Lecture 4 & 5 Innate Immunity Part II
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
Pathogen-Associated Molecular Patterns (PAMPs)
specific molecular structures commonly found on the surface of pathogens, such as bacteria, viruses, fungi, and parasites
Damaged-Associated Molecules Patterns (DAMPs)
Molecular motifs expressed on infected or damaged host cells (interferons are DAMPs)
Pattern Recognition Receptors (PRRs)
a class of receptors that recognize common pathogen and damaged cell surface structures
PRRs are found
on (and in) innate immune cells
-Primarily expressed by antigen-presenting cells (APCs) -- macrophages, Dendritic cells
-Often expressed on other immune and non-immune cells -- Neutrophils, NK cells
Innate immune recognition ≠ adaptive immune recognition
Common PRR Families
-Toll-Like Receptors (TLRs)
-C-Type Lectin Receptors (CLRs)
-F-Met-Leu-Phe Receptors (FPRs)
-NOD-Like Receptors (NLRs)
-RIG-I-Like Receptors (RLRs)
found in different combinations on all innate cells
Toll-Like Receptors (TLRs)
expressed by macrophages, dendritic cells, and non-immune cells like fibroblasts
-Classified based on their cell localization
-In humans, the TLR family has ten members (TLR 1-10)
-Activated TLRs facilitate the initiation of adaptive immunity through pro-inflammatory cytokines
-Adaptor proteins function as flexible molecular scaffolds
TLRs function
regulate the expression of cytokines, chemokines and type 1 IFNs that protect the host from microbial infection
TLR10
the only member of the human TLR family with an inhibitory function at the start of innate immune responses
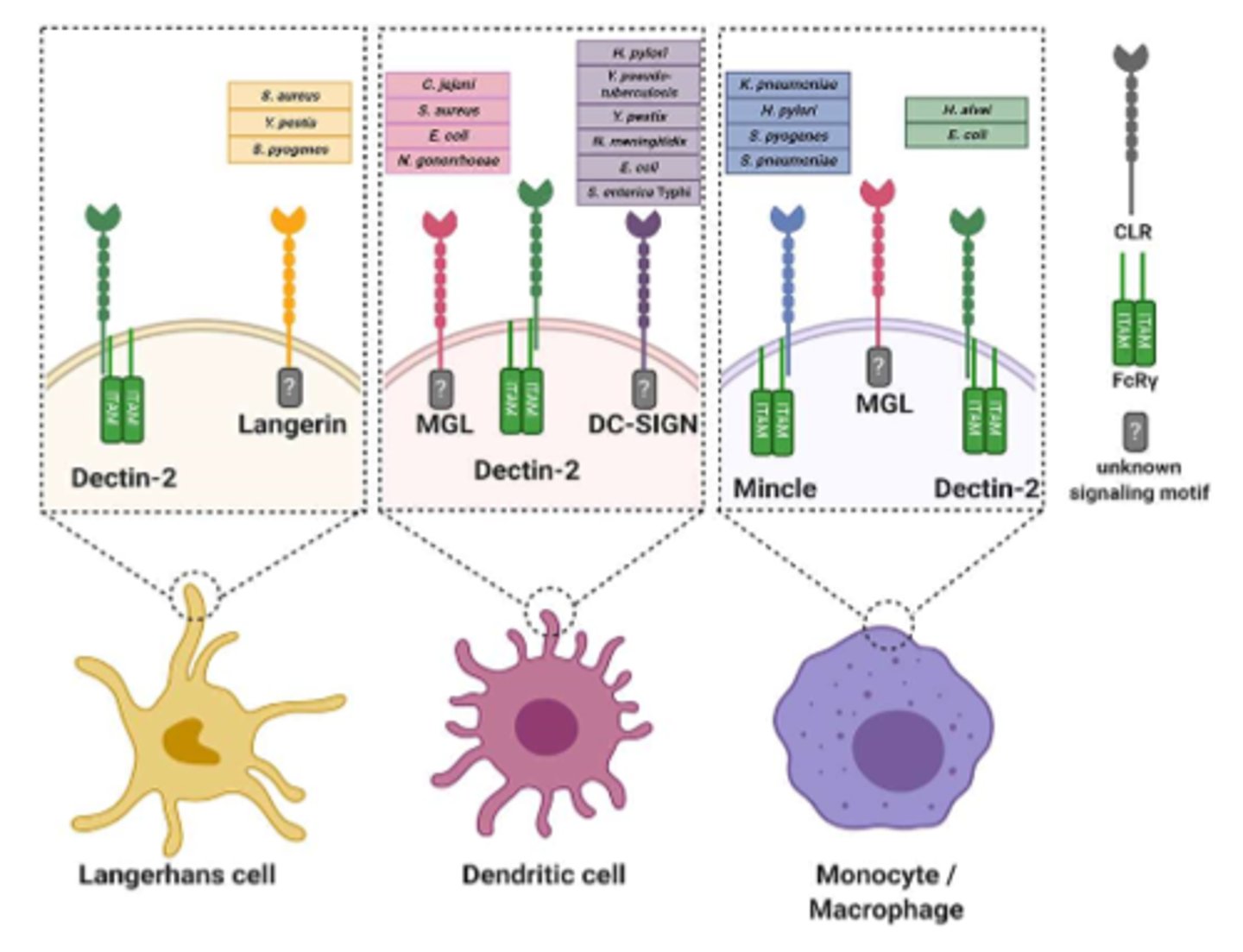
C-Type Lectin Receptors (CLRs)
Membrane-bound receptors
-Bind to carbohydrates in a calcium dependent manner
-Involved in bacterial and fungal recognition
-Modulate (adjust) the innate immune response
NOD-Like Receptors (NLRs)
Intercellular PRRs
-Detect intracellular PAMPs and danger signals, including bacterial peptidoglycans; form inflammasomes
-A core unite of an inflammasome involves a three-part nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain (NOD) and leucine-rich repeated tail (LRRs)
