U2: Cells - The Building Blocks of Life Flashcards
1/60
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Anatomy and Physiology AB Unit 2: CBL Flashcards
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
61 Terms
Cells
smallest units of life.
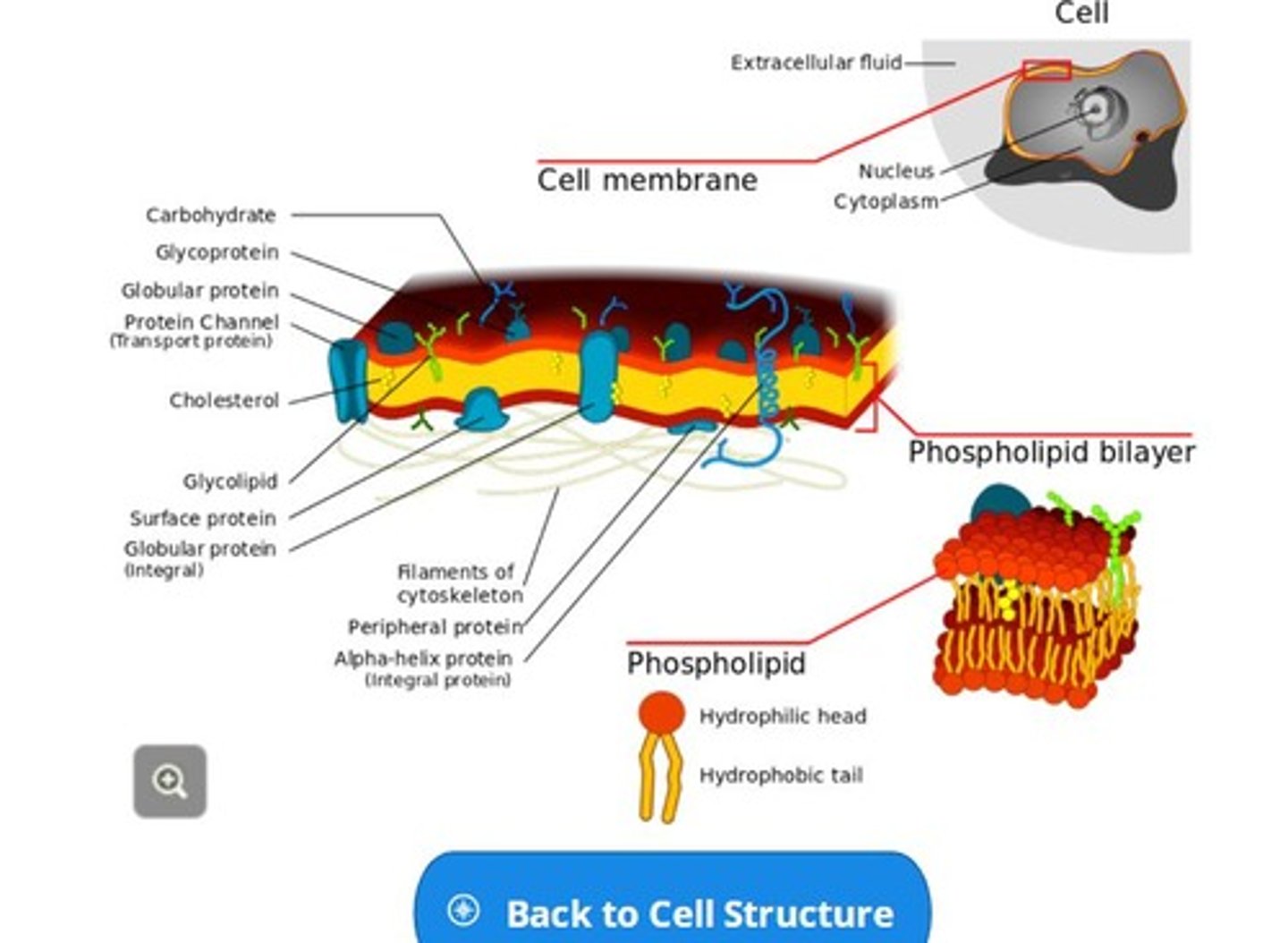
Cell Membrane
the outer protective covering of the cell.
