Biology Semester 2 Freshman Year - Unit 7: Cell Division
1/72
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
73 Terms
A normal human cell can only divide about…
40-60 times
A normal human cell can only divide about 40-60 times. What happens after this
apoptosis (programmed cell death)
Cells in the body divide at ___ rates.
different
Some cells don’t even divide. True or False
True
What are some examples of cells that constantly divide?
cells that line the gut
What is an example of cells that divide only rarely?
liver cells
What are some examples of cells that do not divide?
neurons and mature red blood cells
Why do cells divide?
1) To increase the Surface Area to Volume ratio - this allows for more efficient material exchange
2) To solve information overload in the cell
3) To replace damaged or dying cells (For example: when you have a cut, your cells are trying to rebuild that tissue)
4) Growth and Development of an Organism
5) Reproduction
If the cell is large, does it have a smaller or larger Surface Area to Volume Ratio?
smaller SA/V Ratio
If the cell is small, does it have a smaller or larger Surface Area to Volume Ratio?
larger SA/V Ratio
Is a larger or smaller Surface Area to Volume ratio better for the cell?
larger
When a cell divides, does its Surface Area to Volume Ratio increase or decrease?
increases (that is one of the reasons why cells divide. The increasing SA/V ratio allows for efficient nutrient exchange because there is more cell membrane available)
What are the two types of cell division?
Mitosis and Meiosis
What is Mitosis and in which organisms does it occur?
Results in cells that are identical to the original cell.
Body cells also known as somatic cells use this
Used for asexual reproduction as well
happens in eukaryotes
What is meiosis and which organisms does it occur in?
Results in cells that are genetically different from the original cell
Used by sex cells also known as gametes
occur in eukaryotes that sexually reproduce
What is asexual reproduction and which organisms does it occur in?
Results in producing genetically identical offspring (clones) from a single parent.
Used by single-celled organisms (prokaryotes) & some
Prokaryotes use Binary Fission
Pros = rapid population increase.
Cons = lack of genetic diversity, which means a decreased chance of survival.
Eukaryotes use Mitosis
Sexual Reproduction via Meiosis
Offspring produced inherit some of their genetic information from each parent
Occurs in eukaryotes that sexually reproduce
Formed by the fusion of reproductive cells of each parent (sperm & egg)
Pros: Increases genetic diversity, increased chance of survival
Cons: Requires more time
Sexual Reproduction =
Meiosis
Asexual Reproduction =
Mitosis
Mitosis occurs in what type of cells??
Somatic cells also known as body cells
Meiosis occurs in what type of cells??
Gametes (sex cells)
What are some limits to cell size?
The larger a cell becomes, there is…
Information overload - more demands placed on its DNA
(info in DNA is used to build molecules for cell growth)
Lowering Surface Area to Volume Ratio
The surface area is not increasing as fast as the volume increase
And less cell membrane available is less efficient for cells to exchange nutrients
Also causes a buildup of waste
Results in cell division
If the cell is not able to divide,
Apoptosis will occur
Programmed cell death
When cell is large, it has lower or higher Surface Area to Volume Ratio?
lower SA/V Ratio
When cell is small, it is lower or higher Surface Area to Volume Ratio?
higher SA/V Ratio
When a cell divides, does the Surface Area to Volume Ratio increase or decrease as the cell divides?
SA/V Ratio increases
Binary Fission - Asexual or Sexual Reproduction?
Asexual
Prokayotic Chromosomes
single circular DNA chromosome
undergo rapid cell division
Called binary fission
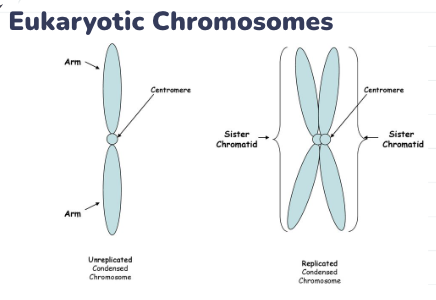
Eukaryotic Chromosomes
More DNA than prokaryotes
DNA tightly coiled around proteins called histones
forms chromatin
Chromatin supercoils to form chromosome
Somatic cells? - diploid or haploid
diploid
Somatic cell
every body cell EXCEPT reproductive cells
Another term for sex cells
gametes
Gametes = haploid or diploid?
haploid
Chromosomes in Somatic Cells
Somatic cells (aka body cells) are any cells of the living organism EXCEPT the reproductive (sex) cells
Somatic cells are diploid (2n) - two sets of chromosomes
Each human somatic cell contains a total of 46 chromosomes (23 from mom, 23 from dad)
N= the # of chromosomes in a single set
So 2N=46 for humans
Chromosomes in Gametes
Gametes are another term for sex cells (sperm and egg)
Gametes are haploid:
Haploid is represented by N, which is a cell with one set of chromosomes.