-Inflammasomes help resolve infections (cleave immature cytokines into mature cytokines)
-Contribute to cytokine-driven inflammation (made worse during autoimmune or autoinflammatory diseases)
RIG-I-Like Receptors (RLRs)
-Family of three cytoplasmic RNA helicases search for double-stranded RNA (viruses)
-Produce type I interferons (interferon-α and interferon-β) in infected cells
-Essential for host antiviral responses
F-Met-Leu-Phe Receptors
-Mononuclear and PMN phagocytes
-fMet is exclusively used by bacteria for protein synthesis initiation (Not used by eukaryotes)
-Formylated peptides attract phagocytes to migrate to their position (chemotaxis)
Complement System
-made up of 30 proteins produced in the liver (hepatocytes)
-Function to assist (complement) the action of antibodies in destroying bacteria
-Helps to remove antibody-coated antigens (opsonized antigens)
Complement Cascade
precise chain of events leading to forming a membrane attack complex (MAC)
Membrane Attack Complex (MAC)
A configuration of complement proteins designed to be inserted into bacterial cell walls and induce lysis, phagocytosis, or inflammation
Complement Activation Pathways
classical, alternative, lectin
Complement triggers
-Opsonization (phagocytosis)
-Inflammation
-Lysis (membrane attack)
Endocytosis
engulfment of macroparticles and intracellular materials by certain innate immune cells
Pinocytosis
engulfment of extracellular tissue fluid through membrane invagination or receptor-mediated endocytosis
Phangocytosis
ingestion of invading foreign particles by individual cells
Opsonins
antibodies and various complement serum components that make foreign particles easier to target
Respiratory burst
During phagocytosis, toxic metabolites are produced for use against pathogens
-Nitric oxide
-Superoxide anion
-Hydrogen peroxide
-Hypochlorous acid
To avoid collateral host cell damage, protective enzymes (catalase) are released with the toxins
Inflammation
a major body defense mechanism - initiated by tissue damage
Inflammation is a normal immunologic process.