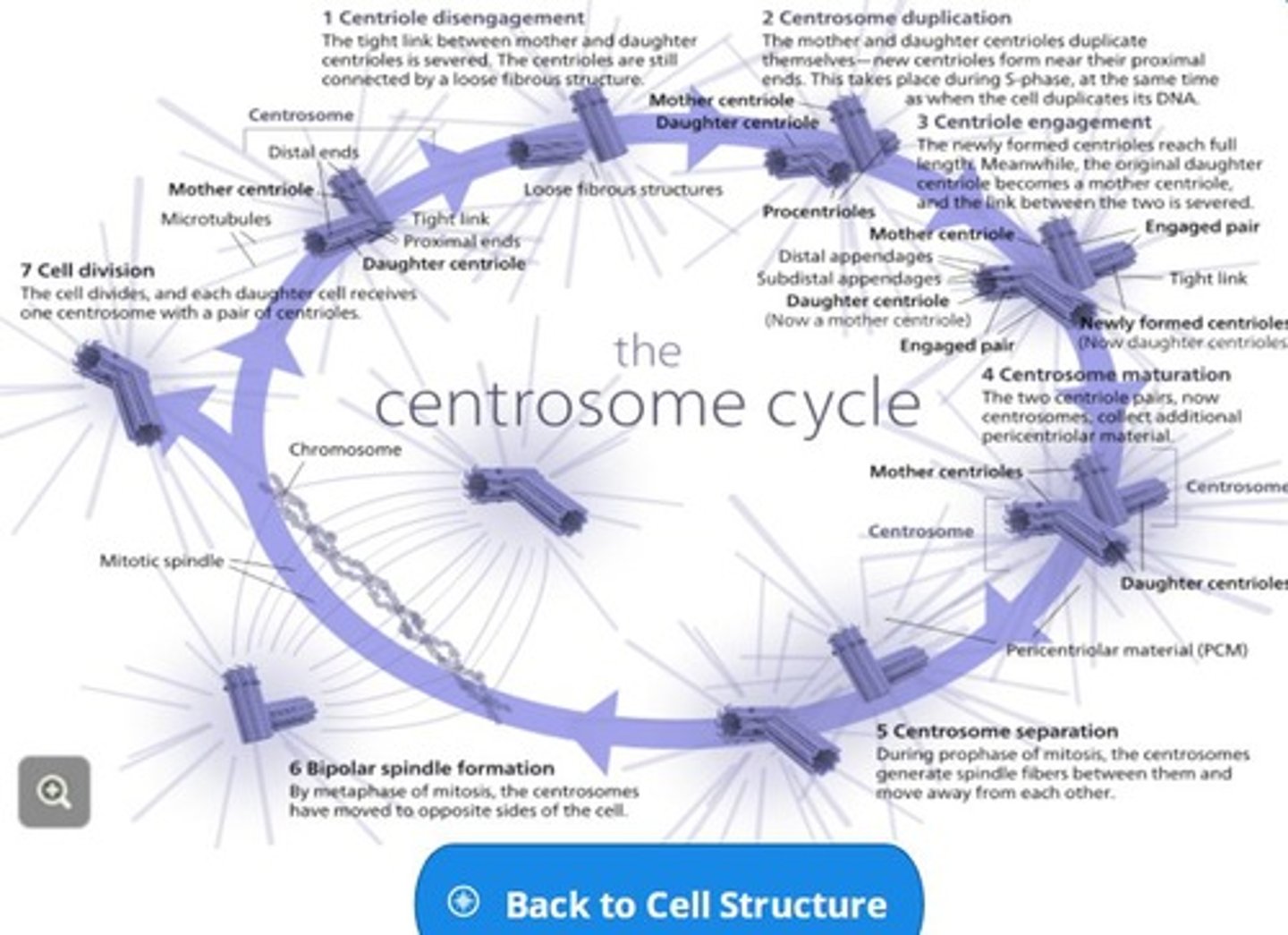
Centrosome
the centriole containing region of clear cytoplasm adjacent to the cell nucleus.
Chomatin
a complex of a nucleic acid with basic proteins (as histone) in eukaryotic cells that is usually dispersed in the interphase nucleus and condensed into chromosomes in mitosis and meiosis.
Cytoplasm
the material or protoplasm within a living cell, excluding the nucleus.
Cytokinesis
the division of the cytoplasm of a plant or animal cell into two.