Gametes only contain 23 of the 46 chromosomes, so N=23
If you have a parent cell that contains 22 chromosomes, how many chromosomes would the daughter cells have in mitosis?
22 chromosomes
If you have a parent cell that contains 22 chromosomes, how many chromosomes would the daughter cells have in meiosis?
11 chromosomes
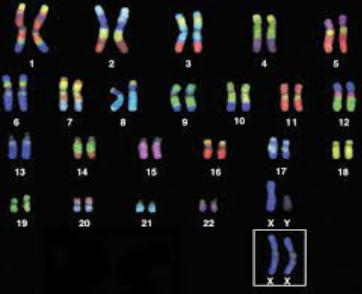
What is the imaging of chromosomes in a cell called?
Karyotype
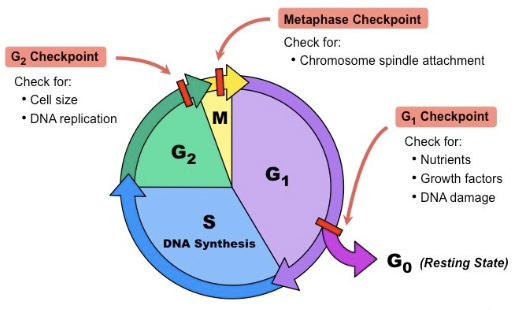
Eukaryotic Cell Cycle
The cell cycle is composed of interphase (G1, S, and G2, phases), followed by the mitotic phase (mitosis and cytokinesis)
Interphase:
G stands for Gap, S stands for Synthesis
G1 Phase: Cell growth, synthesizes proteins
S Phase: DNA replication - doubles DNA
G2 Phase: Preparation for division - more growth, organelle production & checks DNA before Mitosis
Mitotic Phase:
Mitosis occurs - splitting of the nucleus
Cytokinesis -cytoplasm division that officially splits into two daughter
cells
In what phase is DNA is in its uncondensed form, chromatin?
Interphase
What is the longest stage of the cell cycle?
Interphase
What happens in the Mitotic Phase?
Genetic information that is contained in the nucleus must be condensed into packages of DNA called chromosomes
Those replicated chromosomes are separated into two new nuclei, so daughter cells are exact copies of the parent cell.
True or False: Interphase includes G1, S, G2 phases
True
What happens in the G1 (Gap 1) phase in the eukaryotic cell cycle?
Cell growth and synthesis of proteins
what happens in the S Phase (Synthesis) in the eukaryotic cell cycle?
DNA gets copied (also known as DNA Synthesis)
What happens in the G2 (Gap 2) phase of the eukaryotic cell cycle?
Prep for division
more growth
organelle production
checks DNA before the Mitotic Phase (PMAT)
What happens in Prophase in Mitosis?
Genetic material condenses into chromosomes and become visible
Nucleolus disappears & Nuclear envelope begins to break down
Spindle fibers form
What happens in Metaphase in Mitosis?
Centromeres of chromosomes line up on metaphase plate
Spindles connect centromere of each chromosome to the two poles
What happens in Anaphase in Mitosis?
Sister chromatids begin to separate/move apart
Each sister chromatid is now considered an individual chromosome
What happens in Telophase in Mitosis?
Chromosomes begin to decondense into chromatin
Nuclear envelope reforms
Nucleolus becomes visible
Spindle fibers break apart
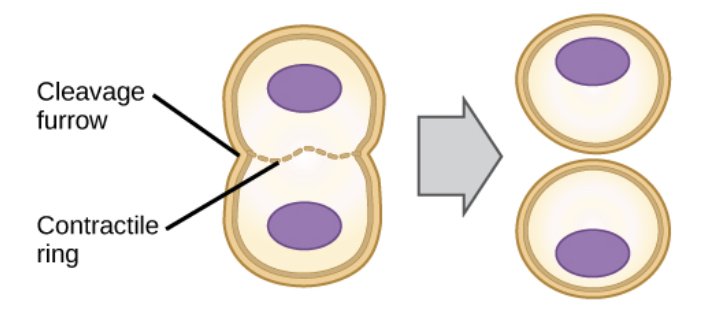
What happens in Cytokinesis?
the cytoplasm divides and makes two cells
What happens in Cytokinesis in Animal Cells?
