Para midtherm past test exams Cartes | Quizlet
1/77
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
78 Terms
Which one of the following stages dors not happen in Oestrus ovis life cycle ?
a)Egg
b)Larva 1
c)Larva 2
d)Larva 3
a)Egg
Which one of the following stages does not happen in Anoplura life cycle ?
a) Egg
b)Larva
c)Nymph
d) Adult
b)Larva
What is the name of the special appendix in female Anoplura ?
a) Gonopods
b) Claspers
c) Cercus
d) Cirrus
a) Gonopods
This structure is useful to classify different species of fleas...
a) Antenna
b) Mouthparts
c) Ctebidiums/Combs
d) Sensilium
c) Ctebidiums/Combs
Which one, of the following parasites is not solenophagous ?
a) Pulex flea
b) Aedes mosquito
c) Phlebotomus sandfly
d) Pediculus lice
c) Phlebotomus sandfly
In the flea population, what is the amount of larvae ?
a) 5%
b)10%
c)35%
d) 50%
c)35%
What is the WRONG statement about Anopheles mosquitoes ?
a) Only females are hematophagous.
b) Are vectors of malaria.
c) Larvae have respiratory siphon.
d) Have a complete metamorphosis.
c) Larvae have respiratory siphon.
What is the wrong statement about Phlebotomus ?
a) Only females are hematophagus.
b) Have a short proboscis.
c) Males have appendages to hold the female during the copula.
d) Lay eggs in standing water.
d) Lay eggs in standing water.
9. Where are located the spiracles in fly larvae ?
a) After the last coxa
b) Before the thorax.
c) They don't have spiracles, but gills.
d) All the given options are wrong
b) Before the thorax.
Tse-tse flies belong to genus...
a) Stomoxys
b) Hippobosca
c) Glossina
d) None of the given options
c) Glossina
What is the function of the halteres ?
a) To provide cement during egg laying.
b)To provide proprioceptive information.
c)Are piercing mouthparts.
d)Are breathing structure
b)To provide proprioceptive information.
12. Who are the hosts of genus Pseudolynchia?
a) Birds
b)Horses
c)Humans
d)Ruminants
a) Birds
13. Flies develop the pupation in the ground, except for :
a) Gasterophilus
b) Hypoderma
c) Melophagus
d) Oestrus
c) Melophagus
What is the function of the apical gland in trematodes life cycle ?
a) To cross throughout the snail tegument.
b) To detect the snail's chemical track.
c) Is related to phototaxis.
d) Creates the shell for the metacercaria.
a) To cross throughout the snail tegument.
Detect the WRONG statement about Schistosoma eggs.
a) They have a spine.
b) Are embryonated when laid.
c) They are not operculated.
d) The embryo have to break the eggshell.
d) The embryo have to break the eggshell.
Wich is the infective stage of Fasciola?
a) Cercaria
b) Furcocercaria
c) Metacercaria
d) None of the given answers
c) Metacercaria
Galba truncatula affected by larval stages of Fasciola hepatica will suffer...
a) Poor body development.
b) Lethargy.
c) Death.
d) None of the given options
c) Death.
The function of the Hailer's organ is :
a) To detect the light.
b) To detect host's smell.
c) To detect host's breathing
d) All the options are right.
d) All the options are right.
What stage is skipped in D.dendriticum life cycle ?
a) Miracidium
c) Sporocyst
b) Redia
d) Cercaria
b) Redia
Who is Schistosoma mansoni's final host ?
a) Cattle
b) Human
c) Equids
d) Carnivores
b) Human
What's the difference among Fasciola hepatica and Fasciola magna?
a) Fasciola hepatica is bigger than Fasciola magna.
b) Cephalic cone is absent in Fasciola hepatica.
c) Fasciola hepatica cannot affect humans.
d) None of the given options.
d) None of the given options.
A parasite able to affect a wide range of host is a/an...
a) Eurixenic
b) Stenoxenic
c) Oligoxenic
d) Monoxenic
a) Eurixenic
Where is located an histozoic parasite ?
a) In the cells
b) In the nucleus of the cell.
c) In the cytoplasm of the cell.
d) In the tissues.
d) In the tissues.
Animal species who harbor parasites and do not suffer (or not too much) a parasitic disease.But contribute to the spreading.
a) Bridge host b) Vector
c) Reservoir
d) Paratenic host.
c) Reservoir
An habita shared by different parasite species is an example of...
a) Polyparasitism.
b) Hyperparasitism.
c) Convergent parasitism.
d) None of the given options
a) Polyparasitism.
