DESGIN TEC - Topic 3 : Modeling
1/45
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
46 Terms
Concept modeling
Originates in the mind, primary used is to outline the principles, processes basic functions of a design or system
Graphical Modeling Examples
Sketches (napkin sketches), Drawings, Flow Charts
Physical Modeling Examples
Card, Clay, Rapid Prototype (3D printing), Balsa wood, Blue styrofoam
Virtual Modelling Examples
(CAD) Computer- Aided Design, Surface or Solid Modeling, FEA, DATA modeling
Service Design
The activity of planning and organizing people, infrastructure, communication and material components of a service in order to improve its quality and the interaction between service provider and customers
Advantages and Disadvantages of Concept Modeling
Advantage: Shares “big picture”, Makes it easy for non- designers and non-technical people to understand a complex idea
Disadvantage: Lacks detail, Can be misinterpreted, can be misleading if smaller or bigger than actual product
Graphical Model
A 2D and 3D visualization of an idea, often created on paper or through software
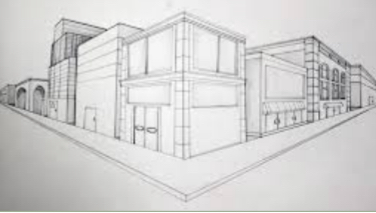
Perspective drawing
Shows what a product will look like when finished in a more lifelike way
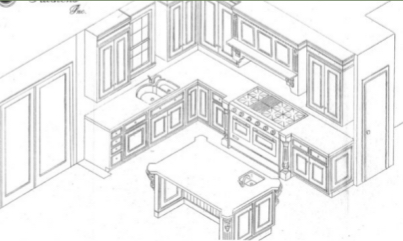
Isometric Drawing
Used to accurately show what a product will look like when it is finished
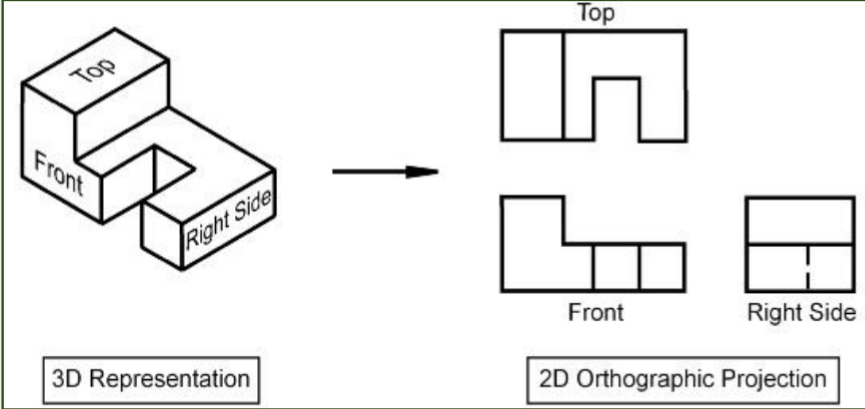
Orthographic Projection
Drawing a 3D object from different directions. ( front, side, top, bottom; must have at least 3 views)
Usually developed when its almost ready to manufacture
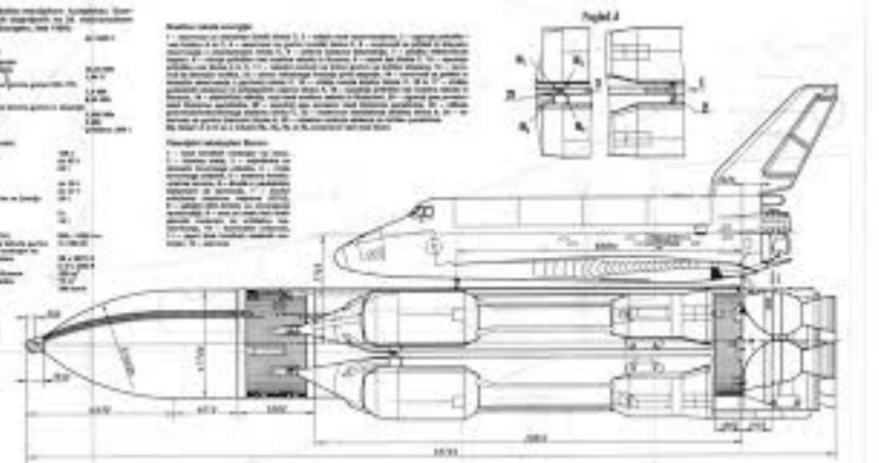
Scale Drawings
Show an object in proportion to its actual size. Used when something needs to be presented accurately or planning or manufacturing
Sketching
Spontaneous and free hand representation and used early in design process
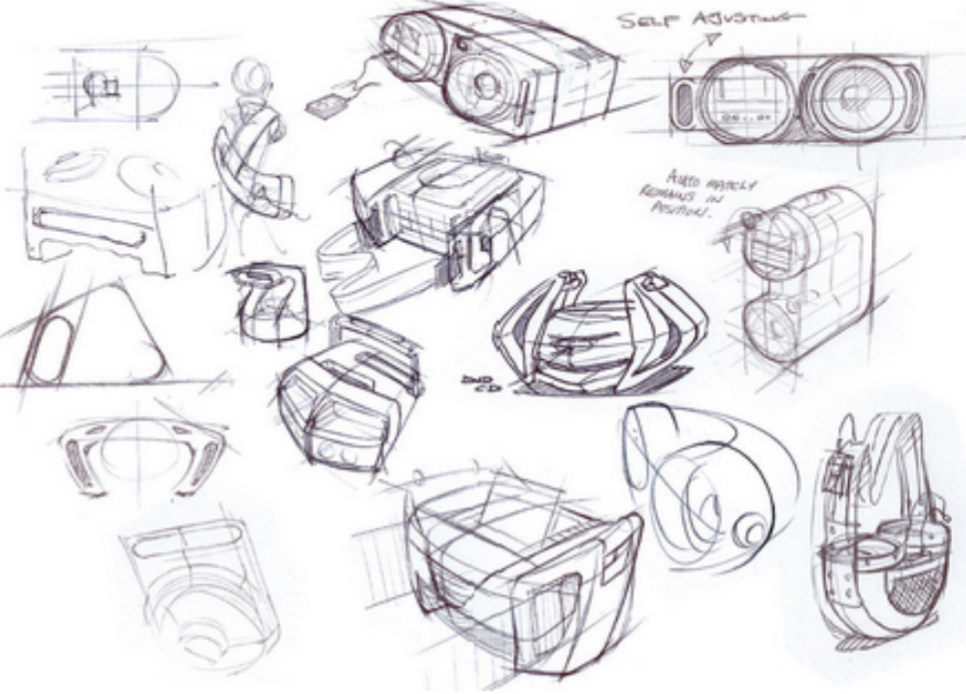
Formal Drawings
Ruled out and accurate drawings, techniques tend to be use in the development phase of a design process
Part Drawing
Provides information to assembly a product in a similar way that an assembly drawing does with additional benefit of having a list of parts [LOP] or Bill of Materials [BOM].
Helps to know which part is broken and how to repair it