Endoplasmic reticulum
network of interconnected structures that function especially in the transport of materials within the cell.
Genes
the structures that carry inherited characteristics.
Genome
a total set of chromosomes with the genes they contain, consisting of strings of DNA Nucleotides.
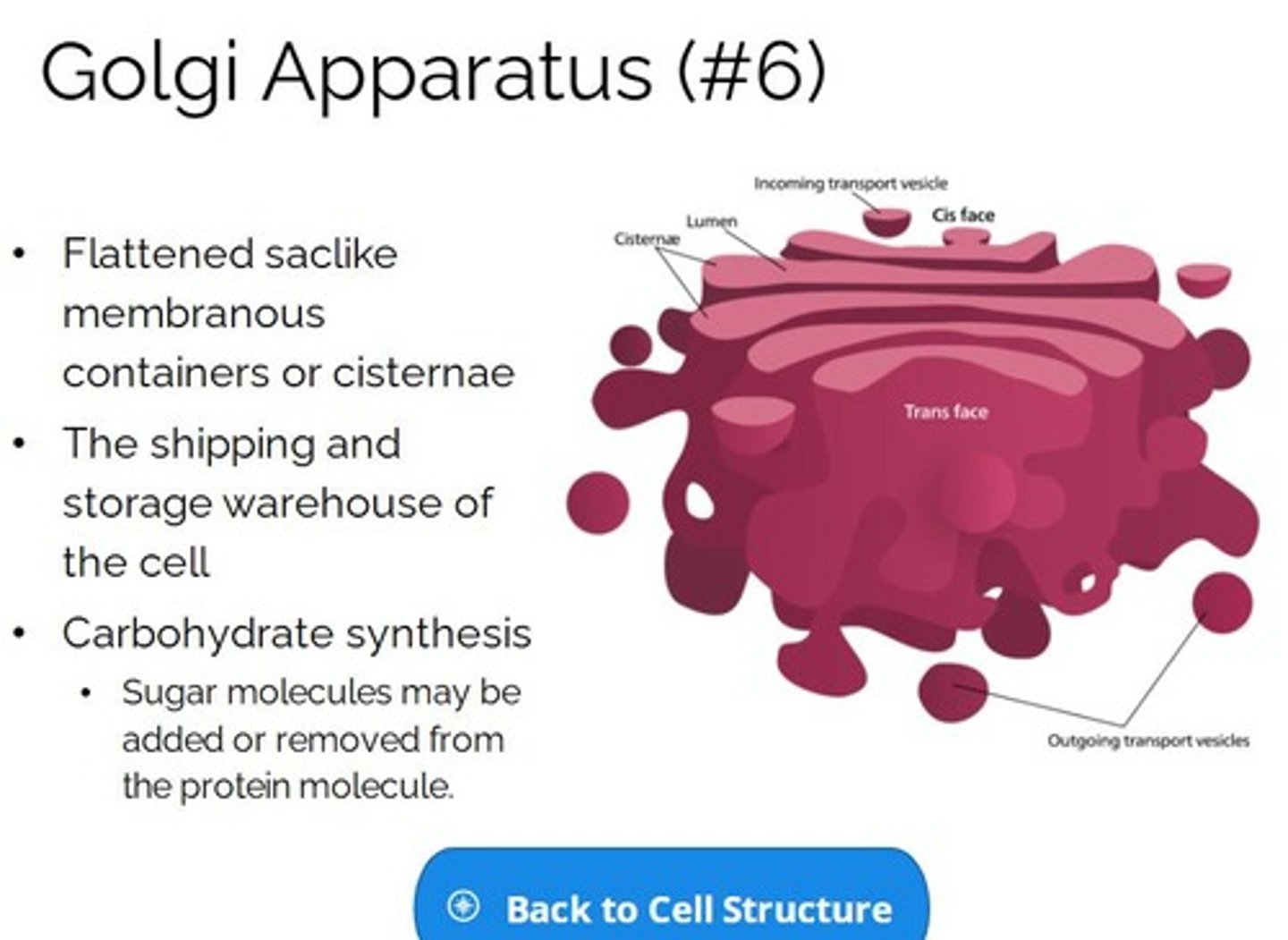
Golgi Apparatus
a cytoplasmic organelle that consists of a stack of smooth membranous saccules and associated vesicles and that is active in the modification and transport of proteins.
