Year 9 Economics 1
1/26
Earn XP
Description and Tags
some flashcards for the Australian curriculum year 9 economics course :)
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
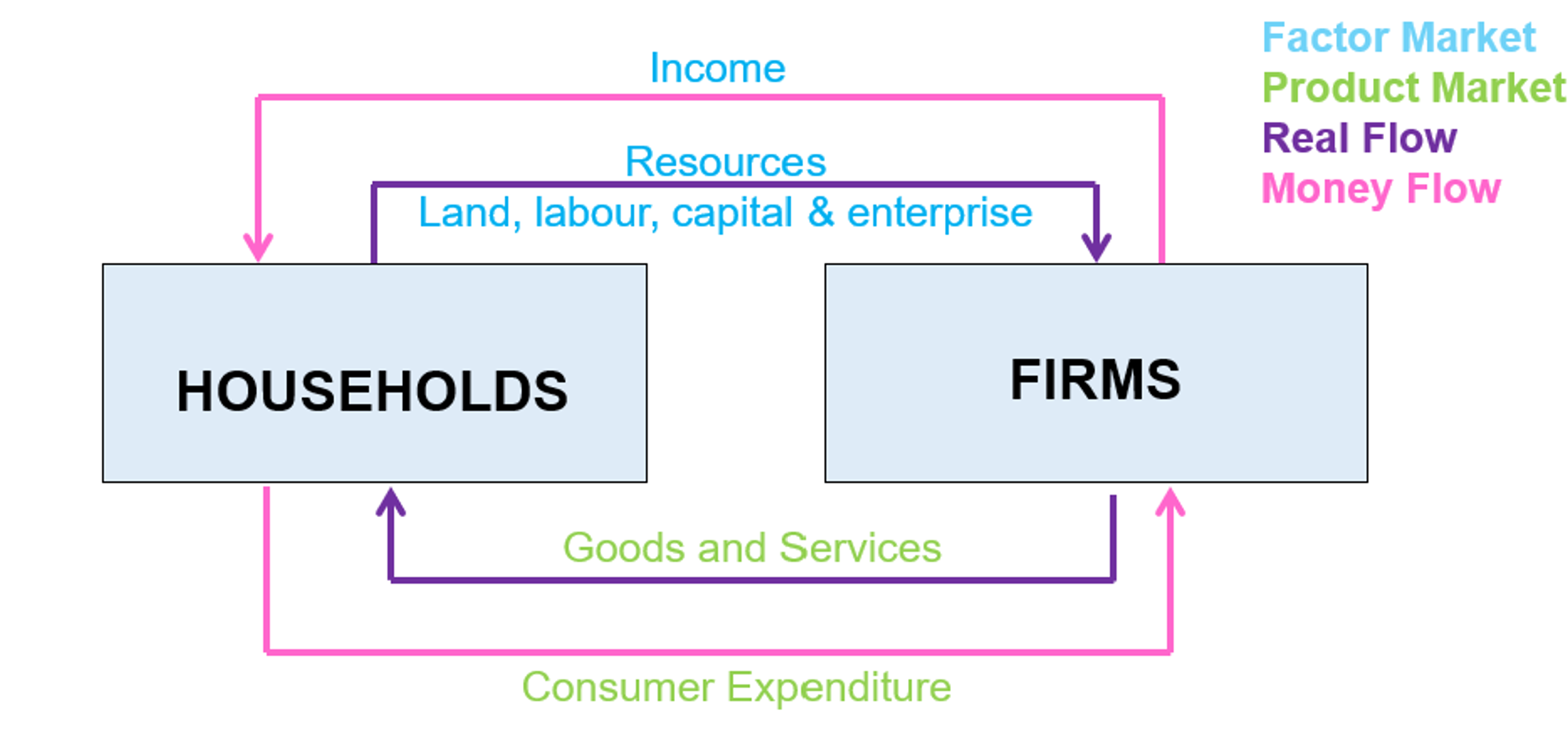
Real flow
the flow of resources and goods and services (between households and firms)
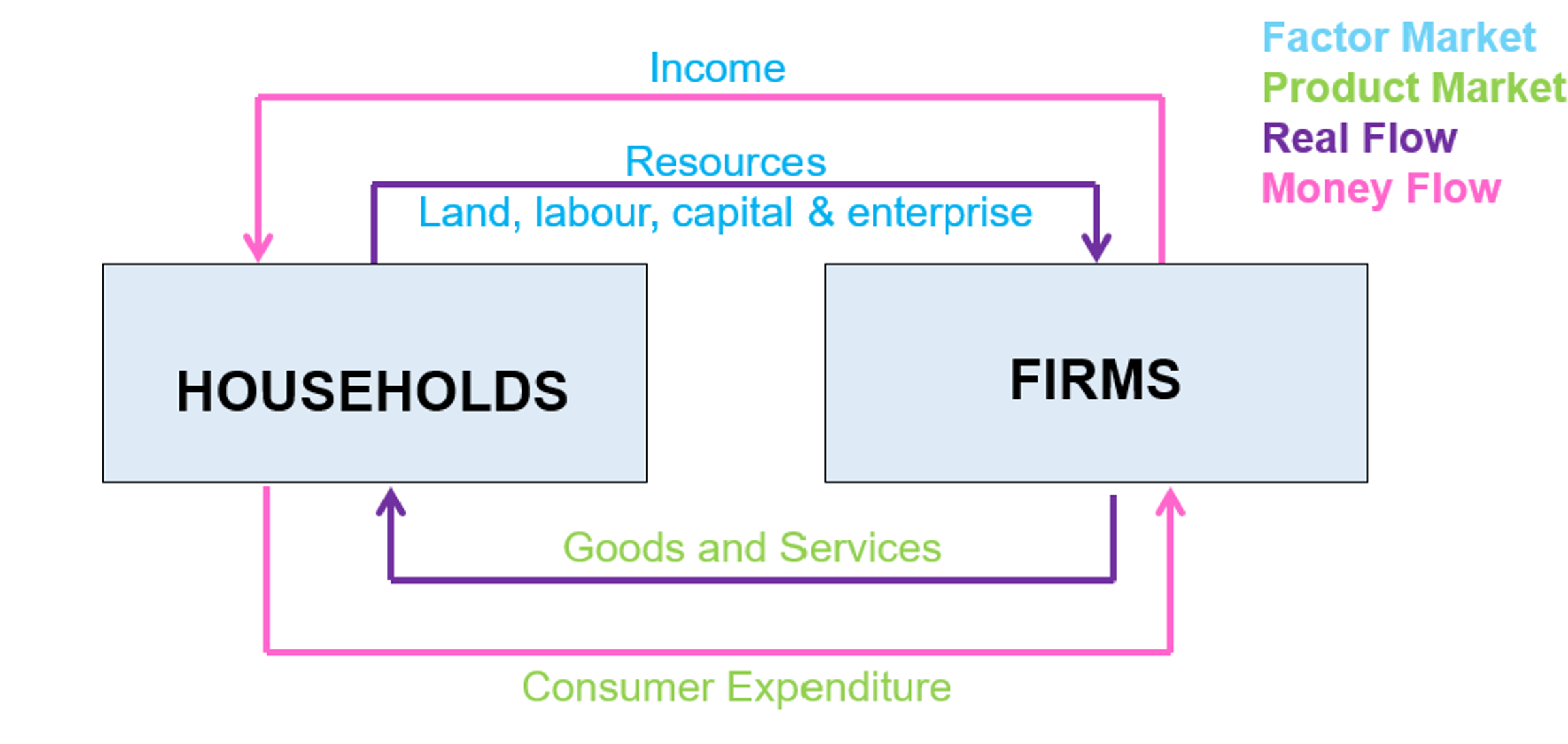
Money flow
the flow of income and consumer expenditure (between firms and households)
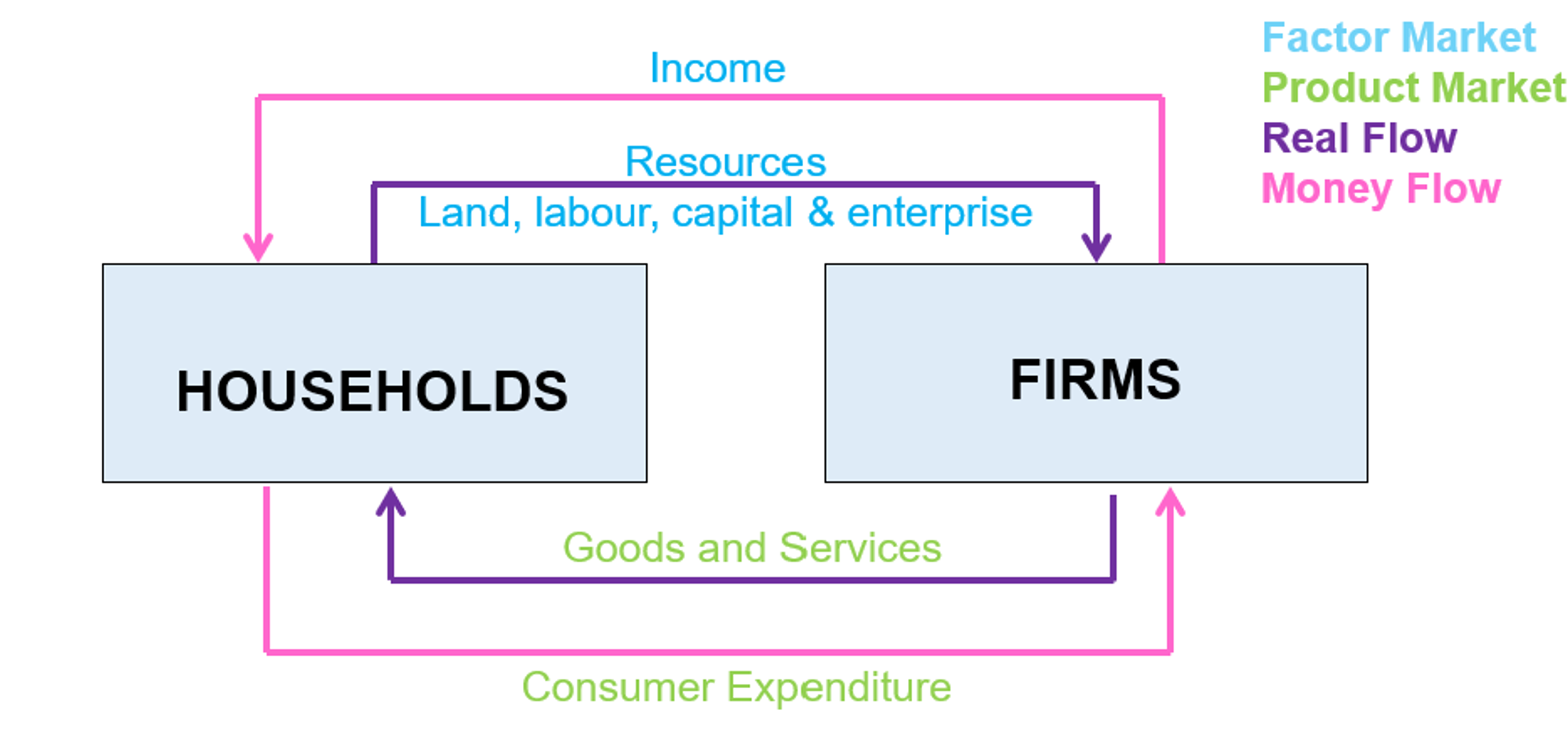
Product market
goods and services from firms in exchange for consumer spending from households (households buying stuff from firms)
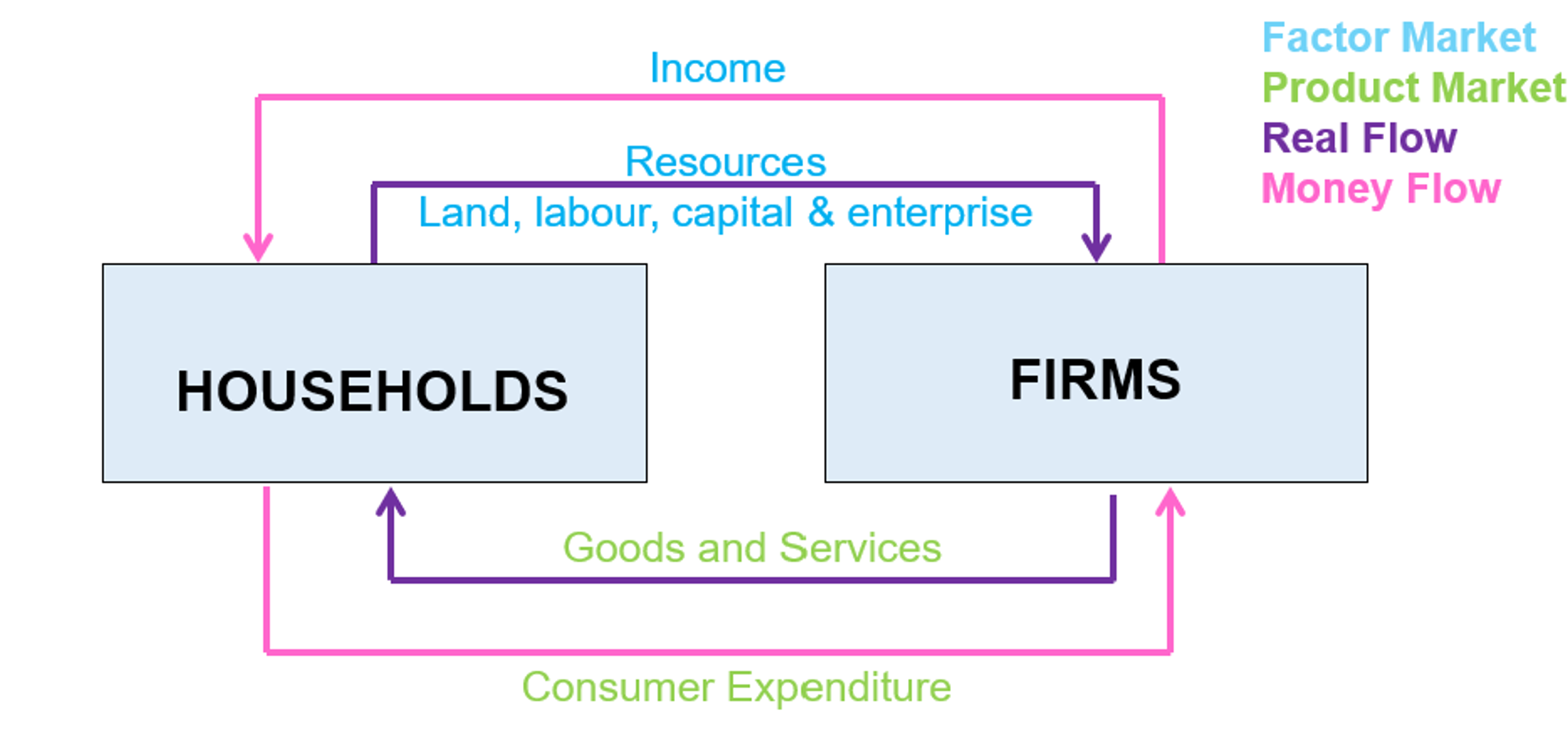
Factor market
resources (land, labour, trade, enterprise) in exchange for for income from firms (households working for firms)
Households 🏠
The owners of productive resources (land, labour, capital, enterprise) who provide resources to firms in exchange for income (factor market)