![<p>Provides information to assembly a product in a similar way that an assembly drawing does with additional benefit of having a list of parts [LOP] or Bill of Materials [BOM]. </p><p>Helps to know which part is broken and how to repair it </p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/33550649-eed6-4d65-9430-01f5a06bf65f.jpeg)
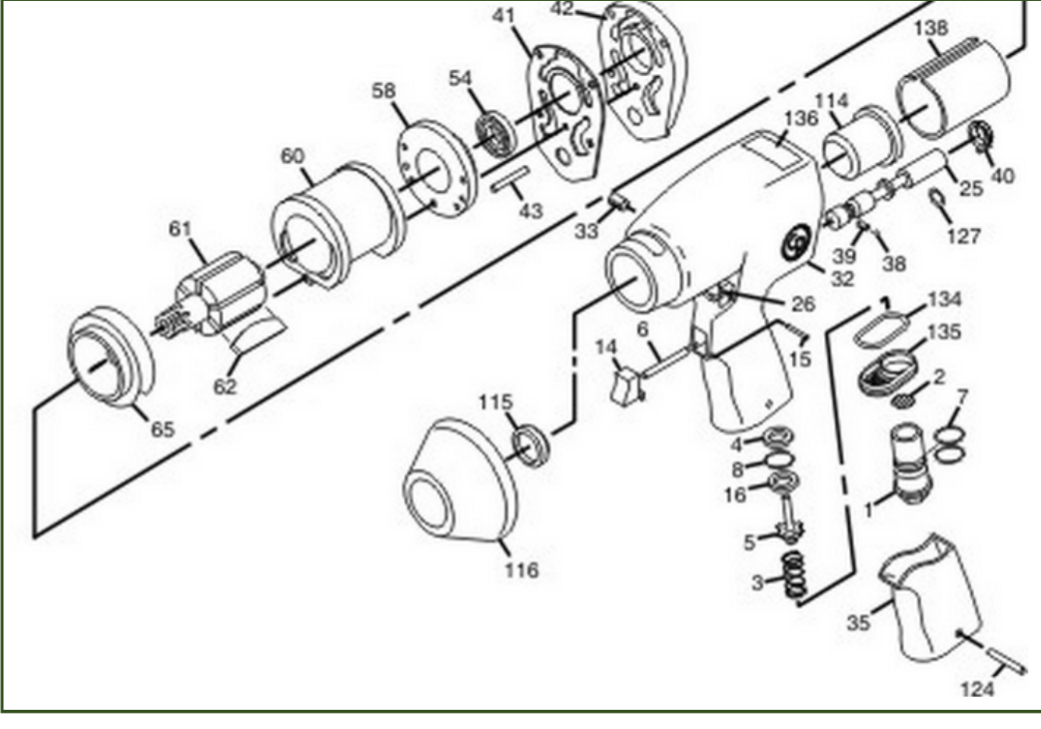
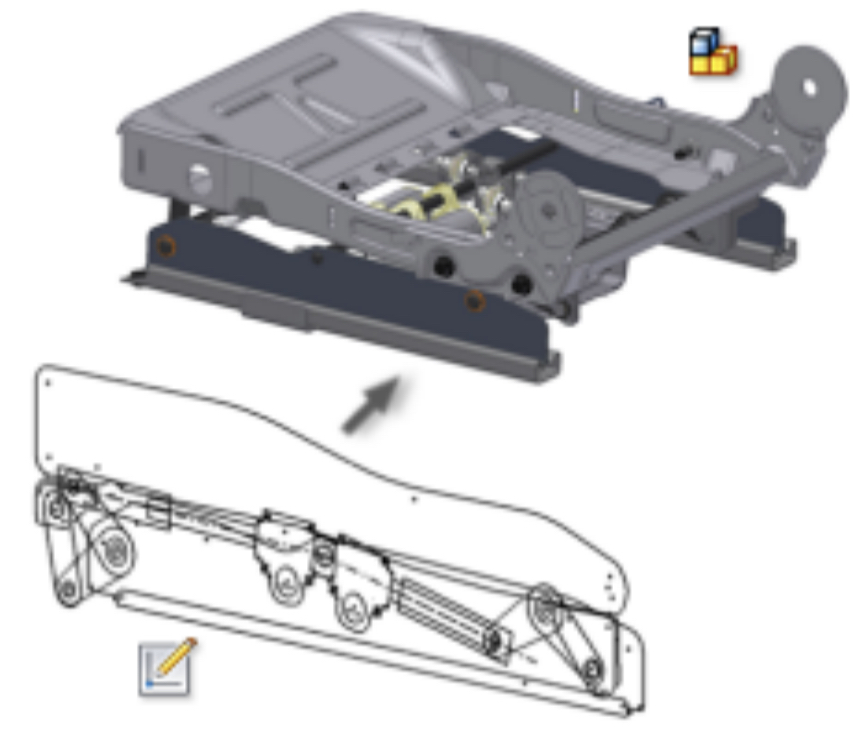
Assembly Drawings (Exploded isometric)
Shows how parts of a product fit together. Often used to show how to assemble parts of model kits and flat packet furniture
Algorithm
A self- contained step-by-step set of operations to be preformed
Physical Modelling
A three-dimensional, tangible representation of a design or a system. (Appearance model)
Advantages and Disadvantages of physical Modelling
Advantages: They allow the used to visualize the product and identify any problems easily on, understand how product would look it real life
Disadvantages: Can be a time consuming process, can’t be manipulated the same way a digital model can be
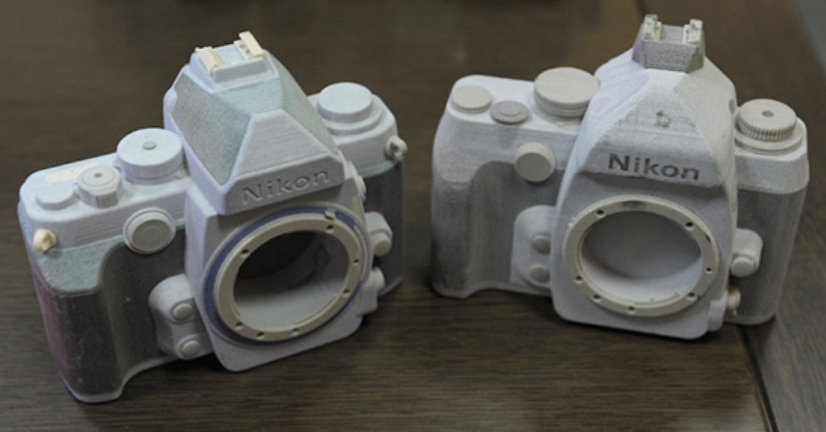

Scale Models
A smaller or larger physical copy of an object.