Glycolysis
the breakdown of glucose inside of the cell.
Lysosomes
a saclike cellular organelle that contains various hydrolytic (digestive) enzymes.
Meiosis
form of cellular reproduction specific to sex cells in all sexually reproducing single celled and multicelled eukaryotes.
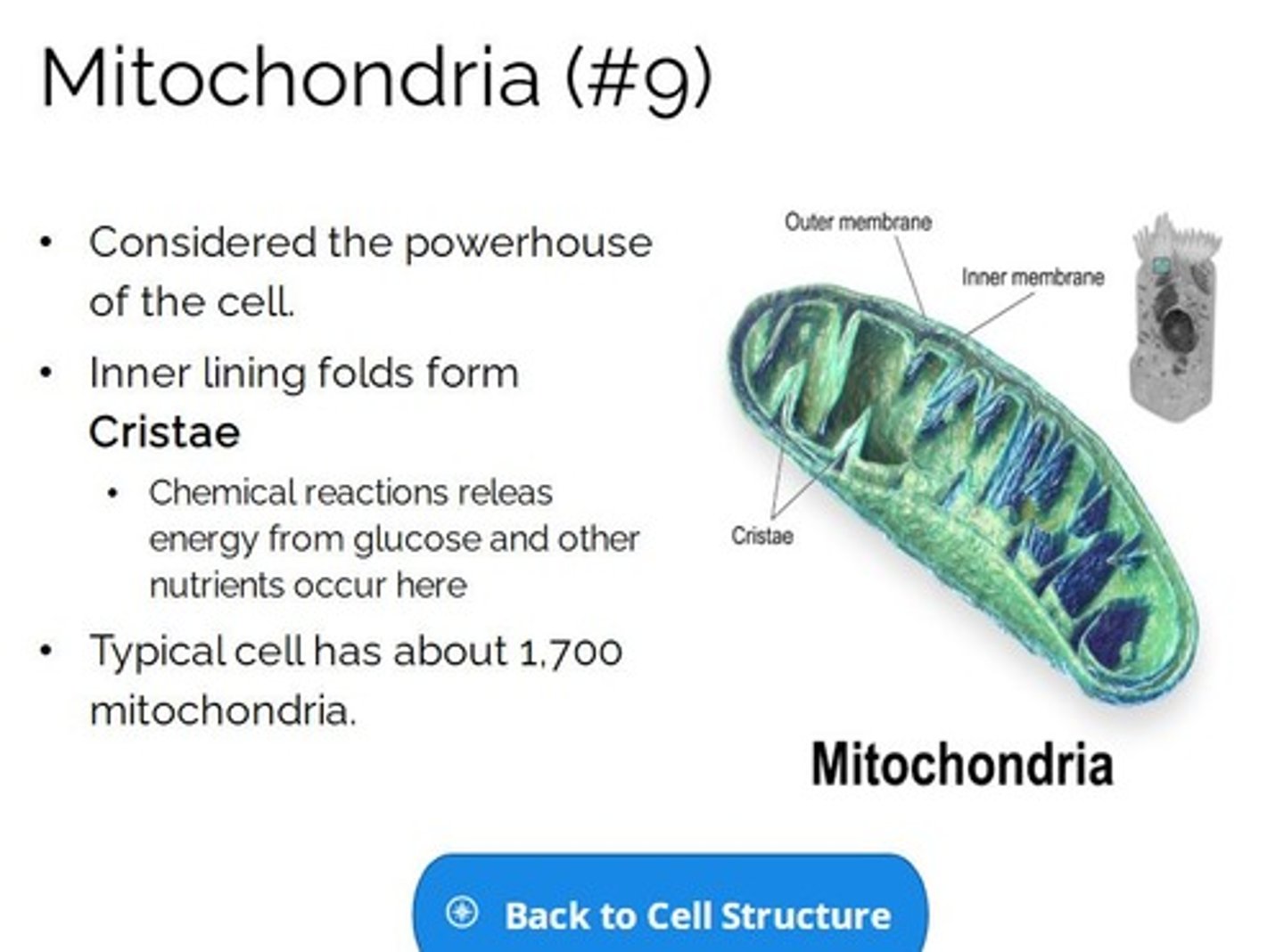
Mitochondria
found outside the nucleus. Responsible for producing energy for the cell through the breakdown of carbohydrates, proteins, and fats.