Because Hyperparasitism is when a parasite parasitizes an other parasite.
Which one, of the following routes of infection, is the most common one ?
a) Genitourinary
b) Transplacental
c) Oral
d) Nasal
c) Oral
Sensorial hair located in the epicuticle of arthropods :
a) Microtriquia
b) Pedicel
c) Gill
d) Seta
d) Seta
Which one, of the following, is not segment of the arthropods thorax:
a) Prothorax
b) Interthorax
c) Mesothorax
d) Metathorax
b) Interthorax
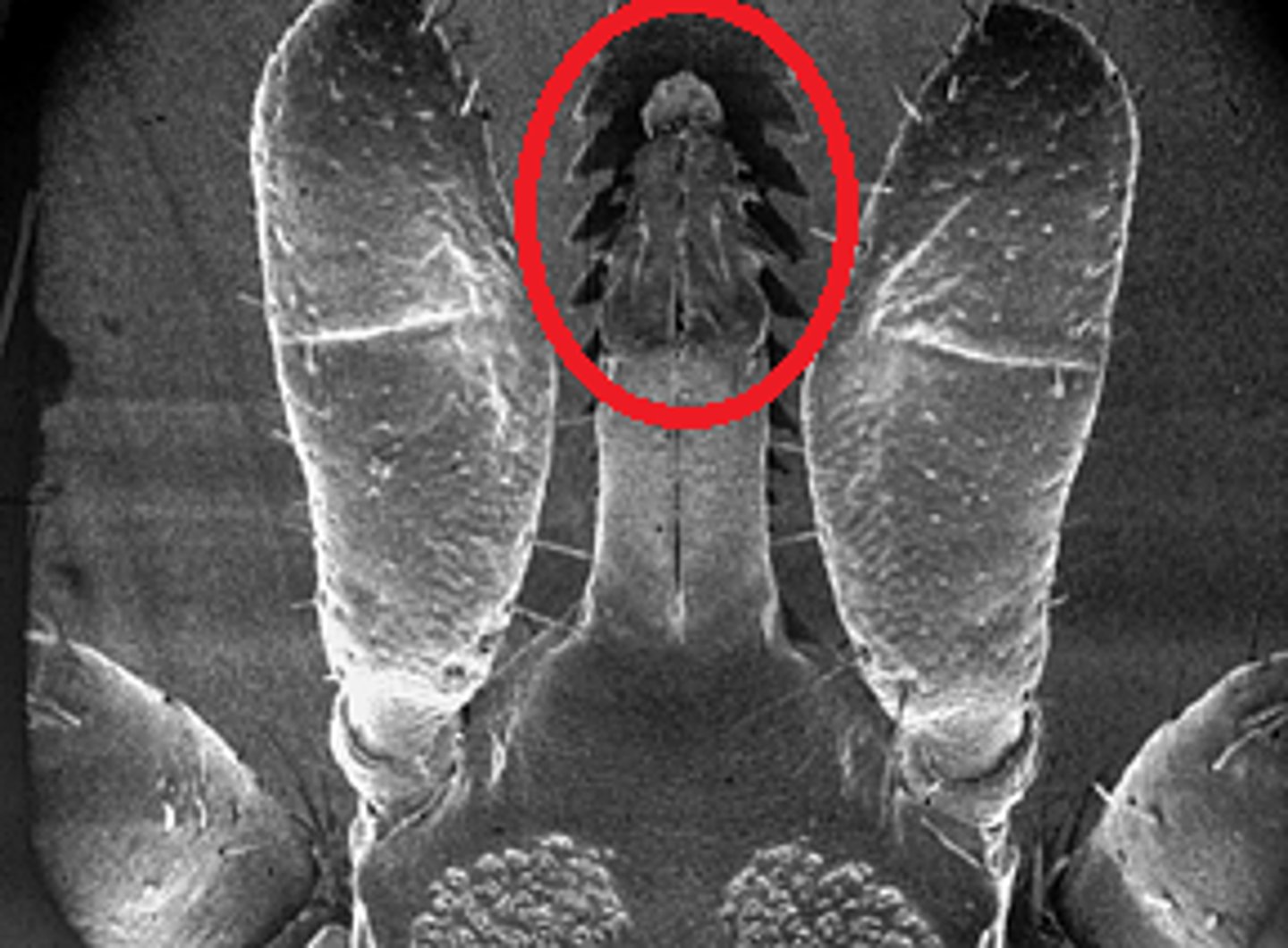
29. What is the structure circled in red?
a) Chelicerae
b) Hypostome
c) Palps
d) Proboscis
b) Hypostome
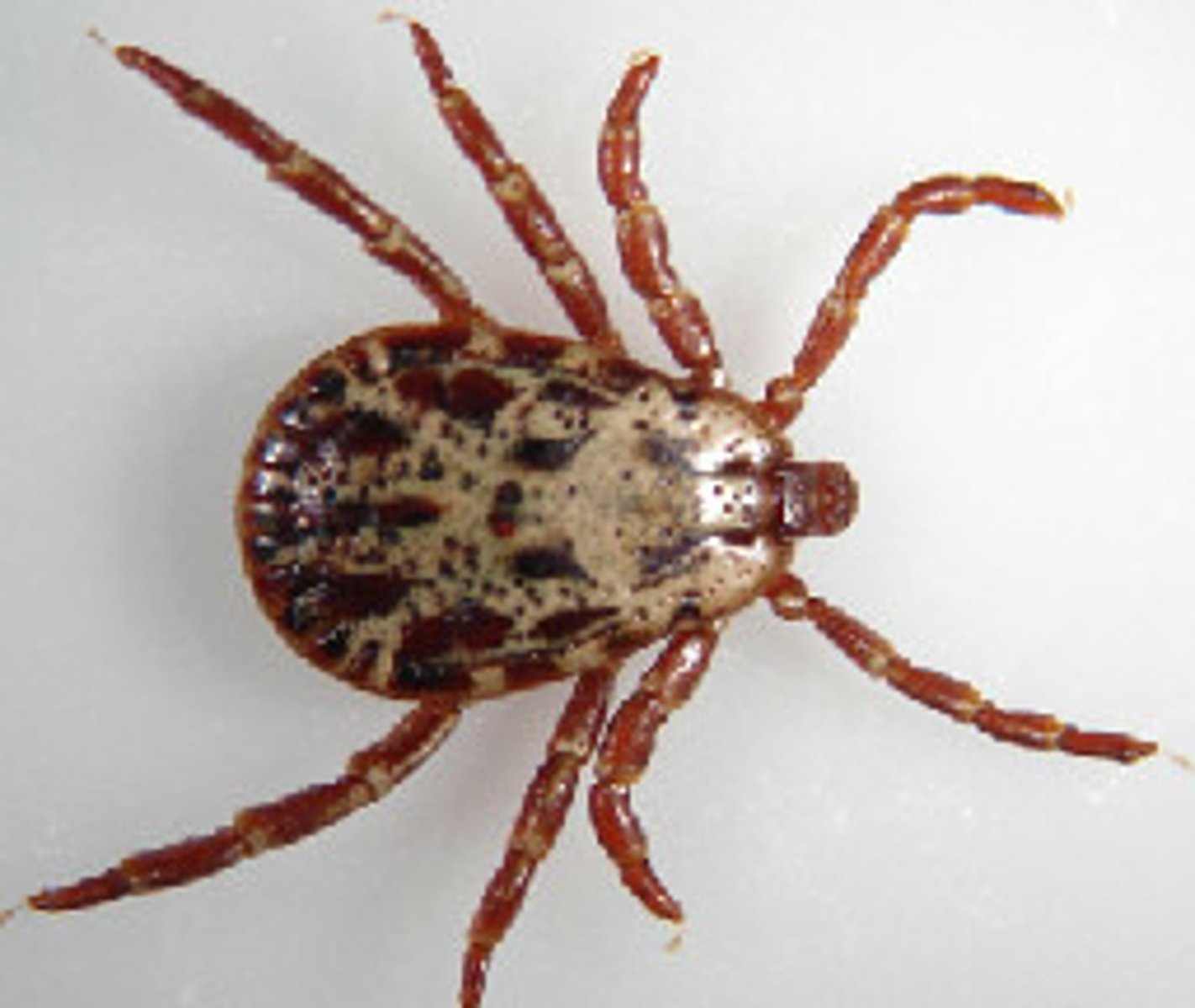
How do we differentiate the sex in ticks ?
a) With the dorsal scutum
b) With the shape of the antennae
c) With the body size
d) None of the given options
a) With the Dorsal scutum:
This is the hard shield on the back.
Male ticks: Scutum covers almost the entire dorsal surface.
Female ticks: Scutum covers only part of the dorsal surface, allowing the body to expand during blood feeding. ✅
Based on this morphological feature shown on the image, which of the following genera does this tick most likely belong to?
a) Ixodes
b) Rhipicephalus
c) Hyalomma
d) Dermacentor
d) Dermacentor

African swine fever (ASF) is a highly contagious viral disease affecting domestic and wild pigs. The primary vector responsible for transmitting the African swine fever virus belongs to which genus?
