Major Opioids and Chronic Opioid Therapy
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
____Receptor: Mediates analgesia, respiratory depression, euphoria, and constipation.
___Receptor: Modulates visceral and chemical pain.
____Receptor: Influences inflammatory and mechanical pain.
μ-
κ-
δ-
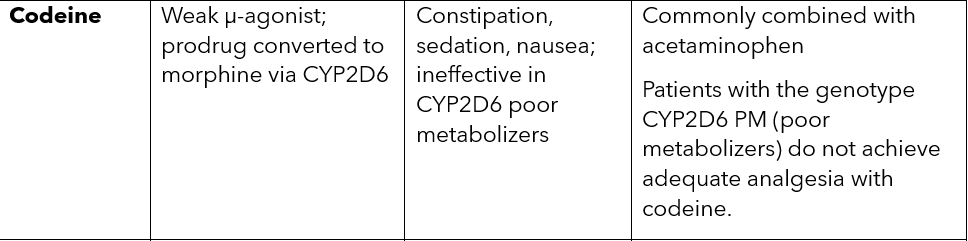
codeine MOA, SE and special notes
morphine MOA, SE and special notes

oxycodone MOA, SE and special notes

hydromorphone MOA, SE and special notes

meperidine MOA, SE and special notes:

fentanyl MOA, SE and special notes:

