Chapter 11 Hairs and Fibers
1/200
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
201 Terms
Hair Evidence
Common trace evidence type in criminal investigations.
Shed Hairs
Hairs easily lost from individuals during growth.
Forensic Hair Analysis
Examines hair to establish associations in crimes.
Association Demonstration
Shows links between suspects and crime scenes.
Exculpatory Evidence
Evidence that can prove a suspect's innocence.
Microscopic Hair Examination
Analyzes hair but cannot definitively identify individuals.

Morphological Characteristics
Physical traits used to analyze and compare hairs.
Human vs Animal Hair
Distinguishes hair origin based on characteristics.
Known Sample Comparison
Compares unknown hair to a known sample.
Identification Phase
Initial analysis to categorize hair types.
Telogen Root
Hair root phase indicating shedding or rest.
Microscopic Comparison
Evaluates hair samples for shared characteristics.
Pattern-Recognition Process
Instantly identifies similarities in hair characteristics.
Step-by-Step Analysis
Detailed examination of hair comparison points.
Points for Comparison
Specific features analyzed in hair samples.
Association Criteria
Microscopic traits must match in questioned hair.
Subjective Interpretation
Examiner's judgment on the significance of traits.
Animal Hair Identification
Used by biologists and researchers for analysis.
Significance of Animal Hair
Less than human hair but still useful.
Dog Hair Evidence
Can link a suspect to a victim's item.
Caucasian Characteristics
Specific traits found in human hair samples.
Growth Phases of Hair
Includes anagen, catagen, and telogen stages.
Forensic Investigation Utility
Animal hair can provide valuable forensic insights.
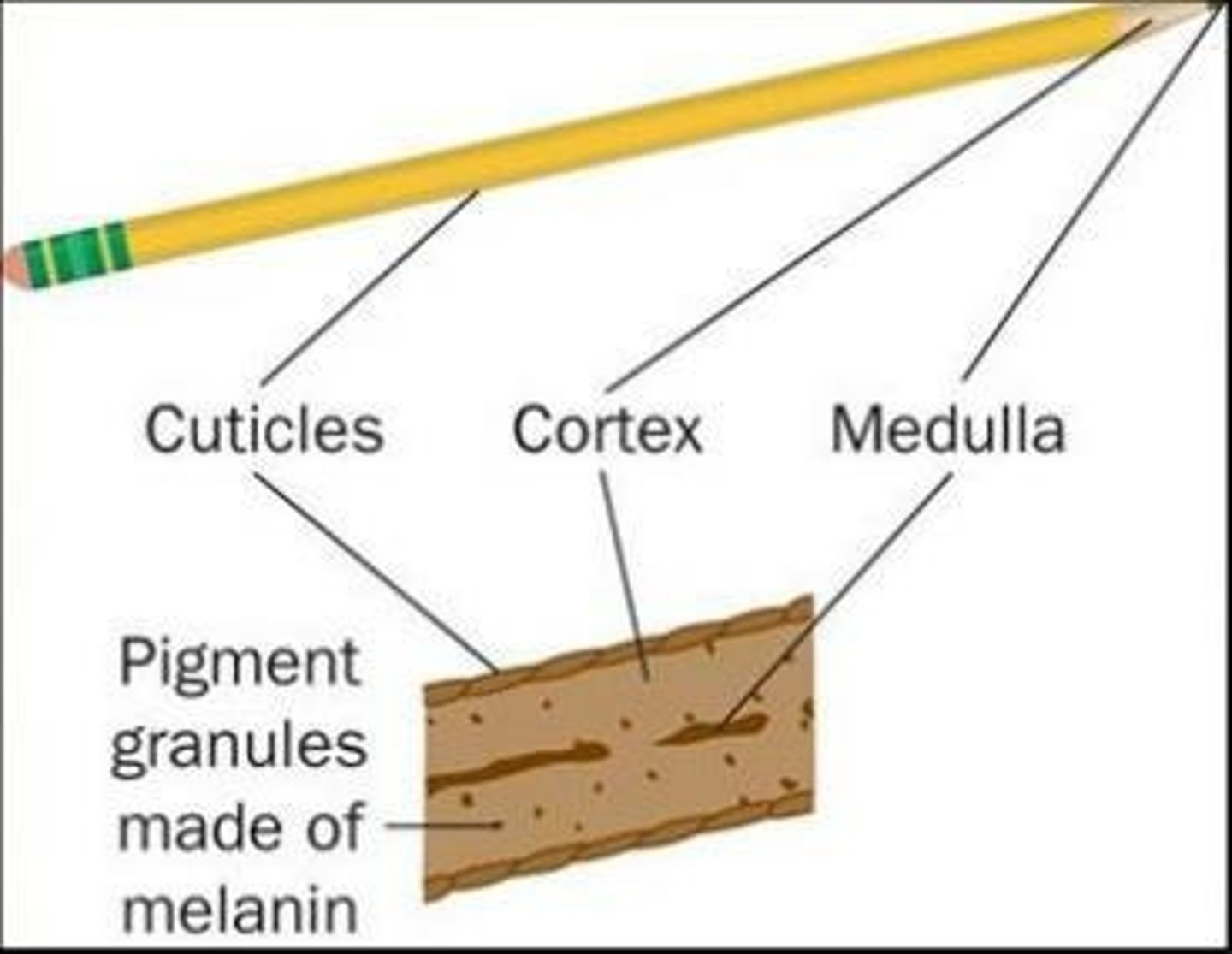
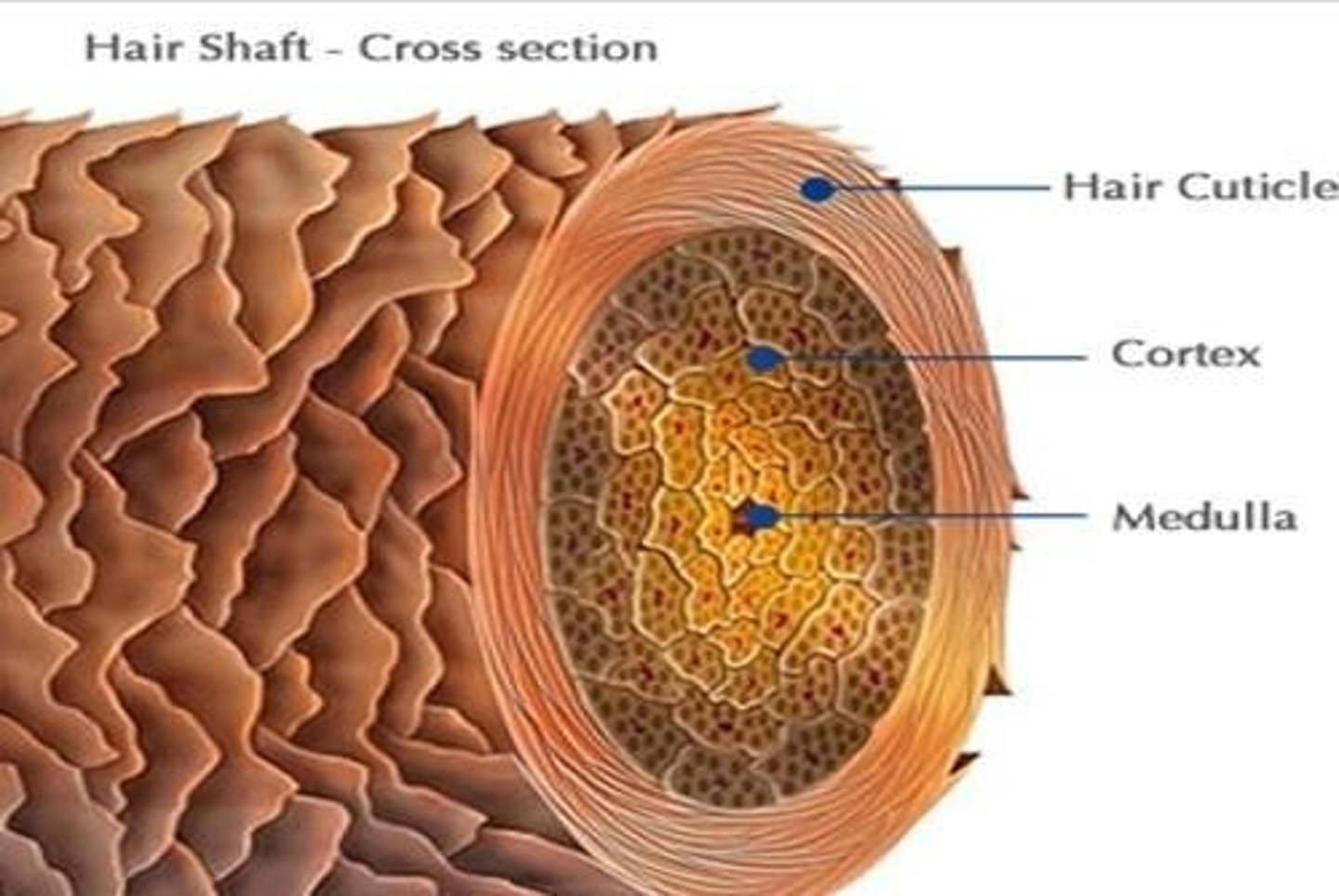
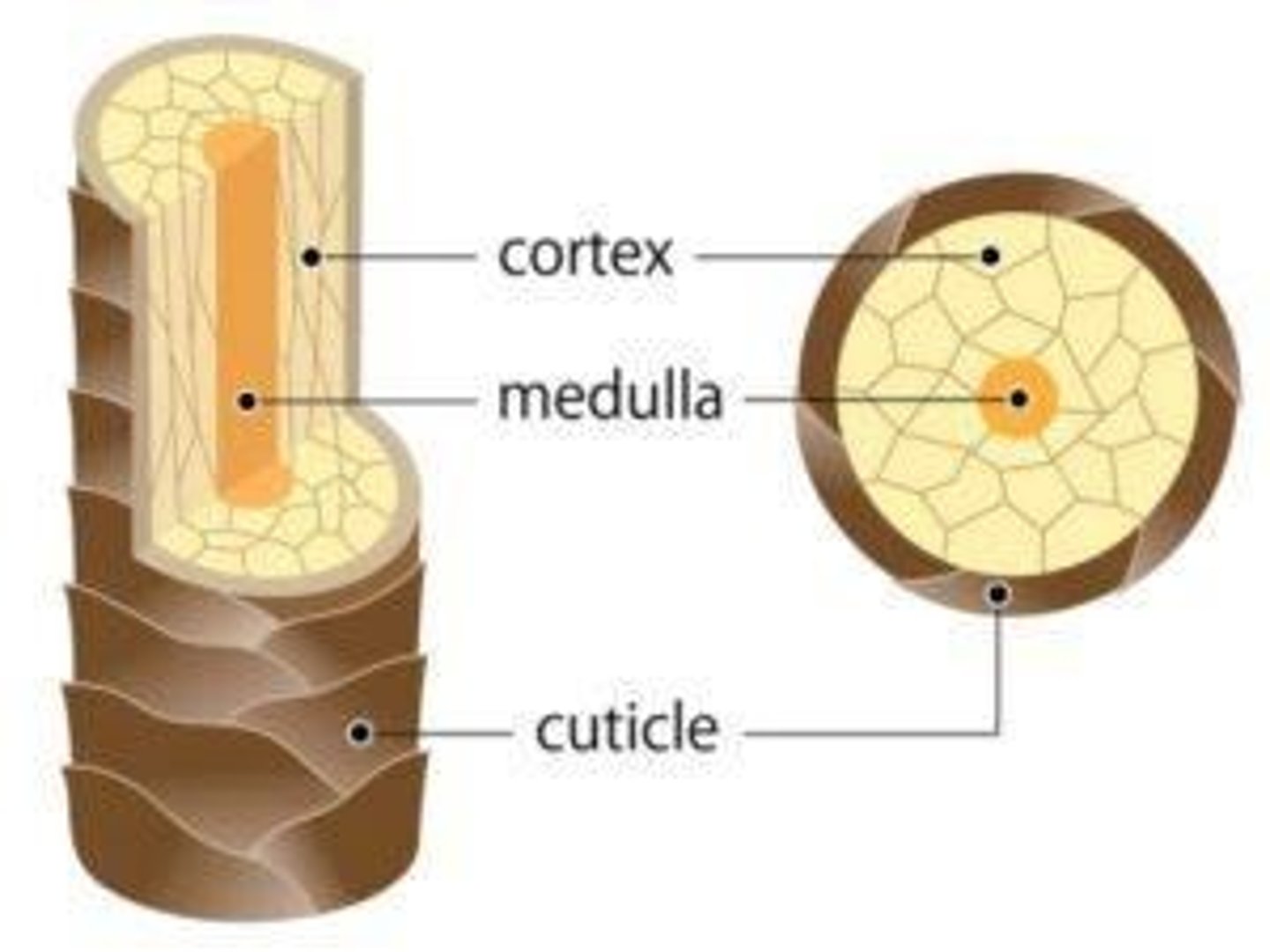
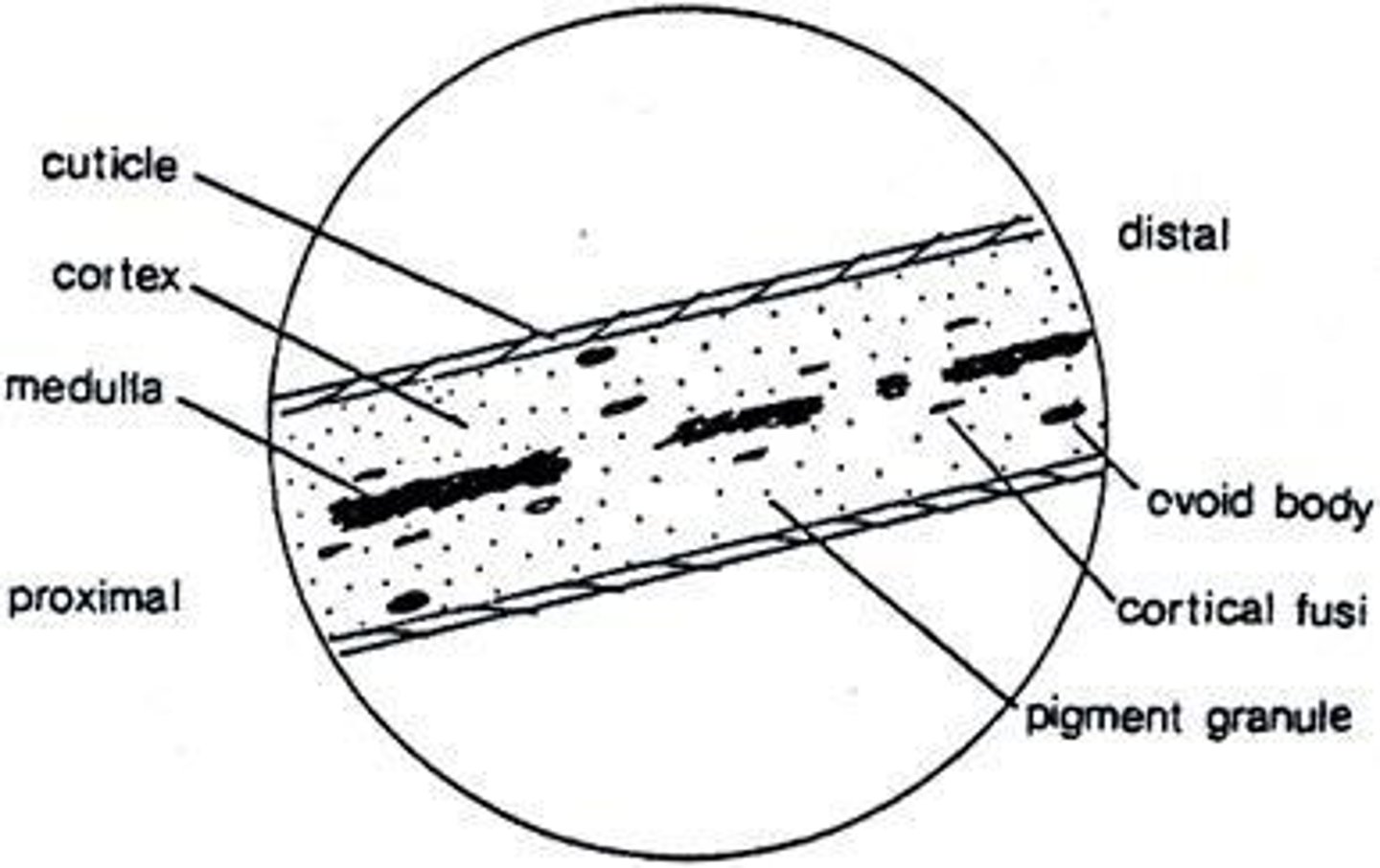
Cuticle
Outermost hair layer protecting from damage.
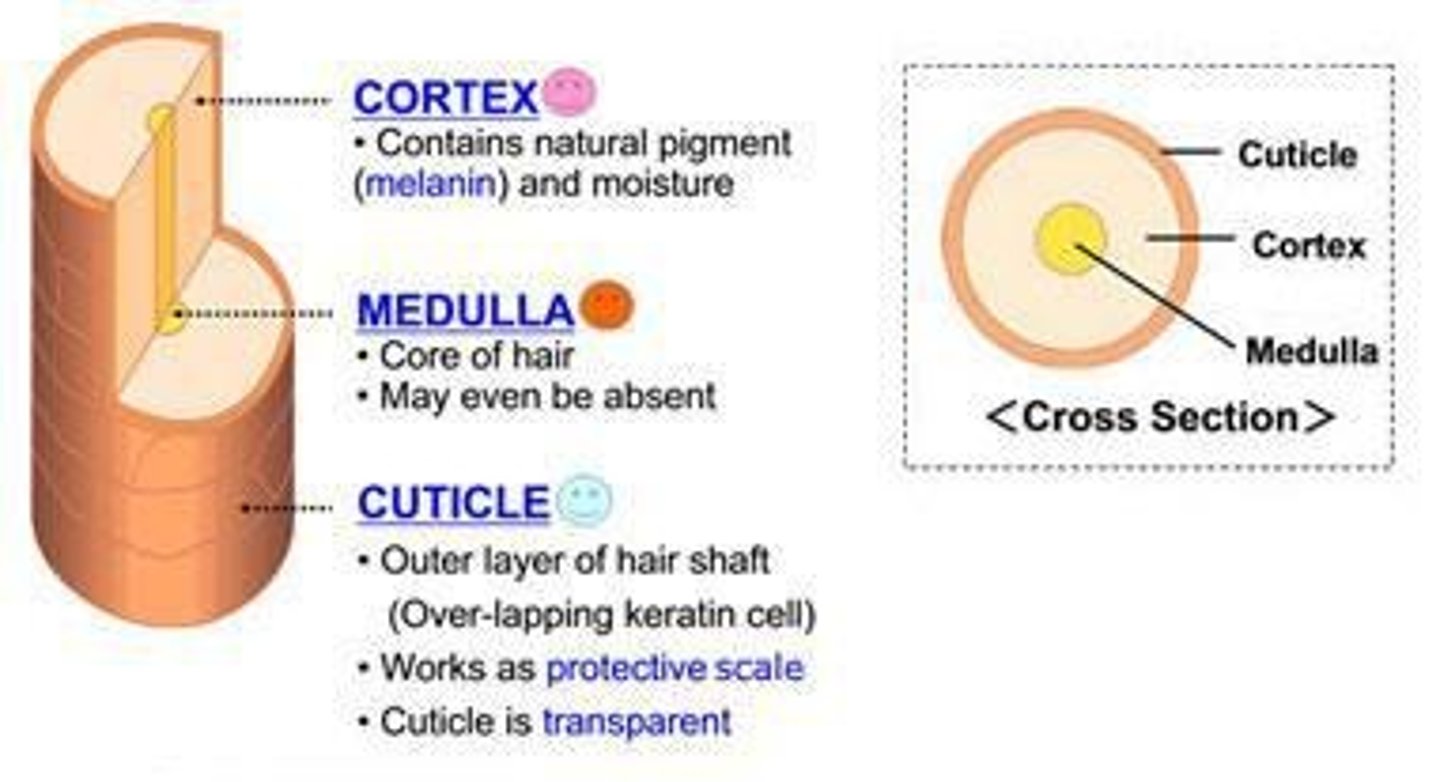
Cortex
Main body of hair containing pigment granules.
