Biology: Microscopes, Cells, and the Cell Cycle
1/78
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
79 Terms
Microscopes
Essential tools for observing cells and other tiny specimens.
Total Magnification
Ocular lens magnification × objective lens magnification (E.g. Ocular Lens 5X × Objective Lens 10X = 50X).
Common magnifications for classroom microscopes
Include 40x (low power), 100x (medium power), and 400x (high power), using a 10x ocular lens.
Field of View (FOV)
The visible area through the microscope; as magnification increases, the FOV becomes smaller, but more detail becomes visible.
FOV Formula
HP FOV × HP Magnification = LP FOV × LP Magnification.
Actual Cell Size
FOV (mm) ÷ # Specimens across.
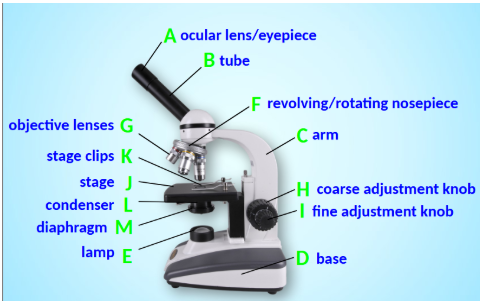
Ocular Lens/Eyepiece
Contains a lens to magnify the image (usually 10x magnification).
Body Tube
Connects the eyepiece to the objective lenses and ensures correct alignment.
Arm
Connects the body tube to the base and is used for carrying the microscope.
Base
Supports the microscope's weight and contains electronics and the light source.
Lamp/Light Source/Illuminator
Sends light upwards through the hole in the stage onto the specimen.
Revolving/Rotating Nose Piece
Objective lenses are attached to it; rotating allows switching between lenses.
Objective Lenses
Further magnify the image (e.g., 4x, 10x, 40x).
Coarse Adjustment Knob
Used to help put the specimen in focus, primarily under low power.
Fine Adjustment Knob
Used for exact focusing, especially under higher power; both knobs move the stage up and down.
Stage
Where the slide containing the specimen is placed; it has a hole for light to pass through.
Stage Clips
Secure the slide on the stage.
Condenser Lens
Located under the stage, it focuses light from the illuminator through the stage hole onto the specimen.
Cells
The fundamental units of life, with various structures and functions.
Cell Theory
All living organisms are composed of one or more cells; the cell is the most basic unit of life; all cells arise from pre-existing, living cells.
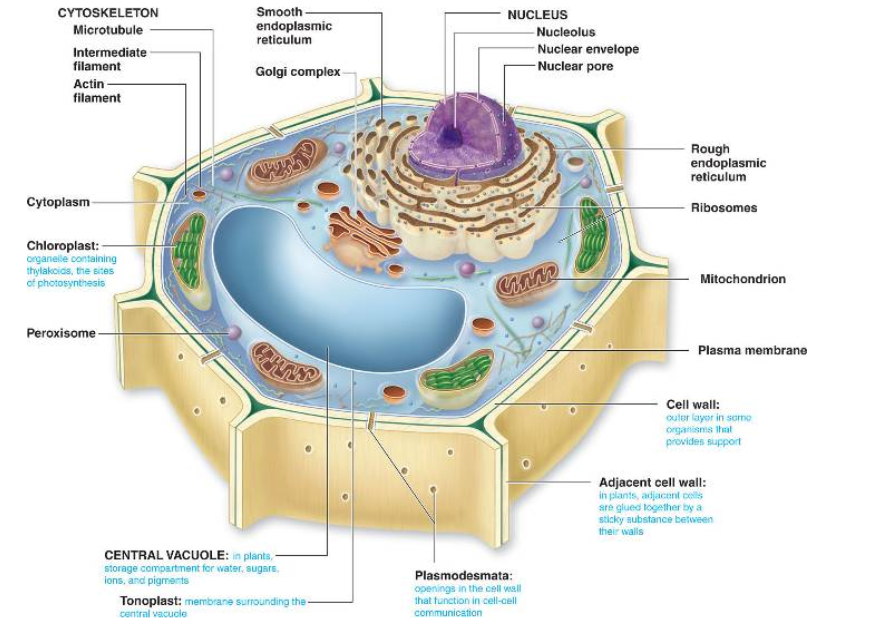
Vesicle
Stores and transports substances throughout the cell.
Mitochondria
"The powerhouse of the cell," supplying energy by converting sugar into useful energy.
Lysosomes
The "clean-up system," responsible for digestion and breaking down bacteria and damaged organelles.
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
Carries material and is associated with making proteins; has ribosomes attached.