Mitosis
form of cellular reproduction that occurs in the nucleus of a dividing cell resulting in the formation of two new nuclei each having the same number of chromosomes as the parent nucleus.
Nucleolus
located inside the nucleus. Responsible for the production of ribosomes.
Nucleus
a mass located in the cytoplasm of a cell, separated from the cytoplasm by a nuclear membrane, Considered the control center of the cell.
Organ
a differentiated structure (as a heart or kidney) consisting of cells and tissues and performing some specific function in an organism.
Organelles
a specialized cellular part (as a mitochondrion or ribosome) that is analogous to an organ.
Pinocytic Vesicles
pocketlike folds located in the cell membrane allowing the entrance and storage of large molecules such as proteins and fats.
Tissues
an aggregate of cells usually of a particular kind together with their intercellular substance that form one of the structural materials of a plant or an animal and that in animals include connective tissue, epithelium, muscle tissue, and nerve tissue.
Protoplasm
the basic substance of all life; this substance forms the cell.
Stem cells
an unspecialized cell that gives rise to differentiated cells.
System
a group of body organs or structures that together perform one or more vital functions.
Vacuoles
pouchlike storage structures located throughout the cytoplasm.
Hypertrophy
cells enlarge caused by an increase of proteins in the cell membrane and cell structures, not an increase in the cell's fluid.
Hyperplasia
the number of cells increases; there is an increased rate of cell division.
Dysplasia
the size, shape, or organization of mature cells becomes abnormal; also called atypical hyperplasia.
Neoplasia
the formation of tumors, either cancerous (malignant) or noncancerous (benign).
Cell Cycle
the series of events involving the growth, replication, and division of a eukaryotic cell.
Human Body Cell Count
Research published in The Annals of Human Biology (2013) estimates that the human specimen consists of 37.2 trillion cells.
Cell Theory
Cells in the human body are described as eukaryotic cells, indicating that the nucleus is separated from the cytoplasm by a membrane.
Cell Membrane Function
The cell membrane functions as a selective filter allowing certain materials to either enter the cell or exit the cell.
Metabolic Processes
The many chemical reactions occurring inside the cell membrane are described as metabolic processes.
Catabolism and Anabolism
The cycle of catabolism and anabolism requires an efficient control system for proper function.
Cellular Damage Risk
If the catabolism process fails to yield the proper energy-releasing reactions and does not meet the needs (or exceeds the needs) of the building-up reactions, the risk of cellular damage exists.
Cell Differentiation
Cell differentiation allows for specialized metabolic processes in different cells.
Basic Reactions in Cells
All cells perform the basic reactions including the buildup and breakdown of carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids.
Energy Production
Cellular function depends on energy production and transportation of substances within the individual cell and among cells in general.
Food as Energy Source
Food functions as the primary source of energy to the body.
Calories Conversion
Calories must be converted to ATP to power cellular processes.
Cellular Respiration
This is accomplished through cellular respiration.
ATP to ADP Conversion
ATP to ADP conversion occurs when the terminal high-energy phosphate bond ruptures.
Release of Energy
The third phosphate is liberated energy stored in the chemical bond is therefore released.
Recycling of ATP
Mitochondrial enzymes then reconvert ADP and the liberated phosphate to ATP.
Mitochondria Function
To obtain the energy needed for the reattachment, mitochondria oxidize food nutrients.
Diffusion
The tendency of atoms, molecules, and ions to move from areas of higher concentration to areas of lower concentration, resulting in an equal distribution of solutes.
Osmosis
The passive movement of fluid from a region of higher water concentration to a region of lower water concentration across a selectively permeable membrane, stopping when fluid levels equalize solute concentrations on both sides.
Active Transport
Movement of atoms, molecules, and ions across a selectively permeable membrane from lower concentration to an area of higher concentration.