Advantages and Disadvantages of Scale Models
Advantages: Model can be overviewed easily, especially if the original design is exceptionally large. Gives an idea of how large model will be when actually built/ produced
Disadvantages: Can be time consuming to create perfect scale model. Hard to manipulate to show how it works
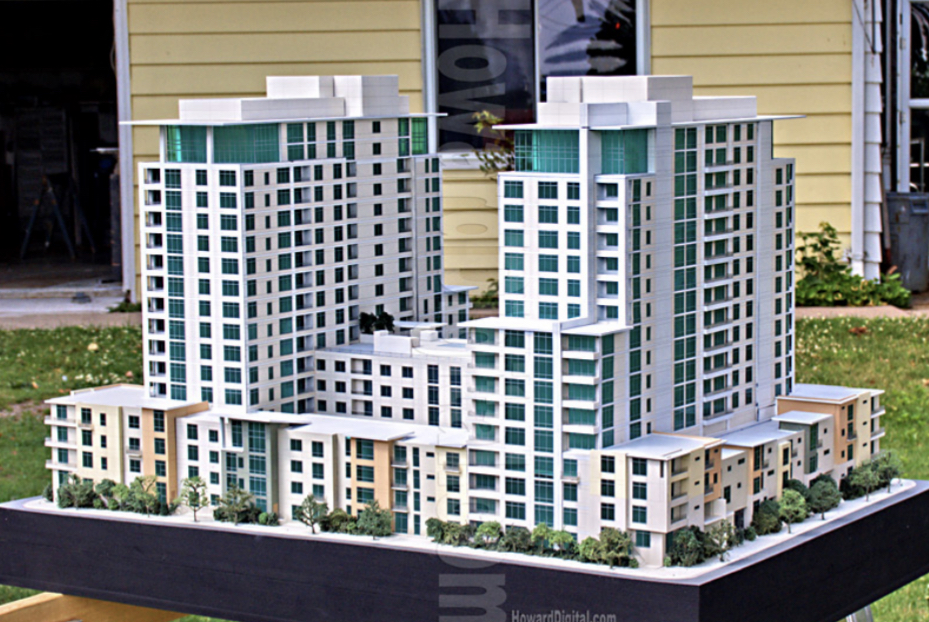
Aesthetic Models
Developed to look and feel like final product. Used for ergonomic testing and evaluation visual appeal. Do not work like final product

Advantages and Disadvantages of Aesthetic Models
Advantages: Can be used instead of digital models to give user an idea of how the product would look like in a real environment. Production engineers use data to assess the feasibility of producing the product.
Disadvantages: Are non working models and only provide a visual model of product. Fairly expensive to produce as the surface can be difficult to recreate