The cell membrane is drawn inward until cytoplasm pinched in 2 equal parts
What happens in Cytokinesis in Plant Cells?
cell plate forms halfway between divided nuclei
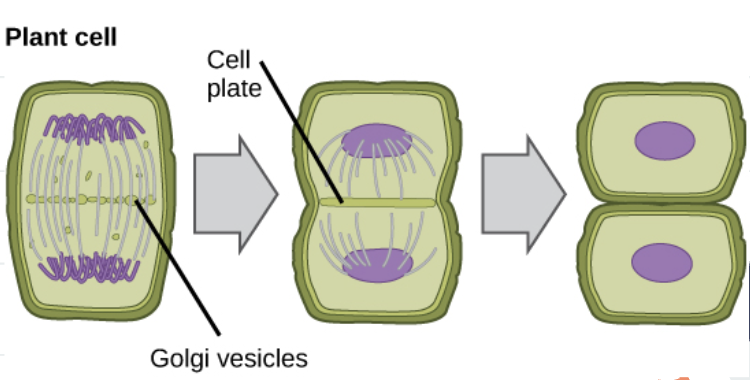
Does the cell cycle happen randomly?
No
Can the cell cycle (growth or division) be turned on or off?
Yes (this is done by internal and external regulators)
What are Internal Regulators?
Proteins that allow the cell cycle to proceed only when certain things in the cell have occurred
What is an example of an internal regulator?
Cyclins (they regulate the timing of the cell cycle in eukaryotic cells)
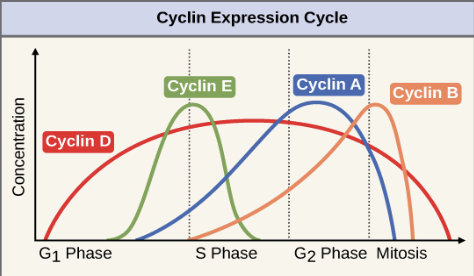
What are external regulators?
Proteins that respond to events outside the cell
Direct the cells to speed up or slow down the cell cycle (controls can be turned on or off)
Important for embryonic development (baby development) and wound healing
What are examples of external regulators?
Growth Factors - stimulate growth and division
Contact inhibition - cells stop dividing when they come into contact with neighboring cells
What is contact inhibition?
when cells stop dividing when they come into contact with neighboring cells
(cancer cells do not respond do this external regulator and this leads to uncontrolled cell growth)
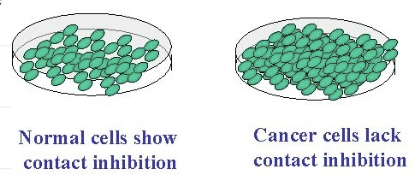
What is Apoptosis?
Programmed cell death
happens when things aren’t right in the cell
Goal: eliminate dangerous mutations
When apoptosis doesn’t function properly…
Can lead to cancer because damaged cells multiply rapidly
Then these mass of cancer cells become a tumor
Why is there uncontrolled cell division in cancerous cells?
They do not respond to the signals that regulate cell growth and division
Due to a defect in genes that produce the proteins that become regulators
Gene defects could be from tobacco use, radiation, other defective genes, viral infection
P53 - a gene that is commonly defective in cancer cells
Normally, it stops the cell cycles until all chromosomes have been
replicatedBecause of the defect in this gene, cells lose info needed to respond to signals that regulate
Then leads to rapid, uncontrolled cell division
leads to a mass of cells called a tumor
What is the gene that is commonly defective in cancer cells?
P53
What are stem cells?
undifferentiated cells (lack a specific job or function)
What are specialized cells?
They perform one job and have physical and chemical differences that allow them to perform one job. (they get this job during cellular differentiation)
What are the benefits of stem cells?
Stem cells are helping to develop a new field of regenerative medicine, in which undifferentiated cells are used to repair or replace damaged cells and tissues.
Scientists have found adult stem cells in various tissues and are also able to revert some specialized cells back
What is a diploid cell and what cells are diploid cell in our bodies?
Diploid cell means that we have 2 sets of chromosomes (2n) and somatic cells in our body have 2 sets of chromosomes.
What is a haploid cell and what cells are haploid in our bodies?
Haploid cell means that we have 1 set of chromosomes in and gametes (sex cells: sperm, eggs) in our body have 1 set of chromosomes.
How many chromosomes does a gamete have if a normal, somatic (body) cell has 22 chromosomes?
11 chromosomes (This is because gametes are haploid (n) meaning they have only one set of chromosomes. Somatic (body) cells are diploid and they have 2 (2n) set of chromosomes)
What organelle in the cell makes the spindle fibers which is used to split the sister chromatids apart?
centrioles
What is a zygote?
A single cell that is the result of the fusion of the sperm and the egg. Then this zygote keeps dividing and becomes a blastocyst. It then becomes an embryo. Its next stage is a fetus.
What does Mitosis and Meiosis mean?
the splitting of the nucleus
Does mitosis occur in prokaryotes?
No (Why? Because prokaryotes lack a nucleus. Mitosis and Meiosis both refer to the splitting of the nucleus and because there is not nucleus in a prokaryotic cell, it just goes through binary fission for reproduction.
What is the G0 stage in cell division?
Rest Stage (the cells are active, just not preparing for division. It also happens when conditions are not favorable for division. Ex. neurons)