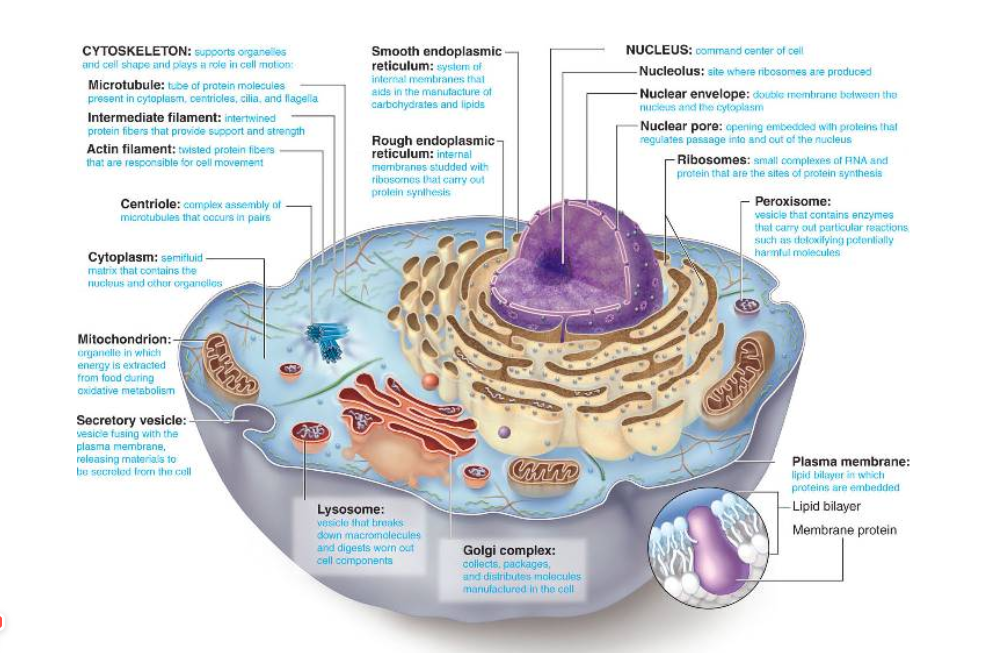
Ribosomes
Sites where proteins are assembled; can be attached to the rough ER or free in the cytoplasm.
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum
Produces fats and oils; does not have ribosomes.
Golgi Apparatus
Receives, modifies, sorts, and packages proteins for delivery inside and outside the cell.
Cytoskeleton
An internal network of fibres that helps maintain the cell's shape.
Centriole
Involved in cell division; found only in animal cells.
Chloroplasts
Contain chlorophyll, enabling plants to use sunlight for photosynthesis (converting CO2 and water into sugar and O2); found only in plant cells. They contain thylakoids (sacs of chlorophyll) stacked into grana.
Cell Wall
Provides strength, protection, support, and structure to plant cells; found only in plant cells.
Cell Membrane
Forms a protective barrier around the cell, allowing some substances to move through it via diffusion; made of lipids.
Cytoplasm
Jelly-like substance that fills the cell and suspends organelles, allowing nutrients and organelles to move within the cell.
Nucleus
Control center of the cell, determining growth and reproduction; typically found near the center of the cell and surrounded by the nuclear envelope.
Nuclear Envelope/Membrane
Surrounds the nucleus and contains pores for material transport.
Nucleolus
Small, dense area within the nucleus that contains most of the cell's DNA and manufactures ribosome parts.
Chromatin
Granular substance in the nucleus where DNA is bound; condenses to form chromosomes during cell division.
Vacuole
Stores wastes and other substances; in plants, a large central vacuole stores water.
Cell Division
Helps with growth, repair of tissues, and replacing old or damaged cells; prevents cells from becoming too large to function.
DNA
Long and must be packed tightly to fit in the nucleus.
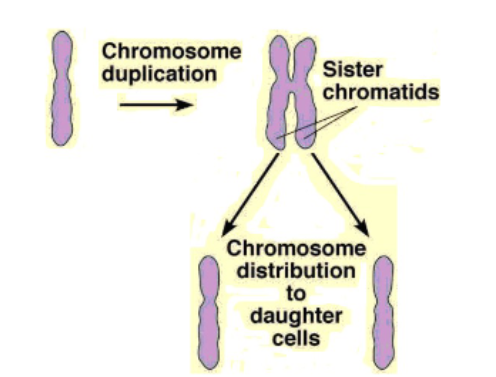
Chromosomes
Before division, chromatin coils further into chromosomes.
Sister Chromatids
Each chromosome copies itself to form sister chromatids, joined at a point called the centromere.
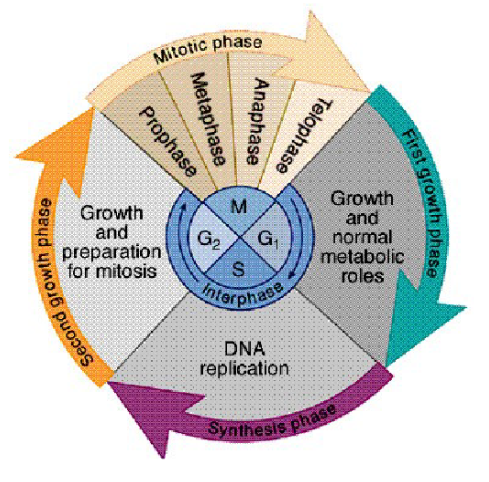
Interphase
90% of cell life; includes G1 Phase, S Phase, and G2 Phase.
