Biology FINAL T2
1/90
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
91 Terms
Which body systems influence behavior?
Nervous and Endocrine systems
Are maternal tendencies genetic or acquired?
Genetic
Fixed Action Pattern (FAP)
Innate behavior pattern that is stereotyped, spontaneous, independent of immediate control, genetically encoded, and independent of individual learning.
Examples of fixed action patterns
infants instinctively grasp objects placed in their hands.
seeing someone yawn often triggers others to yawn, and the action cannot be stopped once started.

Imprinting
Learning that occurs when a young animal forms an association with the first moving object it is exposed to.
Associative learning
Acquired ability to associate two stimuli or between a stimulus and a response.
Examples of Associative learning
Training an animal with treats when they are good or punishments when they are bad.
The most famous example is Pavlov's dogs, where the dogs learned to associate the sound of a bell with food, eventually responding to the bell alone by salivating.
Operant conditioning
Learning that results from rewarding or reinforcing a particular behavior.
Examples of Operant conditioning
Positive Reinforcement (Social Media 'Likes')
using treats to consistently praise a particular behavior you want your dog to keep doing, like sitting and staying
Insight learning
Ability to apply prior learning to a new situation without trial-and-error activity.
Chemical Communication
the process through which organisms send and receive messages using chemical signals, often in the form of pheromones or hormones.
Examples of Chemical communication
Ants and termites mark their trails with pheromones.
Cheetahs and other cats mark their territories by depositing urine, feces, and anal gland secretions at the boundaries.
Auditory Communication
Communication through sound
Examples of auditory communication
Chirps, croaks, howls, barks, gobbles, and other such vocalizations are obvious examples of auditory communication.
Visual Communication
Examples of these signals include gestures, facial expressions, body postures, and coloration.
Basically communication you can see
Tactile communication
Communication through touch; for example, when a chick pecks its mother for food, chimpanzees groom each other, and honeybees “dance.”
What are the advantages and disadvantages of each communication type?
Chemical: works day and night but not instant.
Auditory: works day and night and easily modified but there needs to be a listener present
Visual: doesn’t need company of chemical and auditory signals but always needs light
Tactile: allows bonding between individuals but recipients need to be close
Territory
Area occupied and defended exclusively by an animal or a group of animals.
Territoriality
Marking and/or defending a particular area against invasion by another species member. The area is often used for the purpose of feeding, mating, and caring for young.
Foraging (for food)
Foraging for food is when animals are actively looking for nutrition.
optimal foraging model
The optimal foraging model states that it is adaptive for foraging behavior to be as energetically efficient as possible.

Polygamy
Practice of males having several female mates.

Polyandry
Practice of female animals having several male mates.