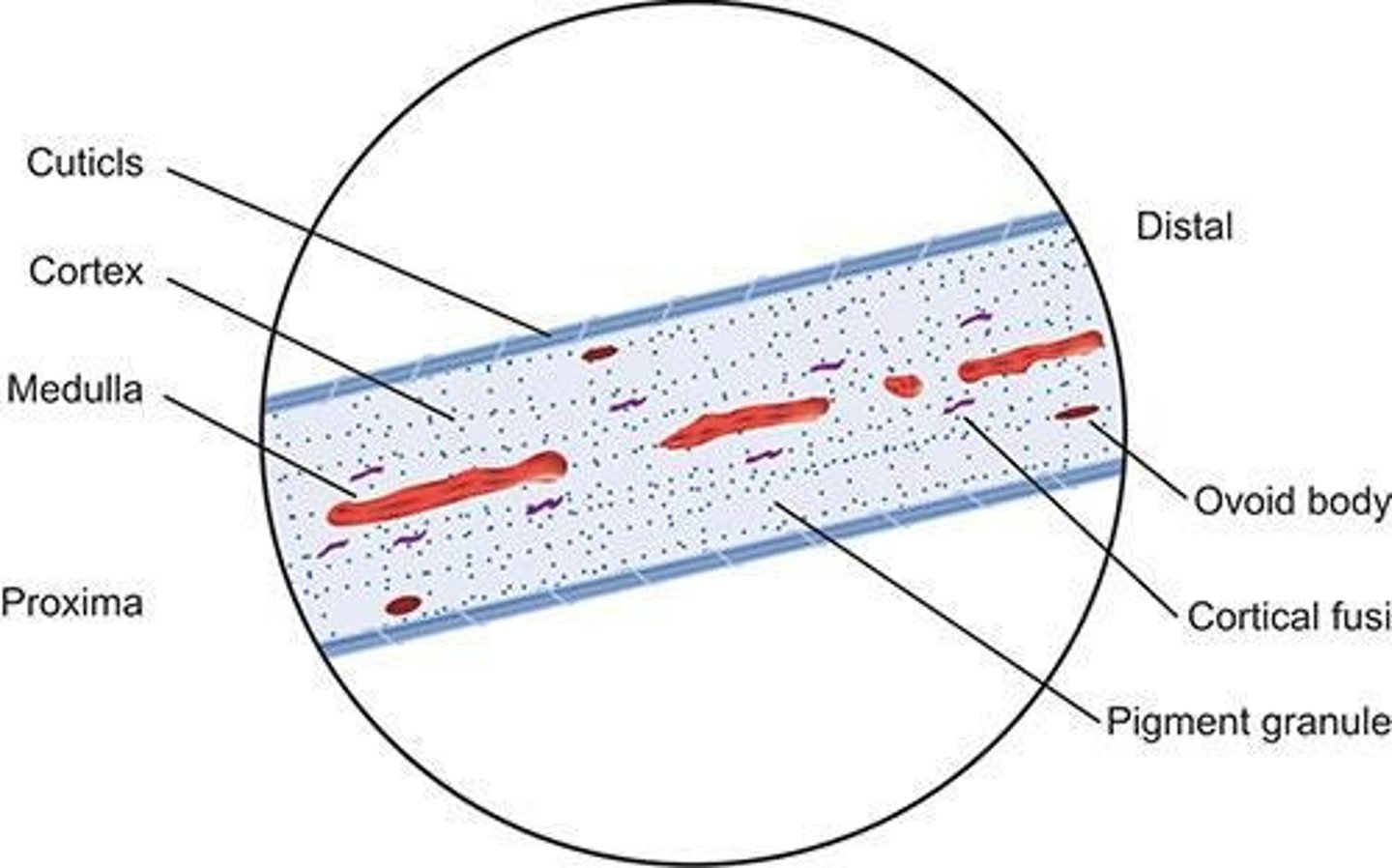
Medulla
Central core of hair, varies in thickness.