G1 Phase
The Cell grows and does normal jobs.
S Phase
DNA and proteins are copied.
G2 Phase
Prepares organelles and structures for division.
Mitotic Phase (M Phase)
Includes Mitosis (nuclear division) and Cytokinesis (cytoplasm division).
Prophase
Chromosomes become visible; centrioles move to opposite ends; spindle fibres form; the nuclear membrane breaks down.
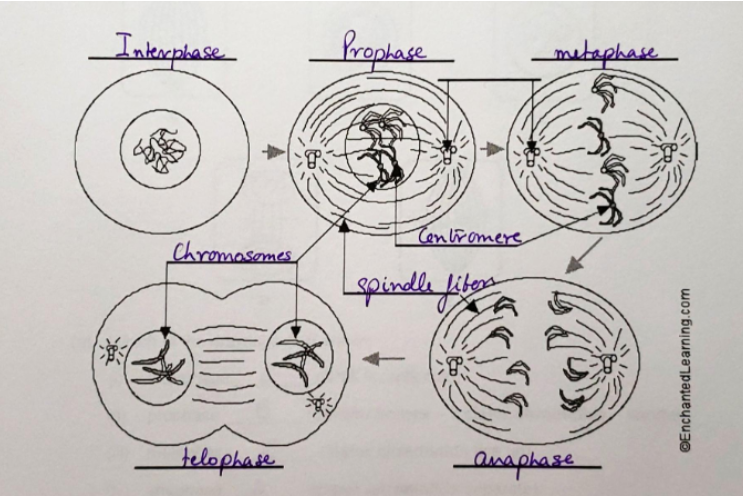
Metaphase
Chromosomes line up in the middle; each attaches to spindle fibres at the centromere.
Anaphase
Sister chromatids separate and move to opposite poles.
Telophase
Chromatids reach the poles; new nuclear membranes and nucleoli form; the cell starts to split.
Cytokinesis
In animal cells, a ring tightens at the center, forming a cleavage furrow that splits the cell; in plant cells, vesicles create a cell plate that becomes the new wall.
Apoptosis
Programmed cell death; normal and necessary
Cancer
Cells ignore apoptosis and divide uncontrollably
Normal cells
Stick together, self-destruct when damaged
Cancer cells
Don't stick, divide endlessly, and move to other areas
Benign Tumour
Non-cancerous, doesn't spread
Malignant Tumour
Cancerous, invades nearby tissue
Metastatic Tumour
Spread to other body parts via blood or lymph
Inherited mutations
Genetic changes that can lead to cancer (e.g. BRCA genes)
Carcinogens
Substances that can lead to cancer (e.g. tobacco smoke, UV radiation)
Viruses
Infectious agents that can cause cancer (e.g. HPV, Hepatitis B/C)
Detection & Risk
~45% of men and ~40% of women in Canada will develop cancer
Early detection
Improves survival (e.g. colonoscopy for colon cancer)
Surgery
Physical removal of tumour
Chemotherapy
Cytotoxic drugs that stop mitosis (e.g. Taxol blocks spindle)
Radiation
Gamma/X-ray beams damage DNA in cancer cells
Stem Cells
Unspecialized cells that can become other cell types
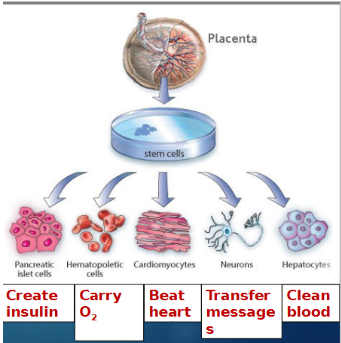
Differentiation
Process where stem cell becomes specialized cell (e.g. red blood cell)
Embryonic stem cells
Found in embryos/placenta, can become any type (~200)
Adult stem cells
Found in skin, blood, and bone; help with repair
Regeneration in Humans
The liver can regenerate up to 75%; children <12 can regrow fingertips
Epithelial Tissue
Covers surfaces, lines organs (e.g. skin, intestine lining)
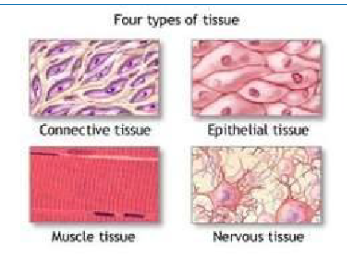
Connective Tissue
Supports/connects (e.g. bone, fat, blood)
Muscle Tissue
Enables movement (Skeletal, Smooth, Cardiac)
Nervous Tissue
Transmits signals using electrochemical impulses
Meristematic Tissue
Stem cells for growth (root tips, shoots)
Xylem
Moves water/minerals (dead cells)
Phloem
Moves sugar (alive cells)