Monogamy
Breeding pair of organisms that reproduce only with each other through their lifetime.
Mono = one mate at a time.
Sexual Selection
a form of natural selection that favors features that increase an animal's chances of mating.
Population
Group of organisms of the same species occupying a certain area and sharing a common gene pool.
Community
Assemblage of different species interacting with one another within the same environment.
Demography
Demography is the statistical study of a population that includes information about its density, distribution, and rate of growth (which are dependent on the population’s mortality pattern and age distribution).
Population density
The number of individuals per unit area or volume living in a particular habitat.
Limiting factor
Resource or environmental condition that restricts the abundance and distribution of an organism.
Population distribution
The way individuals are spaced within a habitat.
Name the 3 population distribution patterns
Clumped
Random
Uniform
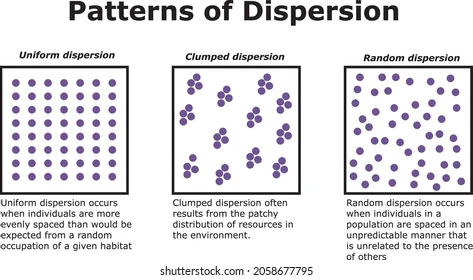
What’s the difference between population density and population distribution?
Population density is the number of individuals per unit area.
Population distribution is the pattern of dispersal of individuals across an area of interest.
rate of natural increase (r)
Growth rate that is determined by calculating the number of individuals that are born each year and subtracting the number of individuals that die each year.
biotic potential
Maximum population growth rate under ideal conditions.
cohort
Group of individuals having a statistical factor in common, such as year of birth, in a population study.
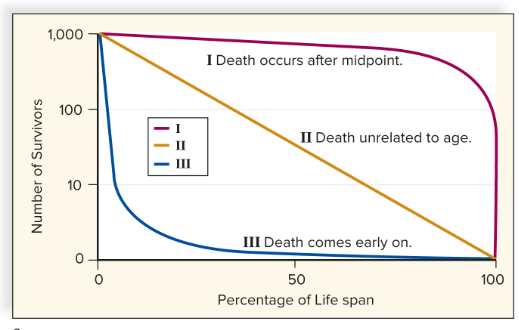
survivorship
Probability of newborn individuals of a cohort surviving to particular ages.
What are the 3 survivorship curves?
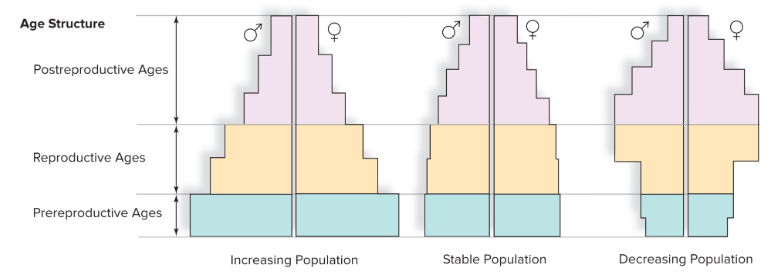
Which of these pyramids represent a developing country?
no. 1 because birth rate appears to be higher since there are more young people which applies to developing countries.
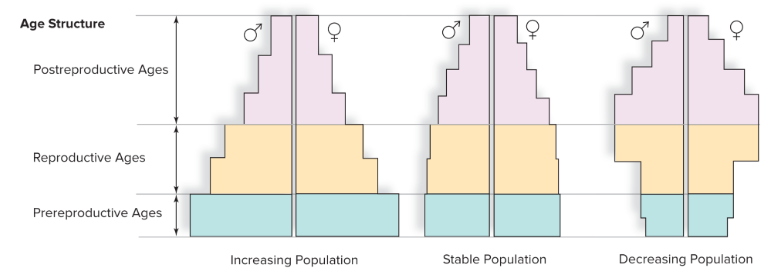
Why are pyramids number 2 and 3 associated with developed countries?
Because in developed countries, there isn’t a need to reproduce more due to improved healthcare and stable living conditions so people likely only have few children (pyramid 2)
and in the case of (pyramid 3), often times the birth rate declines in developed countries because people do not see the need to have children due to social or economic factors.
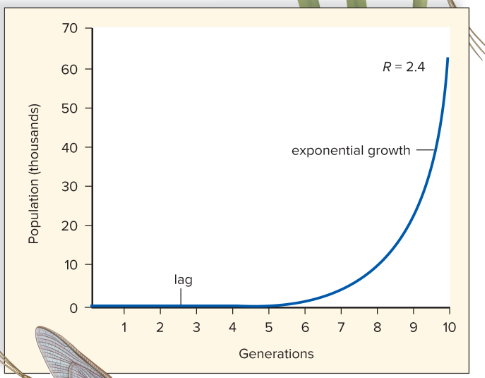
Name this growth pattern
Exponential (grows to infinity ideally)
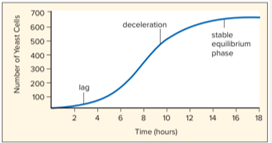
Name this growth pattern
Logistic (reaches a state of stability / carrying capacity)
The formula of logistic growth:
N = population size
N/t = change in population size
r = rate of natural increase
K = carrying capacity
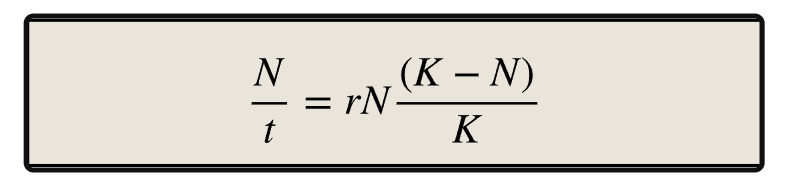
Carrying capacity (K)
Largest number of organisms of a particular species that can be maintained indefinitely by a given environment.
Formula of exponential growth:

Density-independent factors
Abiotic factors include events such as droughts, freezes, hurricanes, floods, and forest fires.
Any one of these natural disasters can kill individuals and lead to a sudden and catastrophic reduction in population size.
Density-dependent factors
Biotic factors such as diseases, predation and competition.
Species richness
Number of species in a community.
Species diversity
Variety of species that make up a community.
Species composition is also called
Species richness
ecological niche
Role an organism plays in its community, including its habitat and its interactions with other organisms.
competitive exclusion principle
Theory that two species cannot occupy the same niche in the same place and at the same time.
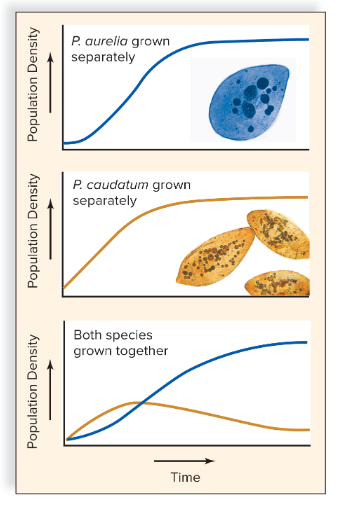
resource partitioning
Mechanism that increases the number of niches by dividing the resource, such as food or living space, among species.
For example: Eagles hunting in the day, and owls hunting at night in the same forest.
character displacement
Character displacement happens when two similar species evolve to become more different from each other because they compete for the same resources.
Example: If two bird species eat the same seeds, but one starts eating bigger seeds while the other eats smaller ones, their beaks may evolve to be different sizes over time.
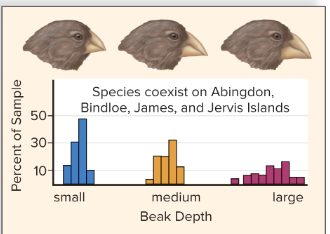
camouflage
Process of hiding from predators in which an organism’s behavior, form, and pattern of coloration allow it to blend into the background and prevent detection.

mimicry
Superficial resemblance of two or more species; a survival mechanism that avoids predation by appearing to be noxious.
Basically, a species copying another species to protect itself.
Name the 3 symbiotic relationships:
Parasitism
Mutualism
Commensalism
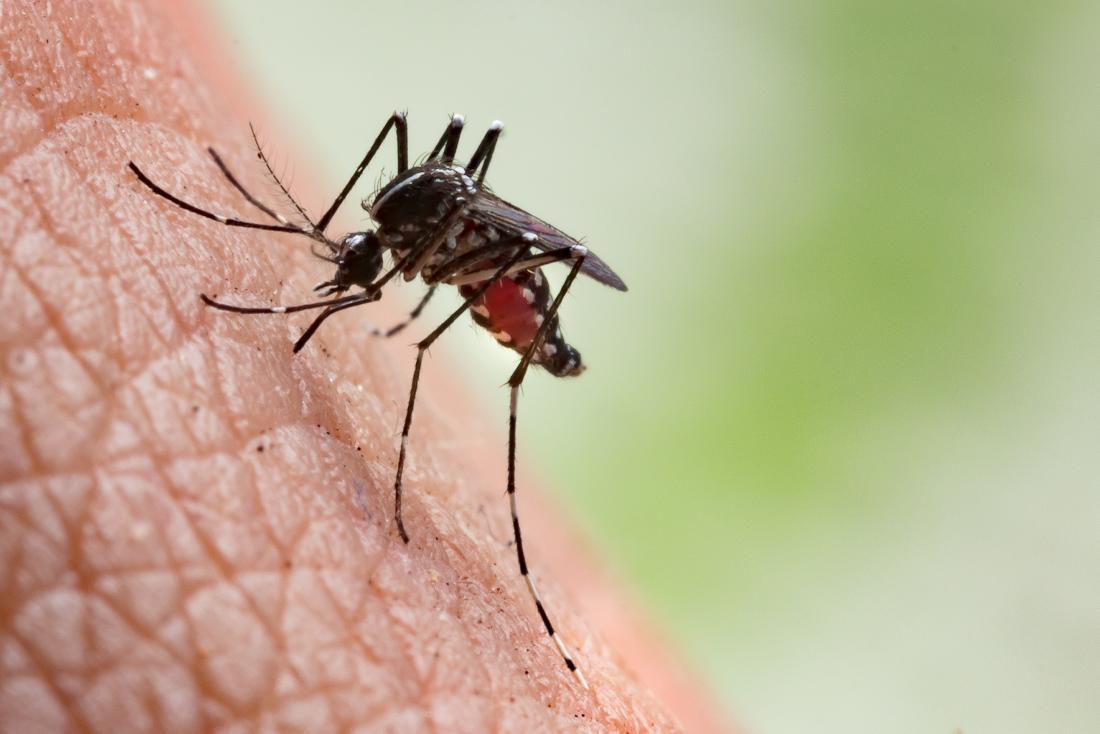
parasitism
One organism benefits from harming the other organism.
Example: Mosquitos feeding on human blood.
commensalism
Symbiotic relationship in which one species is benefited, and the other is neither harmed nor benefited.
Example: Barnacles use the whale’s skin as their home while the whale doesn’t gain or lose anything.