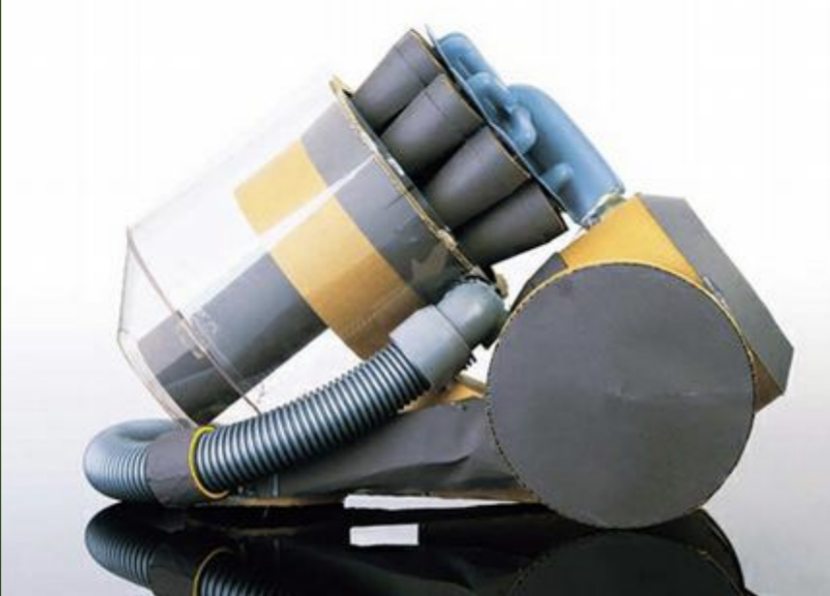

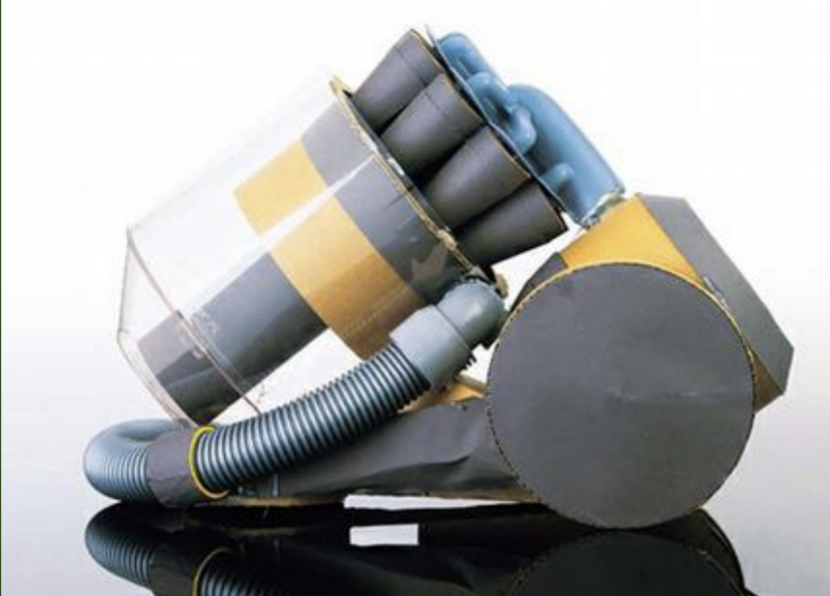
Mock-ups
Used to test ideas. Usually scale or full-size representation of a product used to gain feedback from users. Can be considered prototype if includes some functionality(“Work-like” and “Look-like” .
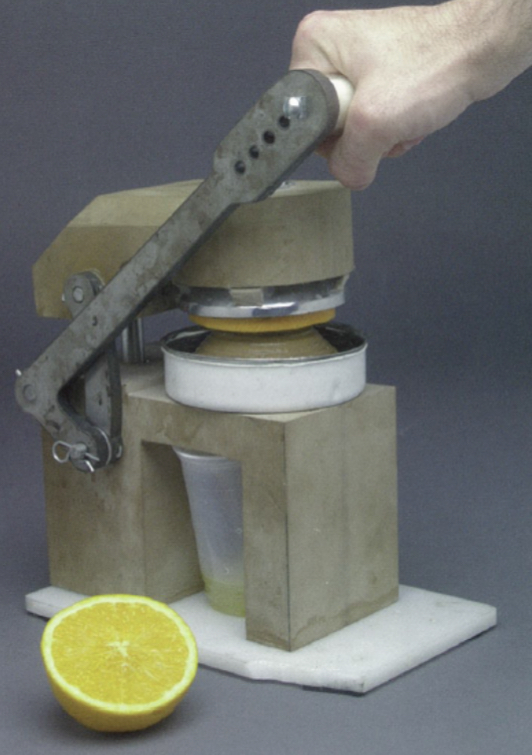

Advantages and Disadvantages of Mock-ups
Advantage: used to get feedback from the user. Models are made to a 1:1 scale and offer a full size representation of the product
Disadvantage: Does not offer as much functionality as a prototype. Can be difficult and time consuming to create
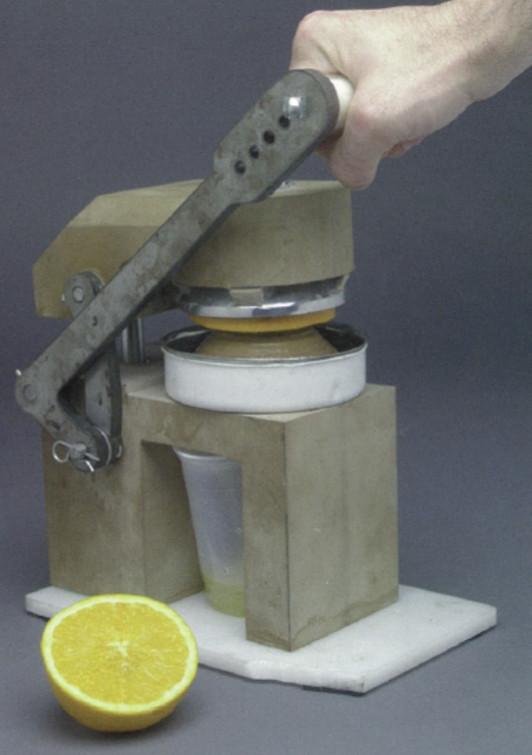

Functional Prototypes
A sample or model built to test a concept or process or to act as an object to be replicated or learned from. Used to test and validate ideas and can be used throughout design development.