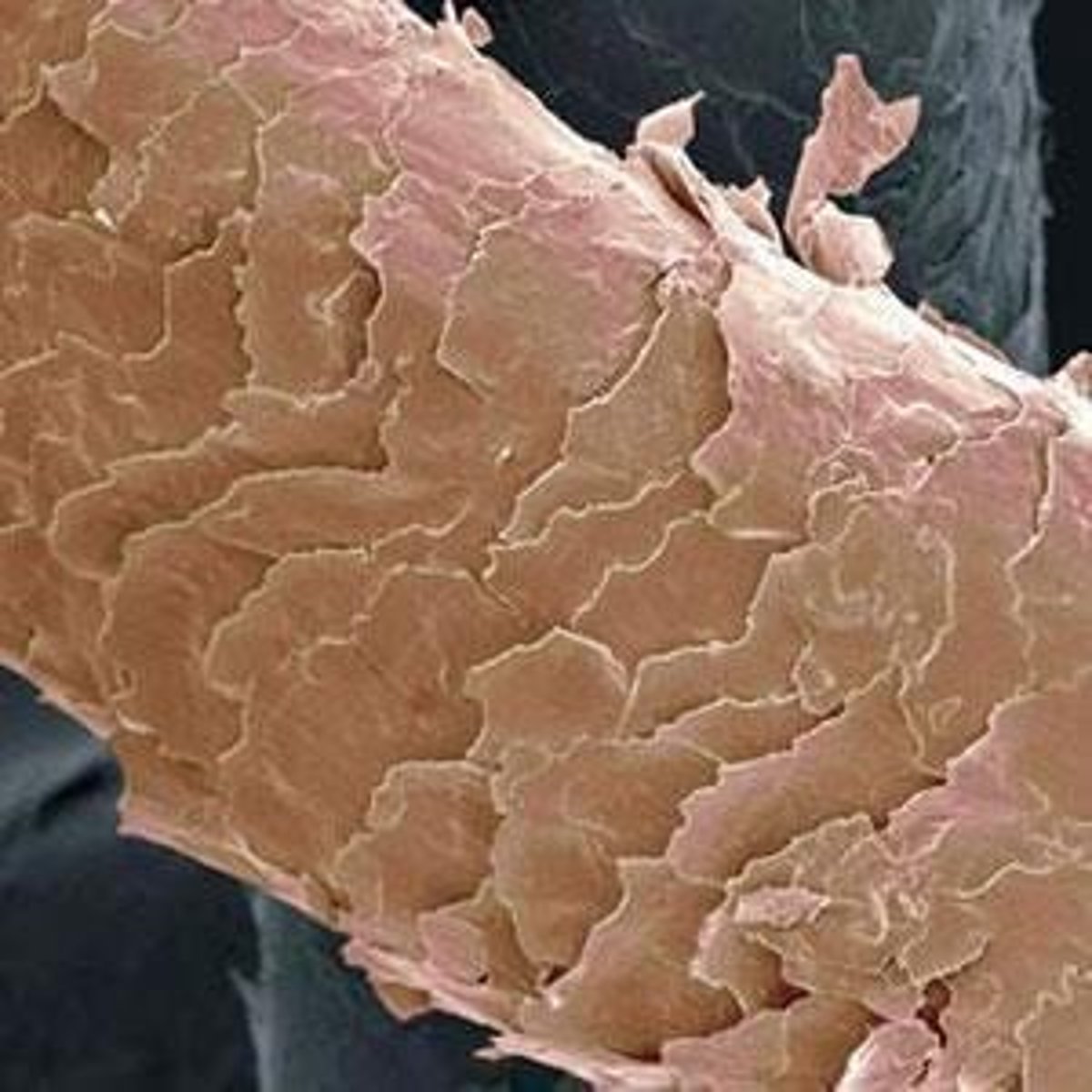
Imbricate pattern
Irregular scale pattern in human hair cuticle.
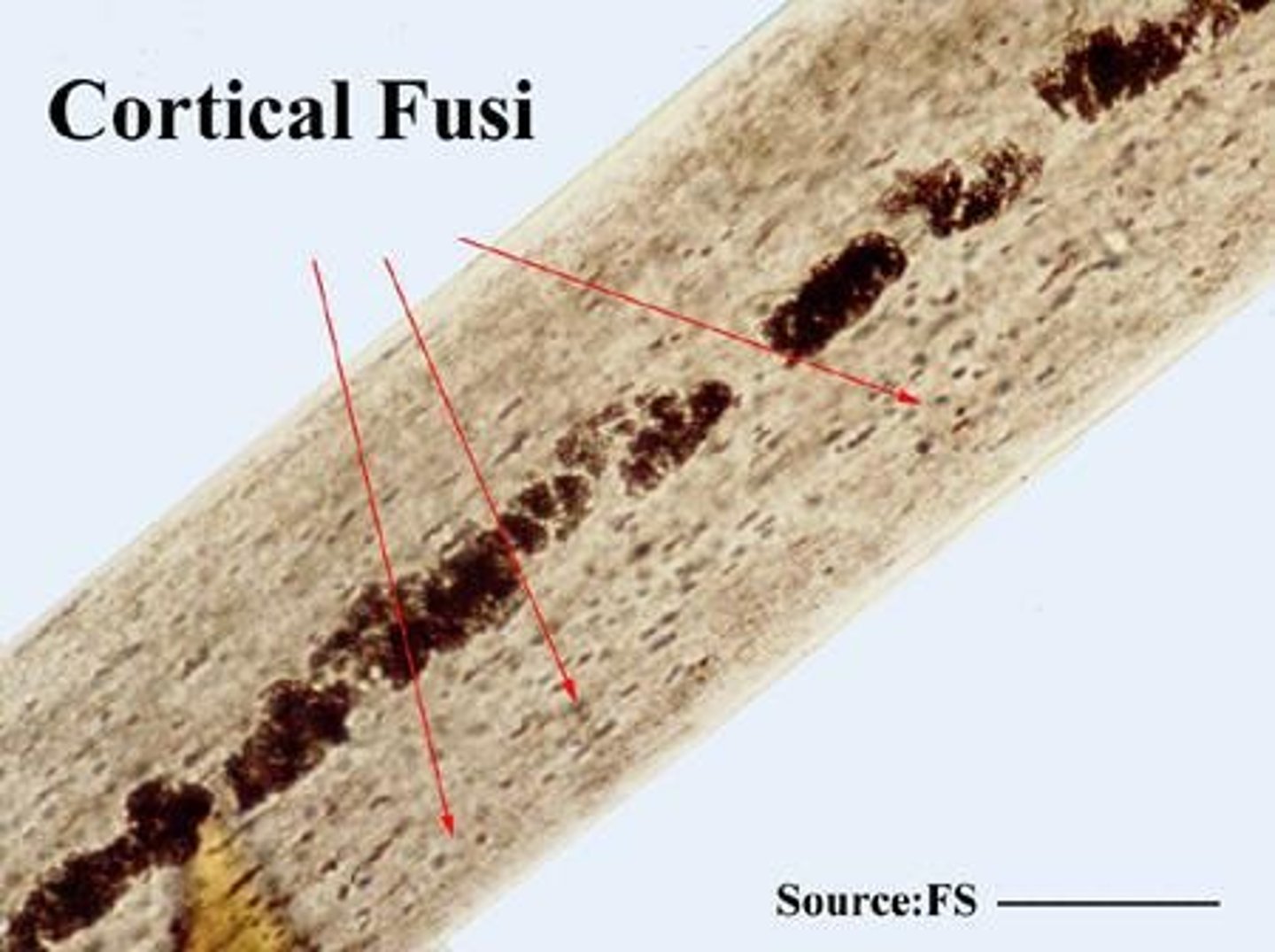
Cortical fusi
Small air spaces in the cortex of hair.