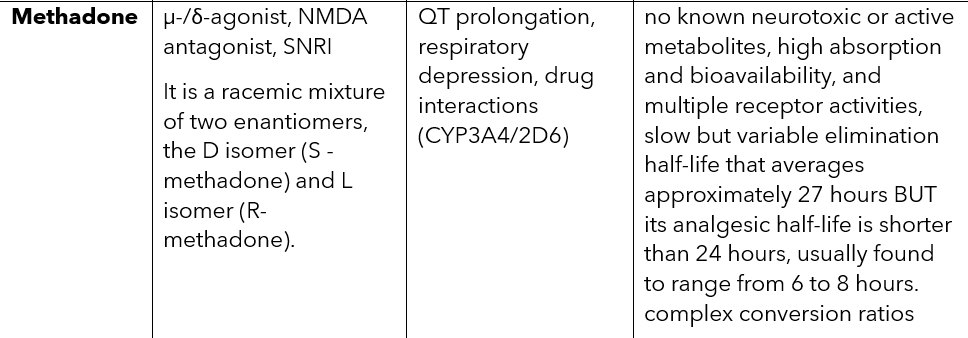
Methadone MOA, SE and special notes:
The onset, duration, and intensity of analgesia depend on the delivery of drug to the target AND ______
the length of time that the receptor is occupied.
The number of receptors occupied and the length of time that the opioid activates its target receptor depend on the ____
perfusion
plasma concentration
pH
permeability coefficient of the drug
o The cytochrome P-450 (CYP) system contains two polymorphic isoforms that metabolize certain opioids.
The first CYP isoform, responsible for the biotransformation of codeine, oxycodone, and hydrocodone, is ___.
It is estimated that up to 10% of ___individuals lack this enzyme, thus making them “poor metabolizers” of certain opioids
o The ____ isoform of the CYP system is involved in the biotransformation of fentanyl and methadone to their inactive forms.
2D6
white
3A4
The goal of effective opioid therapy for chronic pain is to provide ________
sustained analgesia over regular intervals.
Fixed vs PRN dosing:
Fixed: consistent blood levels; useful for chronic pain. One problem for opioid-naïve patients who receive fixed doses of opioids that have longer half-lives is that they may experience excessive side effects or toxicity because of the difficulty in predicting the exact opioid requirement and potential accumulation
PRN: preferred during titration or for breakthrough pain.
_______ are generally used for acute pain, whereas ____are prescribed for patients with chronic pain syndromes.
Short acting opioids [SAO]
LAOs
____are often combined with other analgesics such as acetaminophen, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), or aspirin, which may offer drug-sparing effects because less medication may be used.
BUT now you need to look out for harm to ____
SAOs
major organs from the nonopioid components (e.g., acetaminophen, NSAIDs, aspirin). Be aware of renal and liver function problems, as well as the potential harm that could occur to the GI system.
_______uses established conversion ratios or tables to determine an equivalent dose of the new opioid or route that should provide comparable pain relief to the previous one.
Equianalgesic conversion
Most common SE of opioids:
management of this SE:
Constipation (most common):
No tolerance develops.
Managed with senna, bisacodyl, lactulose; stool softeners ineffective alone.
Methylnaltrexone a quaternary derivative of naltrexone- μ-antagonist. It blocks the peripheral actions of opioids while sparing their central analgesic effects and reverses the slowing of bowel motility
Alvimopan: peripheral μ-antagonist that can treat constipation without affecting analgesia or precipitating withdrawal.
Nausea/Vomiting is also common w/ opipids
Usually transient (___ days).
Mechanisms: ____
Treated based on symptom profile -___
2–3
vestibular activation, CTZ stimulation, constipation.
(e.g., ondansetron, meclizine, scopolamine).
Pruritus w/ opioids
Common with _____opioids.
Related to ____release which activates C-fiber itch receptors on C fibers that are distinct from pain-transmitting C fibers.
_____(μ-antagonist/κ-agonist) effective if antihistamines fail.
neuraxial
histamine
Nalbuphine
Sedation w/ opioids
Initial effect; typically resolves in __ days.
Persistent sedation management: ____
Respiratory Depression w/ opioids
μ-receptor inhibition in the ____.
Naloxone used cautiously. Often packaged in an ampule containing 0.4 mg, which can then be diluted in 10 mL of normal saline and administered as ______
Use pulse oximetry if risk is high.
7
lower dose, opioid rotation, psychostimulants if needed.
brainstem
0.5-mL boluses (0.02 mg/0.5 mL) every 2 minutes
hormonal and immune effects w/ opioids:
sleep disturbances w/ opioids:
Hormonal Effects:
↓ testosterone, LH, estrogen → sexual dysfunction, depression, fatigue.
Immune Suppression:
Exogenous opioids may impair immunity via central and peripheral mechanisms.
It has been postulated that central opioid receptors mediate peripheral immunosuppression via the hypothalamic pituitary-adrenal axis and autonomic nervous system
Sleep Disturbances:
Reduced REM/delta sleep; likely via GABAergic inhibition.
define opioid tolerance:
Tolerance
Reduced response over time → dose escalation.
May involve NMDA receptor activity; ketamine/dextromethorphan studied (limited clinical evidence).
Opioid rotation can mitigate tolerance.
define physical dependence :
what medication can help with withdrawal S&S?
Physical Dependence
Predictable with chronic use; not the same as addiction.
Withdrawal: anxiety, nausea, chills, diarrhea; managed with slow tapering and clonidine.
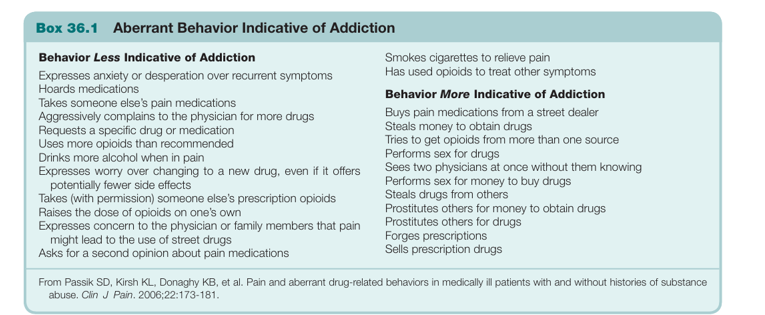
define opioid addiction: EX
Addiction
Defined by maladaptive use despite harm.
Different from undertreated pain (relieved by appropriate dosing).
Red flags: drug-seeking, forging prescriptions, using multiple providers.
EX of aberrant behaviors that are indicative of addiction
key points for opioid prescribing
Opioids are not first-line for chronic non-malignant pain.
Requires thorough evaluation:
Functional status
Psychiatric/substance abuse history
Organ function (hepatic, renal, pulmonary)
Prior opioid experience
Informed consent, opioid agreements, urine drug screening, and clear treatment goals are essential.
treatment goals w/ opioids:
Pain relief + improved function—not elimination of pain alone.
Establish clear end points: e.g., improved ADLs, return to work.
Prescribing Considerations for opioids:
Start with SAOs in opioid-naïve patients.
Transition to LAOs if sustained control is needed.
Use opioid-sparing strategies (e.g., adjuvants, procedures).
Monitor for side effects, aberrant behavior, and treatment efficacy.