Developed from 2 perspectives, from the development team and the user
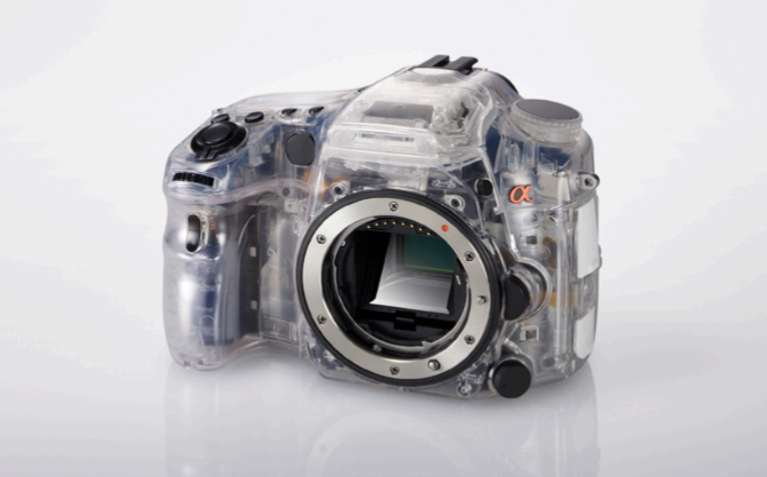

Advantages and Disadvantages for Functional Prototypes
Advantages: A semi to fully functioning model of a product a thus it can be used to test the functions of the final product out. Can provide specifications for the parts involved in a real products and how they function together
Disadvantages: can be slightly expensive to make as prototype needs to function. Does not take aesthetic into account bc primarily tests the function of product
What is Fidelity
A measure of the realism of a model or simulation
Low = just the idea, not where near real
High= mock up of the idea, as close as possible to final
Instrumented Physical Models
Equipped with the ability to take measure to to provide accurate quantitive feedback for analysis. Can be used to effectively investigate many phenomena
Ex:an instrumented model of a keyboard can record the actions of the user and provide data on how often keys are used and the number of errors a user makes
Advantages and Disadvantages of Instrumented Physical models
Advantages: Can be used to take accurate measurement related to the performance of the product, to improve the product further
Disadvantages: Can take time and be very expensive to set up
CAD
Computer Aided Design
Used for conceptual design and layout of product. Eliminates high cost of testing an manufacturing. Used in fashion construction, automotive, architecture, planning electrical or mechanical layout
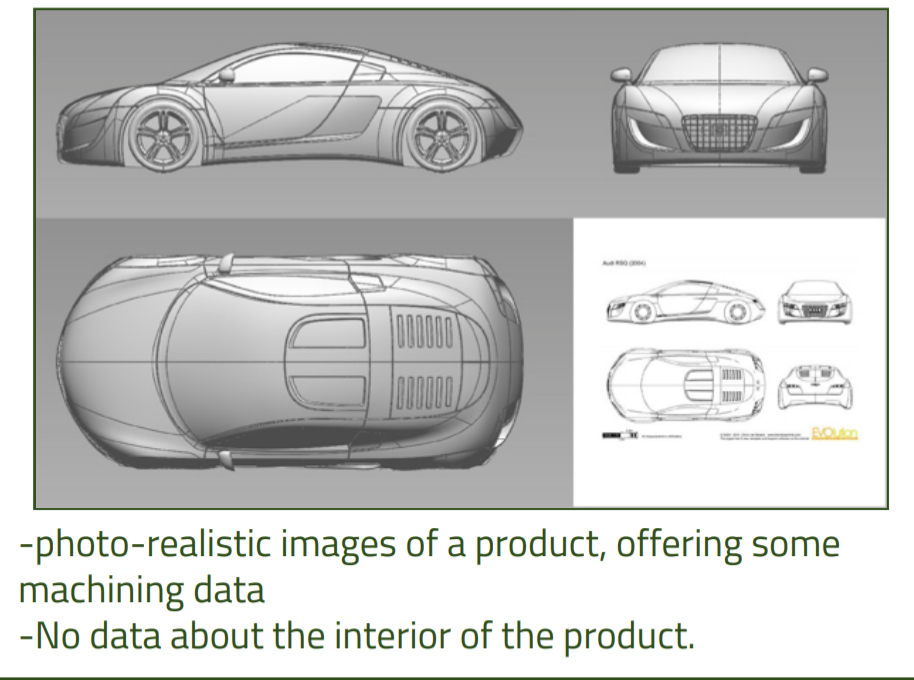
Surface Modelling
Photorealistic images of a product, offering some machining data but no data about the interior of product
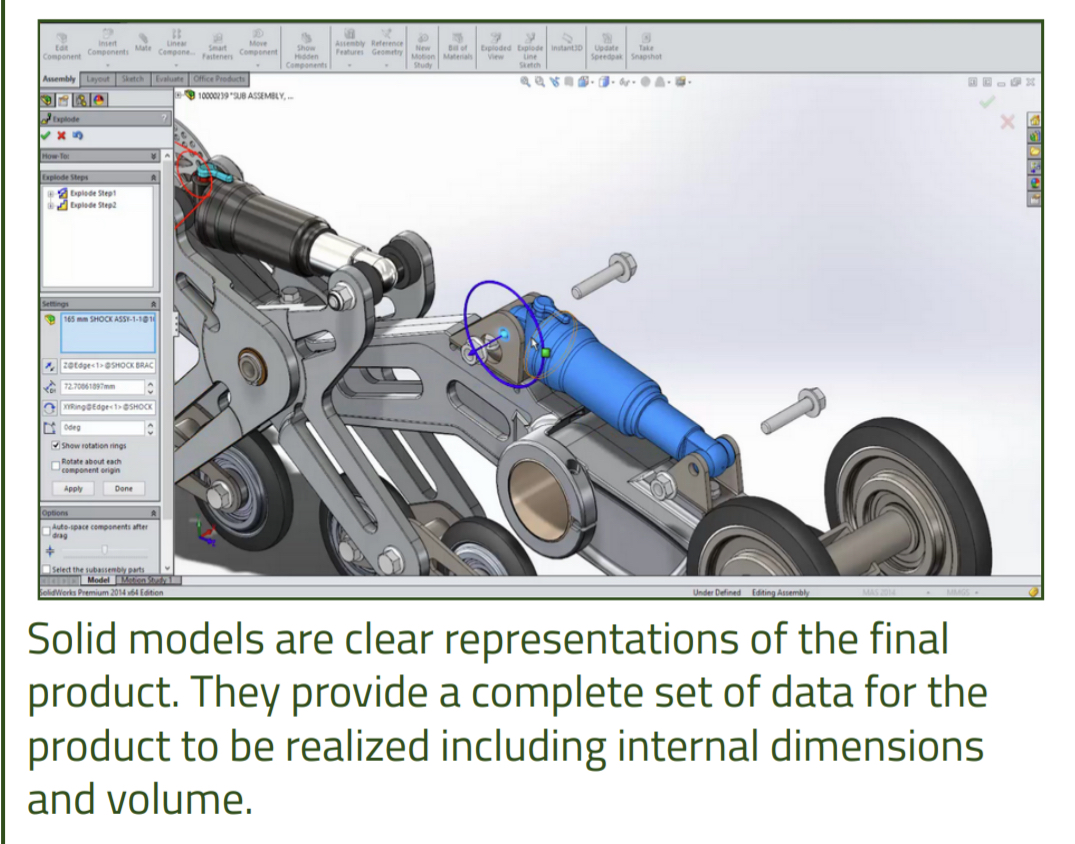
Solid Modelling
Clear representations of final product. Provide a complete set of data for the product to be realized including internal dimensions and volume
Data Modelling
Explicitly determines the structure of data or structured data including statistical modelling