Eumelanin
Pigment granule for brown and black hair.
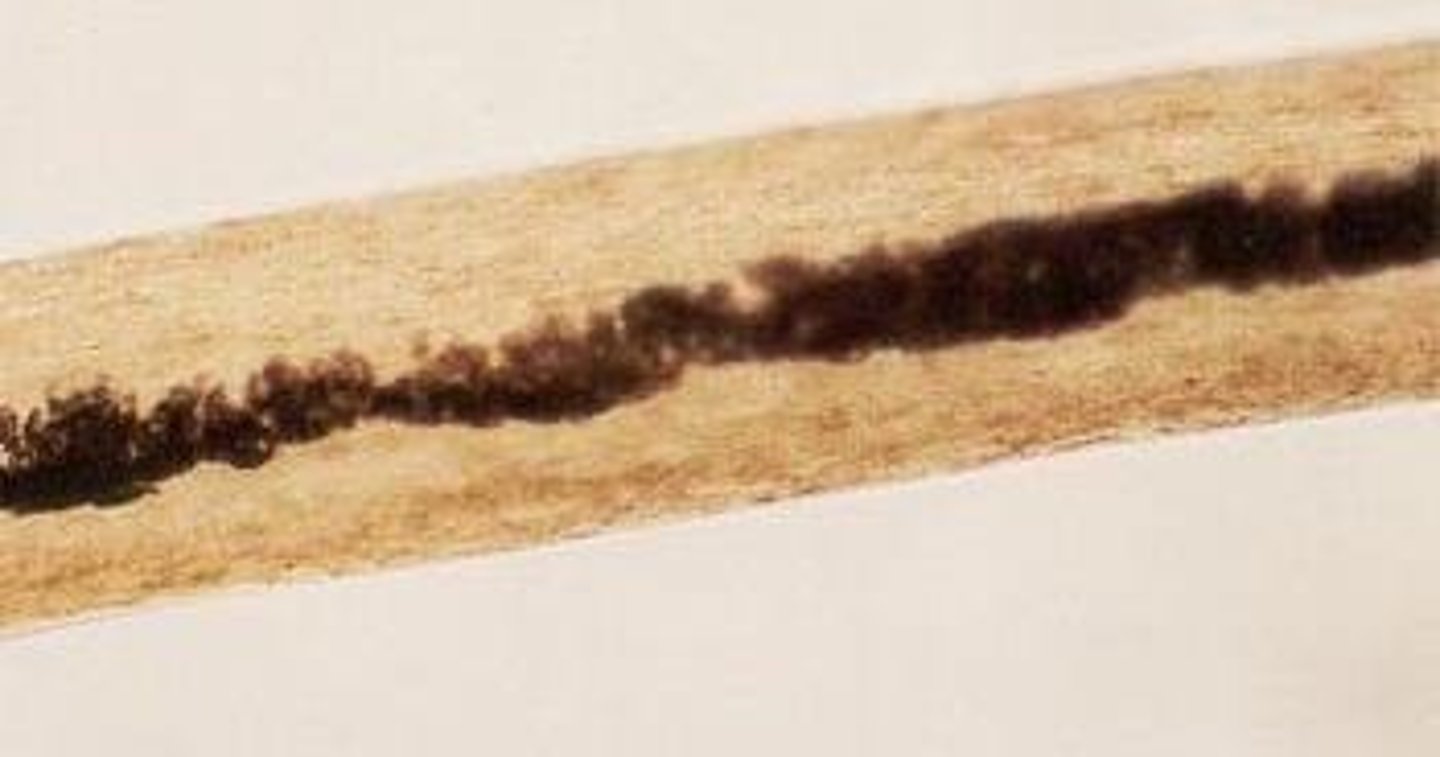

Phaeomelanin
Pigment granule for yellow and red hair.
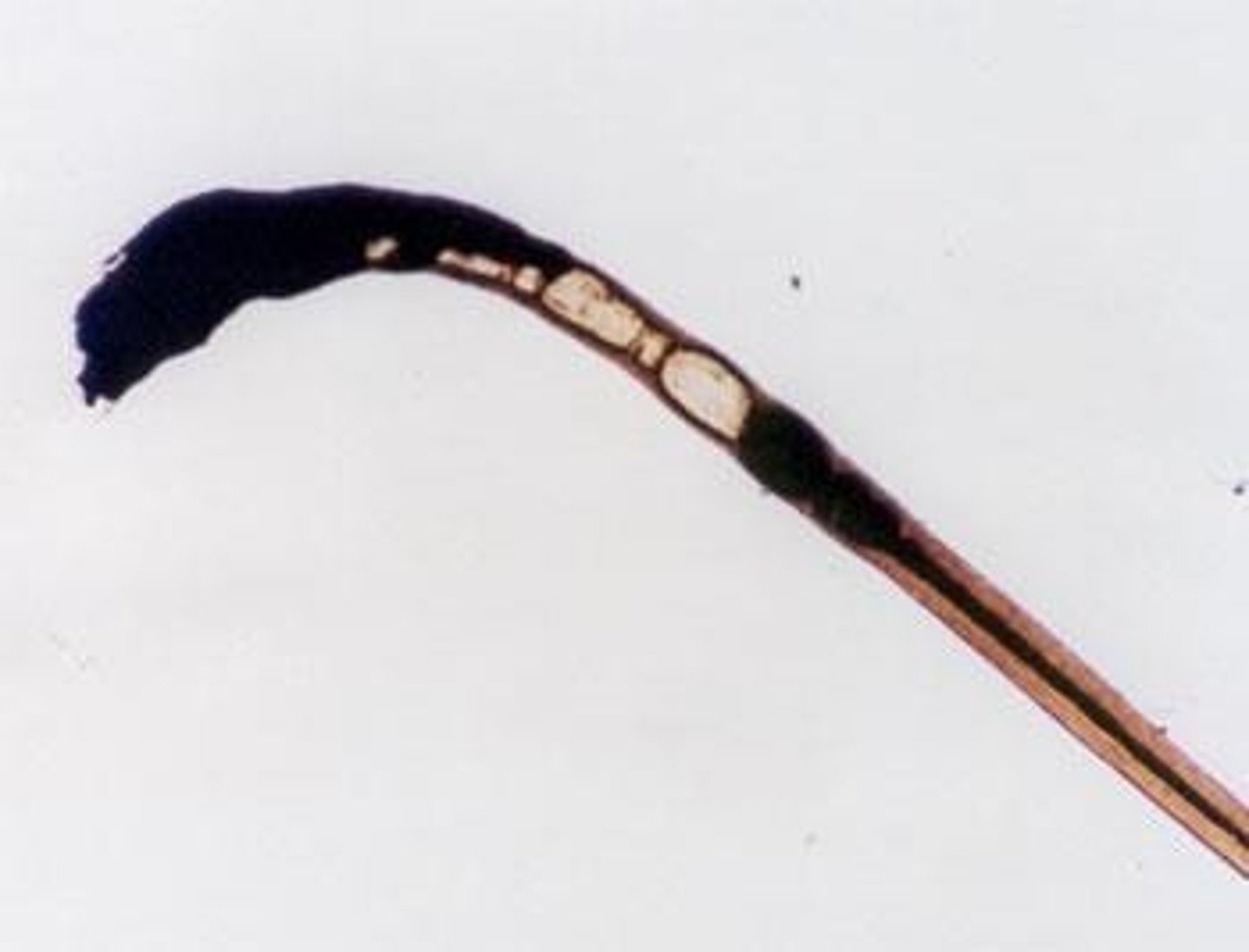
Ovoid bodies
Dense, oval-shaped pigment clumps in hair.