A. Ornithodoros
B. Ixodes
C. Rhipicephalus
D. Amblyomma
A. Ornithodoros
The ear mange in cats is produced due to the presence of:
a. Solenoptes
b. Otadectes
c. Psoroptes
d. Knemidocoptes.
b. Otadectes
About Sarcoptes scabiei:
a. Can produce mange in human beings
b. Has short limbs
c. Is transmitted due to direct contact
d. All the above is right
d. All the above is right
The hematophagus fly, popularly known as "horse ked" or "louse fly", with limited capability to fly, belongs to Genus:
a. Stomoxys
b. Hippobosca-briga
c. Pseudolynchia
d. Glossina
b. Hippobosca-briga
Dermanyssus, also known as bird's red mite:
a. Can affect human beings
b. Feeds in lymph
c. Is active during the daytime
d. Hides among feathers
d. Hides among feathers
only occasionally biters humans
Mark the right statement in relation with ticks from Argasidae Family:
a. Are known as soft ticks
b. Are very specific to the Host
c. Are transmitted by direct contact
d. Adults have three pairs of limbs
a. Are known as soft ticks
For egg laying, Phlebotomus mosquitoes will need...
a. Running water
b. Standing water
c. Fecal material
d. Decomposing organic material
d. Decomposing organic material
Mark the wrong statement about Crab-louse Phthirus pubis:
a. Is found commonly in eyebrows
b. Affects human beings
c. Is considered a sexually transmitted diseasee
d. Feeds on blood
a. Is found commonly in eyebrows
Pathogens transmitted by Siphonaptera can produce:
a. Chagas disease
b. Sleeping sickness
c. Bubonic plague
d. Blue tongue
c. Bubonic plague
Pathogens transmitted by members of Genus Triatoma can produce:
a. Chagas' disease
b. Sleeping sickness
c. Bubonic plague
d. Blue tongue
a. Chagas' disease
because:
-Blue tongue=biting midges (Culicoides)
-Sleeping sickness=tsetse flies (Glossina)
In order to differenciate males and females in subfamily Culicinae we will focus our attention on:
a. The antennae
b. The abdomen
c. The limbs
d. The eyes
a. The antennae
The best adapted arthropods for jumping are:
a. Lice
b. Ticks
c. Bedbugs
d. Fleas
d. Fleas
In relation to Haller's organ:
a. Is located in the first pair of limbs
b. Is a sensitive organ
c. Is typical of ticks
d. All the above is right
d. All the above is right
About Phlebotomus, mark the WRONG statement:
a. Have hairy bodies and wings
b. Are the vectors of Leishmania
c. Are smaller than culicids
d. Both male and female are hematophagus
d. Both male and female are hematophagus
because: only female
Related to Varroa:
a. Are parasites of honey bees
b. Are not visible macroscopically
c. Are insects
d. Can parasitise human beings
a. Are parasites of honey bees
Which is the most characteristic structure of Sporocysts?
a. The germinative cells
b. The ciliated cover
c. The tail
d. None of the above
a. The germinative cells
+ do NOT have ciliated cover
The difference between infestation and infection is...
a. Infestation is related with external parasites, while infection is for the rest
b. Infestation is for macroscopic parasites, while infection is for the rest
c. There are no differences among both concepts
d. All the above is wrong
a. Infestation is related with external parasites, while infection is for the rest
an organism that's not essential to parasites life cycle but whole involvement increases the chances of the parasite reaching its definitive host is called:
a. intermediate
b. paratenic
c. bridge
d. none of above
b. paratenic
What is the stage of the trematode that first gets developed in the intermediate host and contains numerous germinative/pluripotential cells?
a. redia
b. cercaria
c. miracidium
d. sporocyst
d. sporocyst → have ability to clone themselves from pluripotential cells (first larval stage that develops inside the intermediate host (usually a snail))
which one of the next, is an arthropod whose life cycle is completely done on the host?
a. mange producer mites
b. fleas
c. ticks
d. myasis producer flies
a. mange producer mites → dig tunnels, hatching in tunnels, mate on host, transmission thru direct contact so doesn't leave host at all
what parasite is responsible of the ear mange in cats?