Virtual prototyping
Involves the use of surface and solid modelling to develop photo-realistic interactive models, can be considered digital mock-up
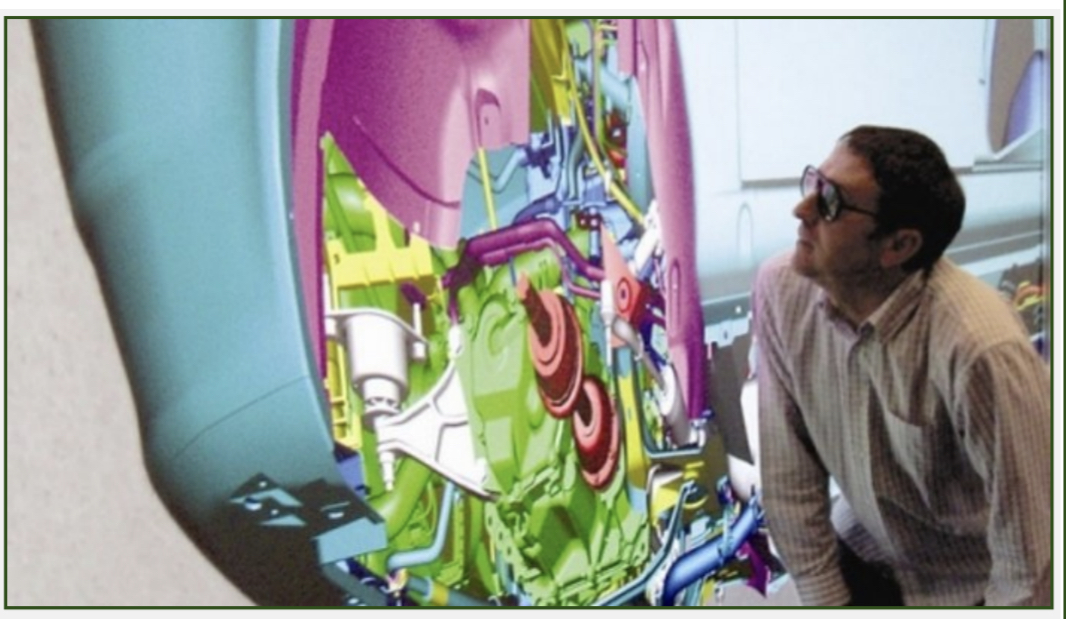

Bottom up Modelling
Designed creates part geometry independent of assembly or any other component. Some design criteria often established before modeling the part this information is not shared between models. Once all part models complete they are brought together in assembly.
“Assembly line”

Top- Down Modelling
A product- development process obtained through 3D. Main feature is that the design originates as a concept and gradually evolves into a complete product consisting of components and sub-assemblies. Begins with design criteria and create components that meet those criteria. List known parameters and create engineering layout. Layout can be 2D deign that evolves throughout design process
Digital Humans
Computer simulations of a variety of mechanical and biological aspects of human body. Can be used to interact with a virtual prototype. Enables product to be developed more quickly. Results in higher product quality that meets human requirements more accurately

Motion Capture
the recording of human and animal movement by any means, for example, by video, magnetic or electro-mechanical devices. A person wears a set of acoustic, inertial, LED, magnetic or reflective markers at each joint. Sensors track the position of the markers as the person moves to develop a digital representation of the motion. Motion capture can reduce the cost of animation, which otherwise requires the animator to draw either each frame or key frames that are then interpolated. Motion capture saves time and creates more natural movements than manual animation but is limited to motions that are anatomically possible.

Haptic Technology