Hair root morphology
Shape of hair root indicating species origin.
Telogen phase
Resting phase when hair naturally falls out.
Animal hair medulla
Thicker than 2/3 of hair shaft diameter.
Human hair medulla
Less than 2/3 of hair shaft diameter.
Environmental influences
Factors affecting hair characteristics and growth.
Growth stage
Phase of hair development at separation.
Hair identification
Process of determining hair origin and type.
Hair pigmentation
Color derived from pigment granules in cortex.
Cuticle thickness
Measurement of cuticle layer's width.
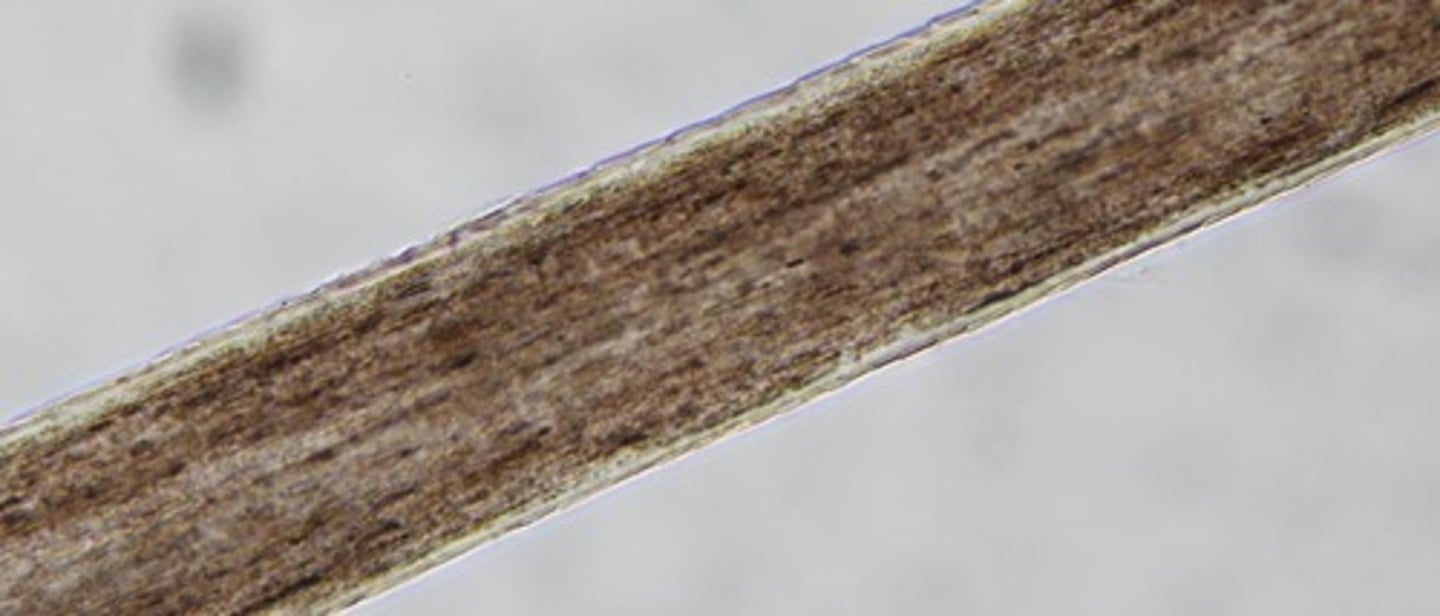
Cuticular margin
Outer edge of cuticle, can be smooth or ragged.
Hair damage
Alterations in hair structure due to external factors.
Scales
Flattened cells in cuticle overlapping like shingles.

Species identification
Determining hair origin based on morphological features.
Microscopic comparison
Analyzing hair under microscope for identification.
Environmental insults
External factors causing damage to hair structure.
Dermal Papillae
Base of hair follicle where growth occurs.
Anagen Phase
Active growth phase; 80-95% of hairs.
Catagen Phase
Transitional growth phase; bulbous root develops.
Telogen Phase
Dormant phase; 10-20% of hairs present.