mutualism
Symbiotic relationship in which both species benefit in terms of growth and reproduction.
Example: the bacteria in your stomach has a home and food while it helps you digest your food.
Primary succession
Primary succession, during which soil is formed, occurs first.
What happens in primary succession?
Bare Surface – No soil, just rock (e.g., after a volcanic eruption).
Pioneer Species – Small organisms like lichens and mosses break down rock into soil.
Soil Formation – Dead lichens and mosses create a thin layer of soil.
Small Plants & Insects – Grasses and small plants start growing.
Larger Plants & Animals – Trees grow, attracting animals.
Stable Ecosystem – A full forest or ecosystem forms (climax community).
Secondary succession
Secondary succession occurs as one species is replaced by another, usually progressing from grasses to shrubs to trees.
What happens in secondary succession?
Disturbance – An event like a wildfire or flood damages the ecosystem.
Soil & Seeds Remain – Soil is still there, making recovery faster.
Pioneer Plants – Fast-growing plants like grasses appear first.
Shrubs & Small Trees – Larger plants return as the soil improves.
Larger Trees & Animals – A full ecosystem regrows.
Stable Ecosystem – The area recovers to its original state (climax community).
climax community
In ecology, a mature and stable community that results when succession has come to an end.
autotroph
Organism that can capture energy and synthesize organic molecules from inorganic nutrients.
Auto = feeds itself
producer
Photosynthetic organism at the start of a grazing food chain that makes its own food (e.g., green plants on land and algae in water and cyanobacteria).
heterotroph
Organism that cannot synthesize needed organic compounds from inorganic substances and therefore must take in organic food.
(eats other organisms and cannot make its own food)
herbivore
plant eater (rabbits, cows, sheep)
carnivore
meat eater (lion, tigers, wolves)
omnivores
can eat either plant or animal (humans, foxes)
detritivore
feed on dead organisms (earthworms, beetles, vultures)
decomposer
break down (not eat) dead matter (mushrooms, bacteria)
food chain
Diagrams that show a single path of energy flow in an ecosystem are called food chains.
trophic level
A trophic level is a level of nutrients/energy within a food web or chain.
In chemical cycling, what kind of organism returns nutrients to the soil?
decomposers
What are examples of human activity altering biogeochemical processes?
. By mining fossil fuels and burning them, releasing carbon into the atmosphere.
By harvesting crops without returning nutrients to the soil.
By excessive groundwater extraction, reducing available fresh water.
topography
Surface features of the Earth. 🌄
rain shadow
Leeward side (side sheltered from the wind) of a mountainous barrier, which receives much less precipitation than the windward side.
(Dry side of the mountain e.g deserts)
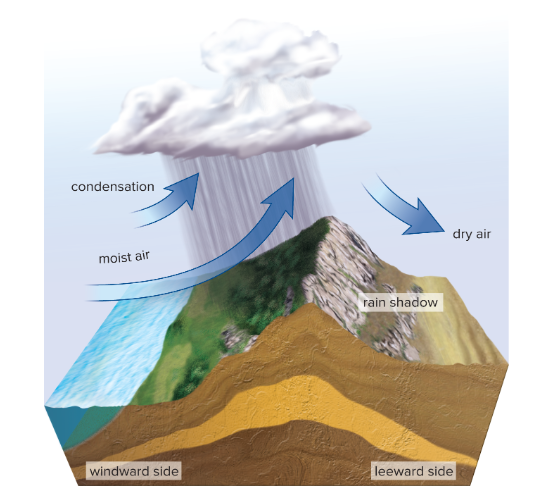
biome
Major terrestrial ecosystems, called biomes, are characterized by their climate and geography.