a technology that interfaces the user via a sense of touch. Also known as force feedback technology, haptic technology works by using mechanical actuators (motor) to apply forces to the user. By simulating the physics of the user’s virtual world, it is possible to compute these forces into real time. Haptic technology allows the user to become part of a computer simulation and to interact with it, enabling the designer to observe the user’s performance and to design a better outcome. ,t can also be used in situations where it is difficult to train in the real environment. Haptic technology is also used in feedback devices used in home entertainment consoles.

Virtual Reality
The ability to simulate a real situation on the screen and interact with it in a near-natural way
Animation
The ability to link graphic screens together in such a way as to simulate motion to a process
Finite element analysis
Involves the calculation and simulation of unknown factors in products using CAD systems
Uses color indication to show ;
Structural load
Aerodynamics
Thermodynamics
Stereolithography
It is a form of 3D printing using a liquid bath of resin combined with an ultraviolet laser. The ultraviolet light hits the liquid Kardening it to form the structure of the object being printed. The Ease plate of the bath then moves down allowing more liTuid to flow over the previously hardened liquid so the same process can be repeated until the object being printed has been completed. The ‘Sweeper’ seen in the image to the right just helps even out the height of the bath every time the laser fires.
Laminated Object Manufacturing
Takes the sliced CAD data from a 3D model and cuts out each layer from a roll of material, using a laser to plotter cutter. Layers are glued together to form model
Fused deposition modelling
Uses additive principle by layering down material in layers. Uses Plastic/ metal from a coil and sent to an extrusion nozzle that can turn the flow on and off. Nozzle heated to melt material and moves horizontally and vertically
Selective Laser Sintering
An additive manufacturing technique that uses a high-power laser to fuse small particles of materials such as plastic, glass, metal