Act as consumers, buy goods and services from firms to satisfy needs and wants (product market)
Aim to satisfy unlimited needs and wants
Firms 🏭
The employers of resources (land, labour, capital and enterprise, from households) in exchange for income
Produce goods and services in exchange for consumer expenditure
Aim to make a profit
💫🦈shark checkpoint🦈💫
keep studying don’t give up!! u gotta lock in 🎀

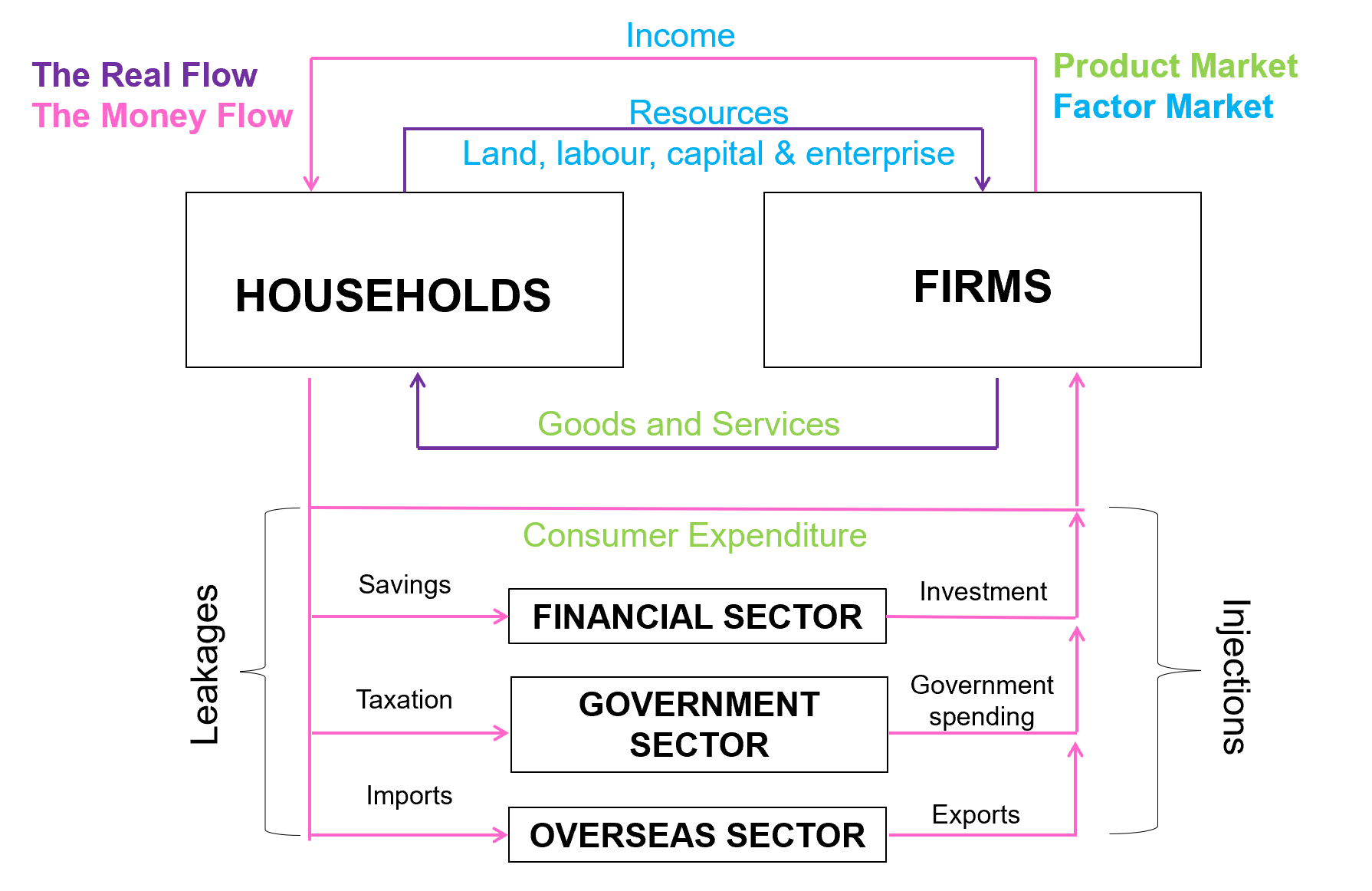
Financial sector 🤑
consists of financial institutions where households deposit their savings into. These institutions then invest it back into the economy as loans
leakages: savings
injections: investments (lent to firms and households)
Government sector
Made up of the revenue and expenditure of the government in the economy
leakages: taxation
injections: government spending (project funding, infrastructure, etc)