Tundra
Definition: Cold and dry with frozen ground (permafrost).
Vegetation: Mosses, lichens, and small shrubs (no trees).

Taiga (Boreal Forest)
Definition: Cold with moderate rainfall, long winters.
Vegetation: Evergreen (coniferous) trees like pine and spruce.

Temperate Deciduous Forest
Definition: Moderate temperature with warm summers and cool winters.
Vegetation: Trees that shed leaves in winter (oak, maple).
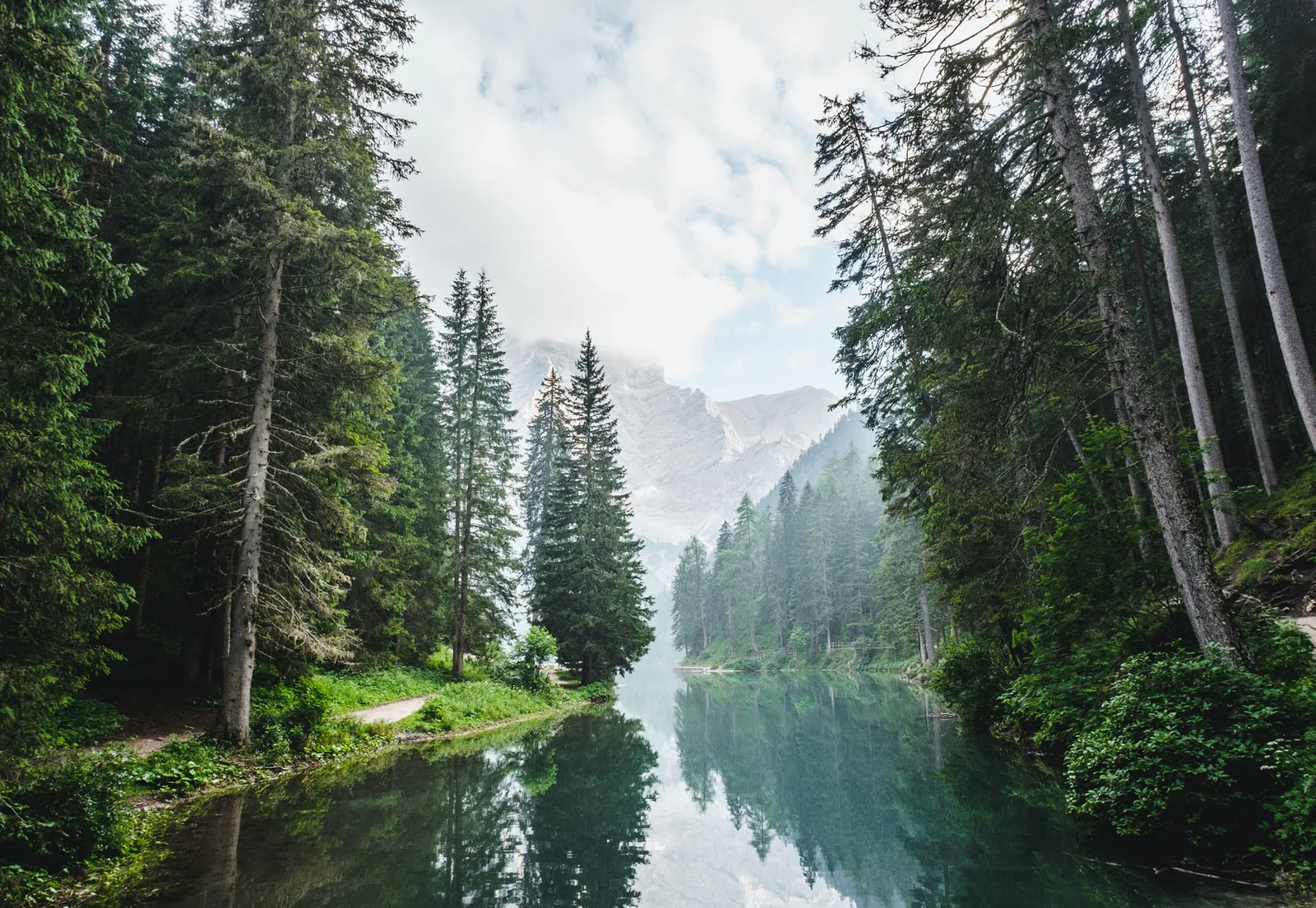