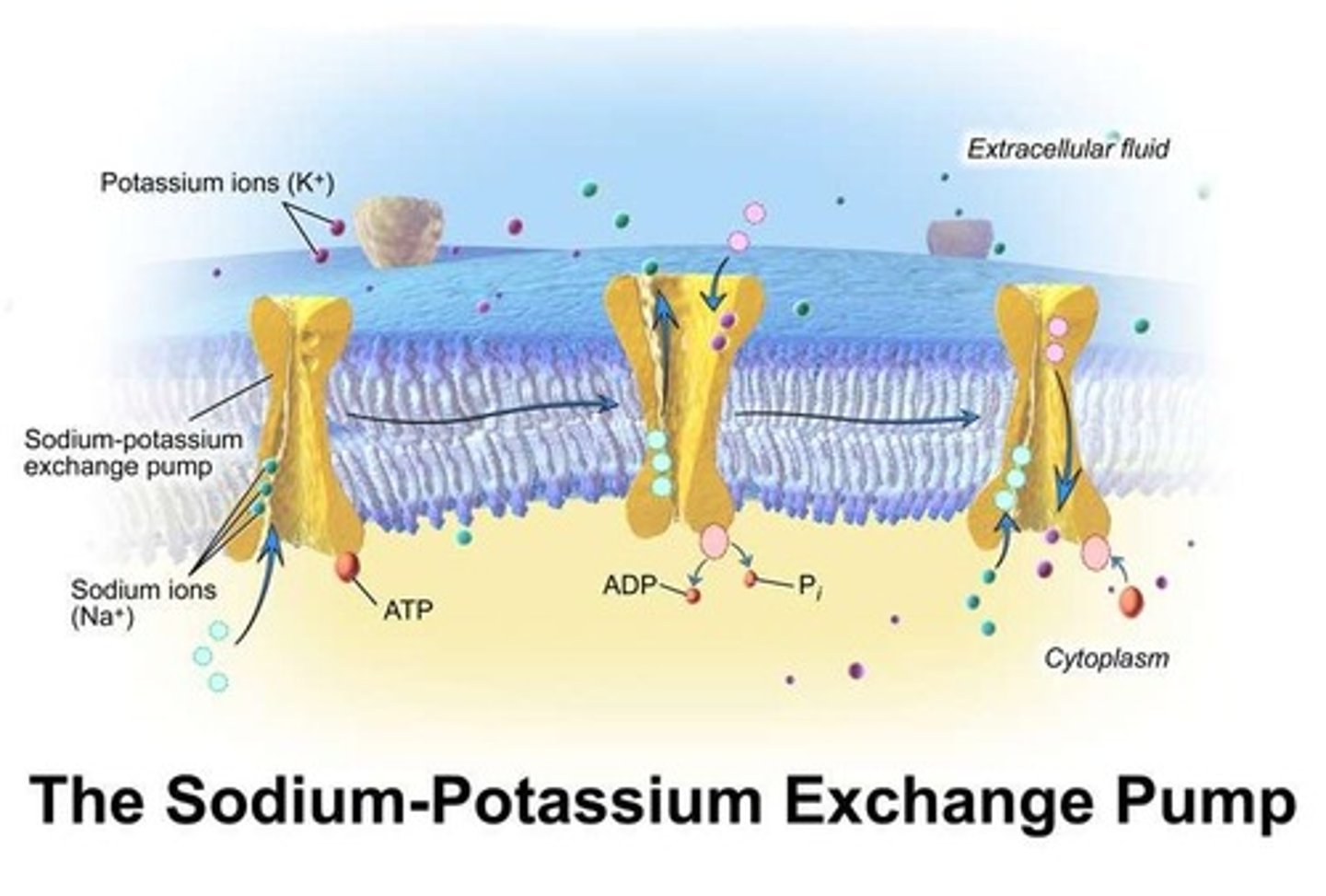
Sodium Potassium Pump
A mechanism that maintains homeostasis by regulating acid-base balance and healthy kidney function.