Restores the injured tissue back to its normal state (Homeostasis)
endogenous factors
Events that originate from within a living system
exogenous factors
events that originate from outside of a living system
Inflammation cardinal signs
-Heat
-Edema
-Redness
-Pain
Hemostasis
(seconds to hours)
-PMN Leukocytes (e.g., neutrophils) and local macrophages and dendritic cells accumulate at the site and begin phagocytosis
-Phagocytes (neutrophils, macrophages, dendritic cells) release their lysosomal enzymes to destroy
Inflammatory Phase
(hours to days)
-Macrophages and lymphocytes infiltrate the area
-Antigen-presenting cells (macrophages and dendritic cells) present antigens to T-cells to activate the adaptive response
Proliferative phase
(days to weeks)
Antibodies produced by B-cells circulate in the bloodstream
-Epithelialization, angiogenesis, fibroblast proliferation, and collagen synthesis begin
Remodeling
Epithelialization slows, and the shape of the tissue is remodeled
-Additional collagen fibers from the proliferative phase have increased the tensile strength of the previous wound
Acute Inflammatory Response
Most of the cells involved in the inflammatory response are phagocytic cells.
Initially, innate immune cells use PRRs to identify microbes expressing PAMPs.
-Results in the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines (IL-1, IL-6, TNF-α)
-Cytokines stimulate hepatocytes in the liver to secrete acute-phase proteins (C-reactive protein (CRP), C3, C4, MBL)
Acute-phase proteins
-Increases white blood cell production/maturation
-Increased synthesis of hydrocortisone and adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH)
-Stimulates the hypothalamus to induce fever
ACTH
simulates your adrenal glands to release cortisol which regulates blood pressure, blood sugar, immune cells and the body's response to stress
C-reactive protein
-Binds to certain microorganism membranes and activates the complement system to lyse the cell.
-Enhances phagocyte activity and other host defense functions
-Non-specific marker for inflammation
How are acute phase proteins clinically assessed?
by measuring CRP (C-reactive protein) and ESR (erythrocyte sedimentation rate) during routine blood tests
Localized inflammatory responses
activate kinins and the coagulation system
Kinins
are potent nerve stimulators and are responsible for the pain and itch associated with inflammation
-Act on local smooth muscle to cause contractions
-Act on axons to block nervous impulses for distal muscle relaxation
-Act on vascular endothelial cells, causing them to contract and increase vascular permeability.
Coagulation system
pathway activation occurs after kinin-induced changes to damaged blood vessels.
-Activates a plasma enzymes cascade, contributing to the inflammatory response
-Forms a physical barrier with platelets called a clot or thrombus
-Prevents microorganisms from entering bloodstream
Cytokines (IL-1, TNK-α) and Chemokine IL-8
Increase expression of endothelial cell adhesion molecules (ECAMs) on endothelial cells
-Increase expression of ECAM ligands on leukocytes
Leukocyte transendothelial migration
-Caused by increased vascular permeability and leukocyte-endothelial adherence
-Also called leukocyte extravasation
-Six sequential steps: tethering, rolling, activation, adhesion, crawling, and transmigration
Chemotaxis
Migration of cells along the concentration gradient of an attractant (e.g., a pathogen, antigen, or PAMP)
Chemokines
Cytokines involved in the migration and activation of primary phagocytic cells during an inflammatory response
Chronic inflammation
occurs when it is difficult or impossible to remove the cause of the inflammation
-Administration of anti-inflammatory agents (e.g., steroids) only temporarily modifies the continued inflammatory response.
--They do not affect the root cause of the inflammation, so when withdrawn, the symptoms return.
Fever
-There is limited information
-Can be caused by the effects of acute phase proteins on the hypothalamus of many different bacterial products, like the endotoxins on gram-negative bacteria.