Overseas sector ✈
made up of all the other countries that Australia trades with
leakages: imports (Australians spending money on goods/services from overseas)
injections: exports (other countries spending money on goods and services from Australia)
Benefits of global trade ✅🌏
consumers have access to a larger variety of goods and services
businesses can sell products to a larger consumer base, and can sell more products, increasing profits
Costs of overseas trade ❌🌏
some businesses won’t be able to keep up with larger world prices and therefore will shut down, leading to unemployment
creates reliance on other economies, meaning global shocks (eg. global pandemics) have more impact on access to goods and services.
Australia’s top exports
Iron ore (21%)
coal (14%)
natural gas (11%)
education (8%)
gold (5%)
Australia’s top imports
personal travel (11%)
refined petroleum (9%)
passenger motor vehicles (6.5%)
goods vehicles (3%)
telecom equipment (2.5%)
Australia’s top trading partners
China - 20% of imports, 32% of exports
Japan - 6% of imports, 13% of exports
European Union - 15% of imports, 4% of exports
United States - 12% of imports, 5% of exports
South Korea - 5% of imports, 6% of exports
🎀🪼jellyfish checkpoint🪼🎀
remember to go drink water! keep studying and focusing!

Comparative advantage
some countries can produce a specific good or service more efficiently than other countries, meaning they can sell it for a lower price.
eg. China can produce a large amount clothing for cheap prices, so a lot of clothes in Australia are made in China
Globalisation 🌎
the process by which individuals or businesses develop international influence or relationships or start operating on an international scale. (increasing globalisation means the world is more interconnected)
Benefits of globalisation ✅🌎