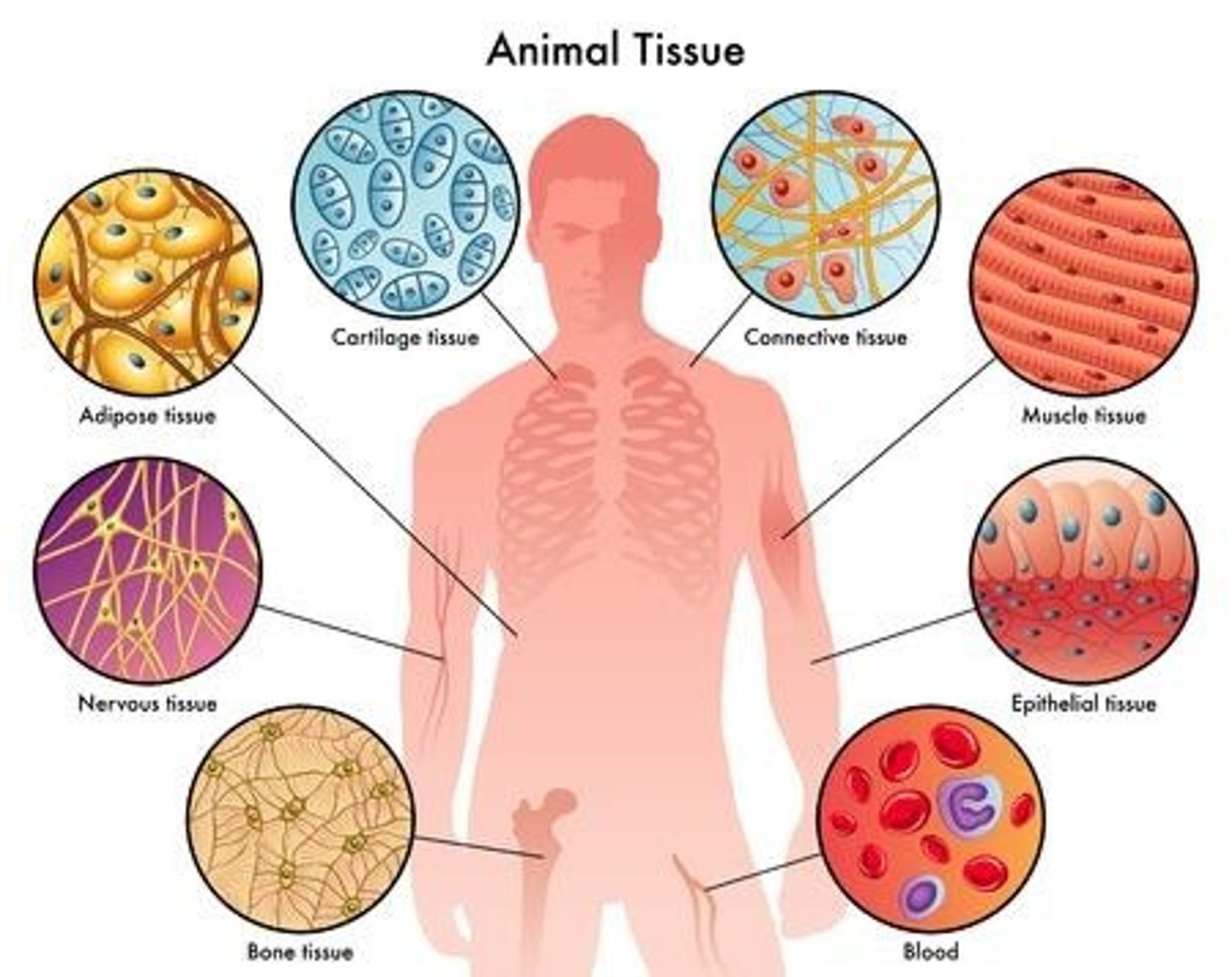
Epithelial Tissues
Tissues that form sheets and cover the outer surface of the body, lining body cavities, and forming certain glands.
Cellular Injury and Death
Conditions affecting the structure of the cell and its parts, which are required for homeostatic balance and the life of the cell.
Cellular Adaptations
Responses of cells to stressors, which can be reversible or irreversible.
Disease Modelling with Cells
A method to understand the conditions affecting cells through video resources.
Defects in Cellular Production
Issues arising from uncontrolled cellular division, which is vital for maintaining homeostasis.
Cell Division
The process that is vital for tissue growth and is affected by the frequency of mitosis.
Tumor Growth
An abnormal increase in tissue caused by too frequent mitosis.

Metastasis
The spread of cancer cells from one part of the body to another.
Aging
The process that affects cells, tissues, organs, and body systems, leading to decreased function and increased waste accumulation.
Cell Atrophy
The loss of tissue mass due to aging, characterized by stiffness and rigidity.
Aging Process with Cells
Research focused on combating the aging process within cells, often explored through video resources.