods of treatment for hypothyroidism?
-T3 (liothyronine)
-T4 (levothyroxine)
-or both
What is the primary drug treatment for metabolic disease?
-Calcium supplements
-Vitamin D
-Biphosphonates
-Calcitonin
-Intermittent parathyroid hormone
-Estrogen
-SERMS
-Usually treated surgically by partial or complete resection of glad
What are the drugs used to control bone mineral homeostasis?
-Biphosphonates
-Calcitonin
-Calcium supplements
-Estrogens
-Vitamin D analogs
What is the suffix for Biphosphonates?
-dronate
What are the special concerns for PTs when pts are taking thyroid gland drugs?
-Syms of opp. disorder is sign of overdose
-Signs of thyroid dysfunction (inappropriate dose)
-Decreased cardiac output & hypotension (via hypothyroidism)
-Cardiac arrhythmias (via excessive calcium supp)
-Exercise & weight bearing activities
(stimulate bone function)
-Vit D facilitates calcium absorption (via sun, ultraviolet light)
What is a common side effect of Vit D and magnesium?
-Diarrhea
What are the characteristics of Type I diabetes?
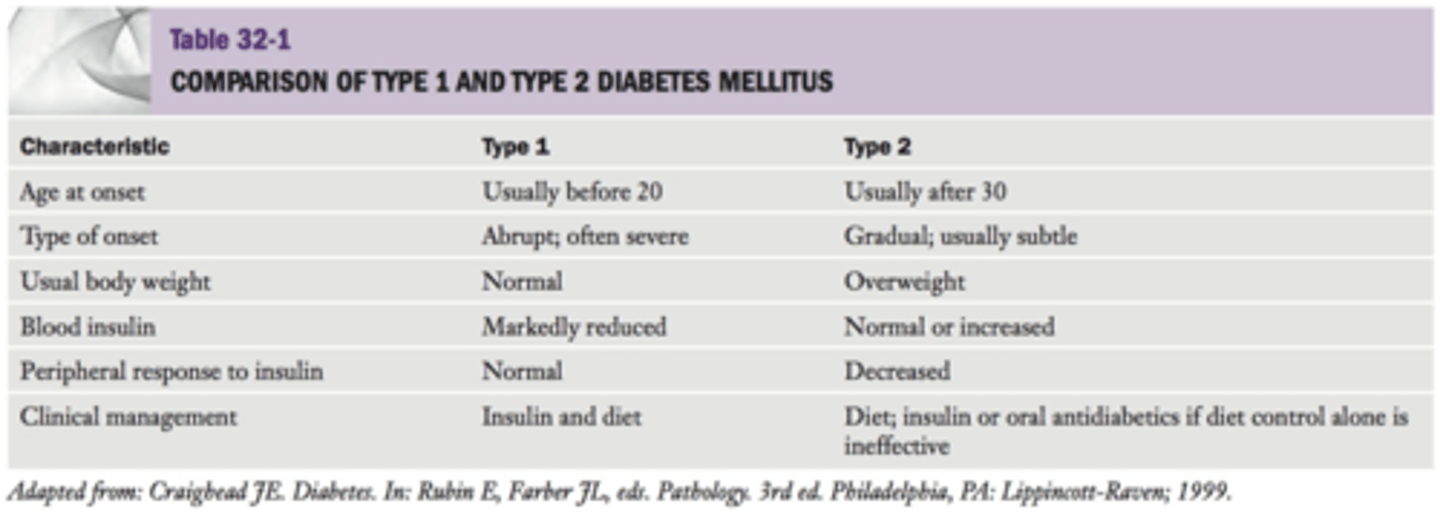
What are the characteristics of Type II diabetes?
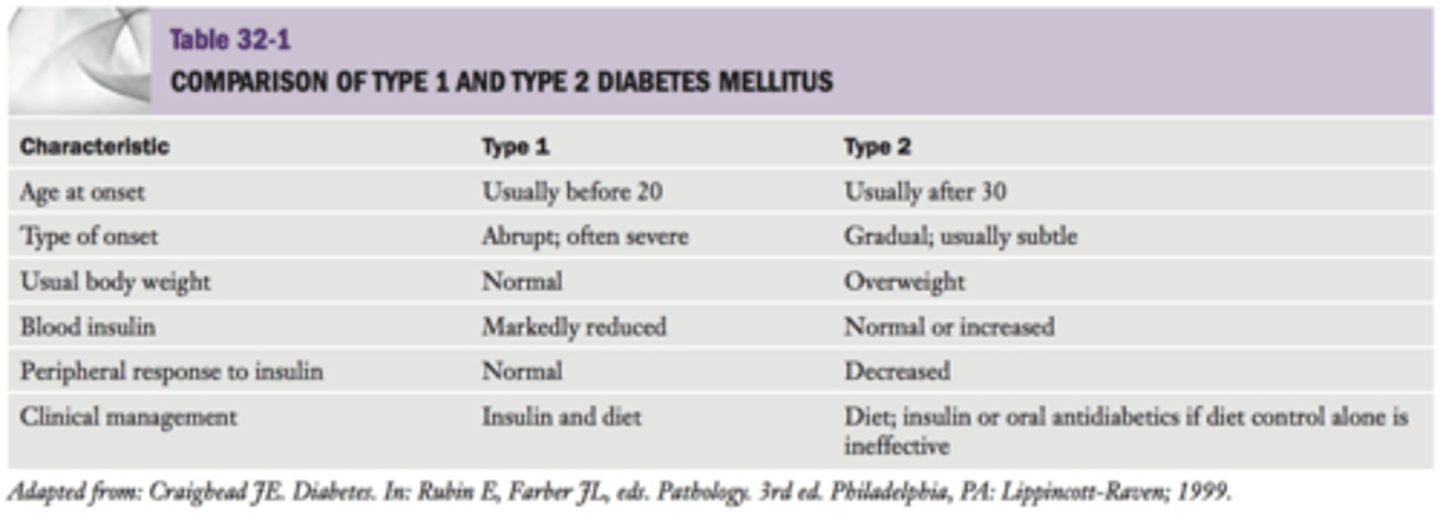
What are the 4 types of insulin drugs?
1.) Rapid acting
2.) Short acting
3.) Intermediate acting
4.) Long acting
What are some rapid acting insulin drugs?
1.) Aspart
2.) Lispro
3.) Glulisine
Assess Live Glide (ALG)
What is a short acting insulin drug?
-Regular insulin
What is an intermediate acting insulin drug?
-Isophane insulin
What is a long acting insulin drug?
1.) Glargine
2.) Detemir
Glows Determine (GD)
What are the two classifications of type II Diabetes M drugs?
1.) Drugs that stimulate insulin integration & supply
2.) Insulin sensitizers
How is type I diabetes management administered?
-Injected or device