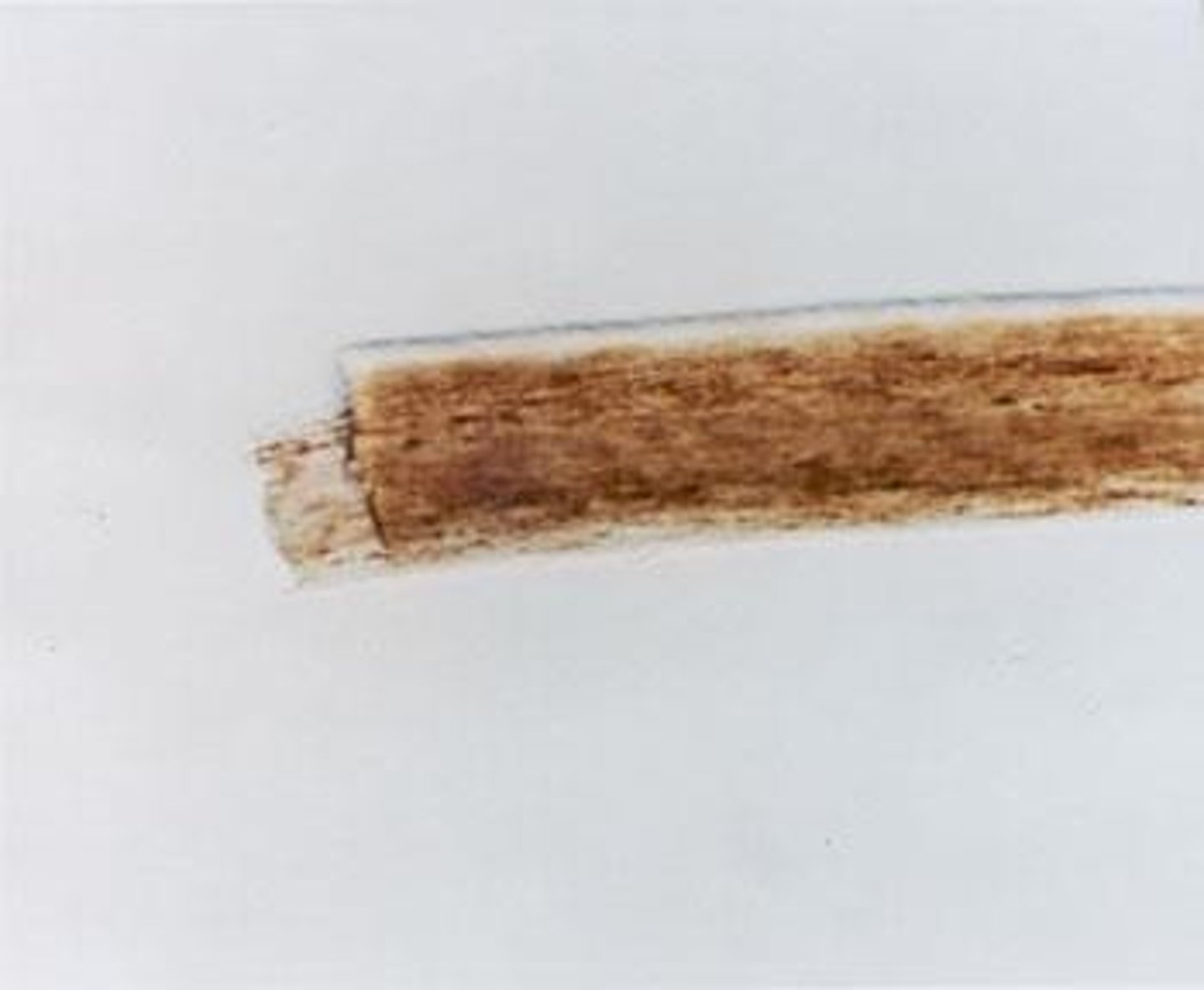
Bulbous Root
Characteristic of human hair roots.
Speared Root
Characteristic of animal hair roots.
Forcibly Removed Hair
May have tissue attached for DNA analysis.
Hair Color
Determined by pigment granules and light properties.
Hair Characteristics
Includes hue, value, and intensity of color.
Distal End
Tip of hair; varies in morphology.
Abraded Hair Tip
Tip altered by grooming or abrasion.
Cut Hair Tip
Tip resulting from cutting hair.
Worn Razor-Cut Tip
Tip from hair cut with a razor.
Decomposed Hair
Hairs from decomposed bodies show specific traits.
Hair Growth Rate
Hairs shed naturally as new growth occurs.
Microscopic Characteristics
Unique features observed under a microscope.
Nuclear DNA Analysis
Used on hair with follicular material attached.
Variation in Hair Color
Less variation within individuals than among them.
Environmental Exposure
Can cause color variation in individual hairs.
Hair Follicle
Structure from which hair grows.
Hair Morphology
Study of hair structure and characteristics.
Hair Comparison Process
Analyzing hair for forensic identification.
Forensic Hair Examination
Analyzing hair for legal investigations.
Hair Sample Growth
Hair may grow over significant time gaps.
Hair Diameter
Ranges from 40-120 micrometers in size.
Racial Classification
Diameter aids in determining racial group.
Hair Collection Importance
Hairs must persist to be meaningful evidence.
Evidence Recovery Locations
Occurs at crime scene and crime lab.
Evidence Packaging
Proper packaging prevents contamination and loss.
Forensic Discipline Order
Trace analysis must precede other forensic tests.
Stereomicroscope Examination
Initial examination done under low magnification.
Glass Slide Mounting
Hairs are mounted for high power examination.
Representative Sample
Includes distinct types of hairs observed.
Targeted Search Method
Focuses on known samples alongside evidentiary items.
Microscopic Analysis
Uses 50x to 400x magnification for details.
Body Area Classification
Determines origin based on hair characteristics.
Head Hairs
Typically longest, uniform diameter, often cut.
Pubic Hairs
Distinctive characteristics differentiate them from head hairs.
Facial Hairs
Includes beard and mustache hair types. Coarse hairs with triangular cross section and razor-cut tips.
Limb Hairs
Hairs from arms and legs categorized separately. Shorter, arc-like, often abraded or tapered at tips.
Chest Hairs
Hair from the chest area, unique morphology.
Axillary Hairs
Hair from armpits, identifiable by specific traits.
Eyebrow/Eyelash Hairs
Short, fine hairs from facial regions.
Environmental Alterations
Conditions like sunlight affect hair appearance.
Chemical Alterations
Dyes and treatments change natural hair characteristics.
Head Hair Samples
Not suitable for comparison years after crime.
Pubic Hair
Coarse, wiry, with diameter variation and medulla.
Pubic Hair Stability
Less change over time, suitable for comparison later.
Known Pubic Hair Sample
At least 25 full-length hairs recommended post-crime.
Nuclear DNA Typing
Requires nucleated cells, effective for hair analysis.
Microscopic Hair Analysis
Distinguishes hair types and provides contextual information.
mtDNA
Maternally inherited, not unique to individuals.
Microscopic Examination Importance
Essential before DNA analysis due to destruction risk.
Hair Examination Techniques
Includes microscopic and DNA analysis for evidence.