Temperate Rainforest
Definition: Mild temperatures with heavy rainfall.
Vegetation: Tall evergreen trees (redwoods, firs) and mosses.
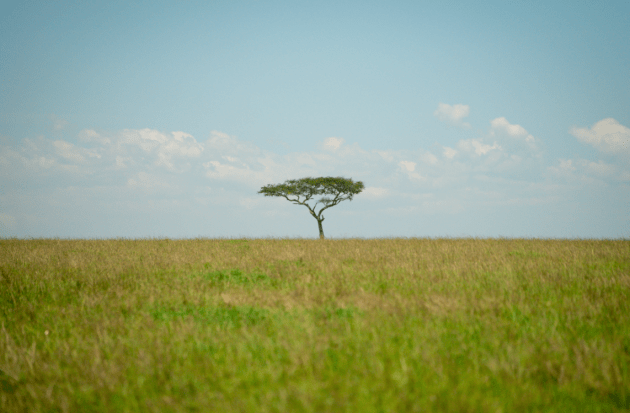

Grassland
Definition: Hot summers, cold winters, and moderate rainfall.
Vegetation: Grasses with few trees (prairies, savannas).
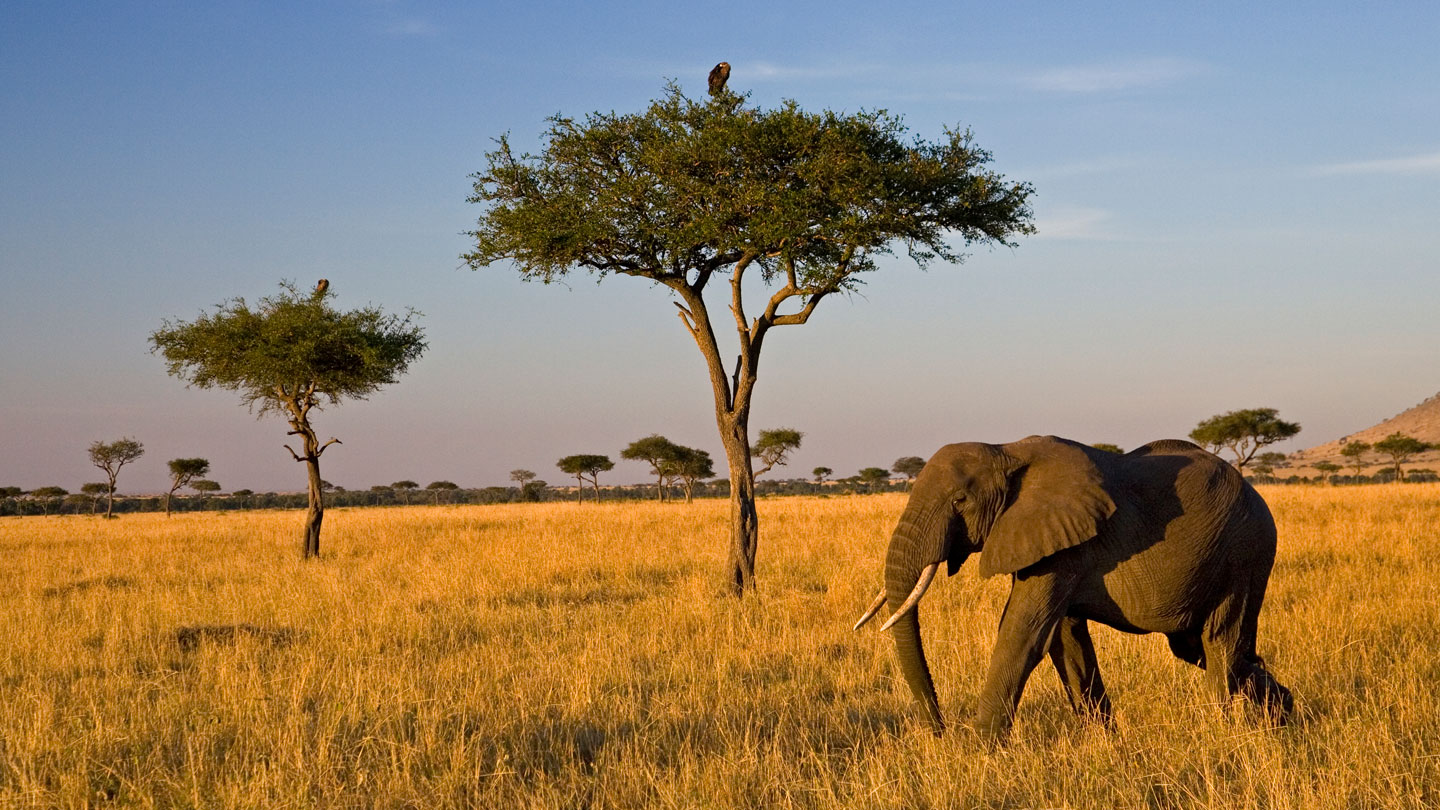