a. sarcoptes
b. knemidocoptes
c. psoroptes
d. otodectes
d. otodectes
regarding route of infection, ticks perform a cutaneous route
a. with active penetration
b. with passive penetration
c. without penetration
d. none of above
c. without penetration → body of tick remains outside of host, mange mites don't cross all layers of skin
mark right statement in relation with ixodid ticks (hard ticks)
a. capitulum is dorsally visible
b. are very specific to host
c. larvae and nymphs have 3 pairs of legs
d. legs are finished in suckers or pedicels
a. capitulum is dorsally visible → yes, can see head, soft ticks can't see head
sensorial hairs located on surface of arthropods
a. pilae
b. setae
c. trichae
d. chitinae
b. setae
demodex mites have very characteristic body shape, with a long
a. gnatosoma
b. propodosoma
c. podosoma
d. opisthosoma
d. opisthosoma → last part
demodex presence and effects in human beings can be related with
a.age
b. sex
c. immunity status
d. all of above
d. all of above
function of haller's organ is detection of
a. CO2
b. vibrations
c. temp
d. all of above
d. all of above
this tick is able to transmit african swine fever in swine
a. ornithodoros
b. argos
c. rhipicephalus
d. ixodes
a. ornithodoros
bubonic plague is transmitted by
a. bedbugs
b. ticks
c. flies
d. fleas
d. fleas → of black rats, not specific
mallophaga lice
a. only parasitic to birds
b. feed on feathers and hairs
c. are low-specific for host
d. have 4 pairs of limbs
b. feed on feathers and hairs
sensorial organs in mosquitoes
a. antennae
b. palps
c. haller's organ
d. 1st limb
a. antennae
what is route of infection for schistosoma bovis?
a. percutaneous by vector
b. percutaneous by action of parasite itself
c. oral
d. nasal
b. percutaneous by action of parasite itself → in water, can swim and have ability to cross healthy skin
immature stages in this parasite are NOT related to water
a. culex
b. schistosoma
c. fasciola
d. dicrocoelium
d. Dicrocoelium → all life cycle is terrestrial
don't pupate on ground
a. melophagus
b. hypoderma
c. oestrus
d. gasterophilus
a. melophagus → lost their wings, won't abandon their host, whole LC on host, including pupation, usually sheep
Affect ruminants
a. melophagus
b. hypoderma
c. oestrus
d. gasterphilus
b. hypoderma → cattle
target loc of adult dicrocaelium dendriticum
a. mesenteric veins
b. gallbladder
c. biliary vessels
d. none
c. biliary vessels → if there's a lot, can find them there too, ex: fasciola
because
-Mesenteric veins - typical of Schistosoma adults.
-Gallbladder - secondary site only in heavy infections.
chain of segments composing most of cestodes body is called
a. strobila
b. rostellum
c. scolex
d. none
a. strobila
in pseudophyllidea, embryo with a ciliated shell is called
a. hexacanth embryo → typical of cyclophyllidea
b. coracidium
c. procercoid plerocercoid
d. Scolex
b. coracidium
immature stage consisting of a vesicle full of liquid with many protoscolexes inside it is called:
a. cysticercoid
b. cysticercus
c. coenurus
d. hydatid cyst
d. hydatid cyst
regarding life cycle of dibothriocephalus intus, mark wrong answer
a. bothria are attachement organ of adult stage
b. consumption of raw fish is related to infection by DH
c. life cycle involves 1 IH and 1 DH
d. Life cycle involves 2 IH
c. life cycle involves 1 IH and 1 DH
BECAUSE:has 2 IH humans can be affected
DH of anoplocephala a.
a. galliform birds
b. dogs
c. equine
d. ruminants
c. equine
because: are cestodes (tapeworms) of horses and other equids.
what is the IH of moniezia if DH is cattle and sheep?
a. oribatid mites
b. fleas cattle
d. ants
d. Snails
a. oribatid mites
mark wrong statements of dipylidium
a. fleas are IH
b. dogs, cats ... can be affected
c. cyticercus is immature stage
d. they have a double set of genital organs
c. cysticercus is immature stage
because: cysticercoid, not a cysticercus.
which one, of following cestodes, is not zoonotic
a. dipylidium caninum
b. taenia solium
c. hymenolepis nana
d. raillietina tetragona
d. Raillietina tetragona
Because: only poultry
IH of taenia saginata
a. human
b. dog
c. galliform birds
d. none
d. none → cattle = IH
coenurus cerebralis is immature stage of
a. taenia multiceps
b. taenia serialis
c. taenia hydatigena
d. echinococcus multilocularis
a. taenia multiceps → ~ "multi heads" related with coenurus cerebralis who has lots of heads
IH of taenia pisiformis
a. cattle
b. sheep and goats
c. lagomorphs
d. none
c.lagomorphs (rabbits and hares), where the cysticercus develops in the peritoneal cavity. Where Carnivores(DH) ingest them.