free trade (countries can exchange goods and services, access to wider variety)
comparative advantage (access to larger variety of goods and services at a cheaper price)
sharing of ideas/technology (economies can share resources and technology, improving efficiency)
Costs of globalisation ❌🌏
harm to developing countries (developing countries struggle to compete with developed countries, increasing divide)
environmental costs (transportation, non-renewable resources)
loss of skilled labour (skilled workers move to higher paying countries, reducing skilled labour in others)
Global supply chain
a world-wide production process where firms have multiple locations for the production of a good/service
Positives of global supply chains
increased profits (lower cost means more profits, since they can produce different components in different places based on the prices)
cheaper production (take advantage of comparative advantages)
Negatives of global supply chains
Unemployment (one country specialised, others reduce production, leading to unemployment)
Costs to Government (government expenditure increases due to unemployment - eg, JobSeeker)
3 Solutions to supply chain shortages
Regionalisation (factories in multiple parts of the world)
Nearshoring (moving production closer to where it is distributed and sold)
Reshoring (moving production back to the country it was previously in)
Regionalisation
setting up factories in multiple parts of the world so that operations in each region are able to supply products to the nearest markets (minimises risks by reducing supply chain size)
Nearshoring
moving production that has been moved far away to a closer country to where products are distributed and sold
Reshoring
moving production back to the country where it was originally in