Savanna
Definition: Warm year-round with wet and dry seasons.
Vegetation: Scattered trees and drought-resistant grasses.

Tropical Seasonal Forest
Definition: Warm with a distinct dry season.
Vegetation: Mix of deciduous and evergreen trees.
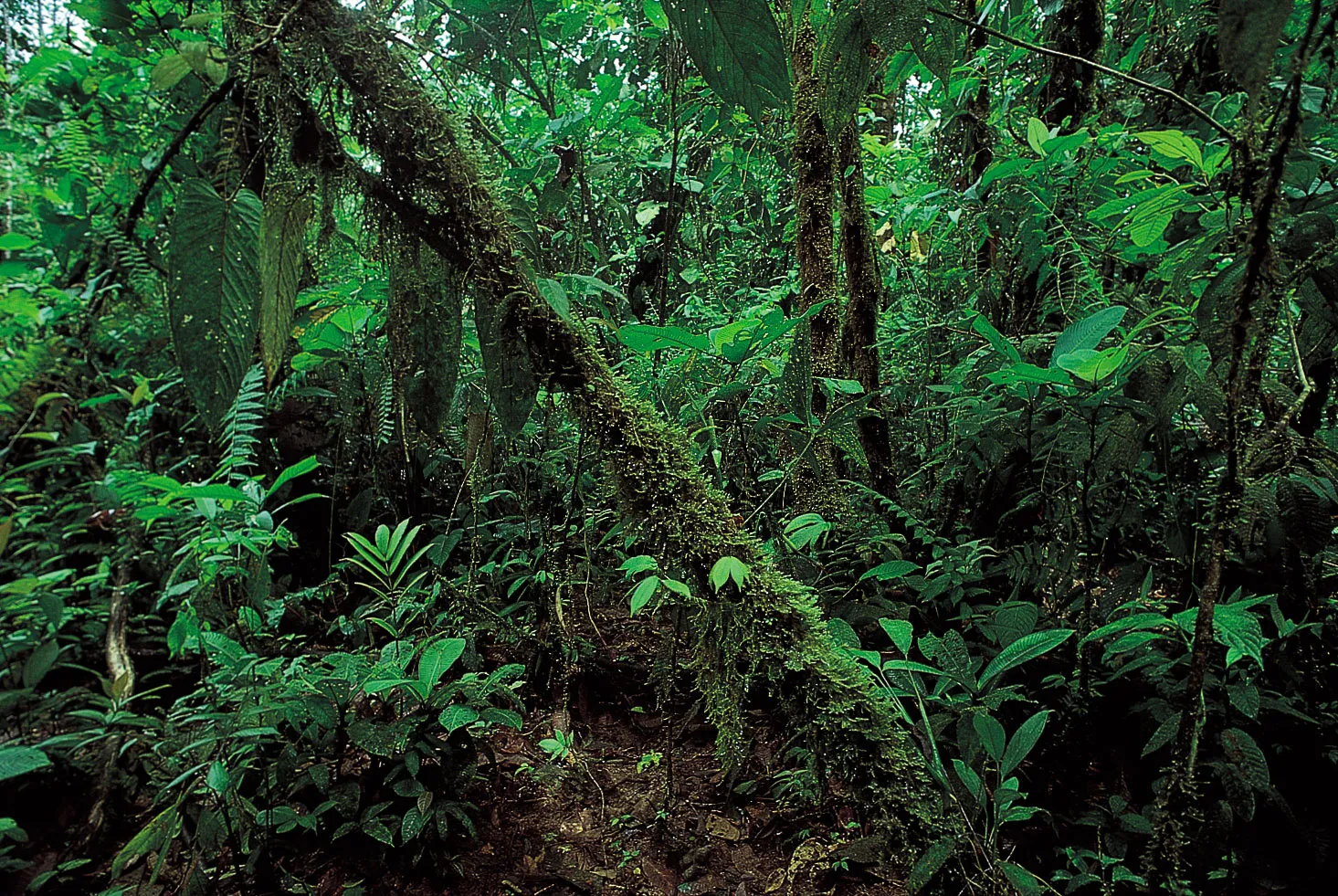

Tropical Rainforest
Definition: Hot and very wet all year.
Vegetation: Dense forests with tall trees, vines, and ferns.

Desert
Definition: Very dry with extreme hot or cold temperatures.
Vegetation: Cacti, succulents, and drought-tolerant shrubs.
Upwelling
Upwelling is a process in which deep, cold water rises toward the surface.
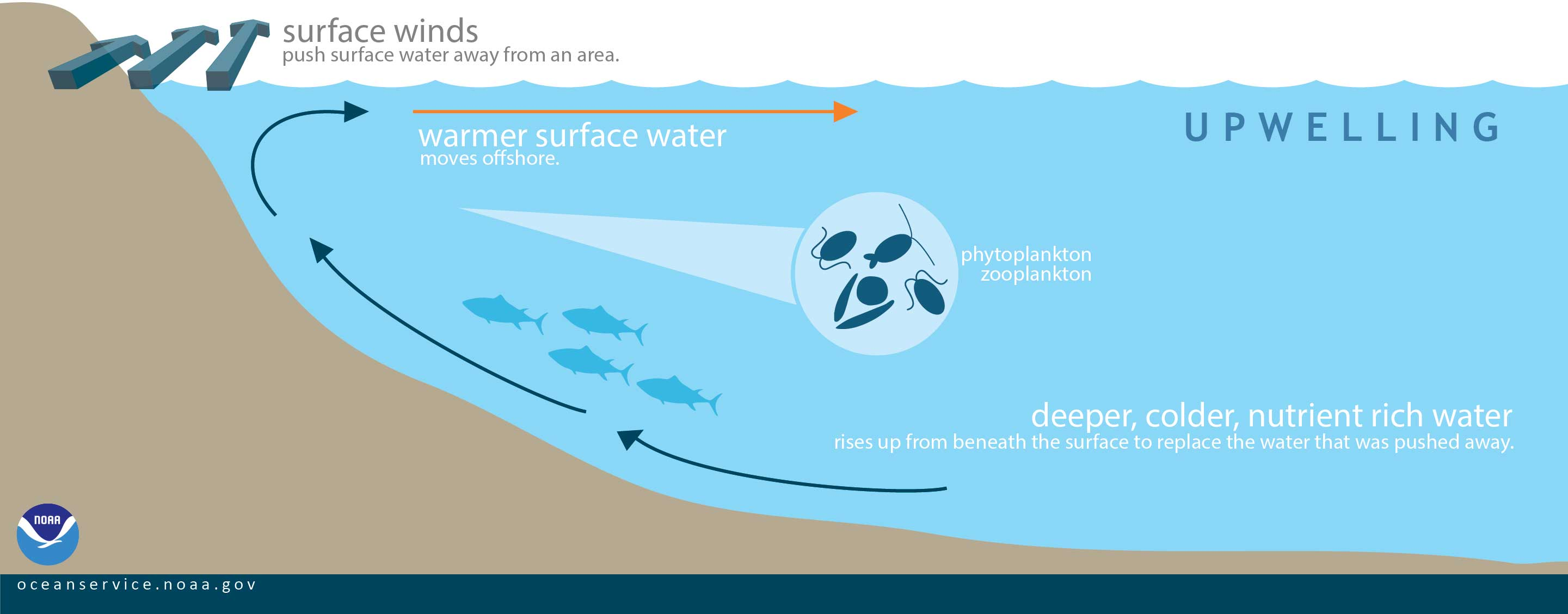
Why is upwelling important for marine ecosystems?
It brings nutrient-rich water to the surface, increasing food availability for marine life.